Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
C Programming Lab Programs
Hochgeladen von
ans_h2003Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
C Programming Lab Programs
Hochgeladen von
ans_h2003Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
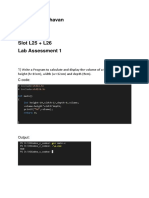
Exercise 1 Solving problems such as temperature conversion, student grading, income tax calculation, etc which expose the
students to use basic C operators. a) Temperature Conversion from Fahrenheit to Celsius. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { float f,c; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter Temperature in F: "); scanf("%f",&f); c=5.0/9*(f-32); printf(" Temperature in C: %f",c); getch(); } Output Enter Temperature in F: 98 Temperature in C: 36.666668 b) Student grading based on his percentage. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int p; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter Percentage: "); scanf("%d",&p); if(p>=70) printf(" Distinction"); else if(p>=60&&p<70) printf(" First class"); else if(p>=50&&p<60) printf(" Second class");
else if(p>=40&&p<50) printf(" Third class"); else printf(" Fail"); getch(); } Output Enter Percentage: 73 Distinction
c) Average of three numbers Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a,b,c; float avg; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter a,b,c: "); scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); avg=(float)(a+b+c)/3; printf(" Avg: %f",avg); getch(); } Output Enter a,b,c: 62 45 90 Avg: 65.666664
d) Largest among three numbers Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a,b,c; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter a,b,c: "); scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); if(a>b) { if(a>c) printf(" a is large"); else printf(" c is large"); } else if(b>c) printf(" b is large"); else printf(" c is large"); getch(); } Output Enter a,b,c: 5 9 3 b is large
e) Income Tax calculation 0 2000000% 200000 30000010% 300000 50000020% Above 500000 Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { long int a,tax=0; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter amount: "); scanf("%ld",&a); if(a<=200000) tax=0; else if(a>200000&&a<=300000) tax=(a-200000)*10/100; else if(a>300000&&a<=500000) tax=10000+(a-300000)*20/100; else if(a>500000) tax=50000+(a-500000)*30/100; printf(" Tax: %ld",tax); getch(); } Output Enter amount: 600000 Tax: 80000
30%
Exercise 2 2s complement of a number is obtained by scanning it from right to left and complementing all the bits after the first appearance of a 1. Thus 2s complement of 11100 is 00100. Write a C program to find the 2s complement of a binary number. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> void main() { char a[20]; int i,j,k,len; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter Binary string: "); gets(a); len=strlen(a); for(k=0;a[k]!='\0';k++) { if(a[k]!='0'&&a[k]!='1') { printf(" Incorrect Binary number..."); getch(); exit(0); } } for(i=len-1;a[i]!='1';i--); for(j=i-1;j>=0;j--) { if(a[j]=='1') a[j]='0'; else a[j]='1'; } printf(" 2's complement: %s",a);
getch(); } Output Enter Binary string: 110101010 2's complement: 001010110 Exercise 3 a) Write a C Program to find the sum of individual digits of a positive integer Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int n,sum=0; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); if(n<0) { printf("Enter positive integer.."); } else { while(n!=0) { sum=sum+n%10; n=n/10; } printf(" Sum of individual digits: %d",sum); } getch(); } Output Enter n: 2346 Sum of individual digits: 15
b) A Fibonacci sequence is defined as follows: the first and second terms in the sequence are 0 and 1. Subsequent terms are found by adding the preceding two terms in the sequence. Write a C program to generate the first n terms of the sequence. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a=0,b=1,c,n,i; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); printf("\n The Fibonacci sequence...\n"); printf(" %d\n %d",a,b); for(i=3;i<=n;i++) { c=a+b; printf("\n %d",c); a=b; b=c; } getch(); } Output Enter n: 10 The Fibonacci sequence 0 1 1 2 3 5 8
13 21 34
c) Write a C program to generate all the prime numbers between 1 and n, where n is a value supplied by the user. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int i,j,n,count=0; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); printf(" Prime numbers between 1 and %d are...",n); for(i=2;i<=n;i++) { count=0; for(j=2;j<=i-1;j++) { if(i%j==0) count++; } if(count==0) printf("\n %d",i); } getch(); } Output Enter n: 45 Prime numbers between 1 and 45 are... 2 3 5 7 11 13 17
19 23 29 31 37 41 43 d) Write a program which checks a given integer is Fibonacci number or not Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int n,i,a[20],count=0; clrscr(); a[0]=0; a[1]=1; for(i=2;i<20;i++) { a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i-2]; } printf("\n Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=0;i<20;i++) { if(n==a[i]) { count++; break; } } if(count>0) printf(" Fibonacci number..."); else printf(" Not a fibonacci number..."); getch(); } Output Enter n: 144 Fibonacci number...
