Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Exam 1 Review Sheet (Exam 1: Friday September30, 11:10 AM-12:00 PM, Packard Lab Aud. 101) Quantum Mechanics
Hochgeladen von
Rose MartinOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Exam 1 Review Sheet (Exam 1: Friday September30, 11:10 AM-12:00 PM, Packard Lab Aud. 101) Quantum Mechanics
Hochgeladen von
Rose MartinCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry 341 Physical Chemistry I Fall 2011
EXAM 1 REVIEW SHEET [Exam 1: Friday September30, 11:10 AM12:00 PM, Packard Lab Aud. 101] Quantum Mechanics
1. Wave theory of light constructive interference destructive interference Planck quantum theory blackbody radiation h 8 2 ( ) = h 3 c kT e 1 average energy of an oscillator
2.
=
3.
h e
h kT
Photoelectric effect 1 k . e. = me v 2 = h 2 de Broglie relation = Wave behavior in 1-D wavelength ( ) period ( )
~ wavenumber ( = 1
4. 5.
h p
frequency ( =
6.
Differential equation for the spatial dependence of a standing wave 2 d2 2 D = D dx 2 Schrdinger equation in 1-D
h2 d 2 + V = E 2m dx 2
7.
8.
Eigenvalue problem $ =
$ is an eigenfunction of the operator with eigenvalue
9. Heisenberg uncertainty principle h x p 2 Three postulates concerning quantum theory Average value theorem $ * dv = * dv Quantum mechanical operators $ x x h $ px = i h x i x Particle in a 1-D box condition for a standing wave in a 1-D box of length a a = n with n=1, 2, 3, 2 h2 n2 En = with n=1, 2, 3, ... 8 ma 2 14. n x 2 n = sin with n=1, 2, 3, a a probability of finding a particle between x1 and x2 x2 2 x = x1 n dx
1/ 2
10. 11.
12.
13.
electronic spectra of polyenes CNHN+2 prediction of lowest energy p-electron transition
Quantum mechanical tunneling through barrier of height Vo and width a light mass particles can tunnel into regions where E<Vo
{ea e a }2 T= + 1 ( ) 16 1
1/ 2 o
1
{2 mV (1 )} with =
h
and =
E Vo
15.
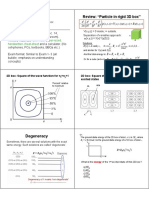
Schrdinger equation in 2-D Particle in 2-D box of dimensions a x b 2 2 h 2 nx n y E n x ,n y = + with nx = 1, 2, and ny = 1, 2, 8 m a 2 b2 Particle in 2-D square box of sides a idea of degenerate levels h2 2 2 E n x ,n y = with nx = 1, 2, and ny = 1, 2, 2 nx + n y 8 ma
16.
Schrdinger equation in 3-D Particle in 3-D box of dimensions a x b x c 2 2 h 2 nx ny nz2 E n x ,n y ,n z = + with nx = 1, 2, , ny = 1, 2, and nz = 1, 2, + 8 m a 2 b2 c2 Particle in 3-D cubic box of sides a idea of degenerate levels h2 2 E n x ,n y ,n z = n 2 + ny + nz2 with nx = 1, 2, , ny = 1, 2, and nz = 1, 2, 8 ma 2 x
17.
Harmonic oscillator 1 V ( x) = k x 2 2 1 Ev = v + h o 2
1/ 2
with v =0, 1, 2,
18.
1 k with o = 2 v the number of nodes ( ) as the energy E v goes ( )
Particle of mass m on a circle on a circle of radius R [also rigid rotor in 2-D where m= ]
En = h 2 ml2 with ml = 0, 1, 2, 8 2 m R 2
1/ 2
1 ml = e i ml 2 with ml > 0 counterclockwise rotation looking down on circle (clockwise rotation looking along positive-z axis) and ml < 0 clockwise rotation looking down on circle (counterclockwise rotation looking along positive z-axis) benzene and porphine group as examples
19.
