Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Electrical Machines 3 2012
Hochgeladen von
NGOUNEOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electrical Machines 3 2012
Hochgeladen von
NGOUNECopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
REPUBLIC OF CAMEROON Peace Work Fatherland GTHS KUMBO/ ELECT DPT
THIRD SEQUENCE EXAM Class: F37 Option: Electrotechnology Duration: 03H Coefficient: 3 Written paper
ELECTRICAL MACHINES
No document is allowed except the one given to the candidates by the examiners.
PART ONE : TECHNOLOGY 1. Explain why the series field DC motor rotates at high speed at no load when it is supplied at his nominal voltage. 2. For each of the following electrical machines, cite a magnetic material which is used in the manufacturing of the magnetic circuit: a) transformer; b) DC machine stator, c) permanent magnet DC motor. 3. Give the role of the isoptherme in an AC electrical machine. 4. Give the role of the excitation resistance in a DC motor. 5. Give the role of auxiliary commutation poles in a DC motor. 6. Give the differences between an asynchronous squirrel cage motor and an asynchronous wound winding motor. 7. Name the test which is conducted in order to determine iron and friction losses in a DC motor.
PART TWO: ELCTROTECHNOLOGY Exercise 1: Shunt generator The open circuit characteristics at 1000rpm of a 4 pole, 220V shunt generator with 72 slots and 8 conductors per slot with armature conductors lap connected is as follows: Field current (A) 0.25 0.5 emf (V) 25 50 1 2 3 4 5
100 175 220 245 255
The field circuit resistance is 75. 1. Explain how this test was carried out
GTHS KUMBO_Electrical Department_Third sequence examJan.2012
2. Plot the curve and determine: a) The emf induced due to residual magnetism; b) The emf generated at the given field resistance when the generator is under normal operation. 3. The useful flux per pole. 4. The residual flux.
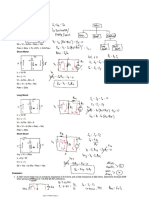
Exercise 2: Series motor The starter of a Peugeot 504 (a series motor) takes 200A under a voltage of 12 V. Under these conditions, it runs at 1000rpm and delivers a useful power of 1500W. The constant losses are estimated at 100W. Calculate: a) The power absorbed by the starter. b) Its efficiency. c) Its useful torque. d) The joule losses. e) The total resistance (armature + field windings). f) The back emf of the motor. g) Determine the direct starting current. h) What is the value of the resistance to be connected in series with the motor to limit the starting current to 240A?
Exercise 3: Three Phase asynchronous motor A three phase asynchronous motor, with the stator coupled in delta, is supplied by a network supply of 380V, 50Hz. Each phase of the stator has a resistance 0.4. At no load the motor rotates at 1500rpm and absorbs a power of 1150W; the current in a line is 3.2A. A test at a nominal load, under the same voltage of 380V, 50Hz has given the following results: Slip g = 4%; Power absorbed: Pa = 18.1kW; Line current: I = 32A. 1. For the no load test, calculate: a) the stator copper losses when the motor rotates at no load. b) The stator iron losses knowing that the mechanical losses are 510W. 2. For the nominal load test, determine: a) The power factor. b) The speed of rotation. c) The frequency of the rotor current. d) The stator copper losses. e) The rotor copper losses. f) The useful power. g) The efficiency of the motor. h) The useful torque
SUBJECT MASTER: NGOUNE Jean-Paul, PLET Electrotechnics, GTHS KUMBO.