Exercise 4 a) Write a C program to calculate the following Sum: Sum=1-x2/2! +x4/4!-x6/6!+x8/8!-x10/10! Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> void main() { long int i,t,f=1,k=1; float sum=1.0,x; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter x: "); scanf("%f",&x); for(i=2;i<=10;i=i+2) { t=i; while(t!=0) { f=f*t; t--; } sum=sum+(pow(-1,k)*pow(x,i))/(float)f; k++; f=1; } printf("\n The Sum of Series: %f",sum); getch(); } Output Enter x: 2 The Sum of Series: -0.416155
10
b) Write a C program toe find the roots of a quadratic equation. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> void main() { float a,b,c,d,p,q,x1,x2; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter a,b,c: "); scanf("%f%f%f",&a,&b,&c); d=b*b-4*a*c; if(d==0) { printf(" Roots are real and equal..."); printf("\n x1=x2=%f",-b/(2*a)); } else if(d>0) { printf(" Roots are real..."); x1=(-b+sqrt(d))/(2*a); x2=(-b-sqrt(d))/(2*a); printf("\n x1=%f \n x2=%f",x1,x2); } else //if(d<0) { printf(" Roots are imaginary..."); p=-b/(2*a); q=sqrt(-d)/(2*a); if(q<0) printf("\n x1=%f+i%f x2=%f-i%f",p,-q,p,-q); else printf("\n x1=%f+i%f x2=%f-i%f",p,q,p,q); } getch();
11
} Output Enter a,b,c: 4 4 1 Roots are real and equal... x1=x2=-0.500000
Exercise 5 a) The total distance traveled by vehicle in t seconds is given by distance = ut+1/2at2 where u and a are the initial velocity (m/sec.) and acceleration (m/sec2). Write C program to find the distance traveled at regular intervals of time given the values of u and a. The program should provide the flexibility to the user to select his own time intervals and repeat the calculations for different values of u and a. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { float s,a,u; int t,n; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter Time Intervals: "); scanf("%d",&n); for(t=0;t<=n;t++) { printf(" Enter u and a: "); scanf("%f%f",&a,&u); s=u*t+0.5*a*t*t; printf(" Distance traveled at %d time interval: %f \n",t,s); } getch(); } Output Enter Time Intervals: 2 Enter u and a: 2 7 Distance traveled at 0 time interval: 0.000000 Enter u and a: 4 9 Distance traveled at 1 time interval: 11.000000 Enter u and a: 3 4
12
Distance traveled at 2 time interval: 14.000000
b) Write a C program, which takes two integer operands and one operator form the user, performs the operation and then prints the result. (Consider the operators +,-,*, /, % and use Switch Statement) Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a,b,c; char op; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter a,b: "); scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); printf(" Enter Operator (+,-,*,/,%): "); op=getche(); switch(op) { case '+': c=a+b; break; case '-': c=a-b; break; case '*': c=a*b; break; case '/': c=a/b; break; case '%': c=a%b; break; default : printf("\n Enter correct operator.."); getch(); exit(0); } printf("\n Result: %d",c); getch(); } Output Enter a,b: 87 34 Enter Operator (+,-,*,/,%): % Result: 19 13
Exercise 6 a) Simple programming examples to manipulate strings. Program #include<string.h> void main() { char a[10]="srinivas",b[10]="KRISHNA",c[10]="srinivas",d[10],e[20]; int len; clrscr(); len=strlen(a); printf("\n Length=%d",len); strcpy(d,a); printf("\n %s",d); strcpy(e,a); strcat(e,b); printf("\n %s",e); strrev(d); printf("\n %s",d); strlwr(b); printf("\n %s",b); strupr(a); printf("\n %s",a); if(strcmp(a,c)==0) //compares with case sensitivity printf("\n Two strings are equal "); else printf("\n Two strings are not equal"); if(stricmp(a,c)==0) //compares without case sensitivity printf("\n Two strings are equal"); else printf("\n Two strings are not equal"); getch(); } Output
14
Length=8 srinivas srinivasKRISHNA savinirs krishna SRINIVAS Two strings are not equal Two strings are equal b) Verifying a string for its palindrome property Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { char a[20]; int len,i; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter String: "); gets(a); len=strlen(a); for(i=0;i<len/2;i++) { if(a[i]==a[len-1]) len--; else { printf("\n Not Palindrome..."); getch(); exit(); } } printf("\n Palindrome"); getch(); } Output Enter String: srinirs Palindrome
15
Exercise 7 Write a C program that uses functions to perform the following operations i) To insert a sub-string in to given main string from a given position. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { int i,p,n,r,k,j=0; char a[20],b[10],c[30]; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter the Main String: "); gets(a); printf(" Enter the String to insert: "); gets(b); printf(" Enter position to insert: "); scanf("%d",&p); n=strlen(a); r=strlen(b); for(i=0;i<p-1;i++) c[i]=a[i]; k=i; for(i=p-1;i<p+r-1;i++) c[i]=b[j++]; for(i=p+r-1;i<n+r;i++) c[i]=a[k++]; c[i]='\0'; printf(" Resultant String: %s",c); getch(); } Output
16
Enter the Main String: srinivas Enter the String to insert: Hari Enter position to insert: 4 Resultant String: sriHarinivas
ii) To delete n Characters from a given position in a given string. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { char a[20]; int i,p,len,n,k; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter String: "); gets(a); len=strlen(a); printf(" Enter Position: "); scanf("%d",&p); printf(" Enter Number of chars to delete: "); scanf("%d",&n); k=p+n-1; for(i=p-1;i<len-n;i++) a[i]=a[k++]; a[i]='\0'; printf(" Resultant String: %s",a); getch(); } Output Enter String: srinivas Enter Position: 4 Enter Number of chars to delete: 2 Resultant String: srivas
17
iii) To replace a character of a string either from beginning or ending or at a specified location. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { char a[20],ch; int choice,pos,len; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter string: "); gets(a); printf(" 1.At Begin \n 2.At End \n 3.At position \n"); printf(" Enter choice: "); scanf("%d",&choice); switch(choice) { case 1: printf(" Enter character to replace at begin: "); ch=getche(); a[0]=ch; printf("\n New string: %s",a); break; case 2: printf(" Enter character to replace at end: "); ch=getche(); len=strlen(a); a[len-1]=ch; printf("\n New string: %s",a); break; case 3: printf(" Enter character to replace at given position: "); ch=getche(); printf("\n Enter position: "); scanf("%d",&pos); a[pos-1]=ch; printf(" New string: %s",a); break;
18
default:printf(" Enter correct choice"); break; } getch(); }
Output Enter string: sri nivas 1.At Begin 2.At End 3.At position Enter choice: 1 Enter character to replace at begin: Q New string: Qri nivas Enter string: sri nivas 1.At Begin 2.At End 3.At position Enter choice: 2 Enter character to replace at end: W New string: sri nivaW Enter string: sri nivas 1.At Begin 2.At End 3.At position Enter choice: 3 Enter character to replace at given position: Z Enter position: 4 New string: sriZnivas
19
Exercise 8 Write a C program that uses functions to perform the following operations: i) Reading a complex number ii) Writing a complex number iii) Addition of two complex numbers iv) Multiplication of two complex numbers Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> struct complex add(struct complex a,struct complex b); struct complex mul(struct complex a,struct complex b); void write(struct complex s); struct complex read(); struct complex { float r,i; }; void main() { struct complex a,b,c; int ch; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter Real and Imag for 1st Complex Number: "); a=read(); printf("\n Enter Real and Imag for 2nd Complex Number: "); b=read(); printf("\n 1.Add \n 2.Multiplication "); printf("\n Enter choice: "); scanf("%d",&ch); switch(ch) {
20
case 1 : c=add(a,b); write(c); break; case 2 : c=mul(a,b); write(c); break; default: printf("\n Enter Correct choice.."); break; } getch(); } struct complex read() { struct complex s; scanf("%f%f",&s.r,&s.i); return s; } struct complex add(struct complex a,struct complex b) { struct complex s; s.r=a.r+b.r; s.i=a.i+b.i; return s; } struct complex mul(struct complex a,struct complex b) { struct complex s; s.r=a.r*b.r-a.i*b.i; s.i=a.r*b.i+a.i*b.r; return s; } void write(struct complex s) { if(s.i>0) printf("\n Result=%f+i%f",s.r,s.i); else printf("\n Result=%f-i%f",s.r,-1*s.i); } Output Enter Real and Imag for 1st Complex Number: 3 -2 Enter Real and Imag for 2nd Complex Number: -5 6
21
1.Add 2.Multiplication Enter choice: 2 Result=-3.000000+i28.000000
Exercise 9 a) Addition of two matrices Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a[4][4],b[4][4],c[4][4],i,j,m,n,p,q; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter Order for 1st Matrix: "); scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); printf("\n Enter Order for 2nd Matrix: "); scanf("%d%d",&p,&q); if((m==p)&&(n==q)) { printf("\n Enter 1st Matrix elements: "); for(i=0;i<m;i++) { for(j=0;j<n;j++) { scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); } } printf("\n Enter 2nd Matrix elements: "); for(i=0;i<p;i++) { for(j=0;j<q;j++) { scanf("%d",&b[i][j]); } } printf("\n Addition of two matrices: \n"); for(i=0;i<m;i++) {
22
for(j=0;j<n;j++) { c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j]; printf("%d \t",c[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } } else { printf("\n Addition not possible..."); } getch(); } Output Enter Order for 1st Matrix: 3 2 Enter Order for 2nd Matrix: 3 2 Enter 1st Matrix elements: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Enter 2nd Matrix elements: 6 5 4 3 2 1 Addition of two matrices: 7 7 7 7 7 7
23
