Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Endocrine System
Hochgeladen von
Benjamin CristobalOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Endocrine System
Hochgeladen von
Benjamin CristobalCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Endocrine System
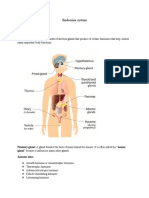
The endocrine system is a system of glands, each of which secretes a type of hormone directly into the bloodstream to regulate the body. It derives from the Greek words endo meaning inside, within, and crinis for secrete.
Endocrine organs and secreted hormones
Hypothalamus
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone- Stimulate thyroid-stimulating hormone Dopamine- Inhibit prolactin released from anterior pituitary Growth hormone-releasing hormone- Stimulate Growth hormone Somatostatin- Inhibit Growth hormone Oxytocin- Uterine Contraction ; Lactation
Pineal Body
Melatonin- Antioxidant; Monitors the circadian rhythm including inducement of drowsiness and
lowering of the middle body temperature sleep cycle
Pituitary Gland
Growth Hormone- Stimulates growth and cell reproduction
Thyroid-stimulating hormone- Stimulates thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) synthesis and release from thyroid gland Beta-endorphin- Inhibits perception of pain Follicle-stimulating hormone -In females: Stimulates maturation of ovarian follicles in ovary -In males: Stimulates maturation of seminiferous tubules -In males: Stimulates spermatogenesis -In males: Stimulates production of androgen-binding protein from Sertoli cells of the testes Luteinizing hormone
-In females: Stimulates ovulation
In females: Stimulates formation of corpus luteum In males: Stimulates testosterone synthesis from Leydig cells (interstitial cells)
Prolactin- Stimulates milk synthesis and release from mammary glands Mediates sexual gratification
Thyroid
Triiodothyronine- Stimulates body oxygen and energy consumption, thereby increasing the basal metabolic rate Stimulates RNA polymerase I and II, thereby promoting protein synthesis
Thyroxine- Stimulates body oxygen and energy consumption, thereby increasing the basal metabolic rate Stimulates RNA polymerase I and II, thereby promoting protein synthesis Calcitonin- Stimulates osteoblasts and thus bone construction
Stomach
Gastrin- Secretion of gastric acid by parietal cells Ghrelin- Stimulate appetite, secretion of growth hormone from anterior pituitary gland Histamine- stimulate gastric acid secretion
Liver
Insulin-like growth factor- insulin-like effects ; regulate cell growth and development Thrombopoietin- stimulates megakaryocytes to produce platelets
Pancreas
Insulin- intake of glucose, glycogenesis and glycolysis in liver and muscle from blood Glucagon- increases blood glucose level
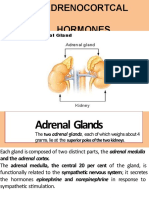
Adrenal Glands
Glucocorticoids
-Stimulates gluconeogenesis
Stimulates fat breakdown in adipose tissue Inhibits protein synthesis Inhibits glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue Inhibits immunological responses (immunosuppressive) Inhibits inflammatory responses (anti-inflammatory)
Adrenal medulla
Adrenaline -Fight-or-flight response:
Boost the supply of oxygen and glucose to the brain and muscles (by increasing heart rate andstroke volume, vasodilation, increasing catalysis of glycogen in liver, breakdown of lipids in fat cells) Dilate the pupils Suppress non-emergency bodily processes (e.g., digestion) Suppress immune system
Testes
Androgens-
Anabolic: growth of muscle mass and strength, increased bone density, growth and strength, Virilizing: maturation of sex organs, formation of scrotum, deepening of voice, growth of beard andaxillary hair.
Ovarian follicle
Estrogens -Structural: Promote formation of female secondary sex characteristics Accelerate height growth Accelerate metabolism (burn fat) Reduce muscle mass Stimulate endometrial growth Increase uterine growth Maintain blood vessels and skin Reduce bone resorption, increase bone formation
Protein synthesis: Increase hepatic production of binding proteins
DISEASES
1.
2.
3. 4. 5.
