Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Low-Pass Filter: Electronic Devices and Circuits Ii
Hochgeladen von
Sachin ParmarOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Low-Pass Filter: Electronic Devices and Circuits Ii
Hochgeladen von
Sachin ParmarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
Low-pass filter
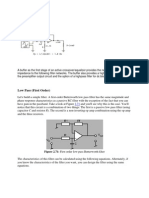
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates (reduces the amplitude of) signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter when used in audio applications. A low-pass filter is the opposite of a high-pass filter. A low pass filter has a constant gain from 0 Hz to a high cut-off frequency, fH. Hence the bandwidth of this filter is also fH. The circuit allows the range of frequencies from o to fH. This range is known as the pass band. The range of frequencies beyond fH, is completely attenuated and hence called as stop band.
1. First Order Low Pass Butterworth Filter
1|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
The first order low pass Butterworth is realized by R-C circuit used along with an op-amp, used in the non-inverting configuration.
2012
FIRST ORDER LOW PASS BUTTERWORTH FILTER This is also called one pole low pass Butterworth filter. The resistances Rf and R1 decide the gain of the filter in the pass band.
Analysis of the filter circuit The impedance of the capacitor C is -jXc where Xc is the capacitive reactance given by Xc= 1/2fC.
2|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
3|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
Thus, for the range of frequencies, 0< f<fH, the gain is almost constant equal to fH which is high cut-off frequency. At f=fH, gain reduces to 0.707 AF i.e. 3dB down from AF. And as the frequency increases than fH, the gain decreases at a rate of 20 dB/decade. The rate 20dB/decade means decrease of 20 dB in gain per 10 times change in frequency. The same rate can be expressed as dB/octave i.e. decreases of 6 dB per 2 times change in the frequency. The frequency fH is called cut-off frequency, break frequency, -3 dB frequency or corner frequency.
4|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
2. Second Order Low Pass Butterworth Filter The practical response of the filter must be very close to an ideal one. In case of low pass filter, it is always desirable that the gain rolls off very fast after the cut off frequency, in the stop band. In case of first order filter, it rolls off at a rate of 20 dB/decade. In case of second order filter, the gain rolls off at a rate of 40 dB/decade. Thus, the slope of the frequency response after f=fH is -40 dB/decade, for a second order low pass filter.
The cut-off frequency fH for the filter is now decided by R2, C2, R3 and C3. The gain of the filter is as usual decided by op-amp i.e. the resistance R1 and Rf.
5|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
6|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
7|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
At the cut-off frequency, fH, the gain is 0.707 AF. i.e. 3 dB down from its 0 Hz level. After, fH, the gain rolls off at the rate of 40 dB/decade. Hence, the slope of the response after fH is -40 dB/decade.
High-pass filter
A high-pass filter (HPF) is an electronic filter that passes highfrequency signals but attenuates (reduces the amplitude of) signals with frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. A highpass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system. It is
8|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
sometimes called a low-cut filter or bass-cut filter. High-pass filters have many uses, such as blocking DC from circuitry sensitive to nonzero average voltages or RF devices.
2012
1. First Order High Pass Butterworth Filter The first order high pass filter can be obtained by interchanging the elements R and C in a first order low pass filter circuit.
9|Page Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
The frequency at which the gain is 0.707 times the gain of filter in pass band is called low cut-off frequency and denoted as fL. So, all the frequencies greater than fL are allowed to pass but the maximum frequency which is allowed to pass is determined by the closed loop bandwidth of the op-amp used. Analysis of the Filter Circuit
10 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
11 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
2. Second Order High Pass Butterworth Filter
12 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
The second order high pass Butterworth filter produces a gain roll off at the rate of +40 dB/decade in the stop band. This filter also can be realized by interchanging the positions of resistors and capacitors in a second order low pass Butterworth filter.
2012
Switched Capacitor Filter
For getting good reliability and high performance, IC active filters are used. But major limitation of such ICs is the values of integrated resistors. The resistor values required for RC active filters are generally very high and such large value resistors require large chip area. Similarly the temperature and linearity characteristics of integrated resistors are poor. Hence it is necessary to find the replacement for the high value integrated resistors. The switched capacitor filters fulfill this requirement. The switched capacitor filters use the on-chip capacitors of small values and MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) switches, to simulate high value resistors. The switches are controlled by the external clock, whose frequency can be easily controlled. Advantages of Switched Capacitor Filter The various advantages of switched capacitor filter are: 1. Very high value of resistors can be easily simulated using small value capacitors, of the order of 10 pF.