b) Calculating transpose of matrix in-place manner Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a[4][4],b[4][4],i,j,m,n; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter Order for matrix: "); scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); printf(" Enter Matrix elements: "); for(i=0;i<m;i++) { for(j=0;j<n;j++) { scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); b[j][i]=a[i][j]; } } printf(" Transpose of Matrix: "); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("\n"); for(j=0;j<m;j++) { printf("%d \t",b[i][j]); } } getch(); } Output Enter Order for matrix: 3 4 Enter Matrix elements:
24
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Transpose of Matrix: 1 5 9 2 6 10 3 7 11 4 8 12 c) Matrix Multiplication by checking compatibility Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a[4][4],b[4][4],c[4][4],i,j,m,n,p,q,k; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter Order for 1st Matrix: "); scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); printf("\n Enter Order for 2nd Matrix: "); scanf("%d%d",&p,&q); if(n==p) { printf("\n Enter 1st Matrix elements: "); for(i=0;i<m;i++) { for(j=0;j<n;j++) { scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); } } printf("\n Enter 2nd Matrix elements: "); for(i=0;i<p;i++) { for(j=0;j<q;j++) { scanf("%d",&b[i][j]); } } printf("\n Multiplication of two matrices: \n"); for(i=0;i<m;i++) { for(j=0;j<q;j++) {
25
c[i][j]=0; for(k=0;k<n;k++) c[i][j]=c[i][j]+a[i][k]*b[k][j]; printf("%d \t",c[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } } else { printf("\n Multiplication not possible..."); } getch(); } Output Enter Order for 1st Matrix: 3 3 Enter Order for 2nd Matrix: 3 2 Enter 1st Matrix elements: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Enter 2nd Matrix elements: 6 5 4 3 2 1 Multiplication of two matrices: 20 14 56 41 92 68
26
Exercise 10 a) Write C programs that use both recursive and non-recursive functions. i) To find the factorial of a given integer. Program using Non-Recursive #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int f=1,i,n; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { f=f*i; } printf("\n Factorial of %d is: %d",n,f); getch(); } Output Enter n: 7 Factorial of 7 is: 5040
Program using Recursive #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main()
27
{ int f,i,n; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); printf("\n Factorial of %d is: %d",n,fact(n)); getch(); } int fact(int n) { int p; if(n==1) return 1; else p=n*fact(n-1); return p; } Output Enter n: 7 Factorial of 7 is: 5040 ii) To find the GCD (greatest common divisor) of two given integers. GCD using Non-Recursive #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a,b,gcd,i,m; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter a,b: "); scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); if(a>b) m=b; else m=a; for(i=1;i<=m;i++) { if(a%i==0&&b%i==0) gcd=i;
28
} printf("\n GCD of %d and %d is: %d",a,b,gcd); getch(); } Output Enter a,b: 36 24 GCD of 36 and 24 is: 12 GCD using Recursive #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a,b; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter a,b: "); scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); printf("\n GCD of %d and %d is: %d",a,b,gcd(a,b)); getch(); } int gcd(int a,int b) { if(b>a) return gcd(b,a); if(b==0) return a; else return gcd(b,a%b); } Output Enter a,b: 36 24 GCD of 36 and 24 is: 12 iii) To solve Towers of Hanoi problem. Program using Recursive #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void towers(int n,char src, char target, char temp); void main()
29
{ int n; clrscr(); printf("\n How Many disks: "); scanf("%d",&n); towers(n,'A','C','B'); getch(); } void towers(int n, char src, char target, char temp) { if(n==1) { printf("\n Move top disk from %c to %c",src,target); return; } towers(n-1,src,temp,target); printf( "\n Move top disk from %c to %c",src,target); towers(n-1,temp,target,src); } Output How Many disks: 4 Move top disk from A to B Move top disk from A to C Move top disk from B to C Move top disk from A to B Move top disk from C to A Move top disk from C to B Move top disk from A to B Move top disk from A to C Move top disk from B to C Move top disk from B to A Move top disk from C to A Move top disk from B to C Move top disk from A to B Move top disk from A to C Move top disk from B to C
30
Exercise 11 a) Write a C Function to find both largest and smallest numbers of an array of integers. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a[10],n,i,max,min; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); printf(" Enter elements: "); for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); min=max=a[0]; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { if(a[i]<min) min=a[i]; if(a[i]>max) max=a[i]; } printf(" Largest=%d \n Smallest=%d ",max,min); getch(); } Output Enter n: 6 Enter elements: 1 5 -65 8 936
