Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Me To Logy 1
Hochgeladen von
krisbhaskar22Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Me To Logy 1
Hochgeladen von
krisbhaskar22Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Metrology and Quality Control
Experiment No. 1
Experiment No. 1
1.0 TITLE:
Study of basic measuring instruments (surface plate, angle plate, v-block, spirit level, combination set, straight edge, feeler gauge, screw pitch gauge, radius gauge)
2.0
PRIOR CONCEPT:
1. 2. 3. Principles of linear measurement Methods of measurement Basic units of measurement
3.0
NEW CONCEPT:
Surface plate, angle plate, v-block, spirit level, combination set, straight edge, feeler gauge, screw pitch gauge, radius gauge. 4.1 Proposition: Surface plate, angle plate, v-block, spirit level, combination set, straight edge, feeler gauge, screw pitch gauge, radius gauge are basic instruments used for engineering measurements. 4.2 Concept structure:
4.0
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
After the study of all the basic instruments the students will acquire
4.1 Intellectual skills
Understand the construction and use of the instruments. Select the appropriate instrument for the given task of measurement.
4.2 Motor skill
Manipulate different basic measuring instruments.
5.0
APPARATUS:
Instruments for use: 1. Surface plate, angle plate, v-block, spirit level, combination set, straight edge, feeler gauge, screw pitch gauge, radius gauge 2. At least 4-6 industrial jobs.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Experiment No. 1
Metrology and Quality Control
6.0
PROCEDURE:
6.1 Brief theory:
1.
Surface Plate:
Surface plates are mostly rectangular having 4:3 length to width ratio. These plates are rigid in design & generally ribbed at the bottom to carry heavy load without deflection. The top surface of the plate is scraped to true flatness. For big surface plates, four leveling screws are provided for adjusting their top surface truly horizontal. The standard available sizes of the plates vary from 100 x 100 mm to 2000 x 1000 mm in about 13 ranges. The four edges of the plates are finished, straight & are square to each other. According to IS-2285-1963, the CI surface plates are classified into two grades as GRADE I & GRADE II. Surface plate is used to provide datum or a reference surface for measurement in workshop & laboratories. It is also used to check flatness of any surface.
Fig. 1.1 SURFACE PLATE
2.
Angle plate:
The two working surfaces of the angle plate are truly perpendicular to each other & these surfaces are scraped. Generally, no sharp edges are allowed in the plate. They are used along with surface plate in workshop & laboratories for measurement. Angle plates are manufactured from cast iron and cast steel. The angle plates are available in two grades depending upon the accuracy (IS 2554 1963). Grade I: either grinding or hand scraping operation finishes all exterior & interior faces and edges. Grade II: planning or milling operations finishes all exterior faces.
Fig. 1.2 ANGLE PLATE
3.
V-block:
V-block is a supporting device for cylindrical work-pieces for marking center accurately and for checking out of roundness. The angle of V in V-block is 90 degree. All the working surfaces of the V-block are polished. Clamps are also provided for holding round bars. According to IS-2949-1964, V-blocks are available in two grades, Grade A & Grade B. While using V-block, it is essential that the cylindrical work piece should rest firmly on the
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Metrology and Quality Control
Experiment No. 1
slides of the vee & not on the edges of the vee.
Fig. 1.3 V-BLOCK
4.
Spirit level:
Spirit level consists of a sealed glass tube mounted on a base. The inside surface of the tube is ground to a convex barrel shape having large radius. A scale is engraved on the glass at the top of the tube. The tube is nearly filled with Ether or Alcohol except a small air or vapor bubble. The bubble always tries to remain at the highest point of the tube. If the base is placed on horizontal surface, then the bubble rests at the center of the scale. If the spirit level is tilted through small angle, the bubble moves & tries to remain at the highest point of the tube. They are used for leveling of machines, for measuring small angle or inclination and for checking straightness & flatness of surface.
5.
Combination set:
The combination set consists of a scale, square head, protractor head, center head and spirit level. Groove is made along the length of the scale. Square head can slide in this groove. It can be locked at any place by a locking nut & bolt. One surface of square head is always perpendicular to the scale. The square head consist of a spirit level for checking parallelism. The square head can be used for height & depth measurements. The center head attachment with scale is used to locate the center of a cylindrical bar. The protractor head consists of a semi-circular disc graduated from 0-90 degree on either side of center. Correct angle can be found out with the help of protractor. Combination set is used in workshops for marking centers, checking squareness and angular measurements.
FIG. 1.4 COMBINATION SET
6.
