Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pre and Post Menopause
Hochgeladen von
Vhutz de ViolethOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pre and Post Menopause
Hochgeladen von
Vhutz de ViolethCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
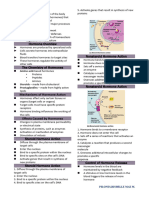
PRE AND POST MENOPAUSE
Definitation of menopause
menopause is a sign of the end of a productive life in a woman. outward signs are: cessation of menstruation that usually comes a month-symptom sekali.gejala Another outward is due to hormonal imbalance; part of the bodybegin to look old. to address it is recommended that women maintain health andbody fitness and mental in order to perform tasks such as sexual before menopause.Other common symptoms are; depression, lack of sleep, brought about by anxiety mental oremotional disturbance. menopause starts at different ages, and not always the same for every woman. commonplace or common around the age of 50 years. changes after menopause; ektrogen affect growth and food supplies for the chest area uterus, vagina, smooth muscles, and skin. He also tends to protect a woman against circulatory diseases that face, and possibly also to the lack of calcium from the bones. the slump that coincided with the ongoing ekstrogen menopause is a prelude to the arrival badqan changes in accordance with the continuation of age.
Etiology
Menopause occurs with increasing age, the ovaries become lessresponsive to stimulation by LH and FSH, produced by the pituitary gland. As a result, the ovaries release less estrogen andprogesterone, and ultimately the process of ovulation (release of eggs) to stop. There are two kinds of menopause, among others: 1. Early menopause is menopause that occurs before the age of 40 years. Possible causes are genetic, autoimmune diseasesand smoking. 2. Artificial menopause caused by medical intervention that reduces or stops the release of hormones by the ovaries. These interventions can include surgery to remove the ovaries or toreduce blood flow to the ovaries as well as chemotherapy orradiation therapy to the pelvis to treat cancer. Hysterectomy(removal of uterus) cause the end of the menstrual cycle, but during the ovaries remain there it will not affect hormone levelsand does not cause menopause.
After experiencing signs of menopause
a) Hair matted nascent b) the skin loses its elastic power c) loss of bone calcium, the spine is affected thereby d) breasts to flatten and droop e) the possibility of disturbances in blood circulation to beincreased f) engorgement of the ovary and uterus g) vaginal walls become thin and sensitive to the allusion (thoughintercourse can be continued) h) wall vulva growth stalled i) pubic hair on a rare j) increasing the danger of gout
Changes in sexual activity
after menopause, often there is a fear in women, such as fear oflosing its appeal he realizes that he can no longer conceive and bear children. hehas no longer the hallmark of feminine. and feelings of another person will not be loved orcaressed darling, would be a deficiency in series of his life. However, such feelings are usually short-lived.Because a woman who has gone through menopause too, still have sexual desire. alsothere is no reason not to treat himself to stay beautiful and fresh and exciting. the only thing that changes is the ability to conceive and give birth children. Sexual desire is more aroused by male hormones thanfemale hormones. the woman is still producing hormone throughout his life. of course not a single woman, howold age though, should be ashamed to enjoy sex. in fact, many people feel more enjoyable sex aftermenopause. because it contains the danger has fully elapsed.
Menopause age
When menopause occurs in a woman, nothing is the same in every person. Orphans (2000) in Kasdu (2002: 85), mentions the results of his study that on average a woman enters menopause is different for each race. Although in one race, remained the same in every person. For example, Asian women experiencingmenopause race at the age of 44 years. According to Rachman(1997) in Kasdu (2002: 53), mentions the age of menopauseoccurs at age 48-50 years. A study was conducted in 1992 by Samil at the Central Java citywith educated female respondents, it is known that women experience menopause at the age of 50.2 years. In women who live in rural areas, occur at the age of 46.5 years. This figure isalmost equal to the average age of American and European women began to enter menopause (Kasdu, 2002: 87).
Sexual life of women during menopause
At the age of women entering the menopause women experience a decrease in the number of levels of the hormone estrogen in the blood. As we know by definition that menopause is the cessation of the menstrual cycle and for all, that case is understood by themajority of our society, especially the older generation that thestate of menopause, women are not allowed to have sex. Suchmyths are on the other side understood by the women that spermentering through her vagina will not be able to come out again so that it can cause edema disease, as well as decreased levels ofestrogen and progesterone before there will be a difficult vaginaldischarge or discharge that is only slightly can serve as rubrikanso will cause pain during penetration so very good husband orwife is feeling uncomfortable during sexual intercourse. It is alsothe one who in use as the basis for the men to justify the skill to doextra marital sex with other women or marry again. Menopause (Klimakterium) is a transition in a woman's life, in which: - Ovary (ovaries) stop producing eggs - Menstrual activity decreases and eventually stops - The formation of female hormones (estrogen and progesterone)is reduced. Menopause is actually happening at the end of the last menstrualcycle. But the newly acquired certainty if a woman has notexperienced the cycle for a minimum of 12 months. Menopauseon average occurs at age 50 years, but it can occur normally in women aged 40 years. Usually when approaching menopause, duration and amount of blood that comes out on menstrual cyclestend to vary, not as usual. In some women, menstrual activity stops suddenly, but usuallyoccur gradually (both the number
and duration) and the distancebetween the two cycles become closer or more rarely. Thisirregularity may last for 2-3 years before the cycle stops.
