Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
À Physical Examination: 3.flame Test
Hochgeladen von
Pushpreet HanspalOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
À Physical Examination: 3.flame Test
Hochgeladen von
Pushpreet HanspalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
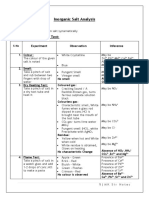
Specimen copy of salt analysis
EXPERIMENT
1.PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Noted the colour of the salt
OBSERVATION
white
INFERENCE
Cu2+,Mn2+,Ni2+,Fe3+,Co2+ May be absent. NH4+,S2- ,CH3COO- MAY be absent
Noted the smell of the salt. 2.Dry heating test Heated a pinch of salt in a dry test tube and noted the following: y Gas is evolved.
No specific odour.
Reddish brown fumes. Colourless gas with smell of vinegar or pungent smell
NO2-/ NO3-/Br- may be present.
CH3 COOCl- may be present
Decrepitation crackling sound Sublimation Pb2+, NO3- , Ba2+ may be present. No/Sublimate formed. NH4+ abs / present.
Colour of the residue
Yellow when hot,white when cold Zn2+ may be present
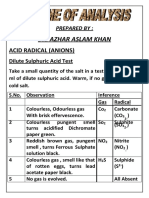
3.Flame Test Prepared a paste of the salt with conc.HCl and performed flame test with a platinum wire. Analysis of Anion 4.Dil. H2SO4 test Treated a pinch of salt with dil. H2SO4.
Green Crimson Brick red
Ba2+ Sr2+ Ca2+
No effervescence No Rotten egg smell No Brown fumes No burning sulphure smell
CO32- abs S2- abs NO2- abs SO3 2- abs
5.Conc.H2SO4 test: Heated a pinch of salt with conc. H2SO4 . A glass rod dipped in NH4OH was shown to mouth of the test tube.
A colourless gas with suffocating smell was evolved. White fumes intensified.
May be Cl-.
OR A colourless gas with smell of vinegar was evolved. OR Colourless gas when passed through lime water, it turns milky. OR Brown fumes evolved,which intensified on addition of MnO2 Brown fumes intensified with copper turnings. Depending on the observation,confirmatory test to be performed there. 6.Test for phosphate Salt solution+ammonium molybdate and heated. 7.Test for sulphate Salt soln+Dil.HCl+BaCl 2 soln Analysis cation 8.test for NH4+ Heated a pinch of the salt with 2-3 ml NaOH solution.
May be acetate.
May be oxalate
May be BrMay be nitrate
canary yellow colour.
confirmed
white precipitate insoluble in Conc.HCl and conc.HNO3 confirmed
Smell of NH3 gas evolved. A rod dipped in Conc.HCl shown to evolved gas,dense white fumes were seen. White precipitate
NH4+ present
9.test for Group-1 To the salt solution,add dil.Hcl solution. Filter the precipitate and dissolve in hot water.Divide the solution into 2 parts. (i) + KI soln (ii) + k2CrO4
Pb2+
yellow ppt Yellow ppt (if Pb2+ is absent,use same soln for gr2) confirmed
10.Test for Group-2 To the above solution, pass H2S. Dissolve the ppt in 50% HNO3 and divide into 2 parts. 1 2 + NH4OH +Pottasium ferrocyanide Black ppt was formed. Cu2+ present
deep blue colour chocolate brown ppt
11.Test for Group-3 To the saltsolution,add 3-4 drops of Conc.HNO3.Boil the content for sometime.Add NH4Cl,NH4OH in excess.
Gelatinous white or Reddish brown ppt Al3+ Or Fe3+ (Confirmatory test)
12.Test For Group-4 To the salt solution,add NH4Cl,NH4OH and H2S
black ppt Buff coloured ppt White ppt
Ni2+,Co2+ Mn2+ Zn2+
(confirmatoty
test for ions)
13.Test for Group-5 To the salt solution,add NH4Cl,NH4OH and (NH4)2CO3 Filter the ppt,dissolve in acetic acid. divide into 3 parts. 1+potassium chromate soln 2+ammonium sulphate soln 3+ ammonium oxalate soln
White ppt
Ba2+,Ca2+,Sr2+
Yellow ppt White ppt White ppt
Ba2+, Sr2+ Ca2+, This sequence has to be followed whether Sr or Ca or Ba is present)
Conclusion: Acid radical-----Basic radical is -----------------Chemical equations for positive detections: 1 2. 3. 4.