31
421 Largest=936 Smallest=-65
b) Write a C function that uses functions to perform the following. i) Write a C program that displays the position or index in the string S where the string T begins, or 1 if S doesnt contain T. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { char s[20],t[10],*found; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter String: "); gets(s); printf(" Enter Substring to find: "); gets(t); found=strstr(s,t); if(found) printf(" Found at %d position...",found-s+1); else printf(" Substring not found..."); getch(); } Output Enter String: srinivas Enter Substring to find: iva Found at 6 position ii) Write a C program to count the lines, words and characters in a given text. Program
32
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> void main() { char a[80],ch; int i,k,end=0,nc=0,nw=0,nl=0; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter the Text and press ENTER at end..\n"); while(end==0) { k=0; while((ch=getchar())!='\n') a[k++]=ch; a[k]='\0'; if(a[0]=='\0') break; else { nw++; for(i=0;a[i]!='\0';i++) { if(a[i]==' '||a[i]=='\t') nw++; } } nl=nl+1; nc=nc+strlen(a); } printf("\n Number of Lines : %d",nl); printf("\n Number of Words : %d",nw); printf("\n Number of Characters: %d",nc); getch(); } Output Enter the Text and press ENTER at end.. Hello World How are you !!!!
33
Number of Lines :2 Number of Words : 6 Number of Characters: 27
Exercise 12 a) Write a C function to generate Pascals triangle. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int p=1,y=0,i,r,x; clrscr(); printf("\n Rows you want to input: "); scanf("%d",&r); printf("\n Pascal's Triangle:\n"); while(y<r) { for(i=40-3*y;i>0;i--) printf(" "); for(x=0;x<=y;x++) { if((x==0)||(y==0)) p=1; else p=(p*(y-x+1))/x; printf("%6d",p); } printf("\n"); y++; } getch(); } Output Rows you want to input: 6
34
Pascal's Triangle: 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 4 2 1 1 3 1 6 4 1 5 10 10 5 1
b) Write a C function to construct a pyramid of numbers. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int n,i,y,x=35; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter n: "); scanf("%d",&n); printf("\n Pyramid Triangle \n"); for(y=0;y<=n;y++) { gotoxy(x,y+4); for(i=-y;i<=y;i++) printf("%2d",abs(i)); x=x-2; } getch(); } Output Enter n: 4 Pyramid Triangle 0 101 21012 3210123 432101234
35
Exercise 13 Write a C program to read in two numbers, x and n, and then compute the sum of this geometric progression: 1+x+x2+x3+.+xn Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> void main() { int i,x,n; long int sum; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter the values for x and n: "); scanf("%d%d",&x,&n); if(n<=0||x<=0) { printf("\n Value is not valid.."); getch(); main(); } else { sum=1; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) { sum=sum+pow(x,i); } printf("\n Sum of series: %ld",sum); } getch(); } Output
36
Enter the values for x and n: 5 3 Sum of series: 156
Write a C function to read in two numbers, x and n (number of terns) and then compute sin(x) and cos(x). cos(x)=1-x2/2!+x4/4!-x6/6!+x8/8!-. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> void main() { long int i,t,f=1,k=1,n; float sum=1,x; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter x: "); scanf("%f",&x); printf(" Enter n: "); scanf("%ld",&n); for(i=2;i<n*2;i=i+2) { t=i; while(t!=0) { f=f*t; t--; } sum=sum+(pow(-1,k)*pow(x,i))/f; k++; f=1; } printf("\n cos(x)= %f",sum); getch(); } Output
37
Enter x: 2 Enter n: 6 cos(x)= -0.416155
sin(x)=x-x3/3!+x5/5!-x7/7!+x9/9!-. Program #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<math.h> void main() { long int i,t,f=1,k=1; float sum,x; clrscr(); printf("\n Enter x: "); scanf("%f",&x); printf(" Enter n: "); scanf("%ld",&n); sum=x; for(i=3;i<n*2;i=i+2) { t=i; while(t!=0) { f=f*t; t--; } sum=sum+(pow(-1,k)*pow(x,i))/f; k++; f=1; } printf("\n sin(x)= %f",sum); getch(); } Output Enter x: 2 Enter n: 4
38
sin(x)= 0.907937
39
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- C Language Basic Programs Which Used For BigginnersDokument112 SeitenC Language Basic Programs Which Used For BigginnersRavikumar VendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-Program-SolutionsDokument40 SeitenC-Program-SolutionssampurnakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- C & C++ Sem 2 Practical SolutionsDokument13 SeitenC & C++ Sem 2 Practical SolutionsShiva Krishna KondaparthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 1Dokument13 SeitenPractical 1SpideyhNoch keine Bewertungen
- C LabDokument33 SeitenC LabMogili sivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C ProgramsDokument27 SeitenC ProgramsKarthica ArumugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of C ProgrammingDokument19 SeitenAssessment of C Programmingप्रविणअर्यालNoch keine Bewertungen
