Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
16
Hochgeladen von
sliversniperOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
16
Hochgeladen von
sliversniperCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
42 Part 4
Chapter 16 Strength of Acids and Alkalis (Extension)
A. Multiple Choice Questions partial ionization
CH3COOH(aq) + water
1. C. SO42(aq) molecules
2. B. (2) and (3) only H+(aq) + CH3COO(aq)
3. A. (1) and (4) only
4. C. (2) and (3) only mobile ion
5. A. (3) only
Therefore, with the same concentration
(e.g. 1 M), hydrochloric acid contains a
B. Fill in the Blanks higher concentration of H+(aq) ions than
ethanoic acid in water. Hence,
1. completely / highly, hydrogen ions hydrochloric acid is a strong acid while
2. weak alkali, hydroxide ions ethanoic acid is a weak acid.
C. Comprehensive Questions 2. Strength of an acid and alkali refers to its
extent of ionization or dissociation in
1. Hydrochloric acid and ethanoic acid with aqueous solution.
the same concentration (e.g. 1 M) do not
give the same concentration of hydrogen 3. Sodium hydroxide solution and ammonia
ions, H+(aq), in water. solution with the same concentration (e.g.
For 1 M hydrochloric acid, the HCl 1 M) do not give the same concentration
molecules ionize completely in water to of hydroxide ions, OH(aq), in water.
form H+(aq) ions and Cl(aq) ions. That is, For sodium hydroxide, ions are present
all the HCl molecules have changed to originally. When it dissolves in water, it
ions. dissociates completely into mobile Na+
HCl(aq) + water ions and OH ions.
molecules
complete ionization Na+OH(s) + water
H+(aq) + Cl(aq) immobile ions
complete dissociation
mobile ions Na+(aq) + OH(aq)
However, for 1M ethanoic acid, only some mobile ions
of the CH3COOH molecules ionize in
water to form H+(aq) ions and For ammonia, it is a covalent compound
with simple molecular structure. Ions are
CH3COO(aq) ions. That is, only a small
not present originally. When ammonia
portion of the CH3COOH molecules have
dissolves in water, only some of the NH3
changed to ions. CH3COOH molecules,
molecules ionize in water to form
H2O molecules, H+(aq) ions and
NH4+(aq) ions and OH ions. That is, only
CH3COO(aq) ions coexist in the acid
a small portion of the NH3 molecules have
solution.
changed to ions. NH3 molecules, NH4+(aq)
Chapter 16 Solutions (EE).doc
Chapter 16 43
ions and OH ions coexist in the solution. 6. Ethanoic acid > nitric acid > sulphuric acid
NH3(aq) + H2O(l)
The pH scale is a measure of the
molecules
concentration of hydrogen ions in solutions
partial ionization and it is used to show the degree of acidity
NH4+(aq) + OH(aq) and alkalinity. The greater the number of
hydrogen ions given out when dissolved in
mobile ions water, the more acidic the solution.
Both sulphuric acid and nitric acid can
Therefore, with the same concentration (e.g. completely (or highly) ionize to give
1 M), sodium hydroxide solution contains hydrogen ions in water, so they are strong
a higher concentration of OH(aq) ions acids. However, ethanoic acid can only
than aqueous ammonia. In other words, partly (or slightly) ionize to give hydrogen
with the same concentration, sodium ions in water, so it is a weak acid.
hydroxide has a higher pH than ammonia. Therefore, both sulphuric acid and nitric
Sodium hydroxide is a strong alkali while acid have a lower pH than ethanoic acid.
ammonia is a weak alkali. Besides, since sulphuric acid is a dibasic
acid which gives two hydrogen ions in
4. (a) D>C>F water and nitric acid is a monobasic acid
(b) B>E>A which only gives one hydrogen ion in
water, the pH of sulphuric acid is lower
5. The relative strength of acids and alkalis than that of nitric acid.
can be compared by measuring the pH
values and electrical conductivities. In 7. HKCEE Question
comparison of the strength of acids with
equal concentrations, a strong acid has a 8. Strength of an acid or alkali refers to its
higher concentration of hydrogen ions extent of ionization or dissociation in
than a weak acid. Thus, a strong acid has a aqueous solution.
lower pH value than a weak acid. Besides, Concentration of an acid or alkali refers to
with equal concentrations, a strong acid the amount dissolved in a unit volume of
has a higher electrical conductivity than a aqueous solution.
weak acid does. This is because a strong
acid contains a higher concentration of D. Essay-type Question
mobile ions than a weak acid does.