Addisons disease is a rare, chronic endocrine disorder where the adrenal glands do not produce [1] sufficient steroid hormones (glucocorticoids and often mineralocorticoids). Lifelong, continuous treatment with steroid replacement therapy is required, with regular follow-up treatment and monitoring for other health problems. Diabetes mellitus type 2 formerly non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus or adult-onset diabetes is a metabolic disorder that is characterized by high blood glucose in the context [2] of insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. Diabetes is often initially managed by increasingexercise and dietary modification. If the condition progresses, medications may be needed. Often affecting the obese, diabetes requires patients to routinely check their blood sugar. Thyroiditis is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck below the laryngeal prominence, and makes hormones that control metabolism. Hermaphrodite- having reproductive organs of both genders Kallmann syndrome is a genetic disorder marked by anosmia and hypogonadism - the decreased functioning of the glands that produce sex hormones. Abnormalities in various genes may cause a defect in the hypothalamus, causing a deficiency of gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Thyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!Von EverandThyroid Diet: How to improve and cure thyroid disorders, lose weight, and improve metabolism with the help of food!Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System (Notes)Dokument4 SeitenThe Endocrine System (Notes)Wasim HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Von EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Bewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Endocrine System and Excretion WordDokument10 SeitenEndocrine System and Excretion WordJoachim “Jayrz” MwambireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Hormones and Their Functions: Balete, Berida, BorromeoDokument88 SeitenAnimal Hormones and Their Functions: Balete, Berida, BorromeoRessabela Juniper FayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument4 SeitenEndocrine SystemMarmie Babaran GallibuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFDokument8 Seiten11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFSaurav SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormonal Co OrdinationDokument26 SeitenHormonal Co OrdinationkpnotessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 112: Chapter 11: The Endocrine SystemDokument5 SeitenBiology 112: Chapter 11: The Endocrine SystemLuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDokument9 SeitenEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- Hormones and Nutrient PartitioningDokument36 SeitenHormones and Nutrient Partitioningbwade2_916499061Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesDokument35 SeitenThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesShe JocelynNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System NotesDokument6 SeitenThe Endocrine System NotesRohit AnthuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. SevillenoDokument55 SeitenAnatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. Sevillenocoral jade cuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System NOTESDokument2 SeitenEndocrine System NOTEShuang renjunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument2 SeitenEndocrine SystemHerlene Suelto Tingle100% (1)
- Endocrine System NoteDokument4 SeitenEndocrine System NoteFumzy AdelakunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Dokument3 Seiten11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormone: by Piyush Ingle Shankar BhandalkarDokument63 SeitenHormone: by Piyush Ingle Shankar BhandalkarBharatShethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Endocrine GlandsDokument20 SeitenChapter 11 Endocrine GlandsKatrina ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormone Regulation & Endocrine StructuresDokument28 SeitenHormone Regulation & Endocrine StructuresFujoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OT Endocrine SystemDokument53 SeitenOT Endocrine SystemJei CorbesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniDokument21 SeitenHormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniPadma VishwanathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormones: Hormonal Control Nervous ControlDokument5 SeitenHormones: Hormonal Control Nervous Controlvaibhav trivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Block Endocrine PowerpointDokument70 Seiten4th Block Endocrine PowerpointKevinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDokument7 SeitenChemical Coordination and IntegrationAnshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument22 SeitenEndocrine SystemLen Len Ochinang OchinangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine DiseasesDokument170 SeitenEndocrine DiseasesJustin Ahorro-DionisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Our Bodies HomeostasisDokument20 SeitenControl of Our Bodies HomeostasisJohn Philip VerastigueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Endocrine SystemDokument12 SeitenChapter 9 Endocrine Systemapi-260201878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sistem