Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture Notes Ch10 Unemployment
Hochgeladen von
Katherine SauerOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture Notes Ch10 Unemployment
Hochgeladen von
Katherine SauerCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Macroeconomics Dr.
Sauer
Measuring Unemployment (ch10) I. Measuring Unemployment The Bureau of __________________ Statistics computes unemployment statistics. - monthly The information comes from the Current Population Survey (CPS) - _____________________ survey of households - a sample of 60,000 households - personal and telephone interviews - __________________: labor force unemployment
employment persons not in the labor force
The basic concepts involved are simple: - People with jobs are ________________________. - People who are jobless, looking for jobs, and available for work are ___________________. - People who are neither employed nor unemployed are ______________________________. Excluded from these categories are persons - under 16 years of age - confined to institutions (ex: nursing homes, prisons) - on active duty in the military Why not count the military? - ___________________, it was not counted because service wasnt necessarily voluntary. - In __________, the 10th anniversary of all-volunteer armed forces, the BLS ________________ military personnel. - In 1994 the BLS __________________ counting them. - not accurate reporting from military (ex: fast deployments) - not same data categories as BLS used - didnt seem to matter
1. employed - did any __________________________ or profit during the survey week - at least 15 hours of ____________________ in a _______________________ enterprise operated by someone in their household - _________________________ from their regular jobs, whether they were paid or not Not all of the job situations in the American economy fit neatly into a given category. Persons also are counted as ______________________ if they _________________ at which they _____________________ during the survey week because they were: On vacation Ill Experiencing child-care problems Taking care of some family/personal obligation On maternity or paternity leave Involved in an industrial dispute Prevented from working by bad weather
2. unemployed Persons are classified as unemployed if they - do not have a job - have ____________________ for work in the prior 4 weeks - are currently ______________________ for work Workers expecting to be recalled from layoff are counted as unemployed, whether or not they have engaged in a specific job-seeking activity. In all other cases, the individual must have been engaged in at least one active job search activity in the 4 weeks preceding the interview and be available for work (except for temporary illness).
3. not in the labor force Persons not in the labor force are those who are not classified as _______________________ during the survey week. Many who are not in the labor force are going to school or are retired. Family responsibilities keep others out of the labor force.
The Labor Force is the ______________________________ in the economy, whether they are employed or unemployed. Labor Force = number employed + number unemployed
The labor force is ____________________________ number of people. - It increases with the long-term growth of the population. - It responds to economic forces and social trends - Its size changes with the seasons. The seasonal fluctuations in the number of employed and unemployed people reflect - normal seasonal weather patterns - the hiring (and layoff) patterns that accompany regular events such as the winter holiday season and the summer vacation season To deal with such problems, a statistical technique called ___________________________ is used.
The ______________________________________________ is the percent of the total eligible population that is in the Labor Force: LPF = # in the Labor Force adult population x 100
The _________________________________ is the percent of the Labor Force that is unemployed: U= # unemployed # in Labor Force x 100
www.BLS.gov
The entire US population is about 310 million. Subtracting people under 16, the military and people in institutions, the number of potential workers is:
Of this number, how many are actually in the labor force?
The table says the labor force participation rate is 64.2%. Verify this number using the formula for the labor force participation rate. Of all the potential workers, this is the portion who are working or wish to work.
Verify that the labor force is the sum of employed people and unemployed people:
Verify that the number of people not in the labor force is the eligible population minus the labor force:
Notice that there are people who arent in the labor force, but who want a job. - discouraged workers who have stopped looking for a job but would take one if it were available - some areas have no jobs (dying factory towns, economically depressed areas) so why bother looking? The table says the unemployment rate is 9%. Verify this number using the formula for the unemployment rate.
Which states have the highest unemployment?
Which states have the lowest unemployment?
