Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Untitled
Hochgeladen von
bharathiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Untitled
Hochgeladen von
bharathiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Meaning and Definition of Physical Education: Physical Education is the process by which changes in the individual are brought
about through movements and experiences. Physical Education aims not only at ph ysical development but is also concerned with education of the whole person thro ugh physical activities. Physical education is the play-way method of education. Various Definitions of Physical Education are 1. Barrow defined Physical Education as an education of and through human moveme nt where many of educational objectives are achieved by means of big muscle acti vities involving sports, games, gymnastic, dance and exercise. 2. According to Websters Dictionary Physical education is a part of education whi ch gives instructions in the development and care of the body rending from simpl e callisthenic exercises to a course of study providing training in hygiene, gym nastics and the performance and management of athletics games. 3. Jackson R. Sharman points out that physical education is the part of educatio n which takes place through activities, which involves the motor mechanism of hu man body which results in an individuals formulating behavior patterns. 4. Charles A. Bucher defines physical education, an integral part of total educa tion process, is a field of endeavor which has as its aim the development of phy sically, mentally, emotionally and socially fit citizens through the medium of p hysical activities which have been selected with a view to realizing these outco mes. 5. Central Advisory Board of physical Education and Recreation defines Physical education as an education through physical activities for the development of tot al personality of the child to its fullness and perfection in body, mind and spi rit. Aim of Physical Education Aim of physical education, like general education, is to develop human personali ty in its totality well planned activity programs. In some words, physical educa tion aim at the all round development of the personality of an individual or who lesome development of human personality and it includes physical, mental, social , emotional and moral aspects to make an individual a good citizen who is able t o make contribution in process of nation in ones own way. Thus physical education means at making an individual physical fit, mentally alert, emotionally balance d, socially well adjusted, morally true and spiritually uplifted. Objectives of Physical Education The three Objectives of physical education are 1. The objective of physical fitness It refers to that state where an individual has developed great endurance, speed, strength etc. Physical fitness is essenti al to leading a happy, vigorous and abundant life. 2. The objective of social efficiency It concerned with ones proper adaptation to group living. Physical education activities provides ample opportunities to dev elop traits such as cooperation, respect to others, loyalty, sportsmanship, self confidence etc. All these qualities help a person to make him a good citizen. 3. The objective of culture It aims at developing an understanding and appreciat ion of ones own local environment as well as the environment which is world-wide in scope. By participation in various physical education activities such as danc e, sports and games, a person fully understand the history, culture, tradition, religious practices etc and the aesthetic values associated with these activitie s. Nature of Physical Education: Physical Education is the cultivation of the powers and capabilities of the stud ent as it will enable him/her to maintain his/her bodily condition in the best w orking order, while providing at the same time for the greater efficiency of his /her intellectual and spiritual life. Health and Physical Education: Play is more than a pastime, it is a fundamental tool for the discovery and redi
scovery of the meaning of living. Health is Soundness of body and mind. The mind and the body are not two separate entities. Two qualities essential to human ex istence and growth are ability to think for ones self and physical vitality. Need of Health & Physical Education in School Curriculum: Recent studies on school children have shown that they are prone to regular illn ess due to malnutrition and communicable diseases. Any survey of statistical da ta reveal that society today and specifically the youth are facing an onset of e arly diseases related habits acquired during childhood often have a profound imp act on their later life. Obesity at childhood (urban areas) is an epidemic whi ch is also the result of a decline in regular physical activity. Parents are very much worried about their childrens progress in scores without ca tering the psycho-social dimension in their development. Community awareness on importance of health education and physical education is meager. There is a mis conception among parents, teachers, officials that physical activities, events e tc., will lead to lower performance of the child in scholastic subjects which wi ll affect later life of the child. The other misconceptions of Physical Educatio n include: Physical Education is only for the few who are highly skilled. Physical Education is mainly play and that play needs neither instruc tion nor supervision. Physical training and Physical Education are one and the same. It is matter of exercising of becoming physically fit. Physical Education is for boys not for girls. Physically active and educated children are more likely to thrive academically a nd socially. Children who spent time in physical education in place of a classr oom activity performed no worse academically than students not enrolled in physi cal education. Physical activity has a positive impact on cognitive ability, tob acco use, insomnia, depression and anxiety. The Surgeon General recommends child ren should engage in 60 minutes of moderate activity most days of the week. Schools serve as an excellent venue to provide students with the opportunity for daily physical activity, to teach the importance of health and physical activit y for health and to build skills that support active lifestyles. Schools can bes t contribute to the realistic objectives for fitness and vitality by: teaching the skills of attaining and maintaining fitness. facilitating the development of concepts of fitness. teaching recreational emotional-release skills. logical thinking and research support the concept that early learning i s superior to late learning. Benefits of P.E through Exercises: Exercises aim to enhance physical fitness through dance. A person can improve fl exibility, strength, coordination, balance, cardiovascular fitness and body awar eness through movement .A person can have fun, learn to dance to Folk music, Pop music, Western and E music while becoming trim and fit. Rhythmic exercises can reduce stress and tension, coordinate the movement patter n and gives the benefit of aerobic breathing exercises. Rhythmic exercises serve as a combination of dance and gymnastic to some extent. These can be performed in large groups. Mass rhythmic activities are an excelle nt form of physical activities for people of every age. Physical education is mo stly developmental in nature, its main objective is to develop motor qualities, improve body posture, develop unity, and uniformity in movement and create a sen se of rhythm and co-ordination. Physical Education for Children with Special Needs: Physical Education for a children with special needs will develop Physical and m otor fitness; Fundamental motor skills and patterns; and skills in aquatics, dan ce, and individual and group games and sports (including intramural and lifetime sports). Some activities will have more restrictions than others and some will be less vigorous than others depending on the needs. The teacher in conjunction with other supporting staff will decide if the physical education programme requ
ires mild, moderate or limited participations of children with special need. Tea cher should adapt, modify, and change the activity and or equipment to meet the needs of the students with special needs. This may mean larger balls, bats, part ner assistance, using different body parts, providing more rest time etc. The go al is to ensure the child is progressing and having some form of success. Helpful Suggestions to the teachers: 1. Consult with parents and specialized support staff. 2. Do not require students to do activities they are not capable of. 3. Don t have student selections for teams and games that will leave the child w ith special needs the last to be selected. 4. Whenever possible, create tasks that the child with a handicap is capable of performing, this helps boosting the self-esteem of the child. 5. Adaptive devices and other technology can be incorporated with associations c oncerned with exceptional children. When working towards an inclusive approach, teacher should remember and always n eed to think: How can he/she change the activity to suit the student? How can he/she adapt the activity? How can he/she modify the activity? Teacher should think in terms of action, time, assistance, equipment, boundaries , distance etc. Adaptive or Adapted Physical Education (APE): Adapted Physical Education (APE) may be offered to students with gross motor del ays or other disability-related difficulties that make them unable to participat e productively in a regular physical education class. An Adapted Physical Educat ion class will usually be taught by a person with a background in physical thera py who can adjust the activities so that they will be appropriate, safe, and the rapeutic for each individual student. The class may take place in a gym where re gular education students are also having classes, and the teacher may facilitate appropriate interaction between the classes. In order to get APE for a child it should be put in childs IEP and prepare to justify the need for adaptation. YOGA:
Physical Education and Yoga: Yoga raises the mind to its highest level in order to study its activities on lo wer levels of consciousness. Yoga aims at that command over the body that is th e state of individual existence in which the mind, working smoothly in a physica lly fit body on a high level of consciousness can observe and control all mental activities on the lower level. Yoga has been an integral part of Health and Physical Education that has been a compulsory subject up to the secondary school stage since 1988. The NCF 2005 ado pted a holistic definition of health in which yoga is an integral part of it. Both yoga and physical education contribute to not merely the physical developme nt of the child but have a positive impact on psychosocial and mental developmen t as well. Playing group games have a positive impact on individual self esteem, promotes better interaction among children, imparts values of co-operation, sha ring and to deal with both victory and defeat. Similarly yoga practice contribut es to the overall development of the child and various studies have shown that i t contributes to flexibility and muscular fitness and also corrects postural def ects among school children. There is also a growing realization that the health needs of adolescents, partic ularly their reproductive and sexual health needs, require to be addressed. Sinc