Neatly written Answer sheet impresses every one. Volumetric Analysis
Aim: Apparatus:burette,pipette,volumetric flask,weighing bottle,clamp stand,conical flask,funnel,tile,weight box,balance ,beaker etc Chemicals: Theory: Titration between KMnO4 and Oxalic acid/Mohrs salt solution is a redox titration where KMnO4 oxidises oxalic acd or ferrous ion in Mohrs salt solution to CO2 and ferric ions respectively,itsef is reduced to Mn2+ ions in acidic medium. IONIC EQUATION:
Molecular equation:
Solution in burette:KMnO4 solution in pipette:10 ml oxalic acid / mohrs salt solution
Solution in the conical flask:10ml oxalic acid / mohrs salt solution and half test tube H2SO4 Indicator:KMnO4 is self indicator End point:Colourless-pink Temperature of the reaction:50 60 degree in case of oxalic acid Room temperature in case of mohrs salt solution Medium of the reaction: Acidic Catalyst used: Mn2+ions in case of oxalic acid Calculation for preparation of oxalic acid / Mohrs salt solution: Molarity = no.of moles / vol. of the solution
Wt. of the sample = x g Wt of weighing bottle = W1 g
Wt of weighing bottle + sample = W2 g Wt of the sample = W2 W1 g
OBSERVATION TABLE S.N 1 2 3 Calculation: M1 =molarity of kMnO4 solution M2 =molarity of oxalic acid or Mohrs salt solution V2 = volume of oxalic acid or Mohrs salt solution (10ml) n2 = Stoichiometric coefficient oxalic acid or Mohrs salt solution initial burette reading in ml p q r Final burette reading in ml q r s Difference in volume ( ml) q-p same same
V1 = volume of KMnO4 used
n1 = Stoichiometric coefficient of KMnO4
M1V1 = M2V2 n1 M1 = ? Strength of KMnO4 solution = M1 x 158 = g/l Precautions: Rinse the burette and pipette with respective solutions. Do not heat the mixture in conical flask more than 60 degrr. Add H2SO4 to Mohrs salt while preparing solution. Always take upper meniscus of KmnO4 Take enough care while weighing the sample in analytical balance Do not add KMnO4 soln. from the burette at a stretch. Clean conical flask properly after taking an observation. Add anything u would like to . n2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemistry Practical Std. XI MaterialDokument16 SeitenChemistry Practical Std. XI Materialcrce.9983.ceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Practical 2022 - XIIDokument21 SeitenChemistry Practical 2022 - XIIAayanurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 20Dokument4 SeitenExperiment 20Beenu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Qualitative Analysis ProcedureDokument3 SeitenInorganic Qualitative Analysis ProcedureAbinov Kumar KTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Salt Analysis General ProcedureDokument9 Seiten1-Salt Analysis General ProcedureGovind Singh KhatiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 16Dokument3 SeitenExperiment 16Beenu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Record DDokument9 SeitenRecord DAnonymous 8VJhV1eI2yNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead NitrateDokument3 SeitenLead NitrateAbinov Kumar KTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salt Analysis IIIDokument5 SeitenSalt Analysis IIIrajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Practical 2023 - XIIDokument19 SeitenChemistry Practical 2023 - XIIPhsyics XINoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Chemistry Lab ManualDokument25 SeitenApplied Chemistry Lab Manualsaif.rahaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADokument5 SeitenANaveenKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis Chemistry PracticalDokument8 SeitenQualitative Analysis Chemistry PracticalNicky SebastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- SALT 1 To 4Dokument11 SeitenSALT 1 To 4rkushi0205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Practical Term - 1Dokument6 SeitenGrade 12 Practical Term - 1Altaf Hussain KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - Unit3Dokument6 SeitenChemistry - Unit3123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flame test identification using metal ionsDokument17 SeitenFlame test identification using metal ionsTahir50% (4)
- Qualitatile Inorganic AnalysisDokument9 SeitenQualitatile Inorganic AnalysisRamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salt AnalysisDokument23 SeitenSalt AnalysisflippodynamicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 - Chemistry Practical ContentDokument34 SeitenGrade 12 - Chemistry Practical Contentsskmarketing7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry 12 Term 1 PracticalDokument25 SeitenChemistry 12 Term 1 Practicalakansha chuodharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SALT ANALYSIS (Test For Anion)Dokument5 SeitenChemistry SALT ANALYSIS (Test For Anion)Shivank SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semi-Micro Qualitative Analysis of an Inorganic SaltDokument11 SeitenSemi-Micro Qualitative Analysis of an Inorganic SaltNidhi PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme for Qualitative Analysis of a Mixture containing two SaltsDokument10 SeitenScheme for Qualitative Analysis of a Mixture containing two SaltsMuhammad Shaheer JavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of Simple Inorganic SaltsDokument6 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Simple Inorganic SaltsBinish Cj100% (1)
