Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
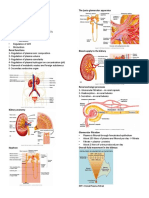
Hormone Structure Functions Pituitary Hormones: Oxytocin
Hochgeladen von
cs134Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hormone Structure Functions Pituitary Hormones: Oxytocin
Hochgeladen von
cs134Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
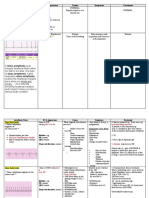
Structure Functions Pituitary Hormones uterine contraction, causes milk posterior pituitary peptide; ejection in lactating females (the
"letpolypeptide of 9 amino Oxytocin down" response), responds to suckling acids CYIQNCPLG (C's are reflex and estradiol, lowers steroid disulfide bonded) synthesis in testes responds to osmoreceptor which + senses extracellular [Na ], blood posterior pituitary peptide; Vasopressin pressure regulation, increases H2O polypeptide of 9 amino (antidiuretic hormone, readsorption from distal tubules in acids CYFQNCPRG (C's ADH) kidney, loss results in dilute urine and are disulfide bonded) polydipsia (constant thirst) condition termed diabetes insipidus -MSH most significant, involved in pigmentation, primary responses are anterior pituitary peptides immunomodulation via melanocortin derived from POMC: receptor (MC-1R)-expressing monocytes, macrophages, and polypeptide = 13 amino Melanocyte-stimulating dendritic cells (DCs), down-regulates acids hormones (MSH) the production of proinflammatory and polypeptide = 18 amino immunomodulating cytokines (IL-1, ILacids 6, TNF-, IL-2, IFN-, IL-4, IL-13) as polypeptide = 12 amino well as the expression of costimulatory acids molecules (CD86, CD40, ICAM-1) on antigen-presenting DCs anterior pituitary peptide Adrenocorticotropic stimulates cells of adrenal gland to derived from POMC; hormone (ACTH) also increase steroid synthesis and polypeptide = 39 amino called corticotropin secretion acids anterior pituitary peptides derived from POMC: increases fatty acid release from polypeptide = 93 amino adipocytes acids polypeptide = 60 amino acids Thyrotropin (thyroidanterior pituitary peptides; 2 acts on thyroid follicle cells to stimulate stimulating hormone, proteins: is 96 amino throid hormone synthesis TSH) acids; is 112 general anabolic stimulant, increases Growth hormone (GH, anterior pituitary peptide; release of insulin-like growth factor-I or somatotropin) protein of 191 amino acids (IGF-I), cell growth and bone sulfation stimulates differentiation of secretory anterior pituitary peptide; Prolactin (PRL) cells of mammary gland and stimulates protein of 197 amino acids milk synthesis Luteinizing hormone anterior pituitary peptides; 2 increases ovarian progesterone Lipotropin (LPH)
Hormone
(LH); human chorionic proteins: is 96 amino gonadotropin (hCG) is acids; is 121 similar and produced in placenta
synthesis, luteinization; acts on Leydig cells of testes to increase testosterone synthesis and release and increases interstitial cell development ovarian follicle development and anterior pituitary peptides; 2 ovulation, increases estrogen Follicle-stimulating proteins: is 96 amino production; acts on Sertoli cells of hormone (FSH) acids; is 120 semiferous tubule to increase spermatogenesis back to Table of Contents Hypothalamic Hormones Corticotropin-releasing acts on corticotrope to release ACTH protein of 41 amino acids factor (CRF or CRH) and -endorphin (lipotropin) Gonadotropin-releasing polypeptide of 10 amino acts on gonadotrope to release LH and factor (GnRF or GnRH) acids FSH Prolactin-releasing this may be TRH acts on lactotrope to release prolactin factor (PRF) Prolactin-release may be derived from GnRH acts on lactotrope to inhibit prolactin inhibiting factor (PIF) precursor, 56 amino acids release Growth hormoneprotein of 40 and 44 amino releasing factor (GRF stimulates GH secretion acids or GRH) Somatostatin (SIF, also called growth hormone- polypeptide of 14 and 28 inhibits GH and TSH secretion release inhibiting factor, amino acids GIF) Thyrotropin-releasing peptide of 3 amino acids: stimulates TSH and prolactin secretion EHP factor (TRH or TRF) back to Table of Contents Thyroid Hormones Thyroxine and iodinated dityrosin responds to TSH and stimulates triiodothyronine derivatives oxidations in many cells produced in parafollicular C cells of the 2+ Calcitonin protein of 32 amino acids thyroid, regulation of Ca and Pi metabolism protein of 37 amino acids, product of the calcitonin Calcitonin gene-related gene derived by alternative acts as a vasodilator peptide (CGRP) splicing of the precursor mRNA in the brain back to Table of Contents Parathyroid Hormone 2+ regulation of Ca and Pi metabolism, Parathyroid hormone stimulates bone resorption thus protein of 84 amino acids 2+ (PTH) increasing serum [Ca ], stimulates Pi secretion by kidneys
