Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Geo Project Tri CNTR 2011
Hochgeladen von
SaraOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Geo Project Tri CNTR 2011
Hochgeladen von
SaraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
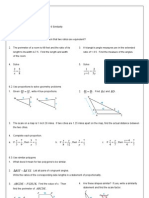
Name: Date: Class: Band: Geometry PBA Project: Triangle Centers You can do it!
You have a wealth of knowledge about triangle centers. Now it is time to apply it! Choose three locations on a map that are important to you. Call them special properties of each point. Due Date:_____________________
A , B and C . Form ABC using these three
locations. Find the circumcenter, incenter, centroid, orthocenter and nine-point center of the triangle and demonstrate the
Part I: Circumcenter 1. Choose three points on a map to form ABC . 2. Find the circumcenter of ABC , and label it O . Label the midpoint of B as M A , the midpoint of A as C C
M B , and the midpoint of A as M C . Erase any unnecessary segments. B
3. What is the approximate address of the circumcenter? 4. Draw in O , O , and O . Measure each segment in centimeters to show that the circumcenter is equidistant A B C from each vertex of ABC i.e. OA OB OC . 5. Draw in the circumcircle. 6. Explain why the circumcenter is special.
Part II: Incenter 1. Choose three different points on a separate map to form ABC . 2. Find the incenter of ABC , and label it 4. Draw in the perpendicular distances from
I . Erase any unnecessary segments.
I to
B , A , and A , and label the intersections as C C B
3. What is the approximate address of the incenter?
D , E , and
F respectively. Measure each segment in centimeters to show that the incenter is equidistant from each side of
ABC i.e. ID IE IF .
5. Draw in the incircle. 6. Explain why the incenter is special.
Part III: Centroid 1. Choose three different points on a separate map to form ABC .
2. Find the centroid of ABC , and label it G . Label the midpoint of B as M A , the midpoint of A as M B , C C and the midpoint of A as M C . B 3. What is the approximate address of the centroid? 4. Measure in centimeters the base and height of the six small triangles created by the centroid. Use the area formula for a triangle and your measurements to show that each of the six triangles have the same area. 5. Explain why the centroid is special.
Part IV: Orthocenter 1. Choose three different points on a separate map to form ABC . 2. Find the orthocenter of ABC , and label it the foot on A as H C . B 3. What is the approximate address of the orthocenter? 4. Measure A H
B
H . Label the foot on
B C as
H A , the foot on A as H B , and C
, H BC , C H
H , H AB , B
, and H C A in centimeters. Use these measurements to verify
that Cevas Theorem i.e.
AH B H BC
A CH B H C C = 1 . HA A
BH
5. Explain why the orthocenter is special.
Part V: Nine Point Center 1. Choose three different points on a separate map to form ABC . 2. Find the circumcenter O , centroid G , and orthocenter and
H of ABC . Label the midpoints of the sides D , E ,
F . Label the feet of the altitudes J , K , and L .
3. Erase the medians and perpendicular bisectors, but NOT the altitudes. 4. Find the nine-point center of ABC , and label it N . 5. What is the address of the nine-point center? 6. Draw in the nine-point circle and label any non-labeled special points on it. 7. Show that