- Experiment 12Dokument2 SeitenExperiment 1210m29satyamsinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Scheme of AnalysisDokument5 SeitenChemistry Scheme of AnalysisarifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of Cations Anad Anions IIDokument7 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Cations Anad Anions IIrevokimaro01Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.magnesium Sulphate-PrintedDokument3 Seiten3.magnesium Sulphate-PrintedSchool pptaccNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11TH STD SALT ANALYSIS 3 - FERRIC CHLORIDE (1)Dokument5 Seiten11TH STD SALT ANALYSIS 3 - FERRIC CHLORIDE (1)Neelavathy PalaniappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnesium Sulphate.Dokument3 SeitenMagnesium Sulphate.Abinov Kumar KTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Answer Sheet SchemeDokument3 SeitenPractical Answer Sheet Schemes svNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnknownDokument3 SeitenUnknownStanley TaNoch keine Bewertungen
- as requested and focuses on the most important keyword "acid radical identificationDokument20 Seitenas requested and focuses on the most important keyword "acid radical identificationPriyansh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 21Dokument4 SeitenExperiment 21Beenu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cuso 4Dokument2 SeitenCuso 4vjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of Anions: Experiment TwentyDokument8 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Anions: Experiment TwentyShaayaan SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Chem - Post Lab NotesDokument11 SeitenAnalytical Chem - Post Lab NotesMare5Der5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test of Cation and Anions-1Dokument19 SeitenTest of Cation and Anions-1HARDIK MISHRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry LabDokument7 SeitenChemistry LabJayani PuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyse Salt Experiment Report: Identifying NH4+, CO32-, NO3- and CH3COODokument6 SeitenAnalyse Salt Experiment Report: Identifying NH4+, CO32-, NO3- and CH3COOchetan sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salt Analysis With EquationsDokument12 SeitenSalt Analysis With Equationsabhikhya aryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis of Cations and AnionsDokument24 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Cations and AnionsNidhi Chaudhary33% (3)
- File Responsi KimiaDokument17 SeitenFile Responsi KimiabarajatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANALYSIS OF ANIONS AND CATIONS IN TOOTHPASTESDokument23 SeitenANALYSIS OF ANIONS AND CATIONS IN TOOTHPASTESmashi sainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SALT 5 To 8Dokument9 SeitenSALT 5 To 8rkushi0205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative analysis of brass and bronze alloysDokument6 SeitenQualitative analysis of brass and bronze alloysSahilMalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis: Identification of The AnionDokument40 SeitenQualitative Analysis: Identification of The AniontwinkledreampoppiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Salt Analysis Manual by SavitriDokument6 SeitenChemistry Salt Analysis Manual by SavitriAadya HarichandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnesium ChlorideDokument6 SeitenMagnesium ChlorideiskypiskybruhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Observations Grade 9Dokument4 SeitenChemical Observations Grade 9Shaunak PadhyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXPERIMENT 1 - MergedDokument32 SeitenEXPERIMENT 1 - Mergedamiagra01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project: By:-Anubhav SharmaDokument12 SeitenChemistry Project: By:-Anubhav SharmaAnubhav SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mangnese ChlorideDokument3 SeitenMangnese ChloridenishchayNoch keine Bewertungen
- salt procedure for copper nitrate and copper sulphateDokument8 Seitensalt procedure for copper nitrate and copper sulphateNeelavathy PalaniappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confirmatory Test For CationsDokument21 SeitenConfirmatory Test For CationsEsther RandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExperimentDokument7 SeitenExperimenttedfsx256Noch keine Bewertungen
- Downloading File:salt Analysis - 2024 - 11 - 12Dokument3 SeitenDownloading File:salt Analysis - 2024 - 11 - 12Siddhi TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem27 Lab Results Post Lab E 1-3 ToolsDokument101 SeitenChem27 Lab Results Post Lab E 1-3 ToolsAngelica Camille B. AbaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDokument14 SeitenChemistry Investigatory ProjectV P SomeshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Purification Experiment Dissolved OxygenDokument2 SeitenWater Purification Experiment Dissolved OxygenJunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanoparticle LabDokument12 SeitenNanoparticle Labglen-576661Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blast furnace burden calculation methods and parametersDokument2 SeitenBlast furnace burden calculation methods and parametersJaymart Hernandez Mojica75% (4)
- List of New Arrival Books in Applied MechanicsDokument69 SeitenList of New Arrival Books in Applied MechanicsKESHAV SINGHALNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM5241 Literature Review Project TopicsDokument3 SeitenCM5241 Literature Review Project TopicsCheryldine LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- LPG PropertiesDokument2 SeitenLPG Propertiesvvk557Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radioisotopes in Smoke AlarmsDokument12 SeitenRadioisotopes in Smoke AlarmsTravleIceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vapor Phase Soldering TechniqueDokument5 SeitenVapor Phase Soldering TechniquealisakeerpkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical and structural defences in sea pansiesDokument9 SeitenChemical and structural defences in sea pansiesEtiene ClavicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast-Drying Hydroxy Acrylic Resin for Industrial CoatingsDokument2 SeitenFast-Drying Hydroxy Acrylic Resin for Industrial CoatingsFadi MagdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science ReportDokument9 SeitenPhysical Science ReportRoschelle ValleNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEST-1 Liquid Solution 06.04.2020Dokument4 SeitenTEST-1 Liquid Solution 06.04.2020tarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find Density, Mass or Volume from Given ValuesDokument1 SeiteFind Density, Mass or Volume from Given ValuesDaniel Dube100% (1)
- Migration From MAterials in Contact With Food StuffsDokument32 SeitenMigration From MAterials in Contact With Food Stuffsmohd shahrukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scince (Assement-1)Dokument4 SeitenScince (Assement-1)ARAF ABDULLAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover Page: Liquids and SolidsDokument20 SeitenCover Page: Liquids and SolidsCHELSEA NEUMANNNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Scalable Analytical Models For Heap Leaching PDFDokument6 SeitenOn Scalable Analytical Models For Heap Leaching PDFInfernuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capillary Flow Technology Solves Difficult GC Problems and Enables New CapabilitiesDokument28 SeitenCapillary Flow Technology Solves Difficult GC Problems and Enables New CapabilitiesTho AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus of Chemistry H NEP 96 105 1Dokument10 SeitenSyllabus of Chemistry H NEP 96 105 1Vijay Kumar VishvakarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batch ReactorDokument4 SeitenBatch ReactorHarini BugattiveyronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Orbital Theory Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument3 SeitenMolecular Orbital Theory Multiple Choice QuestionsRasel Islam100% (3)
- BS en 12449 2016Dokument46 SeitenBS en 12449 2016engr.sshoaibrazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.0 Corrosive Material IndexDokument66 Seiten9.0 Corrosive Material IndexMaria Laura PonceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of Adherence of Porcelain Enamels To MetalsDokument22 SeitenNature of Adherence of Porcelain Enamels To MetalsFernando BarreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making A Standrad SolutionDokument2 SeitenMaking A Standrad SolutionFaridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pogil Photosynthesis and Respiration-SDokument6 SeitenPogil Photosynthesis and Respiration-Sapi-2623786400% (1)
- LG200-FRF Integrated Temperature TransmitterDokument12 SeitenLG200-FRF Integrated Temperature TransmitterYounes El GhandouriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weathering of RocksDokument2 SeitenWeathering of Rocksvee propagandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iyr Phy em 2marksDokument6 SeitenIyr Phy em 2marksBYREDDY 4567Noch keine Bewertungen