Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cardiac Meds
Hochgeladen von
Johan BarriosOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cardiac Meds
Hochgeladen von
Johan BarriosCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
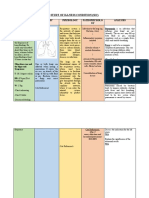
Nitroglycerin Beta-Adrenergic Blockers (Antagonist) Blockade of Beta1 receptors in the heart cause o Decreased heart rate o Decreased force
e of contraction o Decreased rate of AV conduction Naldolo (Corgard) Bradycardia (common), CHF, hypotension, depression, lethargy . fatigue Propanolo (Inderal) Metoprolol (Lopressor) Atenolol (Tenormin) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Evaluate for increase in CHF, or dysrhythmias involving heart block may decrease action of calcium channel blockers uses: angina, hypertension, and cardiac dysrhythmias teach client how to decrease effects of postural hypotension teach client to continue to take medication regardless of feeling better check pulse before administering if client has DM, monitor blood glucose levels carefully
CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS: Blockade of calcium channel receptors in the heart causes decreased cardiac contractility and a decreased rate of sinus and AV node conduction Diltiazem (Cardizem) Verapamil (Calan, Isopt) Nifedipine (Procardia) constipation, exacerbation, of CHF, hypotension, bradycardia, peripheral edema Reflex tachycardia, hypotension, dizziness, HA
1.USES- Chronic stable angina, hypertension, and supraventricular dysrhythmias 2. May intensify cardiosuppressant effects of beta blocker medication 3. Assess for bradycardia Nifedipine1.less likely to exacerbate preexisting cardiac conditions 2. Is not effective in treating dysrhythmias
ANTIDYSRHYTMIC MEDICATION: Decrease cardiac excitability; delay cardiac conduction either in the atrium or in the ventricle. Atropine is cardiac stimulant for bradycardia General Nursing Implications Assess client of changes in cardiac rhythm and impact on cardiac output Evaluate effect of medication on dysrhythmia and resulting effects on cardiac output Patient on cardiac monitor when given IV Atropine available for cardiac depression (bradycardia) All cardiac depressants are contraindicated in patients with sinus node or AV node block Digitalis will enhance cardiac depressant effects Closely monitor for dysrhytmias that are precipitated by the treatment All of these medications can make existing dysrhytmias worse and can create new ones RN or physician will administer IV medication. LPN may assist Medication Quinidine Sulfate (Quindex) Bretylium IV Amiodarone (Cardarone) PO, IV Lidocaine Hydrochloride (Xylocaine) Tocainide (Tonocard) Procainamide (Pronestyl) PO,IV Side effects Vertigo, N/V, and diarrhea, progressive AV block, cinchonism- tinnitus, visual problems HA Hypotension Hypotension, bradycardia Nursing Implications 1.Use: supraventricular dysrhythmias and to convert client to sinus rhythm Use: ventricular dysrhythmia that do not respond to other therapy 1. Asses for severe bradycardia 2. monitor for dyspnea, cough, and fever Use: ventricular dysrythmias Only use preparations labeled for IV use Use: to prevent/ control dysrhythmias 1.Uses: treatment of atrial and ventricular dysrhythmias 2.hypotension is not uncommon 3.Autoimmune problems Lupus symptoms
Drowsiness, confusion, seizures, severe depression of cardiac conduction Nausea, tremors N/V, blood dyscrasia, Hypotension
Propanolo Hydrochloride (Inderal) Atropine Sulfate IV, PO, SubQ, IM
Dry Mouth, blurred vision, dilated pupils
1. increased heart rate. Used to treat bradycardia that causes symptoms 2.carefully asses patients cardiac output in response to the bradycardic episode
Thrombolytic Medication: Bind to fibrin and initiate fibrinolysis to break up a clot. Convert circulating plasminogen to plasmin to begin fibrinolysis General Nursing Implications: Used to treat acute coronary thrombosis (MI) DVT, and massive pulmonary emboli Therapy started as soon as condition identified Follow bleeding precautions Administer by RN or Dr
Streptokinase (Streptase) IV Bleeding, Hypotension Alteplase (tPA, Activase) IV Tenectaplse (TNKase)
1.Moniotor for hypotension not related to bleeding 2.Monitor for development of intracranial bleeding 3. Contraindicated in client with HX of stroke or presence of internal bleeding
ANTIPLATELETS (PLATELET AGGREGATION INHIBITORS) Inhibit aggregation of and clumping of platelets which reduce risk of stroke, or MI or peripheral vascular occlusion in clients with peripheral vascular disease Clopidrogel (Plavix) PO Aspirin PO GI bleeding, dyspepsia, epistaxia, blood dyscrasia Irreversible suppression of platelets, GI hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke 1. May be taken with or without food 2. teach client to watch for bleeding problems 3. A low dose of aspirin (81 mg) is as effective as higher dose 4. take aspirin with food
CARDIAC GLYCOSIDE: INCREASE MYOCARIDAL CONTRACTILITY AND CARDIAC OUTPUT: DECREASES CONDUCTION OF IMPULSE THROUGH AV NODE Nursing Implications: take apical pulse before administering Digoxin (Lanoxin) PO, IV Anorexia, N/V, visual disturbances, fatigue, drug induced dysrhythmias 1.therapuetic plasma levels of Digoxin are 0.5- 2 ng/ml 2.First sign of toxicity is usually GI symptoms 3.Uses: Supraventricular tachycardia, CHF
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cardiac MedicationsDokument9 SeitenCardiac Medicationsnovikane100% (1)
- Anatomy of Pain Trigger Point Therapy For Exercise Professionals Exam Pack 0616Dokument42 SeitenAnatomy of Pain Trigger Point Therapy For Exercise Professionals Exam Pack 0616Dharmender Singh67% (3)
