Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Littelfuse Protection Relay IEEE Device Numbers and Sizing Charts
Hochgeladen von
suni131Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Littelfuse Protection Relay IEEE Device Numbers and Sizing Charts
Hochgeladen von
suni131Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
POWR-GARD Protection Relays
Device Numbers and Sizing Charts
IEEE DEVICE NUMBERS
1 - Master Element 2 - Time Delay Starting or Closing Relay 3 - Checking or Interlocking Relay 4 - Master Contactor 5 - Stopping Device 6 - Starting Circuit Breaker 7 - Rate of Change Relay 8 - Control Power Disconnecting Device 9 - Reversing Device 10 - Unit Sequence Switch 11 - Multi-function Device 12 - Overspeed Device 13 - Synchronous-speed Device 14 - Underspeed Device 15 - Speed - or Frequency, Matching Device 16 - Data Communications Device 17 - Shunting or Discharge Switch 18 - Accelerating or Decelerating Device 19 - Starting to Running Transition Contactor 20 - Electrically Operated Valve 21 - Distance Relay 22 - Equalizer Circuit Breaker 23 - Temperature Control Device 24 - Volts Per Hertz Relay 25 - Synchronizing or Synchronism-Check Device 26 - Apparatus Thermal Device 27 - Undervoltage Relay 28 - Flame Detector 29 - Isolating Contactor or Switch 30 - Annunciator Relay 31 - Separate Excitation Device 32 - Directional Power Relay 33 - Position Switch 34 - Master Sequence Device 35 - Brush-Operating or Slip-Ring Short-Circuiting Device 36 - Polarity or Polarizing Voltage Devices 37 - Undercurrent or Underpower Relay 38 - Bearing Protective Device 39 - Mechanical Condition Monitor 40 - Field (over/under excitation) Relay 41 - Field Circuit Breaker 42 - Running Circuit Breaker 43 - Manual Transfer or Selector Device 44 - Unit Sequence Starting Relay 45 - Abnormal Atmospheric Condition Monitor 46 - Reverse-phase or Phase-Balance Current Relay 47 - Phase-Sequence or PhaseBalance Voltage Relay 48 - Incomplete Sequence Relay 49 - Machine or Transformer, Thermal Relay 50 - Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay 51 - AC Inverse Time Overcurrent Relay 52 - AC Circuit Breaker 53 - Exciter or DC Generator Relay 54 - Turning Gear Engaging Device 55 - Power Factor Relay 56 - Field Application Relay 57 - Short-Circuiting or Grounding (Earthing) Device 58 - Rectification Failure Relay 59 - Overvoltage Relay 60 - Voltage or Current Balance Relay 61 - Density Switch or Sensor 62 - Time-Delay Stopping or Opening Relay 63 - Pressure Switch 64 - Ground (Earth) Detector Relay 65 - Governor 66 - Notching or Jogging Device 67 - AC Directional Overcurrent Relay 68 - Blocking or Out-of-Step Relay 69 - Permissive Control Device 70 - Rheostat 71 - Liquid Level Switch 72 - DC Circuit Breaker 73 - Load-Resistor Contactor 74 - Alarm Relay 75 - Position Changing Mechanism 76 - DC Overcurrent Relay 77 - Telemetering Device 78 - Phase-Angle Measuring Relay 79 - AC Reclosing Relay 80 - Flow Switch 81 - Frequency Relay 82 - DC Reclosing Relay 83 - Automatic Selective Control or Transfer Relay 84 - Operating Mechanism 85 - Communications, Carrier or Pilot-Wire Relay 86 - Lockout Relay 87 - Differential Protective Relay 88 - Auxiliary Motor or Motor Generator 89 - Line Switch 90 - Regulating Device 91 - Voltage Directional Relay 92 - Voltage and Power Directional Relay 93 - Field Changing Contactor 94 - Tripping or Trip-Free Relay
NEUTRAL GROUNDING RESISTOR
SIZING CHART
System Voltage (Line-to-line) 208 V 480 V 600 V 2,400 V 4,160 V 13,800 V 25,000 V 34,500 V NGR Let-through Current and Resistance 5 A / 24 Ohms 5 A / 55 Ohms 5 A / 69 Ohms 5 A / 277 Ohms or 10 A / 139 Ohms 5 A / 480 Ohms or 10 A / 240 Ohms 10 A / 798 Ohms or 200 A / 40 Ohms 200 A / 72 Ohms or 400 A / 36 Ohms 200 A / 100 Ohms or 400 A / 50 Ohms Time Rating Continuous Continuous Continuous Continuous or 10 s Continuous or 10 s 10 seconds 10 seconds 10 seconds
Note: The values shown are for any size transformer and are typical. NOTE: The above table is for illustrative purposes only. Actual values may differ based on a variety of individual system considerations, such as capacitive charging current and co-ordination study results.