H , O , N , and G are all collinear by drawing in the Euler line O . H
8. Measure O , O , G , and N in centimeters. Show that H N O G 9. Explain why the nine-point circle is special.
O N= 12 O H, G O= 13 O H, and N G= 16 O H
Closing Statement
Write a one page dialogue about the triangle centers having a conversation over thanksgiving dinner. Use their attributes to give them personalities. This should be no more than one double spaced page, using a 10 point font. Glossary Words 1. Equidistant 2. Concurrent 3. Point of Concurrency 4. Perpendicular Bisector 5. Angle Bisector 6. Median 7. Midpoint 8. Altitude 9. Foot of an Altitude 10. Circumcenter Pieces of the Project 1. Title Page 2. Table of Contents 3. Glossary of Important Definitions/Terms 4. Part I: 5. Part II: Circumcenter (Construction, Attributes, Demonstration) Incenter (Construction, Attributes, Demonstration) 11. Incenter 12. Centroid 13. Orthocenter 14. Nine Point Center 15. Circumcircle 16. Incircle 17. Nine-Point Circle 18. Circumradius 19. Inradius 20. Euler Line
6. Part III: Centroid (Construction, Attributes, Demonstration) 7. Part IV: Orthocenter (Construction, Attributes, Demonstration) 8. Part V: Nine Point Center (Construction, Attributes, Demonstration) 9. Closing Statement 10. Rubric Notes 1. You can obtain maps at http://maps.google.com. Choose a scale that makes your triangle as large as possible on the page. 2. Each glossary term, must be numbered and in the order given above. You must also include the word, the definition of the word, and an illustration of the word. This section MUST be handwritten. 3. On Parts IV, be sure to state the location center. 4. Each part should use a different set of three points and should be done on a separate sheet of paper. 5. You must label each diagram according to the instructions given, including ALL important markings. You must also write all numerical measurements you make on the diagram e.g. midpoints, angle bisectors, etc. 6. For the closing statement, check mathworld.com, cut-the-knot.org and wikipedia.com for information about the triangle centers.
A , B , and C represent and the location of the given triangle
Name: Date: Class: Band: Geometry PBA Project: Triangle Centers Rubric did it! Title page/Presentation (organization, neatness, dcor, spelling and grammar) Table of Contents/Glossary Part ICircumcenter Construction/Labels Attributes Demonstration Part IIIncenter Construction/Labels Attributes Demonstration Part IIICentroid Construction/Labels Attributes Demonstration Part IVOrthocenter Construction/Labels Attributes Demonstration Part VNine-Point Center Construction/Labels Attributes Demonstration Closing Statement Comments: 8 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 6 6 5 5 4 4 6 6 5 5 4 4 6 6 5 5 4 4 6 6 5 5 4 4 8 8 7 7 6 6 6 5 5 5 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 /15 0 0 0 /15 0 0 0 /15 0 0 0 /15 0 0 0 /15 0 0 0 0 You
Grade: ___________ 99
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Rez Limits ReviewDokument4 SeitenRez Limits ReviewSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Name: Date: Class: Band: 7.3: Similar Right TrianglesDokument2 SeitenName: Date: Class: Band: 7.3: Similar Right TrianglesSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Secant Tangent and Tangent Tangent AnglesDokument4 Seiten11 Secant Tangent and Tangent Tangent AnglesSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Rezvi Review Sheet Exp - LogsDokument4 SeitenRezvi Review Sheet Exp - LogsSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Index Card For CirclesDokument1 SeiteIndex Card For CirclesSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Geo June 10 Final RVW CHPT 6Dokument2 SeitenGeo June 10 Final RVW CHPT 6SaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Limits HW 3Dokument2 SeitenLimits HW 3SaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- 6-Properties of ParallelogramsDokument4 Seiten6-Properties of ParallelogramsMohamed Korra100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Rez Limits ReviewDokument4 SeitenRez Limits ReviewSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- 6-Properties of TrapezoidsDokument4 Seiten6-Properties of TrapezoidsSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- 6-Properties of ParallelogramsDokument4 Seiten6-Properties of ParallelogramsMohamed Korra100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Rez LowhighDokument2 SeitenRez LowhighSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits Rez ReviewDokument2 SeitenLimits Rez ReviewSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Answer Key 8.3-8.10Dokument4 SeitenAnswer Key 8.3-8.10SaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Holes PracticeDokument2 SeitenHoles PracticeSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- D1 CW HW Numerical LimitsDokument1 SeiteD1 CW HW Numerical LimitsSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Classifying QuadrilateralsDokument6 SeitenClassifying QuadrilateralsSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rez Rat FN Review SheetDokument4 SeitenRez Rat FN Review SheetSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tessellation NotesDokument17 SeitenTessellation NotesSara100% (1)