Straight Edge:
Straight edge is rectangular or I shaped in section with beveled edge. Steel straight edges are available up to 2 meter length & CI straight edges are available up to 3 meter length & are widely used for testing machine tool slide ways. It is used in conjunction with surface plate & spirit level for measurement of straightness and flatness of parts. For checking the straightness of the part, the straight edge is placed along the full length of the surface against the bright light. The absence of the light between straight & surface indicates the straightness of the element. Similarly the flatness of the surface can be tested by placing the straight edge in different directions at different places on the surface. By using
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Experiment No. 1
Metrology and Quality Control
Prussian blue & straight edge, the irregularities on the surface can also be found out. According to IS-2220-1962, straight edges are provided into two grades. Grade A for inspection purpose Grade B for workshop purpose Stepwise procedure: 1. Put the straight edge on surface under test 2. Observe the gap between the straight edge and surface under test 3. If there is no gap, the surface is straight.
7.
Feeler Gauge:
Feeler gauge is a narrow strip of steel sheet made up of required thickness. The complete set consists of number of gauging blades of different thickness. Its working is based on the sense of feel & hence it is called as feeler gauge. If necessary, two blades can be joined together to check dimensions. They are available from 0.03 to 1 mm size. Each blade is permanently marked with the nominal thickness & grade. It is used to measure the gap between two parallel flat faces, to measure clearance between piston & cylinder, spark plug gap and setting tappet clearance. Stepwise procedure: 1. Take the job to measure the gap 2. By trial & error method insert the leaf of feeler gauge in the gap. The leaf of feeler gauge that matches exactly with the gap is the gap distance. The dimension is written on each leaf of feeler gauge.
8.
Screw pitch gauge:
In this gauge, one edge of the blade is notched to various pitches & contours of specific threads. The blades are stamped with the pitch size. These gauges are available for metric, British and American form of threads. By matching these gauges with the job to be measured, the pitch of the job can be found easily. Stepwise procedure: 1. Take the threaded job to measure the pitch. 2. By trial and error method match the leaf of pitch screw gauge with the threads. 3. The leaf that exactly matches with the thread form gives the pitch of the thread, which is engraved on the leaf of the gauge.
Fig 1.6 PITCH SCREW GAUGE 4
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Metrology and Quality Control
Experiment No. 1
9.
Radius gauge:
Radius gauge is used for determining radius of a fillet. Radius gauge consist of set of blades on each of which the corresponding radius is marked. By placing the correct gauge & by observing the light source with eyes the correct radius can be checked. Stepwise procedure: 1. Take the job to measure the radius. 2. By trial and error method match one of the leaves of the radius gauge with the job radius. 3. The leaf that matches exactly with the radius of the job gives the radius of the job that is engraved on the leaf of the gauge.
7.0
Questions: (Attempt 3-5 questions as directed by teacher)
1. Write at least two industrial applications of following instruments. i. Feeler gauge: ii. Screw pitch gauge: iii. Radius gauge: iv. V-block: v. Surface plate: Measure the gap of a spark plug using the available set of feeler gauges. Measure the pitch of at least two threaded components by using the available set of screw pitch gauge. Measure the fillet radius of a given component using available set of radius gauges. State the precaution to be taken while using V- block. Give the sizes of the blades in the recommended set of Indian Standard thickness gauge. State reasons for a. Ribs provided under the surface of the surface plate. b. Artificial aging of the surface plate. c. Slot provided along the sides of the V-block. d. Leveling of the surface plate before measurement. e. Inside surface of the spirit level glass tube ground to a convex form with a large radius. Space for writing answers
2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Experiment No. 1
Metrology and Quality Control
Space for writing answers
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- HaiDokument1 SeiteHaikrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBCHGDCBCBCDokument16 SeitenCBCHGDCBCBCkrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Text DocumentDokument2 SeitenNew Text Documentkrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Text DocumentDokument2 SeitenNew Text Documentkrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- GKDokument5 SeitenGKkrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of The Nonlinear Vibrations of Unsymmetrically Laminated Composite BeamsDokument9 SeitenAnalysis of The Nonlinear Vibrations of Unsymmetrically Laminated Composite Beamskrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proposal Engineering Colleges 20112013Dokument22 SeitenProposal Engineering Colleges 20112013krisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- FORM6Dokument9 SeitenFORM6syampnaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Milling MachineDokument4 SeitenMini Milling Machinekrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- SurendraDokument3 SeitenSurendrakrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- FORM6Dokument9 SeitenFORM6syampnaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Cutting TheoryDokument40 SeitenMetal Cutting Theorykrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- FEM in Two-Dimension: Strain Energy DensityDokument14 SeitenFEM in Two-Dimension: Strain Energy DensityBharathi RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAP Proposed Course Structure of Metallurgical EngineeringDokument7 SeitenDAP Proposed Course Structure of Metallurgical EngineeringKrishna ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- At2252 QBDokument6 SeitenAt2252 QBkrisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