Symptom
Some women only experience few symptoms, while other womenexperience the symptoms that are mild to severe. This is normal. Reduced estrogen levels gradually cause the body to slowly adjust to hormonal changes, but in some women this decline in estrogen levels occur suddenly and cause severe symptoms. This oftenhappens when menopause caused by removal of the ovaries.
Symptoms that may be found in menopausal women are:
1. Hot flashes occur due to increased blood flow in blood vessels of the face, neck, chest and back. The skin becomes red andwarm, accompanied by excessive sweating. Hot flashes areexperienced by approximately 75% of menopausal women. Mostexperienced hot flashes for more than 1 year and 25-50% of women experience it more than 5 years. Hot flashes lasted for 30seconds to 5 minutes. 2. The vagina becomes dry due to thinning of the vaginal walltissue so that when sexual intercourse may develop pain. 3. Psychic and emotional symptoms (fatigue, irritability, insomniaand anxiety) could be caused by decreased estrogen levels.Sweating at night causing sleep disorders so that fatigue got worse and increasingly irritable. 4. Dizziness, tingling and palpitations (heart pounding). 5. Loss of bladder control (beser). 6. Inflammation of the bladder or vagina. 7. Cardiovascular disease darah.Penurunan estrogen levelscause increased levels of LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol) and decreased levels of HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol). Estrogenis responsible for the formation of the epithelial layer of the uterine cavity. During the reproductive period, the formation of the uteruslining, followed by the release of the uterine wall at each menstrualcycle. Reduced estrogen levels at menopause causes the non-occurrence of the formation of the epithelial layer of the uterine cavity. But the androgenic hormone produced by the adrenalgland is converted into estrogen, and sometimes this causespost-menopausal bleeding.
8. Osteoporosis (bone loss). High risk of osteoporosis found in women who: a) thin b) smoking c) consume alcohol to excess d) taking corticosteroid e) have a low calcium intake f) rarely exercise. Minor injuries can cause fractures (broken bones). Fractures most often occur in the spine, hip and wrist. It does not need to worry, but because postmenopausal bleedingcould be an indication of an abnormality (including cancer), then thedoctors always check any bleeding that occurs after menopause.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis based on symptoms and physical examination. In thePap smear may note changes in the vaginal lining caused bychanges in estrogen levels. Blood tests and urine can be used to measure levels of estrogen, estrone and estradiol progestero andplasma.
Treatment
Not all postmenopausal women need to undergo hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Each woman should discuss the risksand benefits of HRT with her personal physician.
Many experts recommend HRT for the purpose of :
1. Reduce the unwanted symptoms of menopause 2. Helps reduce vaginal dryness
3. Prevent osteoporosis.
Some side effects of HRT:
- Vaginal bleeding - Breast tenderness - nausea - vomiting - Flatulence - Uterine cramping.
To reduce the risk of HRT and still benefit from HRT, the expertsrecommend :
- Adding progesterone to estrogen - Adding testosterone to estrogen - Use the lowest dose of estrogen. - Perform regular checks, including pelvic examination and Papsmears so that abnormality can be found as early as possible. Estrogen is available in the form of natural and synthetic (made in the laboratory). Synthetic estrogen hundreds of times more potent than natural estrogen that is not routinely given to postmenopausal women. To prevent hot flashes and osteoporosis is needed only natural estrogen in a very low dose. High doses tend to cause problems,including migraine headaches. Estrogen can be given in tablet form or skin patch (transdermal estrogen). Estrogen cream can be applied to the vagina to prevent thinning of the vaginal lining (thereby reducing the risk of urinary tractinfections and beser) and to prevent pain during sexual intercourse.
