Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
B747 Data
Hochgeladen von
pss196203Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
B747 Data
Hochgeladen von
pss196203Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
101
5.4. STABILITY CHARACTERISTICS OF THE BOEING 747
5.4
5.4.1
Stability Characteristics of the Boeing 747
Longitudinal Stability Characteristics
In this section we summarize the longitudinal mass distribution and aerodynamic stability characteristics of a large, jet transport aircraft, the Boeing 747, at selected flight conditions. Data are
summarized from the report by Heffley et al. [2]. Values for aerodynamic coefficients were scaled
directly from plots of these variables, except for the derivatives CLq and CL for which no data are
provided. These values were computed from the values of the corresponding dimensional stability
derivatives Zq and Zw , which are provided in tabular form, with the sign of Zw changed to correct
a seemingly obvious error.
Condition numbers correspond to those in the report; Conditions 5-10 are for a clean aircraft,
Condition 2 corresponds to a powered approach with gear up and 20 flaps. Angles of attack are
with respect to the fuselage reference line.
Condition
h (ft)
M
(degrees)
W (lbf)
2
Iy (slug-ft )
CL
CD
CL
CD
Cm
CL
Cm
CL q
Cm q
CL M
CDM
Cm M
CLe
Cme
2
SL
0.25
5.70
564,032.
32.3 106
1.11
0.102
5.70
0.66
-1.26
6.7
-3.2
5.40
-20.8
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.338
-1.34
5
20,000
0.500
6.80
636,636.
33.1 106
0.680
0.0393
4.67
0.366
-1.146
6.53
-3.35
5.13
-20.7
-.0875
0.0
0.121
0.356
-1.43
7
20,000
0.800
0.0
636,636.
33.1 106
0.266
0.0174
4.24
0.084
-.629
5.99
-5.40
5.01
-20.5
0.105
0.008
-.116
0.270
-1.06
9
40,000
0.800
4.60
636,636.
33.1 106
0.660
0.0415
4.92
0.425
-1.033
5.91
-6.41
6.00
-24.0
0.205
0.0275
0.166
0.367
-1.45
10
40,000
0.900
2.40
636,636.
33.1 106
0.521
0.0415
5.57
0.527
-1.613
5.53
-8.82
6.94
-25.1
-.278
0.242
-.114
0.300
-1.20
Table 5.3: Longitudinal mass properties and aerodynamic stability derivatives for the Boeing 747 at
selected flight conditions.
102
5.4.2
CHAPTER 5. DYNAMIC STABILITY
Lateral/Directional Stability Characteristics
In this section we summarize the lateral/directional mass distribution and aerodynamic stability
characteristics of a large, jet transport aircraft, the Boeing 747, at selected flight conditions. Data
are summarized from the report by Heffley et al. [2]. Values for aerodynamic coefficients were scaled
directly from plots of these variables.
Condition numbers correspond to those in the report; Conditions 5-10 are for a clean aircraft,
Condition 2 corresponds to a powered approach with gear up and 20 flaps. Moments and products
of inertia are with respect to stability axes for the given flight condition. Angles of attack are with
respect to the fuselage reference line.
Condition
h (ft)
M
(degrees)
W (lbf)
2
Ix (slug-ft )
2
Iz (slug-ft )
2
Ixz (slug-ft )
Cy
Cl
Cn
Cl p
Cnp
Cl r
Cnr
Cla
Cna
Cyr
Clr
Cnr
2
SL
0.25
5.70
564,032.
14.3 106
45.3 106
2.23 106
-.96
-.221
0.150
-.45
-.121
0.101
-.30
0.0461
0.0064
0.175
0.007
-.109
5
20,000
0.500
6.80
636,636.
18.4 106
49.5 106
2.76 106
-.90
-.193
0.147
-.323
-.0687
0.212
-.278
0.0129
0.0015
0.1448
0.0039
-.1081
7
20,000
0.800
0.0
636,636.
18.2 106
49.7 106
0.97 106
-.81
-.164
0.179
-.315
0.0028
0.0979
-.265
0.0120
0.0008
0.0841
0.0090
-.0988
9
40,000
0.800
4.60
636,636.
18.2 106
49.7 106
1.56 106
-.88
-.277
0.195
-.334
-.0415
0.300
-.327
0.0137
0.0002
0.1157
0.0070
-.1256
10
40,000
0.900
2.40
636,636.
