Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
CAN Bus Description
Hochgeladen von
Luis Manuel GodoyOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CAN Bus Description
Hochgeladen von
Luis Manuel GodoyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CAN Bus Description
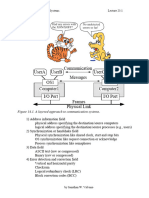
The Controller Area Network (CAN) specification defines the Data Link Layer, ISO 11898 defines the Physical Layer. The CAN bus [CANbus] is a Balanced (differential) 2-wire interface running over either a Shielded Twisted Pair (STP), Un-shielded Twisted Pair (UTP), or Ribbon cable. Each node uses a Male 9-pin D connector. The Bit Encoding used is: Non Return to Zero (NRZ) encoding (with bit-stuffing) for data communication on a differential two wire bus. The use of NRZ encoding ensures compact messages with a minimum number of transitions and high resilience to external disturbance.
CAN Bus Electrical Interface Circuit
A number of different data rates are defined, with 1Mbps (Bits per second) being the top end, and 10kbps the minimum rate. All modules must support 20kbps. Cable length depends on the data rate used. Normally all the devices in a system transfer uniform and fixed bit-rates. The maximum line length is 1Km, 40 meters at 1Mbps. Termination resistors are used at each end of the cable. The worst-case transmission time of an 8-byte frame with an 11-bit identifier is 134 bit times (that's 134 microseconds at the maximum baud rate of 1Mbits/sec).
Can Message Frame
The CAN Bus interface uses an asynchronous transmission scheme controlled by start and stop bits at the beginning and end of each character. This interface is used, employing serial binary interchange. Information is passed from transmitters to receivers in a data frame. The data frame is composed of an Arbitration field, Control field, Data field, CRC field, ACK field. The frame begins with a 'Start of frame' [SOF], and ends with an 'End of frame' [EOF] space. The data field may be from 0 to 8 bytes. The frame check sequence is derived from a Cyclic Redundancy Code (CRC); the coefficients are generated modulo-2: X15 + X14 + X10 + X8 + X7 + X4 + X3 + 1. CAN implements five error detection mechanisms; 3 at the message level and 2 at the bit level [Also incorporates error flags]. At the message level: Cyclic Redundancy Checks (CRC), Frame Checks, Acknowledgment Error Checks. At the bit level: Bit Monitoring, Bit Stuffing. The CANbus pinout is shown in the table below. The Application for CAN bus in the automotive area include;
A low speed CANbus may be employed to operate window and seat controls. A high speed CANbus may be employed for engine management or brake control. Many other applications are possible [Engine Sensors, Anti-Skid Systems]. Equivalent Input and Output IC Schematic Diagrams. For additional information refer to: CAN Bus Specification; Version 2.0, ISO 11898/11519. CANbus is used as a vehicle bus, for other vehicle Buses see Automotive Buses. CANbus is also used as an Industrial Field bus, for other Field Buses see Field Buses. Detailed info on CANbus {Robert Bosch GmbH}, Detailed info on CANbus {Kvaser}
Can Voltages and Currents
CAN may also sometimes be found as Car Area Network
CAN Bus Pin Out
The Can Bus pinout for the 9-pin D connector is shown in the table below. Additional connector styles are listed on the CAN Bus Connector Pin out page, or CAN Bus Round Connector Pin out. Many of the additional connector pin outs are used with CANopen and include: 10-pin header [5 x 2 multipole], RJ10 [Modular Connector Jack], RJ45 [Modular Connector Jack], 5-pin mini [circular], 5-pin micro [circular], Open Style, 7/8/9-pin round connectors.
