Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
POGIL - Heat Transfer Modes
Hochgeladen von
Don SekarOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
POGIL - Heat Transfer Modes
Hochgeladen von
Don SekarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
POGIL Heat Transfer Purpose At the end of the activity, students should be able: - To explain modes of heat transfer
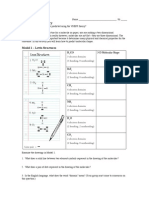
er and understand the mechanism by which each occurs. - To distinguish between methods of heat transfer. Part 1: Heat Transfer We know by now that the transfer of heat occurs always for warmer objects to cooler objects until thermal equilibrium is achieved. At this point, the transfer of heat occurs at the same rate backwards and forwards between the objects. The transfer of heat occurs via three pathways: Conduction The transfer of heat via direct contact of matter is called conduction. Energy is transferred via vibrating atoms or molecules rubbing against other atoms or molecules. The degree to which matter conducts heat depends upon its bonding as well as the presence of mobile valence electrons. Metals tend to be excellent conductors due to their sea of electrons that result from an overlapping of valence shells. Matter with firmly fixed valence electrons are known as insulators. Convection The transfer of heat via the movement of a fluid is called convection. As blobs of matter change temperature, their densities are affected and are buoyed upwards or downwards. Radiation The transfer of heat via electromagnetic waves is called radiation. All matter radiates energy; the higher the energy the higher the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation that is emitted. Key Questions, Part 1: 1. Create a Venn diagram and compare and contrast the three modes of heat transfer.
2. Which modes of heat transfer require a medium? Which does not? Explain why a medium is/is not needed for each response.
Lab Activity & Analysis, Part 1: 1. Obtain a length of copper metal (or other metal) and a cube of shortening. Impale the shortening on one end of the metal and set up the diagram shown below. Light the tea-candle and record your observations.
a. Observations:
b. Explain why this happened.
c.
What would happen if you repeated the experiment, this time substituting the copper wire for a glass rod? Write your prediction below.
d. Try it! Record the outcome and provide an explanation for what happened.
2. Obtain a teabag. Carefully cut the top of the bag off and empty the tea leaves into the garbage. Place the teabag on your desk and light the bag using a match at the top of the bag, as shown in the diagram below.
a. Record your observations and explain what happened.
3. Light a tea-candle and use your observations to respond to the following questions: a. If you place your hand above the tea-candle, you feel its warmth. Via what main method is heat transferring? Explain.
b. If you place your hand to the side of the tea-candle, you feel its warmth, but much less so than in the situation described in 3a. Via what main method is heat transferring? Explain Critical Thinking Questions, Part 1:
1. Many older homes in Chicago and other metropolitan areas rely upon hot water or steam to heat their homes. The hot water or steam is piped to metal radiators, like the one shown below. Often these radiators are placed under windows. (a) Why are the radiators placed beneath the window, as opposed to some other location?
(b) What is the main method of heat transfer using radiators? Explain how the location of the radiators provides a clue to the answer.
2. Why does smoke from a cigar rise, and then settle off?
3. Unlike smoke from a cigar, helium will rise to the very top of the atmosphere. Why is this?
4. Mr. Cook is able to walk over a bed of red-hot coals without harm. Explain how he is able to do this.
5. Imogene is imagining the objects shown in the illustration below. Which of the objects shown continually transfer heat via radiation?
Conclusion In a concise paragraph, thoroughly address the following questions:
How are we affected by each of the types of heat transfer on a daily basis? Why are mediums required for some, but not all of the modes of heat transfer? In homes, much more insulation is placed in the attic than in the walls. What does this indicate about the main mode of heat loss? Identify other ways by which homes are insulated to slow the rate of heat transfer. If you had to design an insulated bottle designed to keep liquids either hot or cold for as long as possible, how would you design the bottle? Include an illustration with your description.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- AccelerationDokument2 SeitenAccelerationMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Heating and Phase ChangesDokument4 SeitenHeating and Phase ChangesMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature and HeatingDokument4 SeitenTemperature and HeatingMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- POGIL - ThermodynamicsDokument4 SeitenPOGIL - ThermodynamicsMar0% (1)
- POGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumDokument5 SeitenPOGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumsydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Bonding WorksheetDokument2 SeitenIonic Bonding WorksheetAnbiya FathimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pogil Describing MotionDokument2 SeitenPogil Describing Motionapi-259781257100% (1)
- Speed and VelocityDokument4 SeitenSpeed and VelocityMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- POGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSDokument3 SeitenPOGIL - Universal Gravitation ANWERSSharmet SolarzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 5 Projectile Motion Circular MotionDokument2 SeitenTutorial 5 Projectile Motion Circular Motionapi-3827354100% (4)