GTHS KUMBO_Electrical Department_Third sequence examJan.2012
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- How To Rewind An Electric MotorDokument12 SeitenHow To Rewind An Electric MotorrjayfranNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Vibrasyon Electrical ProblemsDokument4 SeitenVibrasyon Electrical ProblemsbbulutmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Lesson Final1Dokument94 SeitenMachine Lesson Final1anon_156286001100% (8)
- Elect2 2014Dokument2 SeitenElect2 2014NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Installations: Theme: Electrical Installation of A WorkshopDokument2 SeitenElectrical Installations: Theme: Electrical Installation of A WorkshopNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics: Fourth Sequence TestDokument2 SeitenPower Electronics: Fourth Sequence TestNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: First Sequence TestDokument2 SeitenElectrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: First Sequence TestNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics: First Sequence TestDokument2 SeitenPower Electronics: First Sequence TestNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: Second Sequence TestDokument4 SeitenElectrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: Second Sequence TestNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical TechnologyDokument2 SeitenElectrical TechnologyNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- First Sequence Test in Digital and Analog ElectronicsDokument4 SeitenFirst Sequence Test in Digital and Analog ElectronicsNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Elect Machine Total 2012Dokument22 SeitenElect Machine Total 2012NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- First Sequence Test in Digital and Analog ElectronicsDokument4 SeitenFirst Sequence Test in Digital and Analog ElectronicsNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- CV 2013 NgouneDokument4 SeitenCV 2013 NgouneNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Tech Total 2012Dokument24 SeitenElectrical Tech Total 2012NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Elect1 2012Dokument3 SeitenPower Elect1 2012NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Elect Machine Total 2012Dokument22 SeitenElect Machine Total 2012NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines 5Dokument3 SeitenElectrical Machines 5NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Elect Total 2012Dokument34 SeitenPower Elect Total 2012NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Digi-Ana Total 2012Dokument46 SeitenDigi-Ana Total 2012NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Technology MockDokument3 SeitenElectrical Technology MockNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Digi-Anal3 CorrectpubDokument17 SeitenDigi-Anal3 CorrectpubNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines 5Dokument3 SeitenElectrical Machines 5NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock Ion 2012 BonDokument6 SeitenMock Ion 2012 Bonanon_819404681Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomation - CI6/ Mock 2012 GTHS KUMBODokument4 SeitenAtomation - CI6/ Mock 2012 GTHS KUMBONGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Digi Anal5Dokument4 SeitenDigi Anal5NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics MockDokument4 SeitenPower Electronics MockNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines 3 Correct PubDokument10 SeitenElectrical Machines 3 Correct PubNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines MockDokument3 SeitenElectrical Machines MockNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics MockDokument4 SeitenPower Electronics MockNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing and Technnology - MockDokument3 SeitenDrawing and Technnology - MockNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Automation 3Dokument3 SeitenAutomation 3NGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- MEA Testing Systems LTD CatalogDokument105 SeitenMEA Testing Systems LTD CatalogPawin lothongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 110 TOP MOST POLYPHASE INDUCTION MOTORS - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions PDFDokument32 Seiten110 TOP MOST POLYPHASE INDUCTION MOTORS - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions PDFeinsteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teori MSTEPDokument144 SeitenTeori MSTEPDaniel Sopian FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitolul 13Dokument30 SeitenCapitolul 13Ionescu ViorelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 1001Dokument7 SeitenEe 1001youngmoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Micro Project Report On Synchronous Motor: Matoshri Aasarabai Polytechnic, Eklahare, NashikDokument18 SeitenA Micro Project Report On Synchronous Motor: Matoshri Aasarabai Polytechnic, Eklahare, NashikSudrshan B Barve100% (1)
- DC Motor Interview Questions and Answers: AnswerDokument4 SeitenDC Motor Interview Questions and Answers: Answerশ্রী লিমন চন্দ্র মোহন্তNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of MotorDokument5 SeitenTypes of MotorRoldan CantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW3 AssignmentsDokument4 SeitenHW3 AssignmentsKevin DornerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2 Understanding The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field.Dokument32 Seiten3.2 Understanding The Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field.Ishraqi IlyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing of Double Sided Linear Induction MotorDokument7 SeitenDesigning of Double Sided Linear Induction MotorCalix LeonelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Fan Submittal-ID (New Update 12 Des 2022)Dokument16 SeitenBig Fan Submittal-ID (New Update 12 Des 2022)Wijaya GultomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM)Dokument19 SeitenSwitched Reluctance Motor (SRM)Chakri SaYs AS50% (2)
- ELEC 2032 (3) Electromechanical System: Induction Motor IIIDokument19 SeitenELEC 2032 (3) Electromechanical System: Induction Motor IIIAshvin AshNoch keine Bewertungen
- New CatalogueDokument52 SeitenNew Catalogueprashun123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Electric MotorDokument3 SeitenElectronics Electric MotorLhoraine Selin AblazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Phase Induction Motor BasicsDokument23 SeitenThree-Phase Induction Motor BasicsSaìTejá LãllüNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permanent Magnet Brushless DC MotorsDokument41 SeitenPermanent Magnet Brushless DC MotorskingsekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips Cataloge-MotordcDokument29 SeitenDokumen - Tips Cataloge-MotordcKHOLIFAH NURHASANAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starters For Induction MotorDokument11 SeitenStarters For Induction MotorSomya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee Induction Motors HandoutsDokument2 SeitenEe Induction Motors HandoutsJevan SoberanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Fundamentals of Electric Motors v2Dokument21 Seiten1 Fundamentals of Electric Motors v2Daejoong KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Machines With Worked ExamplesDokument30 SeitenDC Machines With Worked ExamplesMatthew SimeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brushless and Brushed DC MotorsDokument27 SeitenBrushless and Brushed DC MotorsMarc Jairro GajudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Electrical Machines ChapterDokument57 SeitenDC Electrical Machines ChapterSent SesayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines Course HandoutDokument2 SeitenElectrical Machines Course HandoutAdvaitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topology and Preliminary Design Slotless Brushless Motor: of DCDokument3 SeitenTopology and Preliminary Design Slotless Brushless Motor: of DCflorin91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Starter YanmarDokument1 SeiteStarter YanmarĐặng MinhNoch keine Bewertungen