9 Pin (male) D-Sub CANbus PinOut Pin # Signal Names Signal Description 1 Reserved Upgrade Path 2 CAN_L Dominant Low 3 CAN_GND Ground 4 Reserved Upgrade Path 5 CAN_SHLD Shield, Optional 6 GND Ground, Optional 7 CAN_H Dominant High 8 Reserved Upgrade Path 9 CAN_V+ Power, Optional
Some systems may use pin 8 as an error line, to indicate an error on the net. Listing of 'D-sub' Connectors Manufactures ........ Listing of Cable Manufactures
CAN Bus Standard Organizations
CiA: CAN In Automation - International Users and Manufactures Group, http://www.can-cia.org ISO: International Organization for Standardization, http://www.iso.org All other Standard Organizations
CAN Bus Standard/Specifications Information
ISO/DIS 11898-1: Road vehicles -- Controller area network (CAN) -- Part 1: Data link layer and physical signaling ISO/DIS 11898-2: Road vehicles -- Controller area network (CAN) -- Part 2: High-speed medium access unit ISO/CD 11898-3: Road vehicles -- Controller area network (CAN) -- Part 3: Low-speed fault tolerant medium dependent interface ISO/CD 11898-4: Road vehicles -- Controller area network (CAN) -- Part 4: Time triggered communication CAN Bus Specification Version 2.0 All other Interface bus specifications [Non-CANbus]
CAN Bus Interface ICs
CAN Bus uses a Drive Voltage: High; 2.75v to 4.5 volts, Low; 0.5 to 2.25 volts, Differential 1.5v to 3.0 volts
CAN Bus Interface IC Logic Transition Levels
Analog Devices, Inc. {Mixed-Signal-DSPs (ADSP-21992) with 160MIPS and On-Chip CAN V2.0b} Atmel Corp. {8-bit RISC transceivers and microcontrollers. CAN bus standard (2.0A & 2.0B) with 80C51 core and AVR core} austriamicrosystems AG {Smart Power Management device with high speed CAN interface} Bosch {IP Modules; CAN Core, C_CAN, D_Can, TTCAN} Cast {CAN Core, Bus Controller ICs} Dallas Semiconductor 'Maxim' {DS80C390 Dual CAN High-Speed Microprocessor, bus controller ICs} freescale {33389/33388 low speed fault tolerant CANBus transceiver} Infineon {82C900 Stand-alone TwinCan Controller-TLE6250 CAN Transceiver IC Manufacturer} Inicore Inc. {CAN IP Core IC Manufacturer} Intel, Intel App Notes {CanBus Interface 82527 IC} Linear Technology {CAN Transceiver IC Manufacturer} Maxim Integrated Products {DS80C390 Dual CAN High-Speed Microprocessor, bus controller IC} Melexis {CAN Bus Transceiver IC Manufacturer} Microchip {MCP2510 Stand-alone CanBus Controller IC} National Semiconductor {uP with CANBus Interface} NXP {8/16-bit CAN Bus 2.0 Controllers/Transceiver} Renesas Technology Corp {Micro-Controller [uC] with CAN / LIN Interface} STMicroelectronics {uP with CAN Interface} Xilinx {CAN IP Core, Spartan, Virtex}
Yamar Electronics {DC-BUS for digital communication overcome hostile in-vehicle power line communication environment. Power line Communication multiplex semiconductor transceivers for automotive and industrial CAN, LIN networks.} TI {TMS320F241 with CANbus Interface-3.3v Line Transceiver ICs} IC Manufacturers Listing {All other types} V62/09611: SN65HVD233; Controller area network (CAN) transceiver V62/06629: SN65HVD230; 3.3 V CAN transceiver
CANbus Signal Type Output Voltage (High) Output Voltage (Low) Output Voltage Output Current Impedance Circuit Type Bit Times Encoding Format Transmit/Receive Frequency Topology Medium Access Control
CAN Bus I/O Characteristics Digital Interface VOH +4 volts min, +5.5 volts max VOL +0 volts min, +1.5 volts max +16 volts (Absolute Max) 100mA 124 ohm termination between +/- terminals Differential 1uS @ 1Mb/s; 2uS @ .5Mb/s 4uS @ .25Mb/s Non-Return-to-Zero (NRZ) 1Mb/s @ 40 meters Point-to-Point Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) @ 9 pin D-Sub Carrier Sense, Multiple Access with Collision Detect (CSMA/CD). Non-destructive bit wise arbitration
CANbus Electronic Equipment
-----------------OEM COT Cards and Board Manufacturers {With CANbus interfaces} AnaGate {CAN TCP/IP gateways (Ethernet protocol)} Detailed info on CANbus {Robert Bosch GmbH} ESD Electronic Systems {CanBus Cards and Modules} Kvaser {CAN interface for the PCI-X bus, CAN interface for the PCI bus} LeCroy Corp. {Canbus Trigger and Decoding oscilloscope Package} National Instruments {Controller CAN interfaces for PCI, PXI, PCMCIA. CAN Device Simulator, high-speed CAN cables} Squarell Technology {CANbus components for harsh environments and automotive applications. Interfaces, Dataloggers, Sensor devices and Output devices. Configurable without programming.}
Vector-CANtech {CAN-Bus Development Tools-Interfaces} Yokogawa {CAN Bus Signal Analyzer}
CAN Bus Transition Levels
CAN Bus Higher Layer Protocols
Following the ISO/OSI layer model, the protocol layer is implemented over the data link layer [which conforms to CAN 2.0A and/or 2.0B], and the physical layer which specified in the ISO 11898 standard. The data link layer and the physical layer is implemented in hardware.