back to Table of Contents Adipose Tissue Hormones additional discussion of adipocyte hormones and cytokines Adipose Tissue page regulation of overall body weight by limiting food intake and increasing 167 amino acid precursor energy expenditure, regulation of the Leptin processed to 146 amino neuroendocrine axis, inflammatory acids responses, blood pressure, and bone mass 244 amino acid protein with major biological actions are increases Adiponectin 4 distinct functional in insulin sensitivity and fatty acid domains oxidation 108 amino acid pre-protein Resistin induces insulin resistance in humans back to Table of Contents Hormones and Peptides of the Gut additional discussion of gut hormones: Peptide Hormones page and Gut-Brain Interrelationships page Bombesin, also called neuromedin B and 14 amino acids stimulates release of gastrin and CCK gastrin-releasing peptide Glucagon-like peptide 1 Two forms: 31 amino acids, potentiates glucose-dependent insulin (GLP-1) formerly called GLP-1(7-37) and 30 amino secretion, inhibits glucagon secretion, enteroglucagon acids, GLP-1(7-36)amide inhibits gastric emptying Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide of 42 amino inhibits secretion of gastric acid, polypeptide (GIP) acids enhances insulin secretion originally called gastric inhibitory polypeptide contains all of the amino acids of glucagon (see Figure below); inhibits meal-stimulated gastric acid secretion similar to GLP-1 and GLP-2 action; 37 amino acids, the first 29 induces satiety, decreases weight Oxyntomodulin are identical to glucagon gain, and increases energy consumption; has weak affinity for GLP-1 receptor as well as glucagon receptor, may mimic glucagon actions in liver and pancreas 28 amino acids derived appetite stimulation, stimulates NPY from preproghrelin protein; release, regulation of energy acylated on Ser3 with nGhrelin homeostasis, glucose metabolism, octanoic acid, non-acylated gastric secretion and emptying, insulin forms found in circulation secretion also but not bioactive
acts in opposition to ghrelin action on appetite produced by stomach antrum, Gastrin 17 amino acids stimulates acid and pepsin secretion, also stimulates pancreatic secretions secreted from duodenum at pH values Secretin 27 amino acids below 4.5, stimulates pancreatic acinar cells to release bicarbonate and H2O stimulates gallbladder contraction and predominant form is 33 Cholecystokinin, CCK bile flow, increases secretion of amino acids digestive enzymes from pancreas controls gastrointestinal muscles, Motilin 22 amino acids stimulates release of PP, stimulates gallbladder contractions produced by hypothalamus and GI tract, relaxes the GI, inhibits acid and pepsin secretion, acts as a Vasoactive intestinal 28 amino acids neurotransmitter in peripheral peptide (VIP) autonomic nervous system, increases secretion of H2O and electrolytes from pancreas and gut inhibits release and action of numerous gut peptides, e.g. CKK, Somatostatin 14 amino acid version OXM, PP, gastrin, secretin, motilin, GIP; also inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion from pancreas Substance P, a CNS function in pain (nociception), member of the involved in vomit reflex, stimulates tachykinin family that salivary secretions, induces 11 amino acids includes neurokinin A vasodilation; (NKA) and neurokinin B antagonists have anti-depressant (NKB) properties Pancreatic Polypeptide (polypeptide fold) Family suppresses glucose-induced insulin Pancreatic Polypeptide, 36 amino acids secretion, inhibits bicarbonate and PP protein secretion from pancreas inhibits gastric motility by inhibiting Peptide Tyrosine cholinergic neurotransmission, inhibits 36 amino acids Tyrosine, PYY gastric acid secretion, induces sensations of satiety effects on hypothalamic function in appetite, controls feeding behavior and Neuropeptide Y, NPY 36 amino acids, 6 receptors energy homeostasis, levels increase during starvation to induce food intake 2 peptides: 78 amino acid truncated form and 84 homology to EGF and binds to the Amphiregulin amino acid form with 6 EGF receptor (EGFR) additional N-terminal amino Obestatin
23 amino acids derived from preproghrelin protein
acids back to Table of Contents Pancreatic Hormones produced by -cells of the pancreas, disulfide bonded dipeptide increases glucose uptake and Insulin of 21 and 30 amino acids utilization, increases lipogenesis, general anabolic effects produced by -cells of the pancreas, polypeptide of 29 amino increases lipid mobilization and Glucagon acids glycogenolysis in order to increase blood glucose levels Pancreatic polypeptide, polypeptide of 36 amino increases glycogenolysis, regulation of PP acids gastrointestinal activity inhibition of glucagon and Somatostatin 14 amino acid version somatotropin release back to Table of Contents Placental Hormones Estrogens steroids maintenance of pregnancy Progestins steroids mimic action of progesterone 2 proteins: is 96 amino Chorionic gonadotropin activity similar to LH acids; is 147 Chorionic somatomammotropin protein of 191 amino acids acts like prolactin and GH also called placental