Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Anatomy and Physiology of The Brain
Hochgeladen von
gorresOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anatomy and Physiology of The Brain
Hochgeladen von
gorresCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain
The Brain is an incredible collection of ventricles, lobes, and systems, all working together to enable you to function. Since this subject is so extensive, we'll try to focus on the basics.
The human brain is the center of the human nervous system and is a highly complex organ. It is often compared to a computer, because of the vast amount of information it can process and store, however, the human brain is far more complex and functional. It has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over five times as large as the "average brain" of a mammal with the same body size. Most of the
expansion comes from the cerebral cortex, a convoluted layer of neural tissue that covers the surface of the forebrain. Especially expanded are the frontal lobes, which are involved in executive functions such as self-control, planning, reasoning, and abstract thought.
Cerebrum is ones conscious brain. It is separated into two hemispheres and each hemisphere into five lobes. That means there are 2 of each lobe (one in each hemisphere) in the brain. Below are the lobes and what they are associated with. 1. Frontal Lobe: associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, voluntary motor function of skeletal muscles, emotions, and problem solving,personality. 2. Parietal Lobe: associated with movement, orientation, recognition, and perception ofstimuli. 3.Occipital Lobe: associated with visual processing. 4. Temporal Lobe: associated with perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memoryandspeech,smell 5. Cerebellum: associated with regulation and coordination of movement, posture, and balance. Brain Stem: This structure is responsible for basic vital life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure. Mid-Brain: Acts like a complex switchboard, allowing the brain to communicate with the rest of the nervous system. Pons: Relay messages from the cerebrum to the cerebellum and spinal cord. Medulla Oblongata: Located above spinal cord. It regulates vital functions, such as heartbeat and breathing. The Medulla Oblongata is responsible for the 6 Crazy Dwarfs: 1.Coughing 2.Sneezing
3.Vomiting 4.Salivating 5.Swallowing 6. Gaging HYPOTHALAMUS FUNCTIONS To help you remember the 7 functions of the hypothalamus you can use the pneumonic... B Behavior E Endocrine E Emotions T Temperature Control S Sleep/Wake Cycle H Hunger/Thirst A Autonomic Nervous System M Memory
Meninges - these are 3 distinct membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord completely, for protection DAP. D (Dura Mater) - this is the membrane that has direct contact with the bones of the skull. This is the outermost layer or most SUPERFICIAL Mater. A (Arachnoid Mater) - this is a net like membrane that is between the Dura Mater and the Pia Mater. P (Pia Mater) - this membrane is hard if not impossible to see with the naked eye. It attaches directly to the brain and the spinal cord. It follows the contours of the brain. This is the innermost layer or DEEP Mater. Cranial Nerves: There are 12 nerves to remember and here is a acronym to help. O, O, O To Touch A Faithful Very Grateful Very Active Housewife. To also help you remember if it is a sensory or motor or both The acronym for that is
Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Breats Matter Most
Interesting facts about the Brain 1. The brain operates on the same amount of power as 10-watt light bulb. The cartoon image of a light bulb over your head when a great thought occurs isnt too far off the mark. Your brain generates as much energy as a small light bulb even when youre sleeping. 2. Your brain uses 20% of the oxygen that enters your bloodstream. The brain only makes up about 2% of our body mass, yet consumes more oxygen than any other organ in the body, making it extremely susceptible to damage related to oxygen deprivation. So breathe deep to keep your brain happy and swimming in oxygenated cells. 3. Scientists say the higher your I.Q. the more you dream. While this may be true, dont take it as a sign youre mentally lacking if you cant recall your dreams. Most of us dont remember many of our dreams and the average length of most dreams is only 23 secondsbarely long enough to register. 4. The human brain cell can hold 5 times as much information as the Encyclopedia Britannica. Or any other encyclopedia for that matter. Scientists have yet to settle on a definitive amount, but the storage capacity of the brain in electronic terms is thought to be between 3 or even 1,000 terabytes. 5. Nerve impulses to and from the brain travel as fast as 170 miles per hour. Ever wonder how you can react so fast to things around you or why that stubbed toe hurts right away? Its due to the super-speedy movement of nerve impulses from your brain to the rest of your body and vice versa, bringing reactions at the speed of a high powered luxury sports car. 6. The brain itself cannot feel pain. While the brain might be the pain center when you cut your finger or burn yourself, the brain itself does not have pain receptors and cannot feel pain. That doesnt mean your head cant hurt. 7. A typical human brain, has a volume of 1200cc and weighs around 3 pounds.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Reviewer On Nervous System Grade VIDokument4 SeitenReviewer On Nervous System Grade VIKent Francis LayaguinNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Vital Signs ModuleDokument10 SeitenVital Signs ModulelisalovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Lesson Log in Grade9Dokument2 SeitenDaily Lesson Log in Grade9Jowell Obra Oaña88% (25)
