Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pressure Drop Within Ducts
Hochgeladen von
Manoj ThakurCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pressure Drop Within Ducts
Hochgeladen von
Manoj ThakurCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
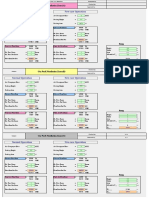
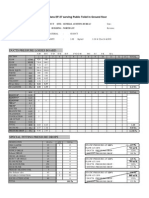
Cyan cells are input cells Yellow cells are output cells
Symbol Vh V g Q Qn Qg D A VP
n
Term Velocity head Gas Velocity in duct Gravitational Acceleration Volume of gas Normal Volume of gas Normal mass of gas Duct Diameter Cross Sectional Area Velocity Pressure Actual Air Density at different temp. and pressure Air Density at NTP Gas Temperature Barometric Pressure Altitude of place in metres Suction Pressure
Formula V/2g
Value 8.384575 12.81943 9.8 146.9405 80.15833 103.4043 3.82 11.46233 5.900353 0.703715 1.29 190 9561.72 650 250
Unit m m/sec m/sec m/sec Nm/sec kg/sec m m mmwg kg/m kg/m deg C mmwg m mmwg
9.868363 m/sec
528985.8 288570 372255.3 2.508244
m/h Nm/h kg/h m
D/4 Vh x n x 273/(273+t) x Pa/10335
5.2 mmwg
t Pa H PS
10335 x (1-0.0000226 x H)^5.255
0.925179
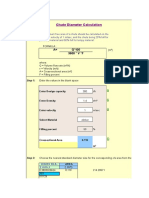
Friction Loss in Straight Duct V Velocity in ducts f coefficient of friction for steel L Length of ducts including developed bends d diameter of duct v specific volume of air, corrected for altitude and temp T Absolute temp of air in Kelvin Floss Friction loss in straight round ducts
Dh p
Hydraulic Diameter wetted perimeter of the duct
13.866 x V x L x f / (d x v x T) (f L V/2gd)x f(L/Dh) (V/2g) 4A/p D
12.81943 0.018 16 3.82 1.42103 463 0.261116 0.444843 0.632136 3.82 12.00244
m/sec m m m3/kg kelvin mmwg mmwg mmwg
2513.318037 0.632135513 4.188481675
Friction Loss in Bends V Velocity in ducts K1 Coefficient of friction for bends (from figure) Floss Friction loss in pipe bends
(K1 x V/2 x g) x
12.81943 m/sec 1.08 6.372381 mmwg 9.055341
Lift Loss L Wm Wa K
Vertical Lift Weight of material being lifted Weight of air/gas lifting the material Constant = density of water/density of air (Operating) Density of water = 1 Density of air at NTP = 1.29 kg/m3 K at NTP = 1/1.29 = 0.775 Lift Loss (W m/W a) RxL/K
10 m 2 kg 2 1
R Lloss
1 10 mmwg
Acceleration Loss m1 mass of material m2 mass of air M m1 + m2 V Final velocity af air and material Wm weight of material Wa weight of air R Aloss Acceleration Loss
18 m1 x g m2 x g (W m/W a) R x V/2g
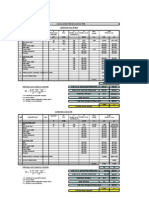
Lift Loss Acceleration Loss Frcition Loss
#DIV/0! #DIV/0! mmwg
12.00434 m/sec
228064 m3/h 124412.4758 Nm/h 160492.0938 kg/h
137.5977 m/sec
181.2576112 8.384575203
Losses in ducts
When material is lifted from one level to When material is introduced in a ducting and attains velocity of Due to flow of gases (also dust laden)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Mechanical Ventilation Calculation SpreadsheetDokument2 SeitenMechanical Ventilation Calculation SpreadsheetDarren Leong67% (3)
- Blower CalculationDokument1 SeiteBlower Calculationvijayamalraj67% (3)
- Chilled Water Pump Head Calculation-Port-214fDokument6 SeitenChilled Water Pump Head Calculation-Port-214fhasanadel88100% (2)
- Dehumidifier CalculationDokument22 SeitenDehumidifier CalculationamitbslpawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fan Static Pressure CalculationDokument6 SeitenFan Static Pressure CalculationVõ Tấn Thùy100% (2)
- Heat Load Calculation SheetDokument1 SeiteHeat Load Calculation Sheetghazi4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Car Park VentilationDokument3 Seiten1-Car Park VentilationSaber Elkassas100% (3)
- Airslide Calculation Form Project: Department: Equipment NoDokument3 SeitenAirslide Calculation Form Project: Department: Equipment NoManoj Thakur0% (1)
- Chute Dia CalculationDokument5 SeitenChute Dia CalculationManoj Thakur100% (1)
- Pneumatic Conveyor Sizing CalculationsDokument3 SeitenPneumatic Conveyor Sizing Calculationsm_nassifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Air Pipe SizeDokument6 SeitenCalculation of Air Pipe SizePhyu Mar Thein Kyaw100% (1)