CURRENT TRANSFORMER
SIZING CHART
Conductor Size (AWG/kcmil) 12 10 8 6 4 3 2 1 1/0 2/0 3/0 4/0 Minimum CT Window Size (Inner Diameter in mm) Number of Conductors 1 4 6 7 9 11 13 14 16 18 20 23 25 28 33 39 48 55 3 8 10 12 15 19 22 25 28 31 35 39 44 48 56 67 82 95 4 9 11 14 18 22 25 28 32 36 40 45 51 55 65 78 95 110 6 11 14 17 22 28 31 35 39 44 49 55 62 67 80 95 117 135 8 13 16 20 25 32 36 40 45 51 57 64 72 78 92 110 135 156 12 15 19 24 31 39 44 49 55 62 69 78 88 95 113 135 165 191
P
PROTECTION OVERVIEW
ANSI DEVICE NUMBERS
AFD - Arc Flash Detector CLK - Clock or Timing Source DDR - Dynamic Disturbance Recorder DFR - Digital Fault Recorder ENV - Environmental Data HIZ - High Impedance Fault Detector HMI - Human Machine Interface HST - Historian LGC - Scheme Logic MET - Substation Metering PDC - Phasor Data Concentrator PMU - Phasor Measurement Unit PQM - Power Quality Monitor RIO - Remote Input/Output Device RTU - Remote Terminal Unit/ Data Concentrator SER - Sequence of Events Recorder TCM - Trip Circuit Monitor SOTF - Switch On To Fault
250 350 500 750 1000
Installation Instructions: When installing the PGC Family CTs, ensure the following: 1. Only the load carrying conductors pass through the center of the CT. This means L1 + N for 1-phase and L1+ L2 + L3 for 3-phase. 2. The power conductors pass through the center of the CT and are preferably bound together to keep the conductors uniformly spaced. 3. The power conductors pass perpendicular to the CT and, where practical, continue perpendicular to the CT on both sides of the CT for 3. 4. The power conductors should not be installed in a way that allows them to run along the side edges of the CT. 5. Where practical, locate the CT away from noise-generating devices such as transformers, frequency converters, etc.
TYPICAL SUFFIXES
AAC BBT CAlarm/Auxiliary Power Alternating Current Battery/Blower/Bus Bus Tie Capacitor/Condenser/ Compensator/Carrier Current/Case/Compressor DC - Direct Current E - Exciter FGMNPRSFeeder/Field/Filament/ Filter/Fan Generator/Ground* Motor/Metering Network/Neutral* Pump/Phase Comparison Reactor/Rectifier/Room Synchronizing/Secondary/ Stainer/Sump/Suction (Valve) T - Transformer/Thyratron TH - Transformer (High-voltage Side) TL - Transformer (Low-voltage Side) TT - Transformer (Tertiary-voltage Side) U - Unit
Note: Descriptions per IEEE Std C37.2-1996 *Suffix N is preferred when the device is connected in the residual of a polyphase circuit, is connected across broken delta, or is internally derived from the polyphase current or voltage quantities. The suffix G is preferred where the measured quantity is in the path of ground or, in the case of ground fault detectors, is the current flowing to ground.
