Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Antipyretics, Nonopioid Analgesics
Hochgeladen von
Leevi Paul LaviñaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Antipyretics, Nonopioid Analgesics
Hochgeladen von
Leevi Paul LaviñaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
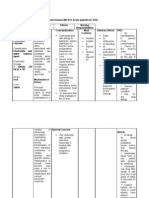
Drug Name/Tra de Name/Gen eric Name/ Classificat ion Acetamino phen(Parac etamol) Classificatio n:n
Dosage/ Route and Frequency
Action
Indication
Contraindication
Side Effects
Nursing Responsibilities
antipyretics, nonopioid analgesics
Inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins that may serve as mediators of pain and fever, primarily in the CNS
Mild to Moderate pain Fever
Previous hypersensitivity Products containing alcohol,asparat ane,sugar, tartrazine.
Hema: hemolytic anemia, neutropenia, leukopenia, pancytopenia. Hepa: jaundice Metabolic: hypoG GI: HEPATIC FAILURE, HEPATOTOXICITY (overdose)GU: renal failure (high doses/chronic use). Derm: rash, urticaria.
BEFORE: ~ Advise parents or caregivers to check concentrations of liquid preparations. Errors have resulted in serious liver damage. ~ Assess fever; note presence of associated signs (diaphoresis, tachycardia, and malaise). ~ Advise mother or caregiver to take medication exactly as directed and not to take more than the recommended amount. AFTER: ~ Advise mother to consult health care professional if discomfort or fever is not relieved by routine doses of this drug or if fever is greater than 39.5C (103F) .
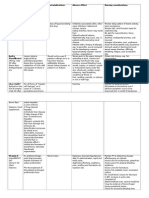
Ferrous Sulfate (Feosol, Feratab) Classificati on: Antianemi c, nutritional Suppleme nt
50mg/capsule & tablet Route: Oral
Acts to normalize RBC production by binding with hemoglobin or by being oxidized and stored as hemosiderin or aggregated ferritin in reticuloendothelia l cells of the liver, spleen and bone marrow. Iron is an essential component of hemoglobin, myoglobin and several enzymes including cytochromes, catalase and perioxidase. Iron is needed for catecholamine metabolism and normal neutrophil function.
To prevent itron deficiency. To replace iron in deficiency states To providfe an iron supplementa tion during pregnancy
Contraindicate d to patients who have hemochromato sis, hemolytic anemia, hemosiderosis, hypersensitivit y to iron salts or their components, other anemic conditions unless accompanied by iron deficiency.
Dizziness Fever Headache Chest pain Tachycardia Abdominal cramps Dyspnea Nausea Stool discoloration vomiting
Give iron tablet and capsules with a full glass of water or juice. Dont crush entericcoated tablets or open capsules. Dilute and administer with a straw or place drops in back of patients throat. Mix the elixir form in water. Protect liquid form from freezing. Monitor patient for signs of overdose which may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, severe vomiting and sharp abdominal cramps. In
Senekot Classificati on: Laxatives
suppository( 312.5 mg) after meals Route: Rectal
Active components of of senna (sennadosides) alter water and electrolyte transport in the large intestine, resulting in the accumulation of water and increased peristalsis.
Treatment of constipation, particularly when associated with: slow transmit time,constip ating drugs,spastic bowel movement,n eurologic constipation.
Contraindicate d in hypertension,a bdominal pain of unknown cause,especiall y with fever, rectal fissures ,ulcerated hemorrhoids,k nown alcohol intolerance. Use cautiously in chronic use(may lead to laxative dependence),p ossible intestinal obstruction, pregnancy or lactation)safet
Diarrhea Cramping Nausea Electrolyte imbalance Pink-red or brown-black Laxative discoloration of urine. Laxative dependence
case of iron toxicity, give deferoxami ne. Dont give tea, antacid or milk because it will decrease iron absorption. Remember that unabsorbed iron turns stool green or black and can mask blood in stool. Assess patient for abdominal disrtention, presence of bowel sounds and usual pattern of bowel function. Assess for color, consistency and amount produced.