- Ventilation CalculationsDokument1 SeiteVentilation Calculationsdhanu_lagwankar75% (4)
- Calculation and Design of Packed Column For AcidDokument14 SeitenCalculation and Design of Packed Column For AcidDavid LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- BF3 Scrubber Column DiameterDokument21 SeitenBF3 Scrubber Column DiameterMuthuKumar Arunachalam0% (1)
- Pressure Drop Within DuctsDokument6 SeitenPressure Drop Within DuctskasvikrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sop For Fan SizingDokument3 SeitenSop For Fan SizingVeerabhadra Rao Korimilli100% (3)
- Cooling TowerDokument27 SeitenCooling Towerjogedhayal100% (1)
- Fans Static Head Calculation SheetDokument1 SeiteFans Static Head Calculation Sheethasanadel88Noch keine Bewertungen
- 35-Duct Weight Calculation SheetDokument11 Seiten35-Duct Weight Calculation SheetAnanth Ganesan100% (1)
- Fan Flow CalculatorDokument1 SeiteFan Flow CalculatorR P Naik100% (2)
- Dehumidifier Calculation 10Dokument2 SeitenDehumidifier Calculation 10amitbslpawar100% (1)
- Bag Filter Selector: Filter Type: C (For This Type of Filter Contact Area Genovese)Dokument8 SeitenBag Filter Selector: Filter Type: C (For This Type of Filter Contact Area Genovese)Ashish GulabaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressor Capacity CalculationDokument4 SeitenCompressor Capacity CalculationHoney Tiwari100% (1)
- Heat Load EstimationDokument5 SeitenHeat Load EstimationSultan FirassuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Pressure CalculationDokument1 SeiteStatic Pressure CalculationFadi Yasin100% (3)
- Bag Filter SpecificationsDokument2 SeitenBag Filter SpecificationsAdarsh PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic Conveying System Design Calculation: Input Parameters Unit ValueDokument6 SeitenPneumatic Conveying System Design Calculation: Input Parameters Unit ValueTECHCONS Consulting and Engineering Pvt Ltd0% (1)
- Ventilation Calculator ASHRAE 62 - 2 Existing HousesDokument23 SeitenVentilation Calculator ASHRAE 62 - 2 Existing HousesSharon Lambert67% (3)
- Mechanical Conveyors: 29 Materials HandlingDokument2 SeitenMechanical Conveyors: 29 Materials HandlingSMNCI Cadet EngineersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilation Fans All RevisedDokument6 SeitenVentilation Fans All RevisedBilal Hussein SousNoch keine Bewertungen
- 300 Lit Water Tanks Stem Heating CalculationDokument8 Seiten300 Lit Water Tanks Stem Heating CalculationEngFaisal AlraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations On An Adiabatic Continuous DryerDokument11 SeitenCalculations On An Adiabatic Continuous DryerCaleb Somai0% (1)
- Steam CalculationDokument27 SeitenSteam CalculationRAVI KUMAR CarpenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line SizingDokument2 SeitenLine SizingHarryBouterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 - Fresh Air Unit Esp CalculationDokument2 Seiten01 - Fresh Air Unit Esp Calculationmefaisal750% (1)
- Ductwork System Calculation Input Data Sheet: Fixture Library Fixture Type, C, and DP Input by UserDokument8 SeitenDuctwork System Calculation Input Data Sheet: Fixture Library Fixture Type, C, and DP Input by UserJaspal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilation CalculationDokument148 SeitenVentilation CalculationFarid Sedeky100% (2)
- Bag Filter CalculationDokument2 SeitenBag Filter Calculationjenifferrayen71% (7)
- Fan Capacity CalculationDokument6 SeitenFan Capacity CalculationAu Tagolimot70% (10)
- Design Conditions Datasheet: Unit Tag Qty Model No Net Cooling Capacity (Ton.r) Nominal Voltage Refrigerant TypeDokument2 SeitenDesign Conditions Datasheet: Unit Tag Qty Model No Net Cooling Capacity (Ton.r) Nominal Voltage Refrigerant TypeFernando CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculat Friction LossDokument2 SeitenCalculat Friction LosssenghyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bag Filter Calculation1234567 IPDokument24 SeitenBag Filter Calculation1234567 IPsujith kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static Pressure FansDokument35 SeitenStatic Pressure FansarifkhadeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Duct CalculatorDokument1 SeiteAir Duct Calculatormanikantan100% (2)
