Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Principles and Elements of Design
Hochgeladen von
Hunain Hayat BangashOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Principles and Elements of Design
Hochgeladen von
Hunain Hayat BangashCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PRINCILES
AND
ELEMENTS OF DESIGN
Design is the organized arrangement of one or more elements and principles (e.g. line color or texture) for a purpose. Design as a noun informally refers to a plan for the construction of an object or a system (as in architectural blueprints, engineering drawing, business process, circuit diagrams and sewing patterns) while to design (verb) refers to making this plan. No generally-accepted definition of design exists and the term has different connotations in different fields. Types of design: 1: Geometrical design Use of designs, such as squares, triangles, oblongs, and circles to form designs on fabric and apparel. 2: Natural design Natural Design is also an approach to psychology and biology that holds that concepts such as "motivation", "emotion", "inner feeling", "development", "adaptation" refer not to down-reductive explanations of things but to up- reductive descriptions of patterns of which those things are part. 3: Abstract design whose forms have been reduced or modified from representational forms or a design using non-representational forms. 4: Stylized design using artistic forms and conventions to create effects; not natural or spontaneous; "a stylized mode of theater production".
Design elements and principles describe fundamental ideas about the practice of good visual design that are assumed to be the basis of all intentional visual design strategies. The elements form the 'vocabulary' of the design, while the principles constitute the broader structural aspects of its composition. Awareness of the elements and principles in design is the first step in creating successful visual compositions. These principles,
which may overlap, are used in all visual design fields, including graphic design, industrial design, architecture and fine art.
Composition of design: Principles of design are as varied as attitudes regarding modern design. They differ both between the schools of thought that influence design, and between individual practicing designers. Elements of design are the basic units of a visual image. These elements include: line, shape, color, shades, texture, form, value etc. Types of composition: 1: Decorative composition is a composition that gives pleasing effect to the design and can attract anyone towards its self. 2: Representative composition is a composition which represents the features of life weather good or bad. It promotes the features of the society and people working around. 3: Expository composition is composition in which religious aspects are exposed. Arts use this composition in their paintings to promote their religion. Point
Point
Even if there is only one point, one mark on a blank page there is something built into the brain that wills meaning for it, and seeks some kind of relationship or order, if only to use it as a point of orientation in relation to the outline of the page. Ifthere are two points, immediately the eye will make a connection and "see" a line. If there are three points, it is unavoidable to interpret
them as a triangle; the mind supplies the connections. This compulsion to connect parts is described as grouping, or gestalt. Gestalt is the fundamental tool the designer or artist uses to build a coherent composition. The example of a student selfportrait seen on the left demonstrates how images may be built from points, with the variations in density producing the illusion of form. Gestalt theory developed in the 1920s in Germany. The term describes a number of concepts that the eye/mind use to group points into meaning. These include Closure, in which the mind supplies missing pieces to complete the image-- this occurs in the Mona Lisa images to the right. A second concept is continuity-- this describes the tendency to "connect the dots" and so accept separate parts or points as part of a contour or form. It is hard to resist, for example, the compulsion to see two dots as implying a line, or three as framing a triangle.Similarity describes the tendency to see and group objects of similar shape or color. Proximity results in a tendency to group points or objects that are close to one another relative to less proximate in the visual field. Alignment, either along edges of the objects or points or through their centers, will persuade us see them as a contour or a line
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- BF Monarchy Report 2017Dokument11 SeitenBF Monarchy Report 2017Hunain Hayat BangashNoch keine Bewertungen
- 228734600 (1) (1)Dokument10 Seiten228734600 (1) (1)Hunain Hayat BangashNoch keine Bewertungen
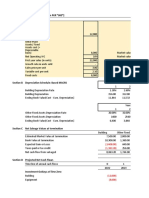
- Template - Cash Flow EstimationDokument6 SeitenTemplate - Cash Flow EstimationHunain Hayat BangashNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA Assignment June 2022Dokument7 SeitenMA Assignment June 2022Hunain Hayat BangashNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS A&f Excel Templete Sep 2018-1Dokument6 SeitenBS A&f Excel Templete Sep 2018-1Aitesam UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mysterious Affair at Styles PDFDokument200 SeitenThe Mysterious Affair at Styles PDFHunain Hayat BangashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semester Schedule Spring 2011Dokument2 SeitenSemester Schedule Spring 2011zaria88Noch keine Bewertungen