In comparison of the strength of alkalis 1. To test the strength of solutions A and B,
with equal concentrations, a strong alkali we can measure their electrical
has a higher concentration of hydroxide conductivity.
ions than a weak alkali. Thus, a strong The reagents and apparatus are arranged
alkali has a higher pH value than a weak as the following:
alkali. Besides, with equal concentrations,
a strong alkali has a higher electrical
conductivity than a weak alkali. This is
because a strong alkali has a higher
concentration of mobile ions than a weak
alkali.
Chapter 16 Solutions (EE).doc
44 Part 4
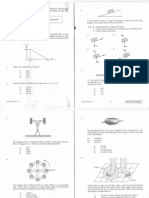
Secondly, concentrated acids of A and B
are compared. Put the solution of
concentrated acid A into a beaker and set
up the apparatus as shown. Then, put the
solution of concetrated acid B into a
beaker and set up the apparatus as shown.
Compare the brightness of the light bulbs
in the two set-ups. The solution which
makes the light bulb glows brighter is the
stronger acid, while the solution which
makes the light bulb glows dimmer is the
weaker acid.
Firstly, dilute acids of A and B are
compared. Put the solution of dilute acid A
into a beaker and set up the apparatus as
shown. Then, put the solution of dilute
acid B into a beaker and set up the
apparatus as shown. Compare the
brightness of the light bulbs in the two
set-ups. The solution which makes the
light bulb glows brighter is the stronger
acid, while the solution which makes the
light bulb glows dimmer is the weaker
acid.
Chapter 16 Solutions (EE).doc
Chapter 16 45
Chapter 16 Solutions (EE).doc
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)Dokument13 SeitenCE Physics 2006 Paper2 (E)08150815whoimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006paper 1 MarkingDokument11 Seiten2006paper 1 MarkingsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 Paper 1Dokument28 Seiten2006 Paper 1sliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2003 Paper IIDokument14 SeitenPhysics 2003 Paper IIapi-26423290Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2002 Paper IIDokument25 SeitenPhysics 2002 Paper IIapi-26423290Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2005paper 2Dokument13 Seiten2005paper 2sliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005paper 1Dokument16 Seiten2005paper 1sliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2003 Paper I Marking SchemeDokument10 Seiten2003 Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3700944Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2004 Paper I Marking SchemeDokument12 Seiten2004 Paper I Marking SchemesliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004paper IIDokument13 Seiten2004paper IIsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2004paper IDokument10 Seiten2004paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2003paper IDokument8 Seiten2003paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1998 PaperIIDokument13 SeitenPhysics 1998 PaperIIapi-26423290Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2000 PaperIIDokument14 SeitenPhysics 2000 PaperIIapi-26423290Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2002 Paper I Marking SchemeDokument9 Seiten2002 Paper I Marking Schemeapi-3700944Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1995paper IIDokument11 Seiten1995paper IIsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2002 Paper 1Dokument20 SeitenPhysics 2002 Paper 1api-3739499100% (2)
- Physics 2000 PaperIDokument19 SeitenPhysics 2000 PaperIapi-26423290Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1996paper IDokument8 Seiten1996paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1999paper IDokument8 Seiten1999paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1998 PaperIDokument6 SeitenPhysics 1998 PaperIapi-26423290Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1999paper IIDokument12 Seiten1999paper IIsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1997paper IIDokument11 Seiten1997paper IIsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1995paper I MarkingDokument10 Seiten1995paper I MarkingsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1997paper IDokument8 Seiten1997paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1994paper I MarkingDokument9 Seiten1994paper I MarkingsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1996paper IIDokument11 Seiten1996paper IIsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1994paper IIDokument11 Seiten1994paper IIsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1995paper IDokument8 Seiten1995paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1994paper IDokument8 Seiten1994paper IsliversniperNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Sulfide: DR 900 Analytical ProcedureDokument4 SeitenSulfide: DR 900 Analytical Procedurewulalan wulanNoch keine Bewertungen