- Heat Transfer Calculations Evaporator #1 Evaporator #2Dokument6 SeitenHeat Transfer Calculations Evaporator #1 Evaporator #2Joshua JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Fire Calc F Mowrer Templates REV 2.0Dokument39 SeitenExcel Fire Calc F Mowrer Templates REV 2.0Argile-assholeNoch keine Bewertungen
- StaticCalc Duct Sizing CalculatorDokument14 SeitenStaticCalc Duct Sizing CalculatorSteve WanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Car Park Extract CalculationDokument5 SeitenCar Park Extract CalculationShivraj SawantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Friction Loss CalculationDokument5 SeitenPipe Friction Loss Calculationapi-26699613100% (6)
- Pump and Line Sizing CalcDokument5 SeitenPump and Line Sizing CalcMuthuKumar ArunachalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilation System CalculationsDokument108 SeitenVentilation System Calculationsscribd99190Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ducts Pressure Losses Board: Carpark Souq Waqif Ahu - A Basement-1Dokument2 SeitenDucts Pressure Losses Board: Carpark Souq Waqif Ahu - A Basement-1Karthy GanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basin Volume CalculationDokument4 SeitenBasin Volume Calculationakill3r100% (3)
- Static Calculation For FansDokument4 SeitenStatic Calculation For FansBadrul HishamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit ConversionsDokument2 SeitenUnit Conversionsangry_granNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalculationDokument8 SeitenCalculationmahaveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air-Cooled Heat Exchanger Specification SheetDokument4 SeitenAir-Cooled Heat Exchanger Specification SheetPanca KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A - Conversion FactorsDokument14 SeitenA - Conversion Factorssaeed65Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design CalculationsDokument43 SeitenDesign CalculationsPravin Nair90% (10)
- TANK Module: Sample PrintoutDokument17 SeitenTANK Module: Sample PrintoutAnonymous J1vjrU2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Clinker Flow Additive Flow Gypsum Flow Tailing Flow Fresh FeedDokument140 SeitenFlow Clinker Flow Additive Flow Gypsum Flow Tailing Flow Fresh FeedRaden Ayu Wilda AnggrainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsDokument6 SeitenQuantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary Unitshb360Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expansion ValuesDokument1 SeiteExpansion ValuesManoj ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rolled Steel Sections - Indian (Bis) (Refr. Hanbook For Structural Engineers Sp:6 (1) - 1964 Rolled Steel BeamsDokument1 SeiteRolled Steel Sections - Indian (Bis) (Refr. Hanbook For Structural Engineers Sp:6 (1) - 1964 Rolled Steel BeamsManoj ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expansion Joints Calculation For Thermal Expansion Vlaues Client Project Project No. Thermal ExpansionDokument1 SeiteExpansion Joints Calculation For Thermal Expansion Vlaues Client Project Project No. Thermal ExpansionManoj ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor Capacity Calculation Form: Remarks Selelct / Insert Values in Orange FieldDokument1 SeiteBelt Conveyor Capacity Calculation Form: Remarks Selelct / Insert Values in Orange FieldManoj ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Dedusting Pipe LayoutDokument4 SeitenImportance of Dedusting Pipe LayoutManoj ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAN HP CalculationDokument3 SeitenFAN HP CalculationManoj ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRAN PICE Development 1 1Dokument1 SeiteTRAN PICE Development 1 1mohdnazirNoch keine Bewertungen