lactogen produced in ovarian corpus luteum, 2 proteins of 22 and 32 Relaxin inhibits myometrial contractions, amino acids secretion increases durin gestation back to Table of Contents Gonadal Hormones steroids: estradiol and maturation and function of female Estrogens (ovarian) estrone secondary sex organs implantation of ovum and maintenance Progestins (ovarian) steroid: progesterone of pregnancy maturation and function of male Androgens (testicular) steroid: testosterone secondary sex organs 1 protein ( is 134 amino Inhibins A and B acids; is 115 and 116 inhibition of FSH secretion amino acids) back to Table of Contents Adrenal Cortical Hormones steroids: cortisol and diverse effects on inflammation and Glucocorticoids corticosterone protein synthesis Mineralocorticoids steroids: aldosterone maintenance of salt balance back to Table of Contents
Epinephrine (adrenalin)
Norepinephrine (noradrenalin)
Adrenal Medullary Hormones classic "fight-or-flight" response, increases glycogenolysis, lipid mobilization, smooth muscle derived from tyrosine contraction, cardiac function, binds to all classes of catecholamine receptors (- and -adrenergic) classic "fight-or-flight" response, lipid mobilization, arteriole contraction, also acts as neurotransmitter in the CNS, derived from tyrosine released from noradrenergic neurons, binds all catecholamine receptors except 2-adrenergic
back to Table of Contents Liver Hormones polypeptide of 8 amino acids derived from angiotensinogen (present in the 2-globulin fraction of plasma) which is cleaved by responsible for essential hypertension the kidney enzyme renin to through stimulated synthesis and Angiotensin II give the decapeptide, release of aldosterone from adrenal angiotensin I, the Ccells terminal 2 amino acids are then released (by action of angiotensin-converting enzyme, ACE) to yield angiotensin II back to Table of Contents Kidney Hormones responsible for maintenance of calcium Calcitriol [1,25-(OH)2- derived from 7and phosphorous homeostasis, 2+ vitamin D3] dehydrocholesterol increases intestinal Ca uptake, regulates bone mineralization back to Table of Contents Cardiac Hormones released from heart atria in response several active peptides Atrial natriuretic peptide to hypovolemia, acts on outer adrenal cleaved from a 126 amino (ANP) cells to decrease aldosterone acid precursor production; smooth muscle relaxation back to Table of Contents Pineal Hormones N-acetyl-5Melatonin regulation of circadian rhythms methoxytryptamine
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Amygdala Brain Physiology - Richard UttDokument33 SeitenThe Amygdala Brain Physiology - Richard UttHuib Salomons100% (11)
- Endocrine System Study GuideDokument5 SeitenEndocrine System Study GuideClaudia SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liverpool SDL CRRTDokument62 SeitenLiverpool SDL CRRTupul85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Approved Reference List For 2015Dokument4 SeitenApproved Reference List For 2015tokionasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspartame and Neuordegenerative DiseasesDokument102 SeitenAspartame and Neuordegenerative Diseasesedi_wsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mordheim Treasure Hunt V2Dokument54 SeitenMordheim Treasure Hunt V2Christian Camacho100% (1)
- Cellular Endocrinology in Health and DiseaseVon EverandCellular Endocrinology in Health and DiseaseAlfredo Ulloa-AguirreNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Hormone in ParturitionDokument36 SeitenThe Role of Hormone in ParturitionDiana HayatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Cupping Therapy in Pain Management A LDokument19 SeitenThe Role of Cupping Therapy in Pain Management A LMohitha Parla100% (1)
- Fisiologi 1 - Introducton Renal PhysiolgyDokument5 SeitenFisiologi 1 - Introducton Renal PhysiolgyHachi Nini Shop IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung Transplant PathwayDokument39 SeitenLung Transplant PathwayMohana Preethi MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physio Reviewer Renal To Acid BaseDokument11 SeitenPhysio Reviewer Renal To Acid BaseNicole ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cupping TherapyDokument20 SeitenCupping TherapyMohamed AttiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trail Guide To The Body: Hand and WristDokument5 SeitenTrail Guide To The Body: Hand and WristBen WisherNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiabetesDokument25 SeitenDiabetesLawrence LarsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Techniques in Physical TherapyDokument61 SeitenNew Techniques in Physical TherapyMohamed Magdy El MeligieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactive Quiz: Deal or No DealDokument7 SeitenInteractive Quiz: Deal or No DealShaira Jean GeminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acls Drug OverviewDokument2 SeitenAcls Drug OverviewShannon Davis100% (1)
- Ar Te Ri Es: Abdominal RegionDokument36 SeitenAr Te Ri Es: Abdominal RegionLeony CrisostomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viscero-Somatic Reflex Anterior Point Posterior Point: Chapman's PointsDokument3 SeitenViscero-Somatic Reflex Anterior Point Posterior Point: Chapman's PointsEman ElzeftawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood PanelsDokument7 SeitenBlood Panelslisalov100% (1)
- Sri Venkateswara Veterinary University: College of Veterinary Science, TirupatiDokument31 SeitenSri Venkateswara Veterinary University: College of Veterinary Science, TirupatiPrabhu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Pregnancy ExercisesDokument2 SeitenPost Pregnancy ExercisesCourtneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Muscles TableDokument9 SeitenPhysiology Muscles TabletiiandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acupuncture in Patients With Osteoarthritis of The Knee: A Randomised TrialDokument9 SeitenAcupuncture in Patients With Osteoarthritis of The Knee: A Randomised TrialDiana PiresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mds 3Dokument3 SeitenMds 3api-434982019Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment of Menopausal Symptoms With Hormone TherapyDokument17 SeitenTreatment of Menopausal Symptoms With Hormone TherapyCésar Vásquez AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2, Introduction To Pharmacology Continued. (Script)Dokument11 SeitenLecture 2, Introduction To Pharmacology Continued. (Script)JustDen0950% (2)
- Fluid and Electrolyte Final OutputDokument19 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte Final OutputNatasha Alaine E. CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Herbs For Healthy Body - Healing Properties of Adalodakam, Arogya Pacha, Ashokam, IrattimadhuDokument4 SeitenIndian Herbs For Healthy Body - Healing Properties of Adalodakam, Arogya Pacha, Ashokam, IrattimadhuNEELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preventive Medical CheckDokument3 SeitenPreventive Medical CheckengrrajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complementary TherapiesDokument7 SeitenComplementary TherapiesNilamdeen Mohamed ZamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument21 SeitenEndocrine SystemMark DimarucutNoch keine Bewertungen
- X.0Y Control of Peripheral Circulation: OutlineDokument4 SeitenX.0Y Control of Peripheral Circulation: OutlineAya ARNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConstipationDokument22 SeitenConstipationash ash100% (1)
- Fluid & Electrolyte ImbalanceDokument47 SeitenFluid & Electrolyte ImbalanceBijeta ThapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Practice Recommendations For Holistic Strategies To Promote and Maintain Skin IntegrityDokument32 SeitenBest Practice Recommendations For Holistic Strategies To Promote and Maintain Skin IntegrityisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constipation: Ekaterine Labadze MDDokument24 SeitenConstipation: Ekaterine Labadze MDsushant jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Kidney Injury: KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice GuidelineDokument40 SeitenAcute Kidney Injury: KDIGO 2012 Clinical Practice GuidelineAbedDabajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- K10 (A1) - 2015pharmacotherapy For ParkinsonDokument41 SeitenK10 (A1) - 2015pharmacotherapy For Parkinsonali100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyJannefer HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypothyroidism: Kommerien Daling, MD Chiefs Conference August 14th 2008Dokument50 SeitenHypothyroidism: Kommerien Daling, MD Chiefs Conference August 14th 2008HaNy NejNoch keine Bewertungen
- MnemonicsDokument20 SeitenMnemonicsKhassmeen Delos Santos AradaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Agents Group 1 Parmacology ReportingDokument415 SeitenCardiovascular Agents Group 1 Parmacology ReportingMajestic RavenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulin Comparison Chart PDFDokument1 SeiteInsulin Comparison Chart PDFsophia onuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Parasitic Adaptations in HelminthsDokument60 Seiten8 Parasitic Adaptations in Helminthsapi-3732735100% (4)
- Arrythmia Name: Normal Sinus RhythmDokument7 SeitenArrythmia Name: Normal Sinus RhythmJulx0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy in The Treatment of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction in WomenDokument9 SeitenPelvic Floor Physical Therapy in The Treatment of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction in WomenGladys Ailing100% (1)