EndokrinaDokument49 SeitenSistem EndokrinaJessiee YeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnP Endocrine System 2Dokument21 SeitenAnP Endocrine System 2Nicole JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry of Hormones: Dr. Rabia HussainDokument24 SeitenBiochemistry of Hormones: Dr. Rabia HussainRabia HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 26 HORMONES and THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMDokument3 SeitenChapter 26 HORMONES and THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEMMickaela Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDokument4 SeitenCH 22 Chemical Coordination and IntegrationRohankanani007100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDokument3 SeitenEndocrine SystemAnne Jillian83% (6)
- TOPIC 3 - The Endocrine SystemDokument34 SeitenTOPIC 3 - The Endocrine SystemKaren Pearl TagleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System - LectureDokument213 SeitenEndocrine System - LectureRosita Antiquina Elopre100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDokument24 SeitenEndocrine Systemfrowee23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemDokument52 SeitenEssentials of Anatomy & Physiology: The Endocrine SystemMarrenSalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormone and Nervous System BioloveDokument28 SeitenHormone and Nervous System BioloveOrkid FazzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System (CSEC Integrated Science)Dokument20 SeitenEndocrine System (CSEC Integrated Science)Nabeel Uddin100% (2)
- 10 Endocrine SystemDokument35 Seiten10 Endocrine SystemALICIA GOMEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Hormones and Their FunctionDokument1 SeiteEndocrine Hormones and Their FunctionDee RavalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System: Presented By, MD Nasir Uddin Mahmood, Product Executive, Opsonin Pharma LimitedDokument24 SeitenThe Endocrine System: Presented By, MD Nasir Uddin Mahmood, Product Executive, Opsonin Pharma LimitedMd Nasir Uddin Mahmood100% (2)
- Physio Endo 4Dokument21 SeitenPhysio Endo 4Hoth HothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - Chapter 37 - Endocrine SystemDokument21 SeitenLecture - Chapter 37 - Endocrine SystemAnonymous SrGzihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Signals in AnimalsDokument60 SeitenChemical Signals in AnimalsAbdul AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.Dokument2 SeitenEndocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.zoha afshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nama Kelompok:: Khorida Ainun Nur Fidya Listia Agnes Sofyan Leti ApriliantiDokument66 SeitenNama Kelompok:: Khorida Ainun Nur Fidya Listia Agnes Sofyan Leti ApriliantiKris AdinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology 1STDokument10 SeitenPhysiology 1STGW LEGENDNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System: Dr. Alisha Noreen Lecturer Iqra UniversityDokument25 SeitenThe Endocrine System: Dr. Alisha Noreen Lecturer Iqra UniversitypashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine ReviewDokument9 SeitenEndocrine ReviewSpencer ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndocrineDokument45 SeitenEndocrineKatrina JornadalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System ProvidedDokument73 SeitenEndocrine System Providedummezainhumayra11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System NotesDokument4 SeitenEndocrine System NotesSashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System: Study: Endocrinology Physician: EndocrinologistDokument5 SeitenEndocrine System: Study: Endocrinology Physician: EndocrinologistSakshi BishnoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dina Al-Amood: Insulin, Glucagon and DiabetesDokument3 SeitenDina Al-Amood: Insulin, Glucagon and DiabetesDina AlamoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Parathyroid & PancreasDokument13 Seiten5 Parathyroid & Pancreasapi-3706483Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Cortical HormoneDokument28 SeitenAdrenal Cortical HormoneTalha MohsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nego Diges 24-29Dokument8 SeitenNego Diges 24-29Benjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRR of RA 9165 Dangerous Drugs ActDokument50 SeitenIRR of RA 9165 Dangerous Drugs ActKarina PulidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Delos Reyes v. SandiganbayanDokument7 Seiten2 - Delos Reyes v. SandiganbayanBenjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consti Law 2 Syllabus (As of 21nov14)Dokument9 SeitenConsti Law 2 Syllabus (As of 21nov14)Benjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- San Beda Alabang Debate SocietyDokument4 SeitenSan Beda Alabang Debate SocietyBenjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project CarDokument1 SeiteProject CarBenjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consortium GuidelinesDokument25 SeitenConsortium GuidelinesBenjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consti Law 2 Syllabus (As of 21nov14)Dokument9 SeitenConsti Law 2 Syllabus (As of 21nov14)Benjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer - Life of Dr. Jose RizalDokument35 SeitenReviewer - Life of Dr. Jose Rizaljava_biscocho122993% (105)