- Endocrine DisordersDokument106 SeitenEndocrine DisordersMansur MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pacemaker Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandPacemaker Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDokument3 SeitenPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure of Neonatal ResuscitationDokument6 SeitenProcedure of Neonatal ResuscitationNishaThakuri100% (2)
- Cardiac MedicationsDokument26 SeitenCardiac MedicationsAngie SaquingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesVon EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure ReportDokument6 SeitenCongestive Heart Failure ReportSunshine_Bacla_4275100% (1)
- Neuromuscular ImagingDokument432 SeitenNeuromuscular ImagingLeticiaElizabethEchevarria100% (2)
- CardiotonicsDokument21 SeitenCardiotonicsmohsen mirdamadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEBOSH IDIP IB NotesDokument46 SeitenNEBOSH IDIP IB NotesSuresh Babu100% (2)
- Hypertensiveemergencies RullDokument60 SeitenHypertensiveemergencies RullagustinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumothorax FinalDokument62 SeitenPneumothorax FinalmithramuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA 2 - CHN Review 50 Items PretestDokument10 SeitenCA 2 - CHN Review 50 Items PretestAlibasher Macalnas100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument7 SeitenDrug StudyAnn Therese C. GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Arrhythmic DrugsDokument91 SeitenAnti Arrhythmic DrugsAlex beharuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urologic Clinics of North AmericaDokument160 SeitenUrologic Clinics of North AmericaHaytham Ibrahim KamelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition 1Dokument5 SeitenNutrition 1Christine PunsalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas of Geriatric Dermatology 2013 - PDF - DR - Carson - VRGDokument334 SeitenAtlas of Geriatric Dermatology 2013 - PDF - DR - Carson - VRGANÔNIMONoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensive Drugs.Dokument35 SeitenAntihypertensive Drugs.Abdul WahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penatalaksanaan Penyulit Gagal JantungDokument17 SeitenPenatalaksanaan Penyulit Gagal JantungarumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio DrugsDokument68 SeitenCardio DrugsIconMaicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 6 Anti HypertensionDokument40 SeitenLecture 6 Anti HypertensionMNGS StudioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antianginal & Vasodilating Drugs: Mrs. Davis, MSN/RN 2020Dokument32 SeitenAntianginal & Vasodilating Drugs: Mrs. Davis, MSN/RN 2020HannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemDokument138 SeitenDrugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemSagun lohalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADHF Wecoc FinalDokument27 SeitenADHF Wecoc FinalNovrian Ali YlberNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiHypertensives (Autosaved)Dokument64 SeitenAntiHypertensives (Autosaved)UsamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntihipertensiDokument39 SeitenAntihipertensiHarri HardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Antihypertensive DrugsDokument14 Seiten1 Antihypertensive DrugsReda SoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTN - Emerg EDDokument37 SeitenHTN - Emerg EDAyesh EKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Medications TemplateDokument5 SeitenCardiac Medications TemplateErinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension Lecture3: Pharmacological TreatmentDokument25 SeitenHypertension Lecture3: Pharmacological TreatmentRam NiwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneDokument28 SeitenAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti HypretensivesDokument18 SeitenAnti HypretensivesLeena AlateeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti HypretensivesDokument18 SeitenAnti HypretensivesLeena AlateeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Side Effects: AmlodipineDokument8 SeitenSide Effects: AmlodipineRobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nadolol (RX) : Category: Beta-BlockersDokument6 SeitenNadolol (RX) : Category: Beta-BlockersSerious BlackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensives Cardiovascular PharmacologyDokument52 SeitenAntihypertensives Cardiovascular PharmacologyAlan LealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholinergic System: e CarbamatesDokument26 SeitenCholinergic System: e CarbamatesAcai BoncaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVS DiseasesDokument15 SeitenCVS DiseasesNaavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypertensionDokument54 SeitenHypertensionBadri KarkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension and AnaesthesiaDokument3 SeitenHypertension and AnaesthesiaVerico PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jerald Silva Olalo, RN Renal Unit: Generic NameDokument4 SeitenJerald Silva Olalo, RN Renal Unit: Generic NameSherlyn KirisakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide For Final Pharmacology HypertensionDokument39 SeitenStudy Guide For Final Pharmacology HypertensionAlejandro Daniel Landa MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Ceiling Loop Diuretics Thiazides and Realted DiureticsDokument3 SeitenHigh Ceiling Loop Diuretics Thiazides and Realted DiureticsDaphne GoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Inotropes in Treatment of Heart Failure Fight (Autosaved)Dokument32 SeitenCardiac Inotropes in Treatment of Heart Failure Fight (Autosaved)Insan IlmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 CVS Lecture 5 - Drugs For Heart FailureDokument55 Seiten6 CVS Lecture 5 - Drugs For Heart FailureCraig DuHaneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTN JmiDokument39 SeitenHTN Jmink999999Noch keine Bewertungen