- Ineffective Coping - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsDokument13 SeitenIneffective Coping - Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan - NurseslabsLester MooreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cad PamphletDokument2 SeitenCad Pamphletapi-546509005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemDokument10 SeitenChapter (10) : Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemSandra GabasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System - NURSINGDokument3 SeitenEndocrine System - NURSINGFrancesca GraingerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Physiotherapy On Writer's Cramp: A Case StudyDokument3 SeitenEffect of Physiotherapy On Writer's Cramp: A Case StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anticancer Drugs PharmacologyDokument19 SeitenAnticancer Drugs PharmacologyZainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermoregulation: Presented by - Mohit Kumar Gupta Nursing Tutor NNC, JamuharDokument10 SeitenThermoregulation: Presented by - Mohit Kumar Gupta Nursing Tutor NNC, Jamuharmacmohit100% (2)
- NR 446 Week 6 ATI Weekly Tips Mental HealthDokument16 SeitenNR 446 Week 6 ATI Weekly Tips Mental HealthChristine LansdownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Management in Ed: Erick Lagleva Ed JhoDokument50 SeitenPain Management in Ed: Erick Lagleva Ed JhoErick Lagleva100% (1)
- Student Handout Meridian MassageDokument2 SeitenStudent Handout Meridian MassageIoana Dragomir100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte TherapyDokument39 SeitenFluid and Electrolyte TherapyrikarzNoch keine Bewertungen
- CartoonDokument19 SeitenCartoonchintujNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gruber-Clay - 2016 - Pan ComparisonDokument14 SeitenGruber-Clay - 2016 - Pan ComparisonCarlos González LeónNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Summoner V3.0 - The HomebreweryDokument20 SeitenThe Summoner V3.0 - The HomebreweryBertran RousseauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Lab ReportDokument3 SeitenNervous System Lab Reportapi-296589906Noch keine Bewertungen
- Highlights November 2015Dokument44 SeitenHighlights November 2015Milena100% (2)
- Caning Dictionary Jun 16Dokument36 SeitenCaning Dictionary Jun 16Hakki YazganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chitale Dairy Uses RFID To Improve Milk YieldsDokument5 SeitenChitale Dairy Uses RFID To Improve Milk YieldsBhanu PathalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1933 ConventionDokument4 Seiten1933 Conventionapi-301726216Noch keine Bewertungen
- Road Encounters PDFDokument23 SeitenRoad Encounters PDFFederico Carrera BuronneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 The Nature of The Human Person 2Dokument21 SeitenCHAPTER 2 The Nature of The Human Person 2Rechienvhel OccianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Meat Product List PDFDokument2 Seiten1 Meat Product List PDFdaiannezipaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 3 Read MeDokument56 SeitenCH 3 Read MeelzianhawkwindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric For Creating A 3 D Model For The Plant and Animal CellsDokument1 SeiteRubric For Creating A 3 D Model For The Plant and Animal Cellsnosheen afzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describing How Muscles Work Activity SheetDokument3 SeitenDescribing How Muscles Work Activity SheetTasnim MbarkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plot Summary of Animal FarmDokument1 SeitePlot Summary of Animal Farm10nov1964Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bedroom TitanDokument70 SeitenBedroom TitanCamillo Granata100% (3)
- Adjective ClausesDokument11 SeitenAdjective ClausesChristine NadyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Crafting - Animal WorkshopDokument1 SeiteAnimal Crafting - Animal WorkshopKathy BrandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mam Level 2 FlashcardsDokument38 SeitenMam Level 2 FlashcardsAhmedSameh100% (1)
- Jaundice in Cultured Hybrid Catfish Clarias BetracDokument6 SeitenJaundice in Cultured Hybrid Catfish Clarias BetracLeeinda100% (1)
- Arteries of AbdomenDokument3 SeitenArteries of Abdomenmero1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grooming Black Russian TerrierDokument15 SeitenGrooming Black Russian TerrierFiorenzo TassottiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leishmania SPPDokument9 SeitenLeishmania SPPanalyn123Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8.sadvritta (Code of Conduct)Dokument47 Seiten8.sadvritta (Code of Conduct)Vanisha AnoepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bobcat Classification and EvolutionDokument3 SeitenBobcat Classification and EvolutionagnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Werewolf in The Crested KimonoDokument17 SeitenThe Werewolf in The Crested KimonoEstrimerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synonyms and Antonyms Reading Comprehension Exercises TBL Task Based Lea - 135200Dokument3 SeitenSynonyms and Antonyms Reading Comprehension Exercises TBL Task Based Lea - 135200Oyuki Torres ChoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid PhysiologyDokument2 SeitenThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)