- C&C++ RecordDokument33 SeitenC&C++ RecordluckyabhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C ProgramsDokument45 SeitenC ProgramsNEERNoch keine Bewertungen
- C AssignmentsDokument120 SeitenC AssignmentsAnonymous i9myaLNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Program Assignments - Matrices, Strings, ArraysDokument20 SeitenC Program Assignments - Matrices, Strings, ArrayssachinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find Out The Perfect Number Using C ProgramDokument13 SeitenFind Out The Perfect Number Using C ProgramM UsmithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming StructureDokument20 SeitenC Programming StructureCGA 21-22Noch keine Bewertungen
- #Include #Include Int Main Int A, B, C Double X, Y, DDokument22 Seiten#Include #Include Int Main Int A, B, C Double X, Y, DChinnaraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- StudyDokument12 SeitenStudytrxxx.axxNoch keine Bewertungen
- C ProgramDokument9 SeitenC ProgramMuddassir kammarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee 152Dokument35 SeitenEee 152rushoeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DA1 SolutionDokument32 SeitenDA1 SolutionPARTH SUNIL CHAVAN 20BCI0055Noch keine Bewertungen
- LabProgramsBCA 1Dokument33 SeitenLabProgramsBCA 1nandishimurgodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical File ON Programming For Problem Solving Lab (: 21BTCS181)Dokument15 SeitenPractical File ON Programming For Problem Solving Lab (: 21BTCS181)Vaibhavi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programs For C Building Blocks:: 1. WAP in C To Print "HELLO WORLD"Dokument86 SeitenPrograms For C Building Blocks:: 1. WAP in C To Print "HELLO WORLD"Gautam VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C ProgramsDokument25 SeitenC Programsshubham shrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACP ProgramsDokument89 SeitenACP Programsmangalmakwana1997Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cse Lab ReportDokument36 SeitenCse Lab ReportShafi Muhammad IstiakNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-Lab ManualDokument59 SeitenC-Lab ManualAaron GurramNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Program Notes For Vintage AcademyDokument32 SeitenC Program Notes For Vintage Academysanjoyvintage5Noch keine Bewertungen
- C ProgramsDokument133 SeitenC ProgramsKulakarni KarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Test 1Dokument11 SeitenComputer Test 1Victor NjisweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Programming: Mayank Sharma 40516100418 Btech BceDokument27 SeitenComputer Programming: Mayank Sharma 40516100418 Btech BceAnkit sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming ExercisesDokument26 SeitenC Programming Exercisestanjim1100% (2)
- C Demo ProgramsDokument15 SeitenC Demo Programsradhikagarg0210Noch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming Lab Codes for Converting Temperature, Calculating Grades, Finding Factorial etcDokument40 SeitenC Programming Lab Codes for Converting Temperature, Calculating Grades, Finding Factorial etcSaiindra ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- C RecordDokument28 SeitenC RecordDragu StelianNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS Lab File-1Dokument115 SeitenCS Lab File-1Muhammad Khursheed Aqueeb SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCP Lab ManualDokument36 SeitenCCP Lab ManualChiranth BONoch keine Bewertungen
- C Lab ProgrammingDokument47 SeitenC Lab ProgrammingSandhya KandikatlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Lab Problems and SolutionsDokument37 SeitenC Lab Problems and Solutionspramod_076Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question:1 Write A Program To Generate Fibonacci Series, Using RecursionDokument9 SeitenQuestion:1 Write A Program To Generate Fibonacci Series, Using RecursionPiyush BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write A C Program To Add Any 10 Numbers Given by The UserDokument10 SeitenWrite A C Program To Add Any 10 Numbers Given by The Useravijit babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- C AssignmentDokument10 SeitenC AssignmentAparanjini PallelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Board Question C Program SolveDokument33 SeitenBoard Question C Program SolvedfdasfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amcat Automata Questions PDFDokument75 SeitenAmcat Automata Questions PDFnav0% (1)
- C Programming Examples and Codes for BeginnersDokument130 SeitenC Programming Examples and Codes for BeginnersDevi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programming Complete Lab 1-17Dokument41 SeitenC Programming Complete Lab 1-17MURALI KARTHIK REDDYNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Program 2Dokument35 SeitenC Program 2oasisolgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Programs to Calculate Sum of Digits, Fibonacci Series, Prime Numbers etcDokument80 SeitenC Programs to Calculate Sum of Digits, Fibonacci Series, Prime Numbers etckishore kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPPMDokument10 SeitenCPPMYASH PATELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clab Internal1 PDFDokument19 SeitenClab Internal1 PDFaaaaaaaasdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fibonacci Series Generator in CDokument28 SeitenFibonacci Series Generator in Ckamera mounikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical File Of “Programming for problem solvingDokument70 SeitenPractical File Of “Programming for problem solvingrohit bishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Sample ProgramsDokument35 SeitenC Sample ProgramsrajalakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code List With CodeDokument22 SeitenCode List With Codetareqabdullah19Noch keine Bewertungen
- FCS Lab Programs (21-11-22)Dokument6 SeitenFCS Lab Programs (21-11-22)Allen JoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yugal Limbu Bce096 Lab Sheet No.5Dokument38 SeitenYugal Limbu Bce096 Lab Sheet No.5khagendra SenchuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTC Lab Record by 20B01A12A7Dokument32 SeitenCTC Lab Record by 20B01A12A7rutvik saiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Coding Examples 1Dokument11 SeitenC Coding Examples 1Sarthak RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- C ProgramDokument60 SeitenC Programpd03487Noch keine Bewertungen
- SQADokument32 SeitenSQAans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Control Structure: Loop: Prof. Kuanquan WangDokument45 SeitenChapter 4 Control Structure: Loop: Prof. Kuanquan Wangans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data CommunicationDokument7 SeitenData Communicationans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- SortDokument54 SeitenSortans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Black-Box Testing: RequirementsDokument17 SeitenBlack-Box Testing: Requirementsans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software Engg NotesDokument15 SeitenSoftware Engg Notesneetks88% (8)
- Black-Box Testing: RequirementsDokument17 SeitenBlack-Box Testing: Requirementsans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Storage ClassDokument14 SeitenStorage Classans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Storage ClassesDokument3 SeitenStorage Classesans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case NotesDokument5 SeitenCase Notesans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- User Interface DesignnotesDokument6 SeitenUser Interface Designnotesans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Black-Box Testing: RequirementsDokument17 SeitenBlack-Box Testing: Requirementsans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- PLSQL QueriesDokument56 SeitenPLSQL Queriessivanaganna90% (10)
- Notes 2Dokument35 SeitenNotes 2ans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- SQADokument32 SeitenSQAans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dbms NotesDokument25 SeitenDbms Notesans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Scheduling and TrackingDokument2 SeitenProject Scheduling and Trackingans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software Specification DocumentDokument19 SeitenSoftware Specification Documentans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- SQADokument32 SeitenSQAans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Software SpecificationDokument68 SeitenSoftware Specificationans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dbms NotesDokument25 SeitenDbms Notesans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- DBMS-B+ and B TreesDokument9 SeitenDBMS-B+ and B TreesMageshwari Dharaneeswaran0% (1)
- TrigerpptDokument28 SeitenTrigerpptans_h20030% (1)