What do we know about unemployment in states that are not on this list?
www.bls.gov
Some _______________________ with the Unemployment rate measure: - people enter/exit the labor force at will - how to know if people are actively looking for work? - discouraged workers dont count - underemployment isnt measured
II . Types of Unemployment 1. Natural Rate of Unemployment = the ______________________ of unemployment in a country 2. Cyclical Unemployment = the _________________________ of the unemployment rate from its natural rate - varies with the business cycle
3. Frictional Unemployment = even in good economic times, it ______________________ to look for a job, apply, get interviewed, and get hired ex: you graduate and start looking for a job 4. Structural Unemployment = caused by a ____________________ between jobs offered by employees and potential workers in some labor markets ex: number of vacancies may be equal to the number of the unemployed but - lack the skills needed for the jobs available - jobs are in a different part of the country 5. Seasonal Unemployment = the unemployment that accompanies ___________________________ ex: ski season, harvest time
Because of structural and frictional unemployment, the unemployment rate is ________________ zero. Even when the economy is doing very well, there will be some unemployment. - the natural rate of unemployment - the full-employment rate of unemployment The natural rate of unemployment is roughly equal to the ______________ of Frictional and Structural unemployment. 5
III. Job Search Because _______________________ from one another in terms of their skills and tastes and jobs differ in their attributes, it is often ______________________ for workers to match with the appropriate job. The faster information spreads about job openings and worker availability, the more rapidly the economy can match workers and firms. Government programs ____________________ to reduce the amount of frictional unemployment. Government-run _________________________ give out information on job vacancies. Public _____________________ can ease the transition of workers from declining to growing industries and help disadvantaged groups escape poverty. Unemployment __________________________ is one way that government intervenes in the labor market. Because unemployment insurance reduces the hardship of unemployment, it also increases the amount of unemployment that exists. Many studies have shown that more generous unemployment insurance benefits lead to reduced job search effort and, as a result, more unemployment.
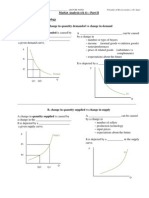
IV. Other Causes of Unemployment 1. Minimum wage laws In the labor market, the supply curve is the workers wanting to work. The demand curve is firms hiring. The market clearing wage is deemed to be too low so a minimum wage is implemented. What is the result?
Who earns the minimum wage? In 2006, the Department of Labor released a study concerning workers who reported earnings at or below the minimum wage. - Of all workers paid an hourly rate in the United States, about 2% of men and 3% of women reported wages at or below the minimum wage. - Minimum-wage workers tend to be young, with about half under the age of 25. - Minimum-wage workers tend to be less educated. Of those workers ages 16 and over with a high school education, only 2% earned the minimum wage. - The industry with the highest proportion of workers with reported wages at or below the minimum wage was leisure and hospitality. - The proportion of workers earning the prevailing minimum wage has trended downward since 1979. Minimum wage laws _________________ the young, least educated and those in the leisure/hospitality industry. Minimum wage laws also contribute to ________________________ among the young, least educated and those in the leisure/hospitality industry. 2. ________________ wages are above equilibrium wages paid in an attempt to increase productivity. reasons: - decrease worker turnover - increase worker effort - attract better workers - improve worker health (only in developing nations) 7
Anytime the wage is above equilibrium, _________________________ will be a result. - more people willing to work at that wage than there are jobs available
3. Unions A Union is a group that tries to __________________________higher wages, better benefits, and better working conditions for __________________. - collective bargaining - strike They play a smaller role in the US economy now than they once did. - still prevalent in many European nations Union workers can earn from 10% to 20% more than non-union workers. Because the wage is pushed up past equilibrium, there will be some ___________________. - union members vs non-union members
Are Unions Good or Bad for the Economy? __________________ of unions argue that unions are a cartel, which causes inefficiency because fewer workers end up being hired at the higher union wage. __________________of unions argue that unions are an answer to the problems that occur when a firm has too much power in the labor market. _________________________________________________________________________________ Summary: The unemployment rate is the percentage of those who would like to work but do not have jobs. The unemployment rate is an imperfect measure of joblessness. Just because someone doesnt have a job, it doesnt mean they are unemployed. In the U.S. economy, most people who become unemployed find work within a short period of time. There are several reasons for unemployment even in good economic times: - takes time to find a job matching your preferences and skills - dynamic, changing economy will always have some sectors that become obsolete - wages paid above equilibrium - minimum wage laws - unions - efficiency wages