13 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2. The switched capacitor filters require no external reactive components like inductors and capacitors. 3. Accuracy is very high. 4. The overall cost of the system is low. 5. Due to good temperature characteristics, the systems have good temperature stability. The only disadvantage of the switched capacitor filters, is that they generate more noise than the standard active filters. Basic Operation of Switched Capacitor Filter A switched capacitor filter is a three terminal device which consists of capacitor and MOS switches. The S1 and S2 are the two MOS switches and C is the capacitor. The three terminals are marked as 1, 2 and 3. The terminal 3 is common at input and output and generally grounded.
2012
14 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
The two switches operated alternately and a capacitor C together is used to simulate high value resistors. Consider a circuit using a basic switched capacitor filter, The two switches S1 and S2 are the MOS transistors which are alternately opened and closed. Thus when S1 is closed, S2 is open and vice versa. The switches are opened and closed alternately by using an external clock with a frequency FCLK. Consider the switch S1 is in position a i.e. it is closed. So capacitor C gets charged to voltage Vin. Hence the total charge on the capacitor is,
15 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
Q = CVin When S1 is open and S2 is in position b i.e. closed then the capacitor C discharges and charge Q flows to the ground. If the switches are ideal i.e. they open and close instantaneously and resistance of the switches is zero when they are closed the charging and discharging of the capacitor takes place instantly. So, let, Iin= Charging Current and Io = Discharging current Then when S1 is closed, Iin flows instantly whose amplitude depends on charge Q flowing per unit time. Hence Iin occurs in pulse form, at the instants when S1 is closed. While when S2 is closed, Io occurs in pulse form. So the capacitor current consists of short bursts every time when switch is closed. The waveforms of Iin and Io , related to the closing and opening of switches.
2012
16 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
The time between closing of switch S1 or S2 is called clock time, denoted as TCLX. This can be controlled by an external clock. Thus if switches are opened and closed at a faster rate, then frequency of occurrence of current pulses will be high but their amplitudes will remain unchanged. But due to frequent occurrence of current pulses, the average current flowing will be more for higher switching rate. This average current is rate of change of flux with respect to the clock time TCLX.
2012
17 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
18 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS II
2012
19 | P a g e Sunday, March 04, 2012
MADE BY:SACHIN PARMAR
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 14-Passive Filter RCDokument12 Seiten14-Passive Filter RCraven anandioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V - Active FiltersDokument14 SeitenUnit V - Active Filterseshwar_worldNoch keine Bewertungen
- احمد تركي كحيوش 2Dokument30 Seitenاحمد تركي كحيوش 2أحمد تركي كحيوشNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filter NotesDokument42 SeitenFilter NotesZaimi Zamaludin100% (1)
- Active Low Pass FilterDokument12 SeitenActive Low Pass FilterSayani GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF SwitchesDokument16 SeitenRF SwitchesName100% (3)
- 8 Signal ProcessingDokument51 Seiten8 Signal ProcessingvenumadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Frequency FilterDokument9 SeitenLow Frequency FilterYahya AbdurrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 4Dokument8 SeitenEce014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 4John Wilfredd CurimoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Basic Introduction To Band-Pass FilterDokument15 SeitenA Basic Introduction To Band-Pass FilterTalal Al-SindiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Pass Filter IntroductionDokument34 SeitenLow Pass Filter IntroductionMichelle Arellano100% (2)
- Analog HP FilterDokument4 SeitenAnalog HP FilterMocanu AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Basic Characteristics of Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filters AreDokument2 SeitenThe Basic Characteristics of Finite Impulse Response (FIR) Filters AreParul KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive Low Pass RC FiltersDokument8 SeitenPassive Low Pass RC FiltersSayuri CastellanosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Signal Conditioning PDFDokument13 SeitenChapter 3 - Signal Conditioning PDFAzrinshah Abu BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive Low Pass FilterDokument5 SeitenPassive Low Pass FilterAnonymous SOQFPWBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 2 Passive LP and HP FiltersDokument12 SeitenExp 2 Passive LP and HP FiltersvallikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emg FiltersDokument48 SeitenEmg FiltersTeheranNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Low Pass FilterDokument5 SeitenThe Low Pass FiltersunraysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Pass - FiltersDokument4 SeitenLow Pass - FiltersNeelam Kapoor100% (1)
- Figure 2.71: First Order Low-Pass Butterworth FilterDokument18 SeitenFigure 2.71: First Order Low-Pass Butterworth Filternavkar_nisitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 FILTER PassiveDokument29 Seiten5 FILTER PassiveLian Ai ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Band Pass Filter Projects ReportDokument48 SeitenRF Band Pass Filter Projects ReportPrateekKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opto Electronic Devices and Wave Shaping Circuits Study MaterialDokument11 SeitenOpto Electronic Devices and Wave Shaping Circuits Study MaterialTejas BorkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sescar de Guzman Experiment PartialDokument9 SeitenSescar de Guzman Experiment PartialKyle ChesterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filters 120427025230 Phpapp01Dokument18 SeitenFilters 120427025230 Phpapp01ramanaidu1Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMC Filter For DCDC Switching Controller OptimizedDokument6 SeitenEMC Filter For DCDC Switching Controller OptimizedPetr BruzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Com306Dokument19 Seiten01 Com306trantrieuvnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics 3: Active FiltersDokument51 SeitenElectronics 3: Active FiltersAdrian ZayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Band Pass FiltersDokument5 SeitenBand Pass FiltersHeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Original PDFDokument6 SeitenOriginal PDFAlaa WahoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACtive Notch Filter DesignDokument43 SeitenACtive Notch Filter DesignDrMohammad Rafee ShaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS EE Assignment Title PageDokument9 SeitenBS EE Assignment Title PageNomi AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC 5 - (Filter) StudentDokument79 SeitenTOPIC 5 - (Filter) StudentAR de SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Signal Conditioning PDFDokument13 SeitenChapter 3 Signal Conditioning PDFBelayneh Tadesse50% (2)
- Examples of Low-Pass Filters: Subtractive SynthesisDokument4 SeitenExamples of Low-Pass Filters: Subtractive Synthesismohamad yousefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active High Pass and Low Pass FilterDokument16 SeitenActive High Pass and Low Pass FilterVINITA AGARWAL50% (2)
- Basic Passive RC FiltersDokument44 SeitenBasic Passive RC FiltersJohnPJojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3 Band Reject FilterDokument14 SeitenLab 3 Band Reject Filterabidrk_21789Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE301 Electronic Circuit Chapter 5 - FILTERSDokument48 SeitenEE301 Electronic Circuit Chapter 5 - FILTERSWann Fariera100% (3)
- Op-Amp Filter - The Active Low Pass FilterDokument6 SeitenOp-Amp Filter - The Active Low Pass FilterBaljinder KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave SapingDokument43 SeitenWave SapinglsrinivasnteceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crosver Cu tl082Dokument4 SeitenCrosver Cu tl082Ionut Cosmin PopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Pass FilterDokument12 SeitenHigh Pass Filter9897856218Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Active FiltersDokument39 SeitenBasics of Active FiltersDr. Shwetha MNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impedance of A Capacitor Decreases As The Frequency IncreasesDokument10 SeitenThe Impedance of A Capacitor Decreases As The Frequency IncreasesTeki ChweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive FilterDokument9 SeitenPassive FilterSankalita BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Pass FLTRDokument7 SeitenLow Pass FLTRYawar ArslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELEC-OPAMP-S7 Active Low Pass Filter - Op-Amp Low Pass FilterDokument8 SeitenELEC-OPAMP-S7 Active Low Pass Filter - Op-Amp Low Pass Filterfelres87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of RF Solid State SwitchesDokument19 SeitenDesign of RF Solid State SwitchesDurbha RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Six FiltersDokument35 SeitenChapter Six FiltersERMIAS AmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lic Project ReportDokument9 SeitenLic Project ReportJayachandra JVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Band