2010 Littelfuse POWR-GARD Protection Relay Catalog
67
www.littelfuse.com/protectionrelays
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- 01-Modeling, Simulation, and Design of Hybrid EV Battery Charger For Optimum Grid Utilization, PSIMDokument108 Seiten01-Modeling, Simulation, and Design of Hybrid EV Battery Charger For Optimum Grid Utilization, PSIMViet Anh DoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor AF and RF Circuits - Allan Lytel PDFDokument127 SeitenTransistor AF and RF Circuits - Allan Lytel PDFYou Look100% (1)
- Clap Switch PresentationDokument39 SeitenClap Switch Presentationghaza0070% (2)
- DC Link Voltage Control of Back-To-Back ConverterDokument6 SeitenDC Link Voltage Control of Back-To-Back ConverterRoshan PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 AnswerDokument7 SeitenAssignment 1 AnswerA E Sahadat IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR4850 Product DatasheetDokument9 SeitenSR4850 Product DatasheetihsanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTCL Internship Report by Fawad AhmedDokument35 SeitenPTCL Internship Report by Fawad AhmedhhshhsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Simulation of Single Phase PWM Rectifier With IEEE 519 ComplianceDokument6 SeitenDesign & Simulation of Single Phase PWM Rectifier With IEEE 519 CompliancepauloNoch keine Bewertungen
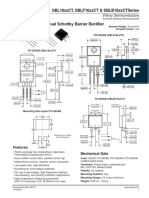
- SBL1640CTDokument4 SeitenSBL1640CTAlejandro Borrego DominguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csvtu Syllabus Diploma Electrical 3 SemDokument23 SeitenCsvtu Syllabus Diploma Electrical 3 SemVenu Kumar SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable Frequency Drive-VfdDokument6 SeitenVariable Frequency Drive-VfdKumaraswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Star Delta Starter Using Relays and Adjustable ElDokument3 SeitenAutomatic Star Delta Starter Using Relays and Adjustable Elodeke aronNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD Tesis ZarriDokument228 SeitenPHD Tesis ZarriperathuselvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profesional Inverters Tig Cemont TX150 Ac/dcDokument23 SeitenProfesional Inverters Tig Cemont TX150 Ac/dcMIGUEL33% (3)
- High Efficiency Thyristor: 1 Triac Three Quadrants Operation: QI - QIIIDokument5 SeitenHigh Efficiency Thyristor: 1 Triac Three Quadrants Operation: QI - QIIIFaulhaber AdrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP133E REV02 D Specifica Tecnica Serie Safepower EVO (ING) - 2Dokument84 SeitenSP133E REV02 D Specifica Tecnica Serie Safepower EVO (ING) - 2Waheed MidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edc Lab-1 Manual-2Dokument91 SeitenEdc Lab-1 Manual-2Ashish SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.syllabus (M.sc. Physics I)Dokument7 Seiten1.syllabus (M.sc. Physics I)Muhammad Hasan RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axis Drive Systems PDFDokument62 SeitenAxis Drive Systems PDFJoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Flex 7000Dokument25 SeitenPower Flex 7000Felipe Rene AucailleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentacion UpsDokument55 SeitenPresentacion UpsArmando CanutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSSR RanDokument42 SeitenTSSR Rananon_275711487100% (1)
- XL7 OCS Datasheet For: 1. SpecificationsDokument10 SeitenXL7 OCS Datasheet For: 1. SpecificationsRegisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens Polymobil - Function DescriptionDokument12 SeitenSiemens Polymobil - Function Descriptionsadeq03100% (1)
- 4.1.2 A Simple Application: The RectifierDokument3 Seiten4.1.2 A Simple Application: The RectifierCarla CardealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Diode Applications PDFDokument122 SeitenChapter 2 Diode Applications PDFObama binladenNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC HipotDokument4 SeitenDC HipotlrpatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDokument13 SeitenLecture - 1 Introduction To Power Electronicsunity123d deewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battery Charger PMI Industrial DC Catalogue PDFDokument8 SeitenBattery Charger PMI Industrial DC Catalogue PDFTaQuangDucNoch keine Bewertungen
- UCC28070 300-W Interleaved PFC Pre-Regulator Design Review: Application ReportDokument27 SeitenUCC28070 300-W Interleaved PFC Pre-Regulator Design Review: Application ReportJean-Yves LAPORTENoch keine Bewertungen