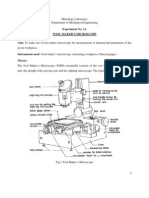
- Experiment No. 1A Tool Maker'S MicroscopeDokument4 SeitenExperiment No. 1A Tool Maker'S MicroscopePraveen KumaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Item 0Dokument1 SeiteItem 0krisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Funcionamiento Motor StirlingDokument4 SeitenFuncionamiento Motor StirlingManuel QueirozNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGA Manual NGA2000 NDIR SW3-3 199908Dokument106 SeitenPGA Manual NGA2000 NDIR SW3-3 199908krisbhaskar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- JD CTM4 PreviewDokument41 SeitenJD CTM4 PreviewEdinael Ramirez hernandez50% (2)
- CIP Handbook v1 PDFDokument84 SeitenCIP Handbook v1 PDFThiagoSilvaOliver100% (4)
- Riv-Ti®: Blind Rivet NutsDokument40 SeitenRiv-Ti®: Blind Rivet NutsKrishna PrasathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel ConnectionsDokument56 SeitenSteel ConnectionsTejas Patel94% (16)
- 721U0201 Rev 03 - Micromate Operator ManualDokument142 Seiten721U0201 Rev 03 - Micromate Operator ManualGerardoSierraTrejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storage Options 53294 8CH DVR Instruction Manual v.1.7Dokument60 SeitenStorage Options 53294 8CH DVR Instruction Manual v.1.7Fernando Ulises Alvarez RecinosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defense Equipment: Track Shoe Assembly and Spare Parts For Combat VehiclesDokument27 SeitenDefense Equipment: Track Shoe Assembly and Spare Parts For Combat VehiclesEnrique Gomez100% (1)
- APRILIA Workshop Manual - RS50Dokument200 SeitenAPRILIA Workshop Manual - RS50YZFMARC787Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piaggio Liberty 100 Indonesia MY 2011 (EN)Dokument179 SeitenPiaggio Liberty 100 Indonesia MY 2011 (EN)Manualles67% (3)
- Joint Evaluation Report: Roseburg Forest Products CoDokument7 SeitenJoint Evaluation Report: Roseburg Forest Products ComurdicksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making and Using C-Ring Stress-Corrosion Test Specimens: Standard Practice ForDokument7 SeitenMaking and Using C-Ring Stress-Corrosion Test Specimens: Standard Practice Forvuqar0979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Motors MAN Part Books PDFDokument158 SeitenMotors MAN Part Books PDFAli Gujir100% (3)
- Iimplant AbutmentsDokument8 SeitenIimplant AbutmentsDr. AtheerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access Covers Grates & AccessoriesDokument60 SeitenAccess Covers Grates & AccessoriesBarrasons Engineers Team100% (1)
- Detailed Estimate Velliyankallu ParkDokument25 SeitenDetailed Estimate Velliyankallu Parklifelinegroups nilNoch keine Bewertungen
- F 670 - 87 R94 - Rjy3mc1sruq - PDFDokument5 SeitenF 670 - 87 R94 - Rjy3mc1sruq - PDFRománBarciaVazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weedeater Mower Ayp Model 259720 Parts ListDokument24 SeitenWeedeater Mower Ayp Model 259720 Parts ListJessica BarnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wellsaw No. 8 Parts ListDokument13 SeitenWellsaw No. 8 Parts ListOliver CollectorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Construction of Oil Expeller Press With Structural Analysis of Screw With AnsysDokument6 SeitenDesign and Construction of Oil Expeller Press With Structural Analysis of Screw With AnsysShahzad AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT6642TXT MT8044XT 805931D PDFDokument222 SeitenMT6642TXT MT8044XT 805931D PDFluis tocoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line VTI: Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsDokument11 SeitenLine VTI: Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsStaman1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Operation ManualDokument77 SeitenPlant Operation ManualMahmoud Abd ElhamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulating Kit - Product BrochureDokument4 SeitenInsulating Kit - Product BrochureSalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LGA1150 GuideDokument36 SeitenLGA1150 GuideGabriel SmolnyckiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil - STD - 2036Dokument79 SeitenMil - STD - 2036Rizky NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elna 792DDokument53 SeitenElna 792DRepuestos PartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FORGED - Gate, Globe & Check Valve Manual - Xomox SanmarDokument20 SeitenFORGED - Gate, Globe & Check Valve Manual - Xomox SanmarSaibabu SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Preload On Natural Frequency of Bolted Joint Under Impact LoadingDokument4 SeitenEffect of Preload On Natural Frequency of Bolted Joint Under Impact LoadingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Fibro Katalog (Stamp Tool)Dokument18 SeitenFibro Katalog (Stamp Tool)Elvis SakicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kubota KX057-4 Service ManualDokument615 SeitenKubota KX057-4 Service ManualJames Hoynacki100% (1)