- Grade 8 GuideDokument39 SeitenGrade 8 GuideBreeza Marie VeralloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingDokument3 SeitenTemperature, Thermal Energy, and HeatingMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WavesDokument4 SeitenWavesusman3686Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Lesson Plans - Newtons Laws of MotionDokument4 SeitenUnit 4 Lesson Plans - Newtons Laws of Motionsiti nurhasanahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pogil - Changes of PhaseDokument4 SeitenPogil - Changes of Phaseapi-293306937Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Change POGILDokument4 SeitenPhase Change POGILSarah UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accuracy and Precision POGILDokument10 SeitenAccuracy and Precision POGILmijaggiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Velocity Acceleration Lab PDFDokument6 SeitenVelocity Acceleration Lab PDFUltramixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action and ReactionDokument2 SeitenAction and ReactionMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements Compounds MixturesDokument44 SeitenElements Compounds Mixturesapi-239694539Noch keine Bewertungen
- POGIL: Force: Physics First NameDokument2 SeitenPOGIL: Force: Physics First NameMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScaleDokument4 SeitenScaleMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WavesDokument4 SeitenWavesMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Determining Activity SeriesDokument5 Seiten3 - Determining Activity Seriescarter0% (2)
- Chap 19 No 3Dokument2 SeitenChap 19 No 3api-24977735833% (3)
- Phase-Changes OriginalDokument4 SeitenPhase-Changes Originalapi-293306937Noch keine Bewertungen
- DLP Science Law of AccelerationDokument4 SeitenDLP Science Law of Accelerationezra mark arriesgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AccelerationDokument4 SeitenAccelerationMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Position, Displacement, VelocityDokument3 SeitenPosition, Displacement, VelocityMark Prochaska0% (1)
- Sound WavesDokument91 SeitenSound WavesSarah Mae Lequin ManzanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Dokument4 SeitenCP Spring Scale POGIL 2012 2013Anthony ButlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accuracy and Precision Mini LabDokument6 SeitenAccuracy and Precision Mini LabAlistair Morgan100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDokument8 SeitenLesson Plan in ScienceBALMACEDA DIANA100% (1)
- Working and PowerDokument4 SeitenWorking and PowerMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 1 q1 Week 3Dokument24 SeitenGeneral Physics 1 q1 Week 3Chool Cydrick B. BascosNoch keine Bewertungen
- VectorsDokument2 SeitenVectorsMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biome Poster RubricDokument1 SeiteBiome Poster Rubricapi-359626316Noch keine Bewertungen
- Perante LessonplanDokument6 SeitenPerante LessonplanJelaine Infante RegulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of Motion (Force A Recall)Dokument79 SeitenNewton's Laws of Motion (Force A Recall)Quenie Balanay AgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Third LawDokument3 SeitenNewton's Third LawMark Prochaska100% (1)
- Electric ForceDokument4 SeitenElectric ForceMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Static ElectricityDokument31 Seiten01 Static ElectricitySkyZz CSGONoch keine Bewertungen
- POGIL Molecular GeometryDokument3 SeitenPOGIL Molecular Geometryliza120750% (2)
- Science Lab Equipment Study SheetDokument2 SeitenScience Lab Equipment Study Sheetapi-314843596100% (1)
- COT-demo PPT (3rd Quarter)Dokument54 SeitenCOT-demo PPT (3rd Quarter)Julie ErispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- POGIL - KinematicsDokument4 SeitenPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is An Isotope in Chemistry?: Isotopes Are Atoms With The Same NumberDokument56 SeitenWhat Is An Isotope in Chemistry?: Isotopes Are Atoms With The Same NumberFrancez Anne GuanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Dokument9 SeitenExamview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Tajay Billings100% (1)
- Transverse V Longitudinal Wave Worksheet 2b107dkDokument2 SeitenTransverse V Longitudinal Wave Worksheet 2b107dkNouiea Bernardelle Acabal100% (2)
- Work Power EnergyDokument28 SeitenWork Power Energymarife gupaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergyDokument3 SeitenEnergyMark ProchaskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cecilia Guzman - IdealGasLawSE GizmosDokument8 SeitenCecilia Guzman - IdealGasLawSE GizmosCecilia GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Graders Speed and Velocity Problems With AnswersDokument2 Seiten8th Graders Speed and Velocity Problems With AnswersArunakirinathan AnapayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Momentum & Collisions Nice Check ItDokument67 SeitenChapter 6 Momentum & Collisions Nice Check Itvenkateshyadav2116100% (1)
- Designing POGIL ActivitiesDokument6 SeitenDesigning POGIL ActivitiesCogut Macan DudutzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lab report on conduction, convection and radiationDokument3 SeitenPhysics Lab report on conduction, convection and radiationnouraNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of The Atoms and Atomic StructureDokument38 SeitenHistory of The Atoms and Atomic StructureAndy RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 8 GeneticsDokument2 SeitenSUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 8 GeneticsMelvin Gayta Failagao100% (1)
- Module Thermodynamics 1-4: Colorado State UniversityDokument28 SeitenModule Thermodynamics 1-4: Colorado State UniversityAsyifa Rizqi UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Afternoon!Dokument79 SeitenGood Afternoon!Perlita CarpenteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliance Netconnect+ Postpaid Plans for Wireless BroadbandDokument7 SeitenReliance Netconnect+ Postpaid Plans for Wireless BroadbandDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donot Use It5421Dokument1 SeiteDonot Use It5421Don SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVBKDJVHBDokument1 SeiteDVBKDJVHBDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donot Use It5421Dokument1 SeiteDonot Use It5421Don SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing Setup File OptionsDokument14 SeitenDrawing Setup File OptionsasimbuttNoch keine Bewertungen
- GFFFBHVKDokument1 SeiteGFFFBHVKDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GFFFBHVKDokument1 SeiteGFFFBHVKDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Donot Use ItDokument1 SeiteDonot Use ItDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVBKDJVHBDokument1 SeiteDVBKDJVHBDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Curve Tutorial: Beginner'S Guide To Solidworks BooksDokument8 SeitenComposite Curve Tutorial: Beginner'S Guide To Solidworks Bookssun5555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Curve Tutorial: Beginner'S Guide To Solidworks BooksDokument8 SeitenComposite Curve Tutorial: Beginner'S Guide To Solidworks Bookssun5555Noch keine Bewertungen
- SFLDokument3 SeitenSFLDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bibin Chans ResumeDokument4 SeitenBibin Chans ResumeDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProE QuizDokument3 SeitenProE Quizgmani100% (2)
- Common Log TableDokument2 SeitenCommon Log TableBis ChemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base PaperDokument15 SeitenBase PaperDon SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProE Tutorial1Dokument2 SeitenProE Tutorial1Don SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-Type Air Conditioner Service Manual GuideDokument67 SeitenMulti-Type Air Conditioner Service Manual GuideValfrido BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument9 SeitenAssignment 1Rie UsunNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC DaikinDokument48 SeitenHVAC DaikinSharon LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Unsteady Flow in Rivers Pp. 122-157Dokument37 Seiten5 - Unsteady Flow in Rivers Pp. 122-157Anonymous 87xpkIJ6CFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Specs for 18,000 BTU Portable Water ChillerDokument3 SeitenTechnical Specs for 18,000 BTU Portable Water ChillerPARTHIBAN RETECHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Viva QuestionsDokument4 SeitenHeat Transfer Viva Questionslrkiran83% (59)
- KTA 3205 - 2 - Engl - 2018 - 10 PDFDokument35 SeitenKTA 3205 - 2 - Engl - 2018 - 10 PDFMIKAEL HENRIOTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Workshop Code_Bright Users Barcelona 2017Dokument69 Seiten9th Workshop Code_Bright Users Barcelona 2017Anonymous RYHrtMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fan Coil 3rowsDokument1 SeiteFan Coil 3rowsJunior VelasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Phenomena. Professor Sunando Dasgupta. Department of Chemical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture-28. DragDokument10 SeitenTransport Phenomena. Professor Sunando Dasgupta. Department of Chemical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. Lecture-28. DragGowri ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aissa Thermo1 Chapter 03Dokument81 SeitenAissa Thermo1 Chapter 03De Lacruz KevinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulating Coastal Morphodynamics With Delft3D: Case Study Egmond Aan ZeeDokument78 SeitenSimulating Coastal Morphodynamics With Delft3D: Case Study Egmond Aan ZeeAli MezaalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1x660 MW Sagardighi TPS, Unit 5 BFP Sizing Calculation (PE DC 445 100 N112)Dokument8 Seiten1x660 MW Sagardighi TPS, Unit 5 BFP Sizing Calculation (PE DC 445 100 N112)proloy biswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- REV207 Applications Type of CompressorsDokument86 SeitenREV207 Applications Type of CompressorsDaniel Arbeláez100% (1)
- The principle of complementary energy in nonlinear elasticity theoryDokument10 SeitenThe principle of complementary energy in nonlinear elasticity theoryDaniel VestergaardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Design and Simulation PDFDokument5 SeitenProcess Design and Simulation PDFChemical EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- m316c Escabadora HidraulicaDokument14 Seitenm316c Escabadora HidraulicaRemberto100% (1)
- KTU BTech ME 2019scheme 2019Scheme-MinorsDokument114 SeitenKTU BTech ME 2019scheme 2019Scheme-MinorsLearn Mechanical EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offshore Riser CalculationDokument10 SeitenOffshore Riser CalculationSergio MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- STI65 TNT Radiosity SolverDokument6 SeitenSTI65 TNT Radiosity SolverAnanto Yusuf WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions DPP 3Dokument3 SeitenSolutions DPP 3Tech. VideciousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biaxial Bending of Long ColumnsDokument97 SeitenBiaxial Bending of Long ColumnsSandeep AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 7 NumericalsDokument11 SeitenLesson 7 Numericalssurya kiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reservoir EngineeringDokument147 SeitenReservoir Engineeringjohn ngandouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Thermal Design of Cooling TowersDokument13 SeitenEffective Thermal Design of Cooling TowersKarthick VelayuthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of TDC in Internal Combustion EnginesDokument28 SeitenDetermination of TDC in Internal Combustion EnginesxavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex PDFDokument4 SeitenEx PDFFernandaFerreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1,2.2 AnsweredDokument5 Seiten2.1,2.2 AnsweredgabiaccbackupNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2537 - York YCAS 690Dokument11 Seiten2537 - York YCAS 690Md JamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of SpringsDokument80 SeitenDesign of SpringsRohan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen