Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Schemdi Nca
Hochgeladen von
Eiram Esoj SalcedoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Schemdi Nca
Hochgeladen von
Eiram Esoj SalcedoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
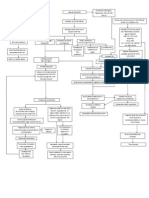
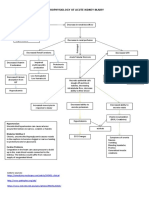
Chronically high levels of glucose and free fatty acids Beta cell (in islet of langerhans) desensitization Insulin
resistance Increased beta cell secretion of insulin In time however, the insulin declines because of increasing beta cell dysfunction Impaired ability of the body to metabolize glucose Chronic elevation blood glucose level Tendency of kidney to excrete excess blood glucose Osmotic diuresis DM TYPE 2 Cortisol secretion due to decreased glucose utilization Glucocorticoid hormones stimulate gluconeogenesis glycoprotein cell wall deposits Production of excess glucagon Production of glucose from protein and fat stores Excess loss of fluid Wasting of lean body mass
Increased glucose level in blood (ideal for bacterial growth)
Decreased erythropoietin production (in nephropathy)
Altered balance between cell destruction and regeneration Disruption of normal blood composition Decreased erythrocyte number volume Decreased circulating leukocytes Impaired immune function Opportunistic Bacteria enter into the lower airway Activation of inflammatory reaction Release of cytokines WBC, mostly neutrophils, migrate into the site of infection Dead bacteria and macrophages or phagocytes form exudates exudates fill the normally air-filled spaces consolidation of the lobe PNEUMONIA Decreased production of thrombopoeitin Impaired coagulation
Increased intracellular concentration of glucose Increased formation of glycoproteins in the basement membrane of small blood vessels and capillaries Structural defects in basement membrane and microcirculation Vascular complication
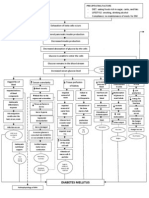
Small vessel disease
Diabetic neuropathy
formation of abnormal blood sugar glycoproteins damage on the glomeruli NEPHROSCLEROSIS decrease GFR
Diabetic retinopathy
alteration in regulatory process Stressed kidney filtration mechanism
activation of renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Renin will be secreted by the kidney alteration in regulatory process angiotensin I production of the adrenal cortex Increased pressure of blood vessels conversion in the lungs by ACE I Angiotensin II Increase in Na and H2O retention RENAL HYPERTENSION
+
Blood protein leak in into the urine Thickening in the renal arteries Diabetic nephropathy Progression of irreversible renal damage Retention of uremic waste products CHRONIC RENAL DISEASE Impaired excretion of metabolic wastes
decreased erythropoietin production decreased red blood cell production ANEMIA
Accumulation of substances into the bloodstream
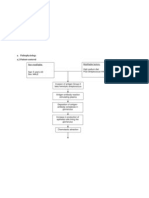
Medication
Drug Induced Hypoglycemia
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Uworld NotesDokument7 SeitenUworld NotesJorge L CastelarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satir Family Therapy: Instructor's ManualDokument50 SeitenSatir Family Therapy: Instructor's ManualDragana ĆorićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromo TherapyDokument11 SeitenChromo TherapyNirav Hiingu50% (2)
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDokument16 SeitenDiabetic Ketoacidosisjoyshe111100% (2)
- BL42-Chi Nei Tsang III (ID-PDF) 12-17-15 PDFDokument90 SeitenBL42-Chi Nei Tsang III (ID-PDF) 12-17-15 PDFJosé Tao75% (8)
- Chronic Renal FailureDokument54 SeitenChronic Renal FailureAkia Cayasan BayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topnotch Pharma Supertable JAN 2016Dokument166 SeitenTopnotch Pharma Supertable JAN 2016Dar AD50% (2)
- UWorld Cards July 14Dokument7 SeitenUWorld Cards July 14smian08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ingredients:: The Lemonade Diet (Adapted From)Dokument2 SeitenIngredients:: The Lemonade Diet (Adapted From)test100% (2)
- Sample of Psychological ReportDokument4 SeitenSample of Psychological ReportRochelle Joyce Olmilla Bersamin67% (3)
- Flat Foot SurgeryDokument5 SeitenFlat Foot SurgeryManoj KandoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of DMDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathogenesis of Micro and Macrovascular Complications of DiabetesDokument4 SeitenPathogenesis of Micro and Macrovascular Complications of DiabetesFrancesca LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusDokument3 SeitenPa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusPong's Teodoro SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of Diabetes An Overview of The PathophysiologyDokument58 SeitenComplications of Diabetes An Overview of The Pathophysiologyrachel0301Noch keine Bewertungen
- CKD PathoDokument5 SeitenCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute and Chronic DM ComplicationsDokument29 SeitenAcute and Chronic DM ComplicationsJennicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of DMDokument5 SeitenPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDokument6 SeitenPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresNoch keine Bewertungen
- GlomerulonephritisDokument59 SeitenGlomerulonephritistressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDokument9 SeitenNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsKimberly Bomediano100% (1)
- CKD - For Concept MappingDokument7 SeitenCKD - For Concept MappingKennette Lim0% (1)
- Nephrotic SyndromeDokument65 SeitenNephrotic SyndromemejulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument37 SeitenCase StudyAnonymous t78m8ku100% (1)
- End-Stage Renal DiseaseDokument3 SeitenEnd-Stage Renal DiseaseAkira Pongchad B100% (1)
- Schematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM FootDokument8 SeitenSchematic Diagram of CKD Sec. To DM Nephropathy, DM Type 2, DM Footbeuwolfagate50% (2)
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenPa Tho PhysiologynhiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology Non-Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsErrol B. TiozonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemical Impact of Diabetic Complications.Dokument22 SeitenBiochemical Impact of Diabetic Complications.nomi kingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDokument1 SeiteNarrative Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeNicaMariannePañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureDokument40 SeitenPresented By: Sonia Dagar: Renal FailureRavanshi ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperglycemic Emergencies 2101Dokument47 SeitenHyperglycemic Emergencies 2101IndahfitriaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDokument11 SeitenPa Tho PhysiologyJonathan CuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho RMCDokument2 SeitenPatho RMCLady Janine de GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute GlomerulonephritisDokument1 SeitePa Tho Physiology of Acute GlomerulonephritismatahfakahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic RenalDokument5 SeitenChronic Renaljazzy penzNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShockDokument53 SeitenShockYazn Amjad Mahmoud ElayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- crf03 1Dokument16 Seitencrf03 1Aswin DamodaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokument36 SeitenChronic Kidney Diseasejabir100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewDokument5 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewAnonymous uziTjed5j100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CKDDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology CKDSugar Capule - ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathological Changes of DM - 2023Dokument53 SeitenPathological Changes of DM - 2023Visura PrabodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Levels of Cholesterol Are Decreased in Hyperthyroidism and Increased in HypothyroidismDokument6 SeitenBlood Levels of Cholesterol Are Decreased in Hyperthyroidism and Increased in HypothyroidismSimina ÎntunericNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiopathology 8Dokument4 SeitenPhysiopathology 8I FNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Med Ward (WK - 1) PathophysiologyDokument3 Seiten6 Med Ward (WK - 1) PathophysiologyZaijean Kate Dianne LigutomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 15 - Kidney ContinuationDokument13 SeitenLec 15 - Kidney ContinuationrajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- MNT Penyakit GinjalDokument41 SeitenMNT Penyakit GinjalNurfitriana DwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hal 106-108Dokument6 SeitenHal 106-108Dirgantari PademmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Mellitus Study GuideDokument5 SeitenDiabetes Mellitus Study Guiderr5633Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec6.nephrotic SyndromeDokument24 SeitenLec6.nephrotic SyndromeMAD Bl00DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal SystemDokument20 SeitenRenal SystemRahul DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreas Aug 4Dokument53 SeitenPancreas Aug 4Dr.Gomathi sivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDanielle Marie SamblacenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Conference 1 Renal PhysiologyDokument24 SeitenCase Conference 1 Renal PhysiologyFrances GrefalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism Study NotesDokument24 SeitenMetabolism Study Notesxxx xNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jawaban PertanyaanDokument13 SeitenJawaban PertanyaantsruliantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram and NarrativeDokument15 SeitenPathophysiology Schematic Diagram and NarrativeKathrina CraveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology DM2, HACVDDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology DM2, HACVDmitzi019Noch keine Bewertungen