- Data StructuresdbmsDokument17 SeitenData Structuresdbmsans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- TransDokument25 SeitenTransans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Con CurrencyDokument23 SeitenCon Currencyans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rdbms LabmanualDokument23 SeitenRdbms Labmanualans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recovery: We Study Two ApproachesDokument21 SeitenRecovery: We Study Two Approachesans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Complete-NotesDokument135 SeitenComputer Networks Complete-Notesans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Silberschatz Ch06 Process SynchronizationDokument63 SeitenSilberschatz Ch06 Process Synchronizationans_h2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- D345 PDFDokument3 SeitenD345 PDFHusseinawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bed Making: Occupied Bed Unoccupied BedDokument16 SeitenBed Making: Occupied Bed Unoccupied BedHakdog ShermolangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leopold ManeuverDokument1 SeiteLeopold ManeuverLego BrickheadzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aws American Welding Society ﺎﻜﯾﺮﻣآ شﻮﺟ ﻦﻤﺠﻧا دراﺪﻧﺎﺘﺳا: Pdf Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionDokument33 SeitenAws American Welding Society ﺎﻜﯾﺮﻣآ شﻮﺟ ﻦﻤﺠﻧا دراﺪﻧﺎﺘﺳا: Pdf Created With Pdffactory Pro Trial VersionAli SASSINoch keine Bewertungen
- My ScramjetDokument13 SeitenMy ScramjetHimanshu GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Marks QA MOMDokument11 Seiten2 Marks QA MOMvasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1TPMB04101 ABB MNS RPP Power Distribution To Critical LoadsDokument21 Seiten1TPMB04101 ABB MNS RPP Power Distribution To Critical LoadsDiego PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isha Lunar Calendar 2021Dokument1 SeiteIsha Lunar Calendar 2021nila67% (3)
- Performance Evaluation of Variable Frequency Single Phase Cascaded Multilevel InverterDokument50 SeitenPerformance Evaluation of Variable Frequency Single Phase Cascaded Multilevel InverterVIJAYARAGAVAN MOORTHYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Station Standards Workshop ReviewDokument24 SeitenHydrogen Station Standards Workshop ReviewDiana DhominicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Worksheet - Grade 10Dokument14 SeitenPhysics Worksheet - Grade 10Faran AssifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Study of Behaviour and Mental ProcessesDokument149 SeitenUnderstanding the Study of Behaviour and Mental ProcessesNaman LadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xtreme Xr1255 Operation Safety ManualDokument8 SeitenXtreme Xr1255 Operation Safety ManualfemudoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIY Underground Greenhouse For Organic FarmingDokument29 SeitenDIY Underground Greenhouse For Organic Farmingwire-of-Information100% (7)
- Chemical Safety HandbookDokument39 SeitenChemical Safety HandbookZach AdamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reg. No. IV SEMESTER B.TECH. (MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING) END SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS, JUNE 2018 DESIGN OF MACHINE LEMENTS MTE 2202Dokument3 SeitenReg. No. IV SEMESTER B.TECH. (MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING) END SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS, JUNE 2018 DESIGN OF MACHINE LEMENTS MTE 2202MeghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Data Formats For Analytical Systems: Status and ChallengesDokument1 SeiteStandard Data Formats For Analytical Systems: Status and ChallengeschatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure LEET 2013 14 FinalDokument114 SeitenBrochure LEET 2013 14 FinalAnsh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHD Proposal - SampleDokument3 SeitenPHD Proposal - SampleZihao QinNoch keine Bewertungen
- De-CP Premium250Pump ManualDokument52 SeitenDe-CP Premium250Pump Manualsubari subariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Price List - Peninsular Malaysia (With 0% SST)Dokument2 SeitenCustomer Price List - Peninsular Malaysia (With 0% SST)RAZAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data types and probability distributions analysisDokument10 SeitenData types and probability distributions analysisAkhil Jidigum100% (1)
- LED VU Meter Circuits Using Transistors 5 To 20 40 LEDDokument11 SeitenLED VU Meter Circuits Using Transistors 5 To 20 40 LEDsameeratoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMC Test Universe AppNote IRIG B Sychronization 2014 ENUDokument24 SeitenCMC Test Universe AppNote IRIG B Sychronization 2014 ENUJonas PedrosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1601R0 Valve, Plastic Valve enDokument6 Seiten1601R0 Valve, Plastic Valve enMella LumanogNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTXM UsDokument2 SeitenDTXM UsvandalizerertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lexical Expressive Means and Stylistic DevicesDokument27 SeitenLexical Expressive Means and Stylistic DevicesTania ShramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement MethodsDokument47 SeitenMeasurement MethodsSharjeel AhmedxNoch keine Bewertungen
- As-Hort 121 PDFDokument4 SeitenAs-Hort 121 PDFTeam MrudgandhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guardians of The Galaxy PDFDokument29 SeitenGuardians of The Galaxy PDFAdhil Krishna SunilkumarNoch keine Bewertungen