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 6Dokument12 SeitenChapter 6Yasin IsikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic D) UnemploymentDokument8 SeitenTopic D) UnemploymentRachel HiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Unemployment in IndiaDokument17 SeitenMeasurement of Unemployment in IndiaRitika PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Assignment On "Unemployment" Course Code: LCM-111: Submitted ToDokument10 SeitenAn Assignment On "Unemployment" Course Code: LCM-111: Submitted ToTonmoy DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 7Dokument3 SeitenLesson 7Maurice AgbayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other IssuesDokument20 SeitenEmployment: Growth, Informalisation and Other Issuesanon_461513108Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 26 - Business Cycle, Unemployment and InflationDokument20 SeitenChapter 26 - Business Cycle, Unemployment and InflationPavan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labour Turnover & AbsenteeismDokument14 SeitenLabour Turnover & Absenteeismshweta.gdp100% (1)
- Labour Economics - Unit 1Dokument34 SeitenLabour Economics - Unit 1RidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guided Notes - LaborDokument6 SeitenGuided Notes - LaboryogurtkingyahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch14 Model of Unemployment 2Dokument34 SeitenCh14 Model of Unemployment 2Richardson HolderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Chapter 6: Productivity and Human Capital I. Standard of Living Around The WorldDokument6 SeitenLecture Chapter 6: Productivity and Human Capital I. Standard of Living Around The WorldKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6fa4a36a-Unemployment SlidesDokument11 Seiten6fa4a36a-Unemployment SlidesdevikarobbiinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument30 SeitenChapter 7Zhihao WangNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unemployment Rate As An Economic Indicator: Jean M. LovatiDokument8 SeitenThe Unemployment Rate As An Economic Indicator: Jean M. LovatiPertiwi PramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnemploymentDokument34 SeitenUnemploymentSimantoPreeomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Private Unemployment InsuranceDokument13 SeitenPrivate Unemployment InsuranceShubhadha IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Uploading 2 Intro To Labor EconDokument50 SeitenFor Uploading 2 Intro To Labor EconcarldomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PART THREE - GrammarDokument5 SeitenPART THREE - GrammarFaris Abdul HafizhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrep Activity 02Dokument4 SeitenEntrep Activity 02KaisenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employment, Migration, and UrbanizationDokument14 SeitenEmployment, Migration, and UrbanizationAlzen Marie DelvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiểu luận gthieu ngànhDokument10 SeitenTiểu luận gthieu ngànhMỹ ThảoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment I: Bm218 Essential of Research Methodology TopicDokument8 SeitenAssignment I: Bm218 Essential of Research Methodology TopicAbdul KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prayoga Dwi N - Summary CH 22Dokument7 SeitenPrayoga Dwi N - Summary CH 22Prayoga Dwi NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economy Today 14th Edition Schiller Solutions Manual 1Dokument11 SeitenEconomy Today 14th Edition Schiller Solutions Manual 1gina100% (37)
- Summary Chapter 28 Unemployment: Current Population SurveyDokument4 SeitenSummary Chapter 28 Unemployment: Current Population SurveyDini KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Labor EconomicsDokument41 SeitenIntro To Labor EconomicsLine RingcodanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unemploy Men 1Dokument22 SeitenUnemploy Men 1shivangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Economics Module 2Dokument9 SeitenApplied Economics Module 2Arap MamboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse Class 11 Economics Indian Economy Revision Notes Chapter-7 Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other IssuesDokument5 SeitenCbse Class 11 Economics Indian Economy Revision Notes Chapter-7 Employment: Growth, Informalisation and Other IssuesiblNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unemployement in India by Vebs111Dokument35 SeitenUnemployement in India by Vebs111Vaibhav Eknathrao TandaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives For Class 24: The Business Cycle and UnemploymentDokument9 SeitenObjectives For Class 24: The Business Cycle and UnemploymentEmmanuel Kwame OclooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Macroeconomics ProblemDokument30 SeitenChapter 5 Macroeconomics Problemtamirat ashagre ijiguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attrition Related To HRDokument36 SeitenAttrition Related To HRreddevils2787Noch keine Bewertungen