- HYPERTENSIONDokument5 SeitenHYPERTENSIONRajesh RamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wesam R KadhumDokument31 SeitenWesam R Kadhumwisam_1by1Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Fib in 60 Yr Old ManDokument32 SeitenA Fib in 60 Yr Old ManNurul HikmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntiarrhythmicsDokument7 SeitenAntiarrhythmicszanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk For: Decreased Cardiac OutputDokument5 SeitenRisk For: Decreased Cardiac OutputJamal HudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Drugs XL ChartDokument4 SeitenCardiovascular Drugs XL Chartcdp158767% (3)
- Cardiovascular Agents PDFDokument118 SeitenCardiovascular Agents PDFgherlethrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiotonic DrugsDokument67 SeitenCardiotonic DrugsLady Mae Ramos100% (1)
- Anti Hypertensive 20191211Dokument35 SeitenAnti Hypertensive 20191211helloitsmenadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antinanginal DrugsDokument43 SeitenAntinanginal DrugsHUZAIFA YAMAANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertensive Emergencies: or How I Learned To Stop Worrying and Love LabetalolDokument31 SeitenHypertensive Emergencies: or How I Learned To Stop Worrying and Love LabetalolNerissa AlvianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio-Vascular DrugsDokument6 SeitenCardio-Vascular DrugsElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihypertensive Drugs: S. Parasuraman, M.Pharm., PH.D.Dokument44 SeitenAntihypertensive Drugs: S. Parasuraman, M.Pharm., PH.D.Shreya SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Medications: Mildred YarboroughDokument51 SeitenCardiac Medications: Mildred YarboroughQueennitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypertensiveDokument2 SeitenHypertensiveReinhard Lumbag PacitengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hipertensi KrisisDokument30 SeitenHipertensi KrisisLuthfan HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac FailureDokument5 SeitenCardiac FailureSafana NazeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 37 Cardiac Glycosides Antianginals and AntidysrhythmicsDokument5 SeitenChapter 37 Cardiac Glycosides Antianginals and AntidysrhythmicsErika Joy Cabison TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Navales Vs Navales GR No 167523Dokument11 SeitenNavales Vs Navales GR No 167523Jonjon BeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apendicita: Abreviere NumeDokument47 SeitenApendicita: Abreviere NumeOvidiu PrundeanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opportunistic Infections: Dr. Baldev S. PrajapatiDokument69 SeitenOpportunistic Infections: Dr. Baldev S. PrajapatiZazzZaffaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is There Still A Role For Abreaction?: PresenterDokument38 SeitenIs There Still A Role For Abreaction?: PresenterNorman PooleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic PathologyDokument21 SeitenSystemic PathologyAijan MurzalievaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Promoting Fetal & Maternal HealthDokument90 SeitenPromoting Fetal & Maternal HealthMarie Angelique Cruz CrestaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 TLE 101 Implementing and Monitoring Infection Control Policies and ProceduresDokument3 SeitenWeek 3 TLE 101 Implementing and Monitoring Infection Control Policies and ProceduresJoel Mamocod100% (1)
- C Difficile ProgramDokument3 SeitenC Difficile ProgramjayjonbeachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Febrile Seizure PDFDokument14 SeitenFebrile Seizure PDFgetnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Serious Side Effects of BeetrootsDokument15 Seiten10 Serious Side Effects of BeetrootsrajanlkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology ProjectDokument23 SeitenBiology ProjectSahil AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dafpus IugrDokument2 SeitenDafpus IugrannisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvement in Lactation With Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Herbal Medicine A Case StudyDokument6 SeitenImprovement in Lactation With Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Herbal Medicine A Case StudyCarleta Stan100% (1)
- Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Score Sheet For CASE Write-UpDokument30 SeitenFaculty of Medicine and Health Sciences Score Sheet For CASE Write-UpJared Khoo Er HauNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIC (Carpio, Kurt Andrew)Dokument5 SeitenSIC (Carpio, Kurt Andrew)Kurt Andrew CarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Approach To The Infant or Child With Nausea and Vomiting - UpToDateDokument47 SeitenApproach To The Infant or Child With Nausea and Vomiting - UpToDatemayteveronica1000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sop of Clo2Dokument4 SeitenSop of Clo2Anup RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case PresentationDokument21 SeitenCase PresentationMae Alleslie TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial Food Intoxication Lecture # 6Dokument17 SeitenBacterial Food Intoxication Lecture # 6muqaddasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Terapi Komprehensif HipertensiDokument4 SeitenJurnal Terapi Komprehensif HipertensiismiNoch keine Bewertungen