TTCAN
TTCAN: Time Triggered CAN protocol. Allows the bus to appear more deterministic
CANOpen
CANopen is based on the CANbus data link layer and high-speed transceiver as specified in ISO 11898, part 1 and 2. In addition, CANopen specifies bit-timing and recommends pin-assignments for connectors. Uses Device profiles [defines four types of messages]; Manufactures follow guidelines in the CANOpen spec producing devices with characteristics which will operate with each other. There are a number of Bit rates based on bus length: [based on 5nS/m cable propagation delay]. 1Mbps [Maximum transfer speed] up to a 25 meter maximum bus length [Nominal bit time is 1uS] 800kbps [Maximum transfer speed] up to a 50 meter maximum bus length [Nominal bit time is 1.25uS] 500bps [Maximum transfer speed] up to a 100 meter maximum bus length [Nominal bit time is 2uS] 250kbps [Maximum transfer speed] up to a 250 meter maximum bus length [Nominal bit time is 4uS] 125kbps [Maximum transfer speed] up to a 500 meter maximum bus length [Nominal bit time is 8uS] 50kbps [Maximum transfer speed] up to a 1000 meter maximum bus length [Nominal bit time is 20uS] 20kbps [Maximum transfer speed] up to a 2500 meter maximum bus length [Nominal bit time is 50uS] 10bps [Maximum transfer speed] up to a 5000 meter maximum bus length [Nominal bit time is 100uS] Pinout for a number of CANopen connectors are listed on the CAN Bus Connector Pin out page. CANopen Software description/ Specs {B.Hallgren ATLAS DCS}
CAN Kingdom
CAN Kingdom defines a set of protocol primitives, based on the CAN protocol. A bus Master is defined during initialization, the Master checks to see which nodes are connected to the network. CAN Kingdom uses either an Event driven or Time driven timing model.
DeviceNet
CENELEC standard - EN50325 DeviceNet identifies the physical layer but does not use the same physical layer interface as ISO 11898, and is based on the CanBus protocol. DeviceNet provides optical isolation for additional protection and does not use 9-pin sub-D connectors.
