Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Topologies: Network Topology Is The Layout Pattern of Interconnections of The
Hochgeladen von
Amrit Pal SinghOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Topologies: Network Topology Is The Layout Pattern of Interconnections of The
Hochgeladen von
Amrit Pal SinghCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
VIPUL ARORA
IT 4th
90680822758
Topologies
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network. Network topologies may be physical or logical. Physical topology means the physical design of a network including the devices, location and cable installation. Logical topology refers to how data is actually transferred in a network as opposed to its physical design. In general physical topology relates to a core network whereas logical topology relates to basic network.Topology can be considered as a virtual shape or structure of a network. This shape does not correspond to the actual physical design of the devices on the computer network. The computers on a home network can be arranged in a circle but it does not necessarily mean that it represents a ring topology.Any particular network topology is determined only by the graphical mapping of the configuration of physical and/or logical connections between nodes. The study of network topology uses graph theory. Distances between nodes, physical interconnections, transmission rates, and/or signal types may differ in two networks and yet their topologies may be identical.A local area network (LAN) is one example of a network that exhibits both a physical topology and a logical topology. Any given node in the LAN has one or more links to one or more nodes in the network and the mapping of these links and nodes in a graph results in a geometric shape that may be used to describe the physical topology of the network. Likewise, the mapping of the data flow between the nodes in the network determines the logical topology of the network. The physical and logical topologies may or may not be identical in any particular network.
1|Page
VIPUL ARORA
IT 4th
90680822758
The study of network topology recognizes seven basic topologies: 1 .Bus (point-to-multipoint) topology 2. Star topology 3. Ring topology 4 .Tree topology 5. Mesh topology
Bus Topology:-
Bus network topology
In local area networks where bus topology is used, each node is connected to a single cable. Each computer or server is connected to the single bus cable through some kind of connector. A terminator is required at each end of the bus cable to prevent the signal from bouncing back and forth on the bus cable. A signal from the source travels in both directions to all machines connected on the bus cable until it finds the MAC address or IP address on the network that is the intended recipient. If the machine
2|Page
VIPUL ARORA
IT 4th
90680822758
address does not match the intended address for the data, the machine ignores the data. Alternatively, if the data does match the machine address, the data is accepted. Since the bus topology consists of only one wire, it is rather inexpensive to implement when compared to other topologies. However, the low cost of implementing the technology is offset by the high cost of managing the network. Additionally, since only one cable is utilized, it can be the single point of failure. If the network cable breaks, the entire network will be down.
Star Topology:In local area networks with a star topology, each network host is connected to a central hub. In contrast to the bus topology, the star topology connects each node to the hub with a point-to-point connection. All traffic that traverses the network passes through the central hub. The hub acts as a signal booster or repeater. The star topology is considered the easiest topology to design and implement. An advantage of the star topology is the simplicity of adding additional nodes. The primary disadvantage of the star topology is that the hub represents a single point of failure
Star network topology
Ring Topology:-
Ring network topology
A network topology that is set up in a circular fashion in which data travels around the ring in one direction and each device on the right acts as a repeater to keep the signal strong as it travels. Each device incorporates a receiver for the incoming signal
3|Page
VIPUL ARORA
IT 4th
90680822758
and a transmitter to send the data on to the next device in the ring. The network is dependent on the ability of the signal to travel around the ring.
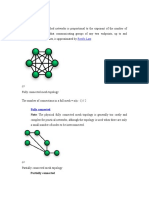
Mesh Topology:The value of fully meshed networks is proportional to the exponent of the number of subscribers, assuming that communicating groups of any two endpoints, up to and including all the endpoints, is approximated.
Tree Topology:-
Tree network topology
Also known as a hierarchy network. The type of network topology in which a central 'root' node (the top level of the hierarchy) is connected to one or more other nodes that are one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the second level) with a point-to-point link between each of the second level nodes and the top level central 'root' node, while each of the second level nodes that are connected to the top level central 'root' node will also have one or more other nodes that are one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the third level) connected to it, also with a point-to-point link, the top level central 'root' node being the only node that has no other node above it in the hierarchy (The hierarchy of the tree is symmetrical.) Each node in the network having a specific fixed number, of nodes connected to it at
4|Page
VIPUL ARORA
IT 4th
90680822758
the next lower level in the hierarchy, the number, being referred to as the 'branching factor' of the hierarchical tree. This tree has individual peripheral nodes. 1.) A network that is based upon the physical hierarchical topology must have at least three levels in the hierarchy of the tree, since a network with a central 'root' node and only one hierarchical level below it would exhibit the physical topology of a star. 2.) A network that is based upon the physical hierarchical topology and with a branching factor of 1 would be classified as a physical linear topology. 3.) The branching factor, f, is independent of the total number of nodes in the network and, therefore, if the nodes in the network require ports for connection to other nodes the total number of ports per node may be kept low even though the total number of nodes is large this makes the effect of the cost of adding ports to each node totally dependent upon the branching factor and may therefore be kept as low as required without any effect upon the total number of nodes that are possible. 4.) The total number of point-to-point links in a network that is based upon the physical hierarchical topology will be one less than the total number of nodes in the network. 5.) If the nodes in a network that is based upon the physical hierarchical topology are required to perform any processing upon the data that is transmitted between nodes in the network, the nodes that are at higher levels in the hierarchy will be required to perform more processing operations on behalf of other nodes than the nodes that are lower in the hierarchy. Such a type of network topology is very useful and highly recommended.
Straight Cable
You usually use straight cable to connect different type of devices. This type of cable will be used most of the time and can be used to: 1) Connect a computer to a switch/hub's normal port. 2) Connect a computer to a cable/DSL modem's LAN port. 3) Connect a router's WAN port to a cable/DSL modem's LAN port. 4) Connect a router's LAN port to a switch/hub's uplink port. (normally used for expanding network) 5) Connect 2 switches/hubs with one of the switch/hub using an uplink port and the other one using normal port. If you need to check how straight cable looks like, it's easy. Both side (side A and side B) of cable have wire arrangement with same color. Check out different types of straight cable that are available in the market here.
5|Page
VIPUL ARORA
IT 4th
90680822758
Cross Cable
Sometimes you will use crossover cable, it's usually used to connect same type of devices. A crossover cable can be used to: 1) Connect 2 computers directly. 2) Connect a router's LAN port to a switch/hub's normal port. (normally used for expanding network) 3) Connect 2 switches/hubs by using normal port in both switches/hubs. In you need to check how crossover cable looks like, both side (side A and side B) of cable have wire arrangement with following different color . Have a look on these crossover cables if you plan to buy one. You can also find more network cable choices and information from Comtrad Cables.
6|Page
VIPUL ARORA
IT 4th
90680822758
7|Page
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Network TopologiesDokument4 SeitenNetwork TopologieskaranmaddiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologiesDokument9 SeitenNetwork TopologiesshijinbgopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcse Note Topology by Wahidullah ShahaadatDokument30 SeitenMcse Note Topology by Wahidullah ShahaadatmcseaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument7 SeitenNetwork TopologyJayvee Puntalba CalinogNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Network TopologyDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Network TopologyGoldy BatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologiesDokument10 SeitenTopologiesMilka ThuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C PPPPPP PPP PPDokument9 SeitenC PPPPPP PPP PPahils100% (1)
- Network BasicsDokument57 SeitenNetwork BasicsPunitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fahad Ali Khan Sp09-Bce-044Dokument6 SeitenFahad Ali Khan Sp09-Bce-044Fahad Ali KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument7 SeitenNetwork TopologykrgcegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topologies: Application NotesDokument8 SeitenNetwork Topologies: Application NotesBassantMohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Network TopologyDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Network TopologyRohit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument2 SeitenNetwork TopologyJason CuarentaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Lab ManualDokument25 SeitenCN Lab Manualsmartharsh22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Types of Network TopologyDokument28 SeitenOverview of Types of Network TopologyFikirte LegesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Networks-4Dokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Networks-4deepheat_008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topologies: Lecture # 2Dokument21 SeitenNetwork Topologies: Lecture # 2Monika RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topology: What Is A Network Topology? in Communication Networks, A Topology Is A Usually SchematicDokument26 SeitenNetwork Topology: What Is A Network Topology? in Communication Networks, A Topology Is A Usually SchematicChaitrali ChawareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cns Practical 2Dokument10 SeitenCns Practical 2How to download AnythingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Star Topology Many Home Networks Use The Star Topology. A Star Network Features ADokument6 SeitenStar Topology Many Home Networks Use The Star Topology. A Star Network Features AsabahafzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument7 SeitenTopologySeraj KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is TopologyDokument7 SeitenWhat Is TopologyManoj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MemunaDokument6 SeitenMemunajallohadrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amie Nbcafe Student Forum: Network TopologyDokument8 SeitenAmie Nbcafe Student Forum: Network TopologySomnath LahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument10 SeitenTopologyAmeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSE Fundamental - TopologyDokument14 SeitenCSE Fundamental - TopologySYED FARHAN REZANoch keine Bewertungen
- Star TopologyDokument7 SeitenStar TopologyadelenyamhuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topologies: Lesson OverviewDokument4 SeitenNetwork Topologies: Lesson OverviewAko Si JhadongNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument11 SeitenTopologyAdilet KenesovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument8 SeitenNetwork TopologyChin JosonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Https en Wikipedia Org Wiki Network TopologyDokument10 SeitenHttps en Wikipedia Org Wiki Network TopologysomeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reed's Law: Fully ConnectedDokument5 SeitenReed's Law: Fully ConnectedYeow Ai LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetworktopologyDokument12 SeitenNetworktopologyNemmar CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet and Interanet Question SolutionDokument55 SeitenInternet and Interanet Question SolutionAbhimanyu RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition - What Does Computer Networking Mean?Dokument3 SeitenDefinition - What Does Computer Networking Mean?Kenneth Jed SolomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inside The InternetDokument21 SeitenInside The InternetSuman AhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking 1.2Dokument7 SeitenNetworking 1.2Echo greenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Devices & Network TopologyDokument2 SeitenNetwork Devices & Network TopologyAabbuu MynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topologies Basic Topology TypesDokument9 SeitenTopologies Basic Topology TypesGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN Lab ManualDokument20 SeitenCN Lab ManualShanu GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topology Networks g10Dokument6 SeitenTopology Networks g10Julie BinwagNoch keine Bewertungen
- 91350869202Dokument2 Seiten91350869202NO NameNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Network Topology and Types of Network TopologyDokument13 SeitenWhat Is Network Topology and Types of Network Topology家星Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument7 SeitenNetwork TopologyBijay NagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Computer NetworksDokument32 SeitenTypes of Computer Networksfunny videos lastest songsNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument6 SeitenTopologyParidhi GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 TopologyDokument11 SeitenLesson 4 TopologyHans Maximus NeilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Network TopologyDokument21 Seiten05 Network Topologyksav yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topology Is The Layout Pattern of Interconnections of The VariousDokument3 SeitenNetwork Topology Is The Layout Pattern of Interconnections of The VariousManoj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art IntegratedDokument12 SeitenArt Integratedheanyvoskowskyl.ar.sy.9.48.6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Network Topologies & Control Flow Techniques: Experiment No. 2Dokument8 SeitenStudy of Network Topologies & Control Flow Techniques: Experiment No. 2Lakshmi IyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cables and TopologiesDokument9 SeitenCables and TopologiesRafayetNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Background of ProblemsDokument15 Seiten1.1 Background of ProblemsMohamad YusronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Chapter 4Dokument19 SeitenComputer Networks Chapter 4Anurag DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Networking ConceptDokument37 SeitenGood Networking ConceptRaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 - Network TopologyDokument3 SeitenLesson 4 - Network TopologyGeorgia Andales TaganahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument7 SeitenTopologyMariam ChuhdryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyVon EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingVon EverandComputer Networking Bootcamp: Routing, Switching And TroubleshootingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens ElvDokument222 SeitenSiemens Elvtsraj10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapters 15-17: Transaction Management: Transactions, Concurrency Control and RecoveryDokument67 SeitenChapters 15-17: Transaction Management: Transactions, Concurrency Control and RecoveryImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Replacing The Lifting ColumnDokument24 SeitenReplacing The Lifting ColumnVlady Lopez CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A10Networks App Delivery HandbookDokument3 SeitenA10Networks App Delivery HandbookabaheabaheabaheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs2204 Digital Logic & State Machine Design Spring 2014Dokument2 SeitenCs2204 Digital Logic & State Machine Design Spring 2014Debashish PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Lab ManualDokument43 SeitenElectronics Lab ManualVijay Kr.100% (2)
- Ieee PaperDokument6 SeitenIeee PaperJayant OjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Library Management System Using QR Code A Project SynopsisDokument13 SeitenLibrary Management System Using QR Code A Project SynopsisSaqlain AjmrtyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDC 3217G-C Automotive Controller: MicronasDokument26 SeitenCDC 3217G-C Automotive Controller: Micronas高立璋Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tips To Repair Your ComputerDokument5 SeitenTips To Repair Your ComputerEihkra ZepolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ups EatonDokument2 SeitenUps EatonAntonio HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigging Types and ConceptsDokument24 SeitenRigging Types and ConceptsBoom DizzleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common SoR 2012-13Dokument455 SeitenCommon SoR 2012-13gsgoud1975100% (1)
- Samsung Printer and Toner May Price List - DealerDokument8 SeitenSamsung Printer and Toner May Price List - DealerYu PohChu100% (1)
- Ge Electrologixs xp4 Users Manual 648611Dokument2 SeitenGe Electrologixs xp4 Users Manual 648611Guilherme E.Noch keine Bewertungen
- DN0005 Design Note: A Three Phase Induction Motor Drive Using A V/F ControlDokument5 SeitenDN0005 Design Note: A Three Phase Induction Motor Drive Using A V/F Controlamey thakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- I2c ProtocolDokument28 SeitenI2c Protocolishapatil86Noch keine Bewertungen
- SCA Six Weeks GuidelinesDokument4 SeitenSCA Six Weeks GuidelinesRahul GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helixdelta T5Brochure02 PDFDokument4 SeitenHelixdelta T5Brochure02 PDFKikiDiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo de Servicos I Td226b Eng Rev1 2011Dokument26 SeitenCatalogo de Servicos I Td226b Eng Rev1 2011AndreyIvanov100% (1)
- Khan New ResumeDokument2 SeitenKhan New ResumekhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber-Optic and Satellite CommunicationsDokument20 SeitenFiber-Optic and Satellite CommunicationssujithsundarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Athena Off Road e Atv PDFDokument248 SeitenCatalogo Athena Off Road e Atv PDF851ducatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 ACM Syrian Collegiate Programming ContestDokument13 Seiten2015 ACM Syrian Collegiate Programming ContestZeyad EtmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5600 - Book For Service Engineers Rev 02Dokument339 Seiten5600 - Book For Service Engineers Rev 02Alghany Kennedy100% (3)
- 3G Mobile Wifi 5200mah Power Bank: FeaturesDokument2 Seiten3G Mobile Wifi 5200mah Power Bank: FeaturesClayton MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor MainMemoryDokument18 SeitenSemiconductor MainMemoryShruti ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Motion Controls DPQNNIE-015A400Dokument11 SeitenAdvanced Motion Controls DPQNNIE-015A400Servo2GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Power and Data Efficiency With Threaded Memory ModulesDokument8 SeitenImproving Power and Data Efficiency With Threaded Memory ModulesAnonymous wrX4MtONoch keine Bewertungen