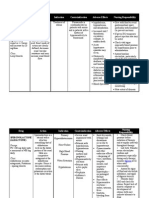
Riopan Classificati on: Antacid
Generally 530ml or 1-2 tablets are given 1-3 hr after meal and at bedtime. Route:Oral
Neutralized gastric acid following dissolution in gastric contentspepsin is inactivated if ph is raised to 4 or greater. Aluminum hydroxide combines with phosphates in the GI tract to form a non absorbable compound.
Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of peptic ulcer pain to promote healing of duodenal and gastric ulcers. Useful in variety of GI complaints including hyperacidity, indigestion, gastroesoph geal reflux disease and heartburn.
Mefenami c Acid Classificati on: NSAID
250 mg tablet Twice a day Route: Oral Onset:Varies Peak: 2-3 hours Duration: 6hours
Antiinflammatory,ana lgesic andantipyretic activitiesrelated to inhibitionof prostaglandinsynt hesis Exact mechanisms of action are not known
Relief of moderate pain when in therapy that will not exceed 1 week. Treatment of primary dysmenorrhe a
y not established: may be used safely during breastfeeding. Contraindicate d in severe abdominal pain of unknown cause .especially if accompanied by fever . Magnesium in anuria ,products containing tartrazine or sugar in patients with known intolerance. Use cautiously in antacids containing magnesium in patients with any degree of renal insufficiency. Contraindicated with hypersensitivit y to mefenamic acid, aspirin allergy, and as treatment of perioperative pain with coronary artery bypass. Use cautiously with asthma, renal or hepatic
Constipation Diarrhea Hypermagnesemi a hypophosphatemi a
Assess for heartburn and indigestion as well s location, duration, character,a nd precipitatin g factors of gastric pain. Monitor serum phosphate , potassium and calcium levels periodically during chronic use.
Headache Dizziness Insomnia Fatigue Rash Pruritis Sweating Nausea Faltulence Constipation Decreased Hgb or Hct Dyspnea Anaphylactoid
Assess patients who develop severe diarrhea and vomiting for dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Discontinue drug promptly if diarrhea, dark stools, hematemesis, ecchymoses, epistaxis, or rash occur and do not use again. Contact physician.
impairment,pe ptic disease, GI bleeding,hypert ension, heartf ailure, pregnancy,lacta tion.
reaction to anaphylactic reaction
Monitor blood glucose for loss of glycemic control if diabetic.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Drug Study (FINAL)Dokument31 SeitenDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology ReviewDokument64 SeitenPharmacology ReviewRichard BakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- FurosemideDokument4 SeitenFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- GI DrugsDokument79 SeitenGI DrugsreecoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument18 SeitenDrug StudyAntonethe DemdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastrointestinal DrugsDokument45 SeitenGastrointestinal DrugsCindy MaslagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument17 SeitenDrug StudyJoan RabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument10 SeitenDrug StudyHelen ReonalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valproic AcidDokument4 SeitenValproic Acidapi-3797941100% (2)
- The Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionVon EverandThe Renal Diet Kitchen: 60+ Quick and Delicious Renal Diet Recipes to Improve Kidney FunctionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDokument12 SeitenDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- Drug StudyDokument3 SeitenDrug StudyBarbara Detaro100% (2)
- Drug StudyDokument9 SeitenDrug StudyJonica CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cimetidine (Drug Study)Dokument2 SeitenCimetidine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument14 SeitenDrug StudyLovely Saad TubañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDokument5 SeitenDrug Therapuetic Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDan DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpironolactoneDokument3 SeitenSpironolactoneapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kalium DuruleDokument3 SeitenKalium DurulenebuchadnezzarkingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- TriamtereneDokument2 SeitenTriamtereneapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- CNS: GI: Assessment & Drug Effects: Generic Name Brand Name Indications Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDokument4 SeitenCNS: GI: Assessment & Drug Effects: Generic Name Brand Name Indications Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJon Adam Bermudez SamatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esomeprazole MagnesiumDokument3 SeitenEsomeprazole Magnesiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study RanitidineDokument1 SeiteDrug Study RanitidineSEAN PATRICK SILADANNoch keine Bewertungen