18.2 106
49.7 106
.35 106
-.92
-.095
0.207
-.296
0.0230
0.193
-.333
0.0139
-.0027
0.0620
0.0052
-.0914
Table 5.4: Lateral/Directional mass properties and aerodynamic stability derivatives for the Boeing
747 at selected flight conditions.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionVon Everand737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Helicopter Pilot Oral Exam Guide: When used with the corresponding Oral Exam Guide, this book prepares you for the oral portion of the Private, Instrument, Commercial, Flight Instructor, or ATP Helicopter CheckrideVon EverandHelicopter Pilot Oral Exam Guide: When used with the corresponding Oral Exam Guide, this book prepares you for the oral portion of the Private, Instrument, Commercial, Flight Instructor, or ATP Helicopter CheckrideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument355 SeitenChapter 5manikandan_murugaiah100% (4)
- Airfoil Selection Guide for Aircraft DesignDokument17 SeitenAirfoil Selection Guide for Aircraft DesignHeshamAl-haydar100% (2)
- CVF Ski-Jump Ramp Profile Optimisation For F-35B 3324 - COLOURDokument7 SeitenCVF Ski-Jump Ramp Profile Optimisation For F-35B 3324 - COLOURskylancer-3441Noch keine Bewertungen
- Uh60 Afcs PDFDokument21 SeitenUh60 Afcs PDFNikolai Pautov100% (3)
- Steady Aircraft Flight and PerformanceVon EverandSteady Aircraft Flight and PerformanceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Aerodynamic Analysis Using XFLR-5Dokument12 SeitenAerodynamic Analysis Using XFLR-5Alejandro García González100% (1)
- 2011 - Design and Wind Tunnel Tests of A Tiltwing UAVDokument11 Seiten2011 - Design and Wind Tunnel Tests of A Tiltwing UAVahmad.yasser123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rotorcraft & VTOL Symposium Virtual Event: VTOL Flight Envelopes and Stall CharacteristicsDokument22 SeitenRotorcraft & VTOL Symposium Virtual Event: VTOL Flight Envelopes and Stall CharacteristicsEstefanía Vega GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Correlations of Flight-Measured AND Wind-Tunnel Measured Stability AND Control Characteristics of High-Speed AirplanesDokument20 SeitenSome Correlations of Flight-Measured AND Wind-Tunnel Measured Stability AND Control Characteristics of High-Speed AirplanesoznalbantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flight MeasurementsDokument29 SeitenFlight MeasurementsewiontkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-Iv Notes Faculty Name: R.Jini Raj Class: B.E Aeronautical Subject Code: Ae8604 Semester: Vi Subject Name: Aircraft DesignDokument28 SeitenUnit-Iv Notes Faculty Name: R.Jini Raj Class: B.E Aeronautical Subject Code: Ae8604 Semester: Vi Subject Name: Aircraft DesignTHE BOISNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potsdam1 AHS04Dokument13 SeitenPotsdam1 AHS04amir_karimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study On Aerodynamic Characteristics of Light Convertible Aircraft ModelDokument10 SeitenStudy On Aerodynamic Characteristics of Light Convertible Aircraft ModelГригорий ОмельченкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- 023 - Chapter 5 - L16 PDFDokument12 Seiten023 - Chapter 5 - L16 PDFKunhu MonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 - Attitude and Cruise Control of A VTOL Tiltwing UAVDokument8 Seiten2019 - Attitude and Cruise Control of A VTOL Tiltwing UAVahmad.yasser123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- REPORT No. 715: Lateral Control Required For Satisfactory Flying Qualities Based On Flight Tests of Numerous AirplanesDokument7 SeitenREPORT No. 715: Lateral Control Required For Satisfactory Flying Qualities Based On Flight Tests of Numerous AirplanesFabián AcevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wing design parameters selection and airfoil characteristicsDokument48 SeitenWing design parameters selection and airfoil characteristicsRidhima KaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Propeller-Wing Aerodynamic InterferenceDokument21 SeitenReview of Propeller-Wing Aerodynamic Interferencekrishnamoorthy_krishNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAT 2.1 Q&aDokument4 SeitenIAT 2.1 Q&aRam RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piper CubDokument84 SeitenPiper CubDavid Scott100% (1)
- (REV1) MiG-21Bis - Pilots Flight Operating InstructionDokument223 Seiten(REV1) MiG-21Bis - Pilots Flight Operating InstructionLGK PUBGNoch keine Bewertungen
- NACA Report of The Grumman F8F-1Dokument48 SeitenNACA Report of The Grumman F8F-1tomay777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Article AEAT Vertical TailDokument21 SeitenArticle AEAT Vertical TailscribdownloaderpassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Landing Gear Concept SelectionDokument10 SeitenLanding Gear Concept SelectionAbo NajjarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module IVDokument25 SeitenModule IVVinay KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of An Unmanned Tail-Sitter: Roman Bapst, Robin Ritz, Lorenz Meier and Marc PollefeysDokument6 SeitenDesign and Implementation of An Unmanned Tail-Sitter: Roman Bapst, Robin Ritz, Lorenz Meier and Marc PollefeysIndira FatihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 026 - Chapter 5 - L19 - (03-10-2013) PDFDokument14 Seiten026 - Chapter 5 - L19 - (03-10-2013) PDFMohamed MansourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap562 9Dokument128 SeitenCap562 9DavidGarcíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17ae73 As&c Module-2 ClassDokument47 Seiten17ae73 As&c Module-2 ClassSanjana ShivaprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advisory Circular: Federal Aviation AdministrationDokument11 SeitenAdvisory Circular: Federal Aviation AdministrationEddy JhetNoch keine Bewertungen
- VTOL Tilt Rotor Equations of Motion, Trim and LinealizationDokument15 SeitenVTOL Tilt Rotor Equations of Motion, Trim and LinealizationRafael TrujilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- AircraftDesign 9 EmpennageGeneralDesignDokument16 SeitenAircraftDesign 9 EmpennageGeneralDesignBart Siwiec ZygmuntNoch keine Bewertungen
- To ReportDokument18 SeitenTo ReportledspiritNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance and Design Investigation of Heavy Lift Tiltrotor With Aerodynamic Interference EffectsDokument19 SeitenPerformance and Design Investigation of Heavy Lift Tiltrotor With Aerodynamic Interference EffectsJr Zdenko VukojaNoch keine Bewertungen
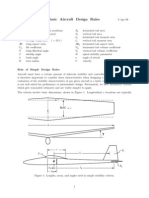
- Basic Aircraft Design RulesDokument8 SeitenBasic Aircraft Design RulesAbdelrahman Nassif100% (1)
- Automatic Path Planning and Control Design For AutonomousDokument6 SeitenAutomatic Path Planning and Control Design For AutonomousNAENWI YAABARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Wing Loading and Thrust LoadingDokument23 SeitenEstimation of Wing Loading and Thrust LoadingAnonymous OFTUeE6Noch keine Bewertungen
- DESEMPENHODokument13 SeitenDESEMPENHOAry guimaraes netoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1965 Datcom Sections6 9Dokument559 Seiten1965 Datcom Sections6 9Immaculate ImmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aileron ReversalDokument5 SeitenAileron ReversalathiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A - Airfoil Characteristic - 2014 - Commercial Airplane Design PrinciplDokument9 SeitenAppendix A - Airfoil Characteristic - 2014 - Commercial Airplane Design PrinciplIeva MisiunaiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uh60 AfcsDokument21 SeitenUh60 Afcsk_goulas100% (4)
- Background On Aircraft AerodynamicsDokument8 SeitenBackground On Aircraft AerodynamicsAbdelrahman NassifNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIAA 1977 High Lift CardinalDokument6 SeitenAIAA 1977 High Lift Cardinalilter79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crosswind Landings TechniqueDokument12 SeitenCrosswind Landings TechniqueReza MahmoudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flight Dynamics AE3-302 ExercisesDokument12 SeitenFlight Dynamics AE3-302 ExercisesDomenico VerbicaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flutter Prevention CriteriaDokument46 SeitenFlutter Prevention Criteriaffontana100% (1)
- Sourish Kundu Day1 Presentation PDFDokument19 SeitenSourish Kundu Day1 Presentation PDFSourish KunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS-LSA - Initial IssueDokument18 SeitenCS-LSA - Initial IssueAnonymous ucJM9AGdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3101Dokument10 Seiten3101Madhavan Jayaraman100% (1)
- CPL Performance MosDokument7 SeitenCPL Performance Mosm.1990.williamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard Landing Inspection ManualDokument26 SeitenHard Landing Inspection Manualom prakash patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handout - AFCSDokument21 SeitenHandout - AFCS김종환Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Technical Characteristics of Fixed-Wing VTOL UAVDokument5 SeitenAnalysis of Technical Characteristics of Fixed-Wing VTOL UAVKependra BhairamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helicopter Flight Dynamics: Including a Treatment of Tiltrotor AircraftVon EverandHelicopter Flight Dynamics: Including a Treatment of Tiltrotor AircraftNoch keine Bewertungen
- A330 Normal Law: Putting Fly-by-Wire Into PerspectiveVon EverandA330 Normal Law: Putting Fly-by-Wire Into PerspectiveBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Aerospace Actuators 2: Signal-by-Wire and Power-by-WireVon EverandAerospace Actuators 2: Signal-by-Wire and Power-by-WireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airplane Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-3CVon EverandAirplane Flying Handbook (2024): FAA-H-8083-3CBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (11)
- Dynamics Note SheetDokument3 SeitenDynamics Note SheetDaniel WieseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics 2.032 Note SheetDokument6 SeitenDynamics 2.032 Note SheetDaniel WieseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental LawsDokument21 SeitenFundamental LawsDaniel WieseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft DataDokument5 SeitenAircraft DataDaniel WieseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flightgear Simulink v1Dokument3 SeitenFlightgear Simulink v1Daniel WieseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cessna 172Dokument1 SeiteCessna 172Daniel WieseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex High PerformanceDokument2 SeitenComplex High PerformanceDaniel WieseNoch keine Bewertungen