- Geo WS Q3 U6 82 83 Outline ProofsDokument4 SeitenGeo WS Q3 U6 82 83 Outline ProofsSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geo WS Q3 U6 82Dokument2 SeitenGeo WS Q3 U6 82SaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Geo WS Q3 U6 82Dokument2 SeitenGeo WS Q3 U6 82SaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rational Functions PDFDokument41 SeitenRational Functions PDFSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- D1 CW HW Numerical LimitsDokument1 SeiteD1 CW HW Numerical LimitsSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- D3 CW HW Quad QuadDokument2 SeitenD3 CW HW Quad QuadSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quad Quad HW1Dokument1 SeiteQuad Quad HW1SaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large Acute TriangleDokument1 SeiteLarge Acute TriangleSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math RubricDokument1 SeiteMath RubricSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- 54 9 Point Center Make CWDokument3 Seiten54 9 Point Center Make CWSaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Primer On Number Sequences by Shailesh ShiraliDokument250 SeitenA Primer On Number Sequences by Shailesh Shiralibabu srivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions For Bmoeg-I (2021) : Buratino'S Mock of Euclidean Geometry-IDokument19 SeitenSolutions For Bmoeg-I (2021) : Buratino'S Mock of Euclidean Geometry-IChính Minh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 120 Geometry Exercises by Romantics of Geometry Vol.1, Issues 01-10Dokument149 Seiten120 Geometry Exercises by Romantics of Geometry Vol.1, Issues 01-10Marcos PalaciosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Classical Triangle CentersDokument17 SeitenThe Classical Triangle CentersOmaru NimagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- We Can Show That The OrthocentreDokument3 SeitenWe Can Show That The OrthocentresagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Diem Dac Biet PDFDokument6 Seiten2 Diem Dac Biet PDFHuy Hữu NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bài giải bài TalinpaDokument17 SeitenBài giải bài TalinpaahoaseoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Point CircleDokument13 Seiten9 Point CircleSeshu PhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 4th Olympiad of Metropolises MathematicsDokument4 SeitenThe 4th Olympiad of Metropolises MathematicsLong NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paul Yiu - Introduction To Triangle GeometryDokument160 SeitenPaul Yiu - Introduction To Triangle GeometryGy SzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- TetrahedronDokument16 SeitenTetrahedronjim1234uNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Note On The Barycentric Square Roots of Kiepert PerspectorsDokument6 SeitenA Note On The Barycentric Square Roots of Kiepert PerspectorsDũng Nguyễn TiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cosmology of Plane GeometryDokument114 SeitenCosmology of Plane GeometryAlexander Skutin100% (1)
- Incenter Symmetry, Euler Lines, and Schiffler Points: Guyen E IldbergerDokument9 SeitenIncenter Symmetry, Euler Lines, and Schiffler Points: Guyen E IldbergerJeffersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry ConfigurationsDokument11 SeitenGeometry Configurationsmichael scottNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMOFall 16 ProbsDokument8 SeitenOMOFall 16 ProbsHoàng LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- FG 2006 Volume 6Dokument364 SeitenFG 2006 Volume 6uthso royNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euler Line: Proofs, Properties, ApplicationsDokument29 SeitenEuler Line: Proofs, Properties, ApplicationsDominik Teiml100% (2)
- Two Special Points 1Dokument6 SeitenTwo Special Points 1Swapnaneel Bhattacharyya100% (1)
- FGvolume7 (Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 2007) PDFDokument254 SeitenFGvolume7 (Forum Geometricorum Volume 7 2007) PDFTirtharaj BasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecchap 4Dokument52 SeitenLecchap 4drhugh3891Noch keine Bewertungen
- MC35 Geometry Ch04 Handout-209Dokument6 SeitenMC35 Geometry Ch04 Handout-209SCARLETT CARSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euclidean Geometry NotesDokument174 SeitenEuclidean Geometry Notesscribd@rekenaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure Euler's LineDokument2 SeitenStructure Euler's LineStudy DBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mock INMO SolutionsDokument8 SeitenMock INMO SolutionsAnant DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cosmology of Plane Geometry: Concepts and TheoremsDokument175 SeitenCosmology of Plane Geometry: Concepts and TheoremsAlexander Skutin75% (4)
- 1.medial TriangleDokument17 Seiten1.medial TriangleA wanderer In this universeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Droz Farny LinesDokument7 SeitenDroz Farny LinesSilentSparrow98Noch keine Bewertungen
- ETC ExtraDokument11 SeitenETC Extraobelix2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeVon EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeVon EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsVon EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)