DeviceNet only supports three baud rates: 125, 250 and 500 Kbaud ( @ 500 meters) with up to 64 devices on the (differential) bus. In addition the cable carries 24 volts which powers the devices. DeviceNet description {ODVA.org} Info {Rockwell Automation ~ Allen Bradley} DeviceNet Cable Specifications (Appendix B)
Smart Distributed System (SDS)
SDS description and Specs, Honeywell, http://sensing.honeywell.com SDS Smart Distributed System defines the physical layer and application layer (based on CANbus). Used for intelligent sensors and actuators, operating over a single 4-wire cable, interfacing up to 64 nodes with a maximum of 126 addresses. Application Layer Protocol Specification (Rev 2.0) Physical Layer Specification (Rev 2.0) J1939 is another protocol based on the Controller Area Network [Canbus]. NMEA2000 is another protocol based on the Controller Area Network. CANaerospace / AGATE databus is a 1Mbps two-wire bus used to interconnect sensors and navigation systems for General Aviation [GA]. The AGATE databus is based on the CANbus. AGATE [Advanced General Aviation Experiments] is an alliance [consortium] of Government [NASA] and Industry.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Applications: AutomotiveDokument8 SeitenApplications: AutomotiveMohammad FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avc Lan and Avc Lan PlusDokument15 SeitenAvc Lan and Avc Lan PlusMario Alberto Abarca Rodriguez100% (1)
- (Owner's Manual) 2007 Subaru Forester XDokument356 Seiten(Owner's Manual) 2007 Subaru Forester XbobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyundai Elantra 1.6 Engine Electrical1Dokument55 SeitenHyundai Elantra 1.6 Engine Electrical1MANUALES2000CLNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAN HandoutDokument16 SeitenCAN HandoutJaffer HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering Angle Sensor ResetsDokument57 SeitenSteering Angle Sensor ResetsAunaunZaa'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Benz - Vehicle NetworkingDokument27 SeitenBenz - Vehicle NetworkingAnanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Diagnóstico de Componentes IntegralesDokument18 Seiten15 Diagnóstico de Componentes IntegralesmongongoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU) : Ankul GuptaDokument20 SeitenElectronic Control Unit (ECU) : Ankul Guptadarkim ajahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pow Powertrain Products PDF enDokument67 SeitenPow Powertrain Products PDF enJesse DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holley Carburetor Model 4160 Instruction Sheet 199R8339: DisassemblyDokument6 SeitenHolley Carburetor Model 4160 Instruction Sheet 199R8339: DisassemblyAlfonso JaureguiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAN TutorialDokument22 SeitenCAN TutorialApoorva BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Listening and Speaking 3 Q: Skills For Success Unit 3 Student Book Answer KeyDokument4 SeitenListening and Speaking 3 Q: Skills For Success Unit 3 Student Book Answer KeyFahd AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIN Basics For Beginners enDokument118 SeitenLIN Basics For Beginners enAleksey Misiura100% (1)
- Diagnosis From The Drivers SeatDokument101 SeitenDiagnosis From The Drivers Seatabul hussain100% (1)
- Hipaa Information and Consent FormDokument1 SeiteHipaa Information and Consent FormJake HennemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAN FinalDokument30 SeitenCAN Finaljyothi bagewadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MST 9000 PDFDokument12 SeitenMST 9000 PDFJorge Alberto Barbosa Perez100% (1)
- Chapter3 Automotive Embedded ApplicationsDokument156 SeitenChapter3 Automotive Embedded ApplicationsKomal KalkutkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canalyzer: Installation & Quick Start GuideDokument84 SeitenCanalyzer: Installation & Quick Start GuideNitish Chiniwar100% (2)
- CAN ProtocolDokument9 SeitenCAN Protocolhaythem.mejri.proNoch keine Bewertungen
- BootLoader Del 78K0-KX2Dokument60 SeitenBootLoader Del 78K0-KX2Anonymous pu1L9ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Canbus: Jason Mccomb FitasDokument15 SeitenIntroduction To Canbus: Jason Mccomb FitasMike100% (1)
- CAN Bus Sloa101bDokument17 SeitenCAN Bus Sloa101bgatotNoch keine Bewertungen
- 012-NetNumen U31 R22 Northbound Interface User Guide (SNMP Interface)Dokument61 Seiten012-NetNumen U31 R22 Northbound Interface User Guide (SNMP Interface)buts101100% (5)