Rigid rotor in 3D Diatomic molecule I = R 2 h2 E J = J ( J + 1) = B h c J ( J + 1) with ( J = 0, 1, 2, ...) 2I h where B = 8 2 c I m $ m L2 Yl l = l ( l + 1) h 2 Yl l with ( l = 0, 1, 2 ...) ml ml $ L Y = m hY with ( m = 0, 1, 2, )
z l l l
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Quantum PhysicsDokument338 SeitenQuantum PhysicsNam Le100% (2)
- Lectures #8 & #9Dokument30 SeitenLectures #8 & #9BOBNoch keine Bewertungen
- DegeneracyDokument4 SeitenDegeneracypradeep khannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 101 - SEAS Quantization Alá Schrödinger: A Summary of Some Exactly Soluble SystemsDokument3 SeitenChemistry 101 - SEAS Quantization Alá Schrödinger: A Summary of Some Exactly Soluble Systemsjesi5445Noch keine Bewertungen
- Particle in A 1d Box Quantum MechanicsDokument22 SeitenParticle in A 1d Box Quantum Mechanicsvivek patel0% (1)
- Quantum Mechanics Course ZeemansplittingDokument29 SeitenQuantum Mechanics Course ZeemansplittingjlbalbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2: Quantum MechanicsDokument43 SeitenModule 2: Quantum MechanicsYashi GoswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matter Waves Wave Function Quantum MechanicsDokument14 SeitenMatter Waves Wave Function Quantum Mechanicsvivek patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Mechanics Tunneling & Harmonic OscillatorDokument33 SeitenQuantum Mechanics Tunneling & Harmonic Oscillatorvivek patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry (1) : Quantum Mechanical PostulatesDokument41 SeitenPhysical Chemistry (1) : Quantum Mechanical PostulatesNAMENoch keine Bewertungen
- Atkins Chapter9.Lect01Dokument34 SeitenAtkins Chapter9.Lect01Fauzan Ramadhan PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhononsDokument25 SeitenPhononsPeter Đình-Khôi NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Iiit NotesDokument11 SeitenPhysics Iiit Notesprabhasavvaru0609Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure: Erg Per AtomDokument3 SeitenAtomic Structure: Erg Per AtomSandeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sky IsDokument31 SeitenSky IsGopimarappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Sheet 1Dokument4 SeitenFormula Sheet 1Abhimanyu DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Bands For Electrons in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 7)Dokument10 SeitenEnergy Bands For Electrons in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 7)ZakkiSciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3: Particles, Waves & Superposition Principle: Debroglie Particle-Wave DualityDokument7 SeitenLecture 3: Particles, Waves & Superposition Principle: Debroglie Particle-Wave DualityGadis PolosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mulliken AnalysisDokument10 SeitenMulliken AnalysisCan VurduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equation SheetDokument4 SeitenEquation SheetBhaskar TupteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 02Dokument31 SeitenLecture 02yinglvNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR TMMP (Quantum)Dokument50 SeitenDR TMMP (Quantum)Tmmp SmileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Propagation in Optical FibresDokument31 SeitenLight Propagation in Optical FibresWail HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drude Model For Dielectric Constant of MetalsDokument24 SeitenDrude Model For Dielectric Constant of MetalsRupesh ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ni Putu Indah Pratiwi - 6B - Chapter3Dokument47 SeitenNi Putu Indah Pratiwi - 6B - Chapter3Indah pratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ugc Csir Net Physics 2011 June ModelDokument15 SeitenUgc Csir Net Physics 2011 June ModelBhargav AlavaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PChem 9 QuantumDokument18 SeitenPChem 9 QuantumNajia ShirazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 2 Formula SheetDokument5 SeitenPhysics 2 Formula SheetJames KrirkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laser Fundamentals: Basic Processes (A.Einstein, 1916)Dokument11 SeitenLaser Fundamentals: Basic Processes (A.Einstein, 1916)sivamadhaviyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outside: Sin Cos 2 12 Inside: 6: R R A QDokument13 SeitenOutside: Sin Cos 2 12 Inside: 6: R R A QPauloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch9 HatomDokument30 SeitenCh9 HatomgvarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10 - Ch16 - Dynamics of Bloch Electrons PDFDokument39 SeitenLecture 10 - Ch16 - Dynamics of Bloch Electrons PDFmigueladmNoch keine Bewertungen