- CRFDokument50 SeitenCRFKevin MontoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A Great E-Guide To CKDDokument15 SeitenChronic Kidney Disease: A Great E-Guide To CKDshirley_ling_15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Notes - EndocrineDokument6 SeitenAdrenal Notes - Endocrinekep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of Diabetes MellitusDokument49 SeitenComplications of Diabetes MellitusJennifer WootenNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMD-4 Diagnosis and Dental Managment of Diabetes Mellitus Lecture HandoutDokument13 SeitenOMD-4 Diagnosis and Dental Managment of Diabetes Mellitus Lecture Handouthananalkadi94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoVon EverandFast Facts: Deficiencia de piruvato quinasa para pacientes y familiares: Una enfermedad genética rara que afecta a los glóbulos rojos Información + Asumir el control = El mejor resultadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Facts: Le déficit en pyruvate kinase pour les patients et les accompagnants: Une maladie génétique rare qui affecte les globules rouges Informations + Prise de contrôle = Meilleur résultatVon EverandFast Facts: Le déficit en pyruvate kinase pour les patients et les accompagnants: Une maladie génétique rare qui affecte les globules rouges Informations + Prise de contrôle = Meilleur résultatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0009 Rheumatology Notes 2015 PDFDokument56 Seiten0009 Rheumatology Notes 2015 PDFMuhammad HaneefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluoroquinolones Full ListDokument2 SeitenFluoroquinolones Full ListAvelox FloxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Learning-Pulmo Hour-Tantoco, Justin LareeDokument1 SeiteSummary of Learning-Pulmo Hour-Tantoco, Justin LareeJustin TantocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuromuscular Disorders: Peripheral Nervous System/ Myelopathy Case SessionDokument3 SeitenNeuromuscular Disorders: Peripheral Nervous System/ Myelopathy Case Sessionamitm2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument4 SeitenDaftar PustakaInilah Aqku Appha AdhanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patho SGDDokument2 SeitenPatho SGDAnna Patricia DugayNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Hunger Web QuestDokument5 SeitenWorld Hunger Web Questapi-313403351Noch keine Bewertungen
- s13014 015 0495 4Dokument6 Seitens13014 015 0495 4produxing 101Noch keine Bewertungen
- PRC PT Licensure Exam February 2012 List of PassersDokument5 SeitenPRC PT Licensure Exam February 2012 List of PassersPJHGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Megan McCarthy's ResumeDokument2 SeitenMegan McCarthy's ResumeMegan McCarthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care ManagementDokument40 SeitenNursing Care ManagementɱΘΟθ CuasitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConstipationDokument11 SeitenConstipationAsma SikanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azoospermia Guidelines PDFDokument7 SeitenAzoospermia Guidelines PDFafifberlianNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrochuresDokument6 SeitenBrochuresInforkomm Media Services LTDNoch keine Bewertungen
- DiabetesDokument515 SeitenDiabetesPaola Rivera DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeaslesDokument2 SeitenMeaslesHari SusetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expression of Interest Build For Cancer Care Centre - 2Dokument5 SeitenExpression of Interest Build For Cancer Care Centre - 2arakbaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- James Brooks BME 281 Presentation 1Dokument12 SeitenJames Brooks BME 281 Presentation 1Sumanta BhattacharyyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume 12, Issue 7, June 19, 2011Dokument2 SeitenVolume 12, Issue 7, June 19, 2011Rolland J. BouchardNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1: Nursing Interventions To Promote Healthy Physiologic Responses: Comfort and PainDokument14 SeitenUNIT 1: Nursing Interventions To Promote Healthy Physiologic Responses: Comfort and Painlouie tibarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is TAHbsoDokument2 SeitenWhat Is TAHbsomiskidd100% (2)
- Jurnal Gastritis PDFDokument6 SeitenJurnal Gastritis PDFSholeh Hasan87Noch keine Bewertungen