- Government Economic Objectives and Policies: Textbook, Chapter 26 (PG 317-328)Dokument10 SeitenGovernment Economic Objectives and Policies: Textbook, Chapter 26 (PG 317-328)Vincent ChurchillNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Considered UnemploymentDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Considered UnemploymentKari KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 9 Unemployment PEC100110 Principles of Economics UNILAKDokument10 SeitenUnit 9 Unemployment PEC100110 Principles of Economics UNILAKalexisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unemployment in IndiaDokument21 SeitenUnemployment in IndiaSagar Nawale73% (37)
- Mapeh (Health 10) Fraudulent Health Services: Brief Discussion of The LessonDokument8 SeitenMapeh (Health 10) Fraudulent Health Services: Brief Discussion of The LessonKimberly Camacho CatubigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maddison Gama - Economics InterviewsDokument7 SeitenMaddison Gama - Economics Interviewsapi-598096295Noch keine Bewertungen
- Finalhardcopy AttritionDokument41 SeitenFinalhardcopy Attritionvinivasu06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report On UnemploymentDokument5 SeitenReport On UnemploymentSyed Khizar HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employment and Unemployment & Social DevelopmentDokument12 SeitenEmployment and Unemployment & Social DevelopmentS Sohaib HGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unemployment Rate (%) Unemployed/labour Force X 100Dokument7 SeitenUnemployment Rate (%) Unemployed/labour Force X 100James LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Simple Tips To Beat Age Bias Webinar WORKSHEETDokument6 Seiten5 Simple Tips To Beat Age Bias Webinar WORKSHEETIcq joyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Chapter 15Dokument12 SeitenMacroeconomics Chapter 15Sultan AnticsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Exploration: Disease Spread: Vocabulary: Disease, Epidemic, Infect, Infectious Disease, PathogenDokument6 SeitenStudent Exploration: Disease Spread: Vocabulary: Disease, Epidemic, Infect, Infectious Disease, PathogenNyajah AllaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Unemployment in IndiaDokument5 SeitenTypes of Unemployment in IndianaseemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA 225 Maintenance of Human ResourceDokument2 SeitenBA 225 Maintenance of Human ResourceHoneylet PangasianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macrolecture3 Jobs and UnemploymentDokument21 SeitenMacrolecture3 Jobs and UnemploymentIrwan CrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labour Economics - Unit 2Dokument21 SeitenLabour Economics - Unit 2RidhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of UnemploymentDokument5 SeitenTypes of UnemploymentsotawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics Chap 15 UnemploymentDokument3 SeitenMacroeconomics Chap 15 UnemploymentChau GiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Ethics Midterm ExamDokument3 SeitenBusiness Ethics Midterm ExamCris MillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unemployment Research Paper PDFDokument5 SeitenUnemployment Research Paper PDFenwtyxakf100% (1)
- Types of UnemploymentDokument22 SeitenTypes of UnemploymentKusantha Rohan WickremasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Descent Work Employment and Transcultural Nursing 1Dokument9 SeitenModule 1 Descent Work Employment and Transcultural Nursing 1luke gartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unemployment in IndiaDokument11 SeitenUnemployment in IndiaAbhilash FrancasisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Dokument17 SeitenPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Lecture - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine Sauer100% (1)
- Intermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduDokument5 SeitenIntermediate Microeconomic Theory Katherine M. Sauer, Ph.D. ECO 3010 AD 530-R 303-556-3037 Fall 2012 Ksauer5@msudenver - EduKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionDokument3 SeitenPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Reading Outline - IntroductionKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Dokument4 SeitenPrinciples of MIcroeconomics - Notes - Markets/Supply/Demand - Part 2Katherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Summary TemplateDokument1 SeiteModel Summary TemplateKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Dokument4 SeitenChapter 1: Analyzing Economic Problems 1.1 Why Study Microeconomics?Katherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceDokument7 SeitenIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch04 Consumer ChoiceKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsDokument2 SeitenReadingNotes Chapter02 StatsKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesDokument8 SeitenIntMicro ReadingOutline Ch03 PreferencesKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsDokument2 SeitenReadingNotes Chapter09 StatsKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsDokument2 SeitenReadingNotes Chapter08 StatsKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsDokument3 SeitenReadingNotes Chapter07 StatsKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerDokument6 SeitenReading Notes Economics - Dr. SauerKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsDokument2 SeitenReadingNotes Chapter06 StatsKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadingNotes Chapter08 MathDokument2 SeitenReadingNotes Chapter08 MathKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsDokument4 SeitenChapter 4: Non-Linear Functions 4.1 Quadratic, Cubic and Other Polynomial FunctionsKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingDokument5 SeitenThis Chapter Is Kind of Intense. I Don't Recommend Trying To Read Through The Whole Thing in One SittingKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes - Big Mac IndexDokument2 SeitenLecture Notes - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 3 Information SheetDokument1 SeiteExam 3 Information SheetKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerDokument21 SeitenTaxes Individuals Pay: Citizen's Guide To Economics Dr. Katie SauerKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Price ControlsDokument1 SeiteWorksheet Price ControlsKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - Big Mac IndexDokument11 SeitenLecture - Big Mac IndexKatherine SauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus & Question Paper Sem 8 PDFDokument35 SeitenSyllabus & Question Paper Sem 8 PDFSoham BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employees' State Insurance Corporation E-Pehchan CardDokument3 SeitenEmployees' State Insurance Corporation E-Pehchan CardAravindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Task 4Th Quarter Scaffold No. 1Dokument5 SeitenPerformance Task 4Th Quarter Scaffold No. 1MayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Curry PowderDokument8 SeitenProject On Curry PowderSrj SoorajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article On CompensationDokument9 SeitenArticle On CompensationAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- (U) Labor (S) Digests (C)Dokument263 Seiten(U) Labor (S) Digests (C)Carmii Ho100% (1)
- PDF To DocsDokument72 SeitenPDF To Docs777priyankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rps 2022Dokument2 SeitenRps 2022Durgeswara Rao VangipurapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting Employee'S Motivation in The Fast Food Industry: The Case of KFC Uk LTDDokument10 SeitenFactors Affecting Employee'S Motivation in The Fast Food Industry: The Case of KFC Uk LTDMuhammad Ahmad WarraichNoch keine Bewertungen
- C1 A Perspective On EntrepreneurshipDokument35 SeitenC1 A Perspective On EntrepreneurshipWilnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bar QuestionsDokument24 SeitenBar QuestionsAisha TejadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of UnemploymentDokument2 SeitenTypes of UnemploymentSwapnil PednekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HRM Lectures (Full Notes)Dokument62 SeitenHRM Lectures (Full Notes)Maaz Ahmad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.5 Wellington Investment Vs Trajano 2 PDFDokument2 Seiten4.5 Wellington Investment Vs Trajano 2 PDFAcqua Di GioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Leasing Salary Guide 2016Dokument10 SeitenAircraft Leasing Salary Guide 2016avianovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 Matrixvisa Initial Documents 2018 PDFDokument27 Seiten0 Matrixvisa Initial Documents 2018 PDFBraamNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.R. No. 232870, June 03, 2019Dokument16 SeitenG.R. No. 232870, June 03, 2019SheNoch keine Bewertungen
- La Consolacion v. PascuaDokument1 SeiteLa Consolacion v. PascuaSabritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2007 Year End OverviewDokument28 Seiten2007 Year End OverviewLmoorjaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talent Mangement and Employee RetentionDokument11 SeitenTalent Mangement and Employee RetentionAnonymous cQTp4CgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Closure of Establishment and Reduction of PersonnelDokument3 SeitenClosure of Establishment and Reduction of PersonnelHazel LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finnish Government and Its Civil ServiceDokument4 SeitenFinnish Government and Its Civil ServiceShurel Marl BuluranNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSS Vs Sanico Case Digest G.R. No. 134028Dokument3 SeitenSSS Vs Sanico Case Digest G.R. No. 134028Case Digest CompilationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument39 SeitenChapter 3Ashwin vk100% (1)
- Cost Project ReportDokument11 SeitenCost Project ReportAta u Samad100% (1)
- Colgate Palmolive Case Study: - Monal TandonDokument9 SeitenColgate Palmolive Case Study: - Monal TandonArchana LenkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farm Records NotesDokument6 SeitenFarm Records NotesGodfrey Muchai100% (2)
- Mgmt. Acc. AssignmentDokument1 SeiteMgmt. Acc. AssignmentMuskan DulaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Er-Ee Loan AgreementDokument2 SeitenEr-Ee Loan AgreementDaniel ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- National WelfareDokument10 SeitenNational WelfareSTAR GROUPSNoch keine Bewertungen