- FUROSEMIDEDokument6 SeitenFUROSEMIDEPark JeongyeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmotic LaxativesDokument2 SeitenOsmotic LaxativesACanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugDokument36 SeitenDruggecalian100% (1)
- Furosemide: Online AudioDokument4 SeitenFurosemide: Online AudioDani PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDokument5 SeitenDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoana Marie GuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs StudyDokument35 SeitenDrugs StudyMark CapillanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument44 SeitenDrug StudyLohrhen Lheighh CahreeniyowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenCHF Drug StudyAiza Apelada-NievaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Printed Material Module 7 Gastrointestinal System Drugs - PDFDokument45 SeitenPrinted Material Module 7 Gastrointestinal System Drugs - PDFShang MacarayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Part 5B. Parathyroid AgentsDokument21 SeitenModule 1 Part 5B. Parathyroid AgentsBSN2G- SABLA-ON LORRAINE ANNENoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Name Classifi-Cation Action Indication / Uses Common Adverse Effects Contra-Indications Nursing ConsiderationsDokument5 SeitenGeneric Name Classifi-Cation Action Indication / Uses Common Adverse Effects Contra-Indications Nursing ConsiderationsMe-joy CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs Affecting The Gi Tract: Myla M - Guadiz, R.N., M.A.NDokument37 SeitenDrugs Affecting The Gi Tract: Myla M - Guadiz, R.N., M.A.NRachel CabiguenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drugs GCDokument7 SeitenDrugs GCJharene BasbañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parathyroid AgentsDokument33 SeitenParathyroid AgentsFaith madayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument8 SeitenDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument96 SeitenDrug StudyirismirzigNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI DrugsDokument35 SeitenGI DrugsIconMaicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: History: Hypersensitivity To Any Xanthine or ToDokument2 SeitenDrug Study: History: Hypersensitivity To Any Xanthine or ToJean De Vera MelendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTP DM ParesisDokument4 SeitenHTP DM ParesisTami GemarinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Tract - Nutrition/EliminationDokument51 SeitenGI Tract - Nutrition/Eliminationnick_nock08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study: GENERIC NAME: Acetaminophen TRADE NAME: TylenolDokument3 SeitenDrug Study: GENERIC NAME: Acetaminophen TRADE NAME: TylenolLinda AdamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic UlcerDokument7 SeitenPeptic UlcerNyakie MotlalaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec (10) Word G I TDokument9 SeitenLec (10) Word G I TAhmed EngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potassium Salts Drug StudyDokument2 SeitenPotassium Salts Drug StudyCheezy BreadNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Dokument7 SeitenHEMOdrug Study (Jul 2013)Leoni HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Januvia, Amlodipine, FurosemideDokument4 SeitenJanuvia, Amlodipine, Furosemideyummy_17100% (1)
- Furosemide DSDokument2 SeitenFurosemide DSjhanrey0810_18768Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fosinopril SodiumDokument3 SeitenFosinopril Sodiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- RamiprilDokument3 SeitenRamiprilMichael KuzbytNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indications: Drug Study Kalium DuruleDokument1 SeiteIndications: Drug Study Kalium DurulemelissagabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVS PART 1 DiureticsDokument31 SeitenCVS PART 1 Diureticshishamasmaa5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 8Dokument3 SeitenDrug Study 8Vicky RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vi. Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsDokument4 SeitenVi. Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsMilton CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRUG PantoprazoleDokument1 SeiteDRUG PantoprazoleEngelbert CruzNoch keine Bewertungen