- P2NP To Amine With NaBH4-CopperDokument281 SeitenP2NP To Amine With NaBH4-CopperIo TatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Science PDFDokument9 SeitenFood Science PDFTabasum BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS STD - IS 16714 - 2018 - GGBSDokument11 SeitenIS STD - IS 16714 - 2018 - GGBSSoumyakanti S. Samanta (Pgdm 09-11, Batch II)0% (1)
- Metalshield Info BrochureDokument12 SeitenMetalshield Info Brochuresiva_nagesh_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- History of Cryogenics - A Cryo Central Resource From The CSA PDFDokument7 SeitenHistory of Cryogenics - A Cryo Central Resource From The CSA PDFJaque BauerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment 1 Form 5Dokument12 SeitenAssessment 1 Form 5Masitah Abu BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propriedades Quânticas de Nanomateriais Utilizando A Teoria Do Funcional Densidade (DFT)Dokument13 SeitenPropriedades Quânticas de Nanomateriais Utilizando A Teoria Do Funcional Densidade (DFT)Leandro Costa Sobrinho MutucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tight BiteDokument1 SeiteTight BiteAlex DaniciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Internship Project On Durian Laminates PDFDokument82 SeitenSummer Internship Project On Durian Laminates PDFShubham MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL Series Compact Loose Central Tube Fiberoptic CableDokument5 SeitenSL Series Compact Loose Central Tube Fiberoptic CableJhon SanabriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D2073 Total Primary Secondary and Tertiary Amine Values ofDokument3 SeitenD2073 Total Primary Secondary and Tertiary Amine Values ofRAZA MEHDINoch keine Bewertungen
- SSC-Tech Residential Building Cost EstimatesDokument20 SeitenSSC-Tech Residential Building Cost EstimatesBenmark JabayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packed Beds Safety IssuesDokument4 SeitenPacked Beds Safety IssuesrmaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wax Glue2Dokument6 SeitenWax Glue2Gamal FouadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservado SP: Water-Repellent For Facades With A High Protective PowerDokument2 SeitenConservado SP: Water-Repellent For Facades With A High Protective PoweracarisimovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco-Design Forever PanDokument25 SeitenEco-Design Forever PanDaniel QuijanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enclosure Mansonry Wall Systems WorldwideDokument229 SeitenEnclosure Mansonry Wall Systems Worldwidexxxxx8086Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differences between pure metals and alloysDokument31 SeitenDifferences between pure metals and alloysSinh LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shell Thickness CalculationsDokument2 SeitenShell Thickness CalculationsskocogluNoch keine Bewertungen
- 005-Interlloy Grade 4340 Hardened and Tempered BarDokument3 Seiten005-Interlloy Grade 4340 Hardened and Tempered BarDhruv MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PJK Project 2011 Form 2 (Word 2010)Dokument30 SeitenPJK Project 2011 Form 2 (Word 2010)Charmaine Yeo Shern LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ayvaz - Val - Mariposa - Cmpta O&yDokument4 SeitenAyvaz - Val - Mariposa - Cmpta O&yFranklin Gustavo Zagaceta BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narayangharh-Mugling HighwayDokument85 SeitenNarayangharh-Mugling HighwayRm1262Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Dosage Forms: Tablets: Abhay ML Verma (Pharmaceutics)Dokument5 SeitenSolid Dosage Forms: Tablets: Abhay ML Verma (Pharmaceutics)meet2abhayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lizmontagens Group ProfileDokument5 SeitenLizmontagens Group ProfileRui Carlos Delgado Lopes AlvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Functionally Graded Dental Implant in The Presence of Cancellous BoneDokument7 SeitenDesign of Functionally Graded Dental Implant in The Presence of Cancellous BoneRonin ZxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ucalgary 2020 Du StevenDokument65 SeitenUcalgary 2020 Du StevenmnasiroleslamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nickel Coatings GuideDokument2 SeitenNickel Coatings GuideDavid GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemicalDokument1 SeiteChemicalTimothy John IgnacioNoch keine Bewertungen