- NI Tutorial 2732 enDokument5 SeitenNI Tutorial 2732 enmanumanu12Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Controller Area Network (CAN) Technology: November 12, 2003Dokument20 SeitenAn Overview of Controller Area Network (CAN) Technology: November 12, 2003Dilyan MarinoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 4 Fundamentals of Automotive ElectronicsDokument61 SeitenUNIT 4 Fundamentals of Automotive Electronicsnubla mNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSO Function Generator ExerciseDokument24 SeitenDSO Function Generator ExerciseEdidjo DarwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5500-6600 LMS AdjustmentDokument2 Seiten5500-6600 LMS AdjustmentDon LuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esp32-S3 Technical Reference Manual enDokument787 SeitenEsp32-S3 Technical Reference Manual enANoch keine Bewertungen
- VW/Audi 1.8T Transverse (FWD) Ignition Wiring Replacement Kit Installation Guide Skill Level 2 - ModerateDokument21 SeitenVW/Audi 1.8T Transverse (FWD) Ignition Wiring Replacement Kit Installation Guide Skill Level 2 - ModerateKushal ExpertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding and Using The CAN-1Dokument41 SeitenUnderstanding and Using The CAN-1mail87523Noch keine Bewertungen
- At91sam7 - CanDokument58 SeitenAt91sam7 - Cangopismiles1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sae j1962 1995 PDFDokument8 SeitenSae j1962 1995 PDFmiguelcastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Admit CardDokument1 SeiteAdmit CardMohammed ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Grundlagen FlexRay v10 enDokument39 Seiten06 Grundlagen FlexRay v10 envinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valeo Power ChargerDokument2 SeitenValeo Power ChargercristiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAN Bus - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument16 SeitenCAN Bus - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRakesh S K100% (1)
- Motion Control ReportVon EverandMotion Control ReportBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Massive MIMO (FDD) (eRAN13.1 - 05)Dokument154 SeitenMassive MIMO (FDD) (eRAN13.1 - 05)Shashank Prajapati100% (2)
- Chrysler - CCD (Chrysler Collision Detection) Data Bus - Carprog - 博客园Dokument21 SeitenChrysler - CCD (Chrysler Collision Detection) Data Bus - Carprog - 博客园Francisco López RosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devops ResumeDokument5 SeitenDevops ResumeEkant BajajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrusion Detection System Based On The Analysis of Time Intervals of CAN Messages For In-Vehicle NetworkDokument6 SeitenIntrusion Detection System Based On The Analysis of Time Intervals of CAN Messages For In-Vehicle NetworkPaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart JIG Power DiagnosisDokument102 SeitenSmart JIG Power DiagnosisNicu LiviuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Converting Denary To HexDokument28 SeitenConverting Denary To HexArif WidiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avc LanDokument9 SeitenAvc LanPedro BravoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mosfet & Igbt: Ee3147 Power ElectronicsDokument16 SeitenMosfet & Igbt: Ee3147 Power ElectronicsHoàng TúNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coduri Vag Com OctaviaDokument13 SeitenCoduri Vag Com Octaviagtm55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Electrical and AutotronicsDokument8 SeitenAutomotive Electrical and Autotronicsrocky4bestNoch keine Bewertungen
- PWM Based DC Motor Speed Control Using MicrocontrollerDokument8 SeitenPWM Based DC Motor Speed Control Using MicrocontrollertazebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Gear Shift Technology (AGS) or Auto Manual Transmission (AMT)Dokument5 SeitenAuto Gear Shift Technology (AGS) or Auto Manual Transmission (AMT)Ahmed YousfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brake - Control - 2 TKEDokument26 SeitenBrake - Control - 2 TKETecwyn WebsterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relays and FusesDokument8 SeitenRelays and FusesTesfahun TegegneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAN-bus InterfaceDokument2 SeitenCAN-bus Interfacemohamed abd el razek0% (1)
- Controller Area Network: Submitted By:Chandra Shekar.I.G Dept of E&C 1NH02EC010 NhceDokument22 SeitenController Area Network: Submitted By:Chandra Shekar.I.G Dept of E&C 1NH02EC010 Nhceapi-3760105100% (2)
- Rfid Security Access Control System: Submitted byDokument20 SeitenRfid Security Access Control System: Submitted byVale Conde CuatzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors For Micro Controllers by ShanDokument3 SeitenPull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors For Micro Controllers by Shanshantilaal100% (1)