- FIADokument12 SeitenFIAFahad Dehbar, ACCANoch keine Bewertungen
- Affiliated InstitutionsDokument2 SeitenAffiliated InstitutionsHunain Hayat BangashNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIADokument12 SeitenFIAFahad Dehbar, ACCANoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Mwangi, Thyne, Rao - 2013 - Extensive Experimental Wettability Study in Sandstone and Carbonate-Oil-Brine Systems Part 1 - Screening ToDokument7 SeitenMwangi, Thyne, Rao - 2013 - Extensive Experimental Wettability Study in Sandstone and Carbonate-Oil-Brine Systems Part 1 - Screening ToMateo AponteNoch keine Bewertungen
- HardikDokument21 SeitenHardikGohil HardikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Komatsu Technical BrochurDokument7 SeitenKomatsu Technical BrochurBenjamin MossoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Over Current & Earth Fault RelayDokument2 SeitenOver Current & Earth Fault RelayDave Chaudhury67% (6)
- EQ Cheat SheetDokument7 SeitenEQ Cheat SheetGabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phineas Gage: From The Passage of An Iron Rod Through The Head"Dokument1 SeitePhineas Gage: From The Passage of An Iron Rod Through The Head"GlupiaSprawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faujifood Pakistan PortfolioDokument21 SeitenFaujifood Pakistan PortfolioPradeep AbeynayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
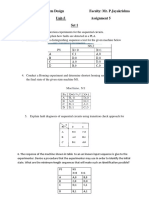
- Subject: Digital System Design Faculty: Mr. P.Jayakrishna Unit-5 Assignment 5 Set 1Dokument2 SeitenSubject: Digital System Design Faculty: Mr. P.Jayakrishna Unit-5 Assignment 5 Set 1Jayakrishna CharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA9275Dokument49 SeitenRA9275znarf_ryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Pelayanan Rawat Jalan Tingkat Pertama (RJTP)Dokument10 SeitenLaporan Pelayanan Rawat Jalan Tingkat Pertama (RJTP)dede komalasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Celly BoostbkDokument15 SeitenCelly BoostbknomikabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double-Outlet Right Ventricle With An An Intact Interventricular Septum and Concurrent Hypoplastic Left Ventricle in A CalfDokument6 SeitenDouble-Outlet Right Ventricle With An An Intact Interventricular Septum and Concurrent Hypoplastic Left Ventricle in A CalfYoga RivaldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytoremediation Acuatic PlantsDokument120 SeitenPhytoremediation Acuatic PlantsFranco Portocarrero Estrada100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry (Some Basic Principles and TechniquesDokument30 SeitenOrganic Chemistry (Some Basic Principles and TechniquesNaveen SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before UseDokument9 SeitenSmart Watch User Manual: Please Read The Manual Before Useeliaszarmi100% (3)
- IFIS - Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome Wa Wa 27-09-2008Dokument18 SeitenIFIS - Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome Wa Wa 27-09-2008JanuszNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tamil NaduDokument64 SeitenTamil Nadushanpaga priyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry NotesDokument11 SeitenChemistry Notesraifaisal9267% (12)
- 2.4 Assembly ManualDokument139 Seiten2.4 Assembly Manualgustavo dlsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionDokument18 SeitenMagneto-Convective Non-Newtonian Nanofluid With Momentum and Temperature Dependent Slip Flow From A Permeable Stretching Sheet With Porous Medium and Chemical ReactionIOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Texas Instruments FootprintsDokument7 SeitenTexas Instruments FootprintsSteve SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- BHLP Year Long Plan Required English Medium 2023 24 Batch Final 991676721629413Dokument3 SeitenBHLP Year Long Plan Required English Medium 2023 24 Batch Final 991676721629413A V GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Engineering and Technology TaxilaDokument5 SeitenUniversity of Engineering and Technology TaxilagndfgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++Dokument5 SeitenPolynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++wlsvieiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Pen MountDokument17 SeitenNon-Pen MountT BagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Augocom Micro 768 Battery Tester User ManualDokument29 SeitenAugocom Micro 768 Battery Tester User ManualJorge PontonNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1-Safety StandardsDokument9 SeitenM1-Safety StandardscarlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master of Business Administration in Aviation Management MbaamDokument10 SeitenMaster of Business Administration in Aviation Management MbaamAdebayo KehindeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kiss Forex How To Trade Ichimoku PDFDokument72 SeitenKiss Forex How To Trade Ichimoku PDFSastryassociates Chartered100% (3)
- Collage Lab PDFDokument145 SeitenCollage Lab PDFmaa siddhi92% (12)