e these needs predominantly relate to sex and sexuality, which is culturally a v ery sensitive area, they are deprived of opportunities to get appropriate inform ation. There is a need to provide children accurate and authentic information an d help them to construct knowledge and acquire life skills, so that they cope up with the concerns related to the process of growing up, counter stress and stra ins and cope up with examination stress.Within this overall framework both yoga and physical education are seen as routes for achieving overall development of c hildren. The precondition for all development is healthy physical growth of all children . This requires that the basic needs in terms of adequate nutrition, physical ex ercise and other psycho-social needs are addressed. Participation of all childre n in free play, informal and formal games, yoga and sports activities is essenti al for their physical and psycho-social development. The range of abilities as a result of games, sports and yoga will improve stamina, fine and gross motor ski lls and dexterities, self-awareness and control, and coordination in team games. Simple adaptation of playgrounds, equipment and rules can make activities and g ames accessible to all children in the school. Children can achieve high levels of excellence in sports, athletics, gymnastics, yoga and performing arts such as dance. When the emphasis shifts from enjoyment to achievement, such training ca n make demands of discipline and practice that can create stress at this stage. Whereas all students must be involved in health and physical education activitie s, those who choose to excel in games and sports need to be provided adequate op portunities. References: http://bodyfitnesshealth.com http://indiacurrentaffairs.org/health-physical-education/ http://www.icbse.com/2009/yoga-schools/ http://www.aicpe.ac.in/ http://www.napess.org/articles.php http://www.preservearticles.com/201105176747/main-function-of-physical-education .html http://specialchildren.about.com/od/specialeducation/g/APE.htm
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- PE N YogaDokument7 SeitenPE N YogabharathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pia GetDokument2 SeitenPia GetbharathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE N YogaDokument7 SeitenPE N YogabharathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Because You Loved Me LyricsDokument8 SeitenBecause You Loved Me LyricsbharathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Lesson Plan With GAD Integration SampleDokument7 SeitenLesson Plan With GAD Integration SampleMae Pugrad67% (3)
- STM32 Lec1Dokument15 SeitenSTM32 Lec1enugraha01100% (1)
- EASTC Course ListingDokument6 SeitenEASTC Course ListingTHABISILE MBATHANoch keine Bewertungen
- B.tech Apjktu (2019 Scheme)Dokument21 SeitenB.tech Apjktu (2019 Scheme)Amarnath RajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
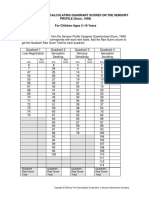
- Quadrant Grid: Worksheet For Calculating Quadrant Scores On The Sensory PROFILE (Dunn, 1999) For Children Ages 3-10 YearsDokument2 SeitenQuadrant Grid: Worksheet For Calculating Quadrant Scores On The Sensory PROFILE (Dunn, 1999) For Children Ages 3-10 YearsLorenzo CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM BTS Over IP Deployment Troubleshooting GuideDokument27 SeitenGSM BTS Over IP Deployment Troubleshooting GuideKeartichai Chomtaku100% (1)
- Basic Consideration in Assessing WritingDokument4 SeitenBasic Consideration in Assessing WritingIsabela TrejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holt Algebra 1 - Chapter 11 - Standardized TestDokument8 SeitenHolt Algebra 1 - Chapter 11 - Standardized TestStanleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank Theoretical Basis For Nursing 3rd Edition McewenDokument8 SeitenTest Bank Theoretical Basis For Nursing 3rd Edition McewenAmber Oneill100% (20)
- Active Listening SkillsDokument2 SeitenActive Listening SkillsMathew LumapasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Week 2Dokument4 SeitenDLL Week 2Jessa SomblingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- George ResumeDokument3 SeitenGeorge Resumeapi-287298572Noch keine Bewertungen
- Varistors Based in The ZnO-Bi2O3 System, Microstructure Control and PropertiesDokument6 SeitenVaristors Based in The ZnO-Bi2O3 System, Microstructure Control and PropertiesJanja TothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Language Writing Challenges for Saudi LearnersDokument31 SeitenSecond Language Writing Challenges for Saudi LearnersRamizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grossman & Salas (2011)Dokument18 SeitenGrossman & Salas (2011)Diane Des RochersNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF 36Dokument3 SeitenPDF 36Armia GaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bansal Institute of Engineering & Technology, LucknowDokument22 SeitenBansal Institute of Engineering & Technology, Lucknowshivansh sahu100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ielts Speaking Part One Long Short Answers PDFDokument7 SeitenIelts Speaking Part One Long Short Answers PDFKaran JariwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SelfDokument2 SeitenSelfglezamaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Dissertation Paper - Role of Open Spaces in LearningDokument8 SeitenFinal Dissertation Paper - Role of Open Spaces in LearninghasnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMCG Marketing and Sales: Organizing Trade Marketing, Category Management, and Shopper Marketing PDFDokument242 SeitenFMCG Marketing and Sales: Organizing Trade Marketing, Category Management, and Shopper Marketing PDFSilmi KaffahNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP L&S TUTO (Speaking)Dokument5 SeitenLP L&S TUTO (Speaking)TESLA-0619 Jenny Laleng NehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Junior HSE AssistantDokument2 SeitenJunior HSE AssistantMuhammad AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 1 Understanding EthicsDokument29 SeitenChap 1 Understanding Ethicsphuonganhvu0310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cold Calling 26 AugDokument4 SeitenCold Calling 26 AugGajveer SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining Applications and TechniquesDokument52 SeitenData Mining Applications and TechniquesDinesh ChandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law UniversityDokument6 SeitenDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law UniversityShivam VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get It Up 1 - DAP AnDokument18 SeitenGet It Up 1 - DAP AnAndreea EliescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Breakdown PDFDokument11 SeitenFamily Breakdown PDFSamantha GordonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program Pandu Puteri KloverDokument33 SeitenProgram Pandu Puteri KloverCy ArsenalNoch keine Bewertungen