- A10 - Chap08A ExproDokument68 SeitenA10 - Chap08A Expro蔡易斈Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 02 11 2022Dokument34 SeitenLecture 6 02 11 2022Alkit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Question PaperDokument5 SeitenPhysics Question Papervasudevan m.vNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter II: Reciprocal Lattice: Read Chapter 2 of KittelDokument39 SeitenChapter II: Reciprocal Lattice: Read Chapter 2 of KittelEdson Jansen MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7Dokument60 SeitenCH 7Paul ArcillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry: CHEM F111Dokument24 SeitenGeneral Chemistry: CHEM F111DIVYAN GOYALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry Study GuideDokument9 SeitenPhysical Chemistry Study Guidekrymxen100% (2)
- ch36 PDFDokument11 Seitench36 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 121111Dokument26 SeitenLecture 121111--Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Density Functional Theory: Marie Curie Tutorial Series: Modeling Biomolecules December 6-11, 2004Dokument29 SeitenIntroduction To Density Functional Theory: Marie Curie Tutorial Series: Modeling Biomolecules December 6-11, 2004hermas67Noch keine Bewertungen
- QM HatomDokument50 SeitenQM HatomgvarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course 18.327 and 1.130 Wavelets and Filter BanksDokument13 SeitenCourse 18.327 and 1.130 Wavelets and Filter Banksdjoseph_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Studysheet For GREDokument15 SeitenStudysheet For GREMuqarraulAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Lattice DynamicsDokument73 SeitenLecture Notes Chapter 1 Lattice Dynamicsd460023100% (1)
- MIT5 Chem Lec 6Dokument8 SeitenMIT5 Chem Lec 6maggiesszzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsDokument16 SeitenElectromagnetic Waves and Quantum MechanicsVishavjeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS1131 Solutions Tut 6 11Dokument14 SeitenPHYS1131 Solutions Tut 6 11Jason Tan100% (2)
- Tutorial 1 CHE 221 - Solutions - (2024)Dokument6 SeitenTutorial 1 CHE 221 - Solutions - (2024)S'thembiso ThwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic StructureDokument41 SeitenAtomic StructuresavisuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolutionDokument27 SeitenSolutionAkshay Kr SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.atomic StructureDokument25 Seiten1.atomic StructureNanda KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Relativistic Quantum Chemistry - Lucas VisscherDokument111 SeitenAn Introduction To Relativistic Quantum Chemistry - Lucas Visscherandrew1553Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrum EstimationDokument39 SeitenSpectrum EstimationDr MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome TO Chemistry Virtual Classes: TopicDokument24 SeitenWelcome TO Chemistry Virtual Classes: TopicBalaraju GurramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4: Hydrogen AtomDokument53 SeitenLecture 4: Hydrogen AtomGagan JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Von EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsVon EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artikel ResonansiDokument4 SeitenArtikel ResonansiLulu RohmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2014 QP - Paper 1P Edexcel Physics IGCSEDokument28 SeitenJune 2014 QP - Paper 1P Edexcel Physics IGCSEShibraj DebNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM E587 - 15 (Reapproved 2020)Dokument9 SeitenASTM E587 - 15 (Reapproved 2020)abdulkadir aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Worksheet (AS) Waves: 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveDokument4 