- DP15&DP16 Error CodesDokument1 SeiteDP15&DP16 Error Codespavlik1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.USB-CAN Adapter ManualDokument18 Seiten1.USB-CAN Adapter ManualFrancisco Santiago GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive ElectronicsDokument100 SeitenAutomotive ElectronicsanushkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I S Bus Specification: 1.0 2.0 Basic Serial Bus RequirementsDokument7 SeitenI S Bus Specification: 1.0 2.0 Basic Serial Bus RequirementseballiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fully Autonomous Vehicles: Visions of the future or still reality?Von EverandFully Autonomous Vehicles: Visions of the future or still reality?Noch keine Bewertungen
- Help Where Can You Get Free Ebook For 8086 Microprocessor by A K Roy and K N Bhurchandi or by Kenneth AyalaDokument3 SeitenHelp Where Can You Get Free Ebook For 8086 Microprocessor by A K Roy and K N Bhurchandi or by Kenneth AyalaasuhassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euler's Method and Logistic Growth Solutions (BC Only) SolutionsDokument4 SeitenEuler's Method and Logistic Growth Solutions (BC Only) SolutionsdeltabluerazeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Praveen Ya (Final)Dokument3 SeitenPraveen Ya (Final)Priyanka VijayvargiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Reliability Test System MODEL 17010Dokument12 SeitenBattery Reliability Test System MODEL 17010G H.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chicago Citation: Chicago Notes-Bibliography Style GuideDokument4 SeitenChicago Citation: Chicago Notes-Bibliography Style GuideElizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Basic TipsDokument21 SeitenVisual Basic TipsbenoycNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeliTrim Manual en PDFDokument9 SeitenHeliTrim Manual en PDFJuan Pablo100% (1)
- Opamp ProjectDokument10 SeitenOpamp Projectbirla_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTPS: - WWW - Whois.com - Whois - Tech-Al - InfoDokument4 SeitenHTTPS: - WWW - Whois.com - Whois - Tech-Al - InfoΛουκάςNoch keine Bewertungen
- STAAD ANALYSIS - Adrressing Requirements AISC 341-10 - RAM - STAAD Forum - RAM - STAAD - Bentley CommunitiesDokument2 SeitenSTAAD ANALYSIS - Adrressing Requirements AISC 341-10 - RAM - STAAD Forum - RAM - STAAD - Bentley Communitieschondroc11Noch keine Bewertungen
- CRT Learning Module: Course Code Course Title No. of Hours Module TitleDokument16 SeitenCRT Learning Module: Course Code Course Title No. of Hours Module TitleEiszel CadacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 5 SerializationDokument7 SeitenChap 5 Serializationelwa3erNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vandana New ResumeDokument1 SeiteVandana New ResumeVandu KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel ExerciseDokument296 SeitenExcel ExerciseshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Advances in Machine LearningDokument374 SeitenNew Advances in Machine LearningMücahid CandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL4000Dokument17 SeitenSL4000Felix EstrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Hygiene Air SamplingDokument8 SeitenIndustrial Hygiene Air SamplingMiguel Gonzalez SaborioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil and Gas Reloaded: Offshore ArgentinaDokument9 SeitenOil and Gas Reloaded: Offshore ArgentinaMuhammad Fahmi AnbNoch keine Bewertungen
- sjzl20070793-NetNumen M3 (ZXC10 BSSB) (V 3.08.19.01) Software Installation Manual (Windows) PDFDokument243 Seitensjzl20070793-NetNumen M3 (ZXC10 BSSB) (V 3.08.19.01) Software Installation Manual (Windows) PDFGus RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlfrescoDokument10 SeitenAlfrescoanangsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Computer NetworkDokument26 SeitenAdvances in Computer NetworkSandesh RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei AC6805 Wireless Access Controller Datasheet - 2Dokument16 SeitenHuawei AC6805 Wireless Access Controller Datasheet - 2irfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pune Institute of Computer Technology PUNE - 411043 Department of Electronics & TelecommunicationDokument12 SeitenPune Institute of Computer Technology PUNE - 411043 Department of Electronics & TelecommunicationNakul SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lea Dardanos Efi-Controller eDokument6 SeitenLea Dardanos Efi-Controller eadfumegaNoch keine Bewertungen