- Hemorrhage Uterine AtonyDokument59 SeitenHemorrhage Uterine Atonygorres100% (1)
- Questions and AnswersDokument15 SeitenQuestions and AnswersTanveerAli01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension Intro TweetDokument4 SeitenHypertension Intro TweetgorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- The United NationsDokument2 SeitenThe United NationsgorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAY 1 Chapter 1 Personnel Mgt. & Nature of Leadership & SkillsDokument32 SeitenDAY 1 Chapter 1 Personnel Mgt. & Nature of Leadership & SkillsgorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gorres, Sierra MaeDokument4 SeitenGorres, Sierra MaegorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuation of PneumoniaDokument6 SeitenContinuation of PneumoniagorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory NotesDokument2 SeitenRespiratory NotesLidy CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphatic System AnatomyDokument2 SeitenLymphatic System AnatomyJowett Andri PatiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood: Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMUDokument40 SeitenBlood: Muhammad Iqbal Lecturer KMUKomal NayabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Terminology For Dummies Cheat SheetDokument5 SeitenMedical Terminology For Dummies Cheat SheetSir SuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature Compensation in Ecto, Endo and HeterothermsDokument24 SeitenTemperature Compensation in Ecto, Endo and HeterothermsKiran Hassan0% (1)
- Histology DigestiveDokument87 SeitenHistology DigestiveAnang Yanuar RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delayed Sleep Phase SyndromeDokument12 SeitenDelayed Sleep Phase SyndromeReshmaNoch keine Bewertungen
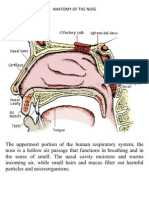
- Anatomy of The NoseDokument2 SeitenAnatomy of The NosePablo PasabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Manual Anatomy Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualDokument4 SeitenLaboratory Manual Anatomy Physiology 6th Edition Marieb Solutions ManualHenry Espinoza100% (33)
- Blood Basics - Unit 5Dokument10 SeitenBlood Basics - Unit 5api-292042538Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organ Systems InteractionsDokument6 SeitenOrgan Systems InteractionsHart OlpendaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ResultDokument1 SeiteLab Resultrakibul islamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Sleep Disorders in ChildrenDokument10 SeitenCommon Sleep Disorders in ChildrenHajrin PajriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grafik EwsDokument4 SeitenGrafik Ewsmfep putriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accessory Respiratory Organ in FishDokument47 SeitenAccessory Respiratory Organ in Fishkoustav kundu0% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of PCAPDokument8 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of PCAPMads0% (1)
- Circulatory System NotesDokument2 SeitenCirculatory System NotesMohamed AbdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silabus HistoDokument7 SeitenSilabus HistoamytenzerNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumengvghtDokument2 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumengvghtKapil ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immune Response ExplainedDokument3 SeitenImmune Response Explainednoreen doraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion: Breaking Down Food in the Digestive SystemDokument25 SeitenDigestion: Breaking Down Food in the Digestive SystemJaymee GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting Sleep: The Quality and Quantity of Sleep AreDokument3 SeitenFactors Affecting Sleep: The Quality and Quantity of Sleep AreBijali sinha100% (3)
- Blood: Chapter 10 - Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument129 SeitenBlood: Chapter 10 - Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDjhica Nicolle TilosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood GroupDokument14 SeitenBlood GroupAnna Kay BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copd - NCPDokument6 SeitenCopd - NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNoch keine Bewertungen
- H & N - Pharynx& Deglutition PDFDokument17 SeitenH & N - Pharynx& Deglutition PDFRamin AmirkhiziNoch keine Bewertungen