Post-menopausal women who take estrogen without progesterone have an increased risk of endometrial cancer. This risk is associated with dose and duration of estrogen use
If abnormal bleeding from the vagina, a biopsy is performed the uterine lining. Consuming progesterone along with estrogen may reduce the risk of endometrial cancer. Estrogen hormone replacement therapy is usually not performed on womenwho suffer from: - Or have had breast cancer or advanced endometrial cancer - The cause of genital bleeding of uncertain - Acute liver disease - Blood clotting diseases - Acute intermittent porphyria. The women are usually given anti-anxiety drugs, progesterone or Clonidine toreduce hot flashes. To reduce the depressed, anxiety, irritability and insomniamay be given antidepressants.
Giving progesterone with estrogen
Progesterone administered with estrogen to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer. Usually estrogen and progesterone administered daily. This delivery schedulewill typically cause irregular vaginal bleeding in the first 2-3 months of therapy, but after that the bleeding will usually stop. Or administration of estrogen and progesterone can be performed alternately;for 2 weeks of taking estrogen every day for a few days ago taking progesteroneand estrogen, then a few days at the end of the month did not take estrogen orprogesterone. With this schedule, vaginal bleeding occurred on the day which the hormone does not drink. Progesterone is available in tablet or injectionthrough the addition of progesterone is otot.Efek abdominal bloating, breastpain, headaches, mood swings and acne.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Health Record TrackerDokument2 SeitenHealth Record TrackerdaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 200 Drugs Class/Use GuideDokument4 SeitenTop 200 Drugs Class/Use GuideEsther AhnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation Disorders: A Brief ReviewDokument5 SeitenFatty Acid Beta-Oxidation Disorders: A Brief ReviewOlgHaENoch keine Bewertungen
- CretinismDokument15 SeitenCretinismJoshua fuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Physiology Theory and Application To Fitness and Performance 10th Edition Powers Test BankDokument39 SeitenExercise Physiology Theory and Application To Fitness and Performance 10th Edition Powers Test BankcrustilyjottercprifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) and Pregnancy TestDokument29 SeitenHuman Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) and Pregnancy Testclarence donqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure-MakatiMed Health Packages 2015Dokument2 SeitenBrochure-MakatiMed Health Packages 2015Mikee FelipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System 2022-23Dokument28 SeitenDigestive System 2022-23Fady Fady100% (1)
- Myo1 Nutrition Products CatalogueDokument6 SeitenMyo1 Nutrition Products CatalogueSAHIR AZMINoch keine Bewertungen
- The Metabolic SyndromeDokument408 SeitenThe Metabolic Syndromelicente100% (4)
- EndocrinologyDokument57 SeitenEndocrinologyeleonora rosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Dokument18 SeitenLearning Packet in Level 1-Anatomy and Physiology: College of Nursing School Year 2021-2022Zyke NovenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADIL BSN - 1C 11. Manual Reproductive SystemDokument4 SeitenADIL BSN - 1C 11. Manual Reproductive SystemReiko SakaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initation of Insulin - Final 2023Dokument27 SeitenInitation of Insulin - Final 2023DEWI RIZKI AGUSTINANoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparation Culture Media SterilizationDokument5 SeitenPreparation Culture Media SterilizationAyella Ôë100% (1)
- Breo Ellipta and Hydralazine Nursing ConsiderationsDokument11 SeitenBreo Ellipta and Hydralazine Nursing ConsiderationsSeth Michael Daniel BenauroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDokument80 SeitenSystemic Lupus ErythematosusLarissa Miguel Severa100% (2)
- ChandanKumar 632972Dokument11 SeitenChandanKumar 632972Chandan JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument59 SeitenAcute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Diseasesho bartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocryn DheaDokument3 SeitenEndocryn DheaRamona VintilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 118 ReferencesDokument2 SeitenNCM 118 ReferencesMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosynthesis of CholesterolDokument20 SeitenBiosynthesis of CholesterolAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry ProjectDokument23 SeitenChemistry Projecttwinklelee123450% (2)
- Anatomy & Physiology Papers QPDokument17 SeitenAnatomy & Physiology Papers QPmajlishbag maldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine SystemDokument9 SeitenChapter 9 - Endocrine SystemrishellemaepilonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 14 NDT Report EditedDokument30 SeitenLesson 14 NDT Report Editedmagicrjay26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cabanin® CSD Replaces Vitamin EDokument3 SeitenCabanin® CSD Replaces Vitamin EMaheshyepuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quarter 1 - 2nd Summative Test (Grade 9)Dokument5 SeitenQuarter 1 - 2nd Summative Test (Grade 9)BryanJAbuloc100% (4)
- Module 6A - Phases of Drug Action - Pharmacokinetic-3Dokument11 SeitenModule 6A - Phases of Drug Action - Pharmacokinetic-3weissNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Action of Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis, and The Search For BiomarkersDokument12 SeitenMechanism of Action of Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis, and The Search For BiomarkersFaMe TanapornNoch keine Bewertungen