- ALW143R Case Digests IIDokument6 SeitenALW143R Case Digests IIBenjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- THEO Nicene CreedDokument1 SeiteTHEO Nicene CreedBenjamin CristobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bobcat Compact Excavator E10 Service Manual 6986788Dokument22 SeitenBobcat Compact Excavator E10 Service Manual 6986788andrewshelton250683psa98% (64)
- Preparing For The NASH Epidemic A Call To ActioDokument11 SeitenPreparing For The NASH Epidemic A Call To ActioDaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemiile Aplastice Copii1Dokument28 SeitenAnemiile Aplastice Copii1Daniela LupanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baveno IVDokument10 SeitenBaveno IVdepe_cutzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver CancerDokument44 SeitenLiver CancerJoyce Ann CumlatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 - Food and Digestion PDFDokument15 SeitenAssignment 3 - Food and Digestion PDFMonique MavronicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat Aliza Mehbin BioDokument1 SeiteCat Aliza Mehbin BioKirti DoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- T CholesterolDokument5 SeitenT CholesterolDuc Nguyen ManhNoch keine Bewertungen
- JawapanLengkap Modul Biology PDFDokument32 SeitenJawapanLengkap Modul Biology PDFT-specialist SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance of Non-Invasive Models of Fibrosis in Predicting Mild To Moderate Fibrosis in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver DiseaseDokument8 SeitenPerformance of Non-Invasive Models of Fibrosis in Predicting Mild To Moderate Fibrosis in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver DiseaseChausarPutraBenagilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual Bio II 201701Dokument79 SeitenLab Manual Bio II 201701Charlie LaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skandalakis Surgical Anatomy The EmbryolDokument2 SeitenSkandalakis Surgical Anatomy The EmbryolArvin Aditya PrakosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver CirrhosisDokument31 SeitenLiver CirrhosisAsniah Hadjiadatu Abdullah100% (1)
- Complications of Parenteral NutritionDokument24 SeitenComplications of Parenteral NutritionAdrián L. VázquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Gastro Tahun Lalu - Tahun IniDokument12 SeitenA Gastro Tahun Lalu - Tahun IniDapot SianiparNoch keine Bewertungen
- .. - Pekana - Ailgeno - Free Shipping On Orders Over $50 - .Dokument3 Seiten.. - Pekana - Ailgeno - Free Shipping On Orders Over $50 - .Anant GomekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma Physiology (1-2020) by DR Khaled A AbulfadleDokument9 SeitenPlasma Physiology (1-2020) by DR Khaled A AbulfadleUzama Binu AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascites PresentationDokument19 SeitenAscites PresentationDanielle FosterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Cirrhosis Case PresentationDokument146 SeitenLiver Cirrhosis Case Presentationjennachristy0395% (21)
- The Nature of Disease Pathology For The Health Professions 2nd Edition Ebook PDFDokument62 SeitenThe Nature of Disease Pathology For The Health Professions 2nd Edition Ebook PDFcarol.williams649100% (41)
- Q.P. CODE:500-A-OR: BiochemistryDokument38 SeitenQ.P. CODE:500-A-OR: BiochemistrySai KiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shackelford S Surgery of The Alimentary Tract Yeo 8 Ed 2019Dokument2.400 SeitenShackelford S Surgery of The Alimentary Tract Yeo 8 Ed 2019Shuler007193% (29)
- Studies of Kidney Cancer and PCBsDokument19 SeitenStudies of Kidney Cancer and PCBsl-cristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Announcement Liver UpdateDokument13 SeitenFinal Announcement Liver Updatenerissa arvianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Sciences Research .ND Development Corporation, In.Dokument24 SeitenAdvanced Sciences Research .ND Development Corporation, In.divya kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wilson Disease in Children and Young Adults - State of The ArtDokument11 SeitenWilson Disease in Children and Young Adults - State of The ArtJosueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Chemistry Notes - LiverDokument5 SeitenClinical Chemistry Notes - LiverJen NovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatomegaly - Differential Diagnosis and Evaluation - UTD 2018 PDFDokument22 SeitenHepatomegaly - Differential Diagnosis and Evaluation - UTD 2018 PDFKrull TTTeam0% (1)
- Jaundice 23-24pdfDokument25 SeitenJaundice 23-24pdfmyarjddbzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallbladder DisordersDokument59 SeitenGallbladder DisordersdrelvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (81)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (29)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningVon EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (170)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainVon EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (95)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (8)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsVon EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlVon EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (59)