Seiten14 Worksheet (AS) Waves: 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveMahad AsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Direction Finding Theory and PracticesDokument57 SeitenRadio Direction Finding Theory and PracticesEnrique Alejandro Pérez SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarea SinusoidalesDokument3 SeitenTarea SinusoidalesRodrigo Nicolas VALENCIA VARGASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Standard Level Paper 2: Instructions To CandidatesDokument397 SeitenPhysics Standard Level Paper 2: Instructions To CandidatesSebastien BerkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Waves Self Study QuestionsDokument27 Seiten5 Waves Self Study QuestionsSteffany GómezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 3232 Optics I: Introduction: Prof. Rick Trebino, Georgia Tech WWW - Frog.gatech - EduDokument38 SeitenPhysics 3232 Optics I: Introduction: Prof. Rick Trebino, Georgia Tech WWW - Frog.gatech - EduTriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meaning of Poisson's Ratio: Sebastian Jaramillo GilDokument8 SeitenMeaning of Poisson's Ratio: Sebastian Jaramillo GilSebastian Jaramillo GilNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP21 HW6 SOL RDokument3 SeitenIP21 HW6 SOL R吳昭亮Noch keine Bewertungen
- Propagation of Sound Waves - Solved Examples - Solved Example - ICSE - 1Dokument5 SeitenPropagation of Sound Waves - Solved Examples - Solved Example - ICSE - 1samadritabiswas36Noch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Interference CurrentDokument5 Seiten06 Interference Current楊畯凱Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7.6 Superpostions of Stationary StatesDokument9 Seiten7.6 Superpostions of Stationary StatesVia Monica DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 3Dokument38 SeitenHW 3Khalid WaleedNoch keine Bewertungen
- He S. (Ed.) - Polymer Composites For Electrical and Electronic Engineering Application-MDPI (2022)Dokument194 SeitenHe S. (Ed.) - Polymer Composites For Electrical and Electronic Engineering Application-MDPI (2022)12 Fakhrel HafrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Armas Escalares Por Christi VerismoDokument85 SeitenArmas Escalares Por Christi VerismoLucas NascimentoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus de OklahomaDokument2 SeitenSyllabus de OklahomaAlvaro RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- VMC JEE Main and Advanced Tests - JEE 2021Dokument1 SeiteVMC JEE Main and Advanced Tests - JEE 2021Dhruv KuchhalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule Jee Main 2023 Full Test SeriesDokument3 SeitenSchedule Jee Main 2023 Full Test SeriesDevkriti SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 342 B.sc.b.ed. Mdsu PDF 4yrDokument135 Seiten342 B.sc.b.ed. Mdsu PDF 4yrDINESH SALVINoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics PDFDokument10 SeitenAcoustics PDFNupur Bhadra100% (1)
- PHY101 Quiz-3 File by Vu Topper RMDokument28 SeitenPHY101 Quiz-3 File by Vu Topper RMDanish TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animating Materials and ModifiersDokument6 SeitenAnimating Materials and ModifiersIuliu Nicolae BorsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three BIG Ideas With Waves: Fill in The Table BelowDokument2 SeitenThree BIG Ideas With Waves: Fill in The Table BelowspreemouseNoch keine Bewertungen
- WavesDokument16 SeitenWavesgabezneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparación Programas ExplosionesDokument22 SeitenComparación Programas Explosionessilvana delcarpio100% (1)
- Analytical Calculation of Uncoupled Heave and Roll, A Parametric Study of A Barge PDFDokument75 SeitenAnalytical Calculation of Uncoupled Heave and Roll, A Parametric Study of A Barge PDFTor Edvard Søfteland90% (10)
- 1st Year Syllabus Physics Cycle SyllabusDokument24 Seiten1st Year Syllabus Physics Cycle SyllabusMuwaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMA NHS Least Learned and Difficult CompetenciesDokument4 SeitenAMA NHS Least Learned and Difficult CompetenciesLa Castellana National High SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen