Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ASSMENT1
Hochgeladen von
satoruheineOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ASSMENT1
Hochgeladen von
satoruheineCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
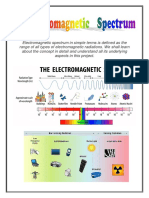
TITLE : Explain definition of Microwave ABSTRACT Around the world we all tune the radio, watch TV, send
a text message, or pop popcorn in a microwave oven, we are using electromagnetic energy. We depend on this energy every hour of every day. Without it, the world we know could not exist. Our Sun is a source of energy across the full spectrum, and its electromagnetic radiation constantly. bombards However, our atmosphere the Earth's
developed a scientific theory to explain electromagnetic waves. He noticed that electrical fields and magnetic fields can couple together to form electromagnetic waves. He summarized this relationship between electricity and magnetism into what are now referred to as "Maxwell's Equations." Heinrich Hertz, a German physicist, applied Maxwell's theories to the production and reception of radio waves. The unit of frequency of a radio wave -one cycle per second -- is named the hertz, in honor of Heinrich Hertz. VISIBLE LIGHT VS INFRARED All electromagnetic radiation is light, but we can only see a small portion of this radiationthe portion we call visible light. Cone-shaped cells in our eyes act as receivers tuned to the wavelengths in this narrow band of the spectrum. Other portions of the spectrum have wavelengths too large or too small and energetic for the biological limitations of our perception. As the full spectrum of visible light travels through a prism, the wavelengths separate into the colors of the rainbow because each color is a different wavelength. Violet has the shortest wavelength, at around 380 nanometers, and red has the longest wavelength, at around 700 nanometers. Infrared waves have longer wavelengths than visible light and can pass through
atmosphere protects us from exposure to a range of higher energy waves that can be harmful to life. Gamma rays, x-rays, and some ultraviolet waves are "ionizing," meaning these waves have such a high energy that they can knock electrons out of atoms. INTRODUCTION Electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. The human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. A radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x-ray machine uses yet another portion. THEORY In the 1860's and 1870's, a Scottish scientist named James Clerk Maxwell
dense regions of gas and dust in space with less scattering and absorption. Thus, infrared energy can also reveal objects in the universe that cannot be seen in visible light using optical telescopes. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has three infrared instruments to help study the origins of the universe and the formation of galaxies, stars, and planets. When we look up at the constellation Orion, we see only the visible light. But NASA's Spitzer space telescope was able to detect nearly 2,300 planet-forming disks in the Orion nebula by sensing the infrared glow of their warm dust. Each disk has the potential to form planets and its own solar system. Credit: Thomas Megeath (Univ. Toledo) et al., JPL, Caltech, NASA. CONCLUSION Electromagnetic waves propagate electric and magnetic energies. The electric field strength E and the magnetic field strength B are perpendicular to each other. The direction of wave motion is perpendicular to E and B. Electromagnetic waves can travel through vacuum, they are planepolarised transverse waves and produced by accelerating charges. The whole range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic waves between a metre and m is REFERENT PHYSICS Volume 2 Cheong Foon Choong Remote Sensing of Environment John R.Jensen
know as the electromagnetic spectrum.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- EM Spectrum Guide in 40 CharactersDokument24 SeitenEM Spectrum Guide in 40 CharactersJedí BelanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument4 SeitenUnderstanding the Electromagnetic SpectrumDenise Marie Dela TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- History: Spectrum IsDokument23 SeitenHistory: Spectrum IsMuhamad NurhudayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument30 SeitenThe Electromagnetic Spectrummaneesh_massey_1100% (1)
- What Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarDokument18 SeitenWhat Can We Learn From The Electromagnetic Spectrum?: A Wjoshi and Alok KumarAndrei Cojanu100% (1)
- Introduction To Electromagnetic WavesDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Electromagnetic WavesDharshana pjr100% (1)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument17 SeitenElectromagnetic SpectrumAviation/Space History Library100% (4)
- Unidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)Dokument32 SeitenUnidad 3 - Espectro Electromagnético (Inglés)bemdasNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Informatio NDokument15 SeitenGeneral Informatio NJenny RoblesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Observations and Measurements of the Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument22 SeitenObservations and Measurements of the Electromagnetic SpectrumOluwaferanmi AwosanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument20 SeitenPhysicsMelanie De SousaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument8 SeitenThe Electromagnetic SpectrumImam A. RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Waves: By: I Nyoman S. (X-8/09) Raka Pandam G. (X-8/21)Dokument11 SeitenElectromagnetic Waves: By: I Nyoman S. (X-8/09) Raka Pandam G. (X-8/21)Nyoman SuryadinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 Electromagnetic WavesDokument45 SeitenLesson 4 Electromagnetic WavesErica QuirobNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTROMAGNETICDokument48 SeitenELECTROMAGNETICMichelle Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation Project PhysicsDokument16 SeitenInvestigation Project Physicskartikdutt.08Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument5 SeitenThe Electromagnetic SpectrumKC KayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWDokument7 SeitenElectromagnetic Waves Class 12 Physics Notes Chapter 8: History of EMWShaku JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Reviewer ScienceDokument7 SeitenGrade 10 Reviewer ScienceAntonette TabilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Energy: Understanding the Power of WavesDokument12 SeitenElectromagnetic Energy: Understanding the Power of WavesJaisha NazNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is Visible Light? Understanding the Spectrum of Light WavesDokument9 SeitenWhat is Visible Light? Understanding the Spectrum of Light WavesJF BatucalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ss3 First Term Physics NoteDokument64 SeitenSs3 First Term Physics NoteAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light: Visible electromagnetic radiation and its propertiesDokument1 SeiteLight: Visible electromagnetic radiation and its propertieslofsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Project 2022-23Dokument28 SeitenPhysics Project 2022-23ZedS1yzNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM WavesDokument2 SeitenEM WavesMyyo TabunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To SS Lecture 2Dokument21 SeitenIntro To SS Lecture 2Muhammad HusnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics1101 - Course MaterialDokument332 SeitenPhysics1101 - Course MaterialAhmad RazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument9 SeitenElectromagnetic SpectrumDhanmeet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDokument42 SeitenSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christine Dianne C. Caisip Teacher IIIDokument82 SeitenChristine Dianne C. Caisip Teacher IIIRyuji ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Physics of LightDokument6 SeitenThe Physics of LightprashantsheetalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Power Transfer and Health EffectsDokument20 SeitenWireless Power Transfer and Health EffectsDevarajanRaghavan0% (1)
- Heat TransferDokument2 SeitenHeat TransferEmmanueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alziya Physics ProjectDokument8 SeitenAlziya Physics ProjectMohammad AyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMSPECTDokument5 SeitenEMSPECTAriana LaynoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Types of Electromagnetic WavesDokument2 Seiten7 Types of Electromagnetic Wavesvee propaganda100% (1)
- What Are Electromagnetic Waves?Dokument8 SeitenWhat Are Electromagnetic Waves?Jay Marie OcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 (B - MARCH 2022Dokument40 SeitenUnit-1 (B - MARCH 2022Vibin SimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateDokument8 SeitenAnatomy of An Electromagnetic Wave - Science Mission DirectorateBhaskarKhersaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EMFT Assignment 5Dokument48 SeitenEMFT Assignment 5M. HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ste Q2-Sci 10 W1-4Dokument24 SeitenSte Q2-Sci 10 W1-4MARK NEIL ARPON100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Yogesh Singh Class: Xii B Submitted To: Ms - Sharaddha NarwariyaDokument36 SeitenChemistry Investigatory Project: Name: Yogesh Singh Class: Xii B Submitted To: Ms - Sharaddha NarwariyaSinghnarwariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Radiation Works: Light Radio)Dokument2 SeitenHow Radiation Works: Light Radio)NabilaPutriClpdhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBJECTIVESDokument7 SeitenOBJECTIVESRegine Estrada JulianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Spectrum ReadingDokument2 SeitenElectromagnetic Spectrum Readingapi-369452118Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDokument21 SeitenSpectroscopy and Its Applicationspkkalai112Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 12 BDokument20 SeitenChemistry Investigatory Project 12 Banitta0% (1)
- Astronomy Basics: See Chart BelowDokument27 SeitenAstronomy Basics: See Chart BelowPrashant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visible Light ExplainedDokument5 SeitenVisible Light ExplainedJef PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument17 Seiten1.1 Electromagnetic SpectrumShreyas SvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Waves: Description: Electromagnetic Waves Are Formed When An Electric Field ComesDokument14 SeitenElectromagnetic Waves: Description: Electromagnetic Waves Are Formed When An Electric Field Comesj_sachin09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gamma Rays: These Are The Most Energetic and Dangerous Form of ElectromagneticDokument4 SeitenGamma Rays: These Are The Most Energetic and Dangerous Form of ElectromagneticmubashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio WavesDokument4 SeitenRadio WavesSophia Nicole ZaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument10 SeitenPresentation On Electromagnetic SpectrumSamuel BellamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument2 SeitenThe Electromagnetic SpectrumMegan CabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- G10 Science Q2 W1 Electromagnetic WavesDokument47 SeitenG10 Science Q2 W1 Electromagnetic WavesnickanormacaraegNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE XII Chemistry Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsDokument21 SeitenCBSE XII Chemistry Project Spectroscopy and Its ApplicationsRichie SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismDokument23 SeitenWhat Is Electromagnetic Energy: Study of ElectromagnetismUma Venkata SumanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itVon EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Office Project - Project1Dokument1 SeiteMicrosoft Office Project - Project1satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5Dokument3 SeitenLab 5satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 9Dokument5 SeitenLab 9satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8Dokument2 SeitenLab 8satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6Dokument3 SeitenLab 6satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument5 SeitenLab 1satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4Dokument3 SeitenLab 4satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3Dokument5 SeitenLab 3satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 7Dokument2 SeitenLab 7satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSMENT7Dokument2 SeitenASSMENT7satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2Dokument6 SeitenLab 2satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title: Automatic Method Used For GeometricDokument3 SeitenTitle: Automatic Method Used For GeometricsatoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSMENT3Dokument2 SeitenASSMENT3satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Concept Antenna Gain With Irradiance: Abstract: in Electromagnetic, An Antenna'sDokument1 SeiteMain Concept Antenna Gain With Irradiance: Abstract: in Electromagnetic, An Antenna'ssatoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review The Effects of Topography and Local Incident Angle On Image BrightnessDokument4 SeitenReview The Effects of Topography and Local Incident Angle On Image BrightnesssatoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- TITLE: Comparison For Different Radar SatDokument3 SeitenTITLE: Comparison For Different Radar SatsatoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title: Different Amplitude Modulation ComparisonDokument3 SeitenTitle: Different Amplitude Modulation ComparisonsatoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSMENT4Dokument1 SeiteASSMENT4satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSMENT5Dokument2 SeitenASSMENT5satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna Gain AsgmentDokument1 SeiteAntenna Gain AsgmentsatoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topographic Normalization LabDokument7 SeitenTopographic Normalization LabsatoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 1 Preprocessing: (Geometric Correction, Atmospheric Correction, Radiometric Correction, Normalization)Dokument20 SeitenTask 1 Preprocessing: (Geometric Correction, Atmospheric Correction, Radiometric Correction, Normalization)satoruheineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gr9 NS (English) November 2021 Question PaperDokument20 SeitenGr9 NS (English) November 2021 Question Paper18118Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 2 Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipDokument24 SeitenChapter - 2 Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipKuba0% (1)
- Journal of Cleaner Production: Agnieszka Woszuk, Lidia Bandura, Wojciech FranusDokument10 SeitenJournal of Cleaner Production: Agnieszka Woszuk, Lidia Bandura, Wojciech FranusCatalinaLixandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology and The Flood of NoahDokument93 SeitenGeology and The Flood of Noahjjp194750% (4)
- CHM1024 Report 3: Identification of HydrocarbonsDokument15 SeitenCHM1024 Report 3: Identification of HydrocarbonsAkmal Adib Fadzil90% (41)
- Ptpu Hidro Cacbon No-Kono-ThomDokument9 SeitenPtpu Hidro Cacbon No-Kono-ThomMai NèNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemscan UV-2150 ManualDokument31 SeitenChemscan UV-2150 ManualTMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Notes For Edx 8.01X "Classical Mechanics"Dokument417 SeitenPhysics Notes For Edx 8.01X "Classical Mechanics"ben TennessenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigerants Q & A 2019bDokument14 SeitenRefrigerants Q & A 2019bJustin MercadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSA+9 Data SheetDokument2 SeitenCSA+9 Data SheetAri WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sun EvolutionDokument7 SeitenSun EvolutionRami AlghamdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Medical Applications of NanotechnologyDokument3 SeitenBio Medical Applications of NanotechnologyPham ThanhTungNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Q3 SLM4 FinalDokument17 SeitenGENERAL CHEMISTRY 2 Q3 SLM4 FinalKairuuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acros Organics Acta N°005Dokument20 SeitenAcros Organics Acta N°005Atomer FormationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecules 24 00714 v2Dokument11 SeitenMolecules 24 00714 v2SyifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (RMU) OCR - Manual - EN - 201909Dokument20 Seiten(RMU) OCR - Manual - EN - 201909Phong DangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co FactorDokument13 SeitenCo FactorMusliza Rashid Noir IpohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2a Theory PDFDokument41 Seiten2a Theory PDF5ChEA DriveNoch keine Bewertungen
- AISI 1015 Carbon Steel (UNS G10150) : Topics CoveredDokument3 SeitenAISI 1015 Carbon Steel (UNS G10150) : Topics CoveredKarthikeyan ShanmugavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NotesDokument55 SeitenNotesKhushi TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsDokument1 SeiteElectric Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muhammad Hamdi Ibrahim - 2110422012 - Water As Plants ComponentsDokument15 SeitenMuhammad Hamdi Ibrahim - 2110422012 - Water As Plants ComponentsHamdi IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- University Physics III Fall 2015 SyllabusDokument4 SeitenUniversity Physics III Fall 2015 SyllabusBrian SeymourNoch keine Bewertungen
- SONY Radio ICF-SW1 Disassembly - RepairDokument9 SeitenSONY Radio ICF-SW1 Disassembly - RepairMicheal speedNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 4 - Final Design ProjectDokument48 SeitenGROUP 4 - Final Design ProjectVince Nixau PadelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis and Spectroscopy of 3D Metal ComplexesDokument34 SeitenSynthesis and Spectroscopy of 3D Metal Complexesmjzapant09100% (1)
- Preinsem PaperDokument1 SeitePreinsem PaperDev PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- CitricAcidProductionTechniquesAndApplicationsDokument25 SeitenCitricAcidProductionTechniquesAndApplicationsj.Madhavi100% (1)
- Catalysis in Organic Chemistry (1922) - Sabbatier PDFDokument442 SeitenCatalysis in Organic Chemistry (1922) - Sabbatier PDFbabithyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AisstatDokument5 SeitenAisstatMarcelo MamaniNoch keine Bewertungen