Pass Filter - Passive RC Filter TutorialDokument6 SeitenBand Pass Filter - Passive RC Filter Tutorialmr mrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working of Pi filter (π-filter)Dokument11 SeitenWorking of Pi filter (π-filter)Joseph B Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE131 UNIT5 Part4Dokument51 SeitenECE131 UNIT5 Part4abhi shekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.10 Phase Locked LoopDokument20 Seiten2.10 Phase Locked LoopRamya KarriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Lecture Notes IIDokument31 SeitenElectronics Lecture Notes IIWaltas KariukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- DSP LabDokument4 SeitenDSP LabajuatcetymailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece-V-digital Signal Processing U8Dokument21 SeitenEce-V-digital Signal Processing U8madhusudhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BME302 1cDokument16 SeitenBME302 1cAYÇA İDİL ATEŞNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency Domain Comparison of RLC CircuitDokument11 SeitenFrequency Domain Comparison of RLC CircuitShaban SattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP 21EC42 2ndIADokument1 SeiteDSP 21EC42 2ndIAKirana007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analog HP FilterDokument4 SeitenAnalog HP FilterMocanu AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIR Filter CodeDokument12 SeitenFIR Filter Codeasma tariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- UAF42 Filtro NotchDokument15 SeitenUAF42 Filtro NotchJuan Jose ArrietaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece V Digital Signal Processing (10ec52) NotesDokument160 SeitenEce V Digital Signal Processing (10ec52) NotesVijay SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assingment 4Dokument1 SeiteAssingment 4khananuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Program: 1 Response of First Order System To Unit Step InputDokument6 SeitenMatlab Program: 1 Response of First Order System To Unit Step InputMartin De Boras PragashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Electronics Iii (Lab) Project Report: Spectrum AnalyzerDokument15 SeitenAnalog Electronics Iii (Lab) Project Report: Spectrum AnalyzerHibba HareemNoch keine Bewertungen
- UAF42 As A Low-Pass Active FilterDokument5 SeitenUAF42 As A Low-Pass Active FilterkosarobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Impulse Response FiltersDokument29 SeitenFinite Impulse Response FiltersSheelaj BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design FilterDokument27 SeitenDesign FilterubaydaturkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti-Aliasing Analog FiltersDokument12 SeitenAnti-Aliasing Analog FiltersDocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational Amplifier ApplicationsDokument17 SeitenOperational Amplifier Applicationslid20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Filter CircuitsDokument15 SeitenFilter CircuitsANWAR SHADMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charles L. Phillips, John M. Parr - Signals, Systems, and Transforms Solution Manual (2008) - Libgen - LiDokument328 SeitenCharles L. Phillips, John M. Parr - Signals, Systems, and Transforms Solution Manual (2008) - Libgen - Li劉士愷Noch keine Bewertungen
- SL - No Questions: MODULE 1: Discrete Fourier TransformDokument5 SeitenSL - No Questions: MODULE 1: Discrete Fourier TransformarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- FiltersDokument41 SeitenFiltersAnusha yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Ex 7Dokument79 SeitenLab Ex 7tranducaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Filters D PDFDokument10 SeitenActive Filters D PDFchandra prakash purbiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Lecture - Digital Filter DesignDokument8 Seiten6th Lecture - Digital Filter DesignaehwnnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Programs ManualDokument18 SeitenMatlab Programs Manualsudharsan100% (1)
- Lattice Ladder Structure For IIR FilterDokument12 SeitenLattice Ladder Structure For IIR FilterjaishpanjwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE407 Lec 15 16 1Dokument67 SeitenEE407 Lec 15 16 1singhhv21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Filters and Tuned AmplifiersDokument13 SeitenFilters and Tuned AmplifiersLasantha AbeykoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.7 All-Pass Filter Design: Figure 16-41. Comparison of Q Between Passive and Active Band-Rejection FiltersDokument8 Seiten16.7 All-Pass Filter Design: Figure 16-41. Comparison of Q Between Passive and Active Band-Rejection FiltersseleneedithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing Digital Filter Banks Using WaveletsDokument11 SeitenDesigning Digital Filter Banks Using WaveletsAnand MattadNoch keine Bewertungen