Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Bush Torts Outline
Hochgeladen von
jeffreyjohnOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Bush Torts Outline
Hochgeladen von
jeffreyjohnCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
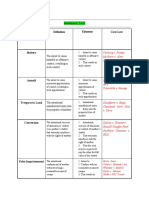
The Bush Torts Outline I. Hammontree v. Jenner epileptic in a car crash A. Strict Liability v. Negligence i.
. Strict Liability if you do harm, you pay ii. Negligence if you do harm, and your conduct was wrong, you pay. B. s argument: SL , : negligence II. Policy Arguments: A. RICH - Social welfare/Deterrence/Productivity maximize product./wealth/deter waste B. JUST Social Justice/ Class Equality avoid creating/widening the gap btw. Strong and weak/rich and poor C. FREE individual freedom/liberty maintain the greatest possible degree, and avoid restricting, the freedom of people to act. D. FAIR individual fairness punishment fit the crime. E. COMPASSION- Compensation/avoidance of suffering- swift and full compensation for injured victims F. SAFE public order no escalation/no violence G. STRONG Civility/harmony avoid increasing animosity between people H. EFFICIENCY administrative economy keep it simple *** Elements of the Negligence Case *** negligence (bad act) cause in fact proximate cause duty (no duty) damages affirmative defenses III. intro- Cause in Fact Is the actor necessary for the act to occur? A. Concept: If no x, no harm. argues: BUTFOR your bad conduct , I would be fine! argues: EVEN IF [no bad conduct], your injury would have occurred. B.TEST: Hypo alt. imagine sit. w/out x: wd. H still happen? if no, then x = necy, c/f if yes, then x not necy, not c/f C. C/F arguments : Both sides * argues: BUTFOR s bad cond., IF NOT FOR s bad cond., no inj. IMAGINE acted DIFF/OK No INJ. So, s conduct made the diff. = C/F * argues: EVEN IF no b/cond., injury anyway IMAGINE acted Diff/OK still Inj. so s cond. made no diff, not C/F
V. Negligence : Negligence = R > C/AV R HI, C/AV LO Unr. Risk DUE CARE (no neg.) = R < C/AV R LO, C/AV HI Rble Risk 1. R/P standard: requires comparison of risk and c/av, never one alone substl risk alone not necy bad trivial risk alone not necy ok Risk = probabil. of harm occurring x amt. damages if harm occurs. C/AV = all dir/indirect risk avoidance costs Youth Standard is the only way to lower the RPS becomes the reasonable child of that age, intelligence, training standard Unless the youth is doing an adult activity then they are held to an adult standard. 2. Risk/Avoidance Calculus : (R/DID v. COST/SHDVE Done) A. R/Did = aggreg. Of f/risks of DID - FRA (fble risk aggregate) -risk of all fble damage to all fble victims of all fble h/events B. C/SHDA = total dir/indir. Cost 3. /s arguments for r/did c/shda - heres what u did heres what you shoulda done -R of Did is Hi, C of SHDA is low - ok, thats what I did, but: -R of Did is Low, C of SHDA done is hi How does each side prove? EVIDENCE OF Risk and C/AV Whose figures for r and c/av? the reasonable persons risk awareness, safety awareness, and skill. RPS: What would RP know/do? -thats what shda done -what would rp know about r & c/av based on facts? N=conduct where r > c/av 2
Brown : hits in eye with stick trying to break up dog fight shifts burden to the to show the s conduct was bad under reasonable care (proto RPS) Adams : r/av analysis , dangling wire boy - railroad not neg. accident not unavoidable but the cost is very high to run the electrified wire underground Carroll Towing: r/av boat crew neg. -b/c- cost was low- risk was high Andrews: cost of installing nets relatively low vs. risk of landing injury. N= conduct < RPS RP always does r/AV analysis before acting held to RP. Std. on good/bad. 3 Steps for R/AV answer: 1) ID the DID/SHDA (choose candidate) 2) ID RISK OF THE DID (R/did) why is the p/risk hi or low ? (facts/investigate) 3) ID COST OF THE SHDA (Imagine) Why is that cost hi or low? (facts) Digwell hypo Did: -no barrier, and entrance on the front Shoulda: -barrier along front of site & side entrance and truck path truck path behind barrier s risk argument: risk very high i. Accident: vehicles from road into pit risk to drivers/workers serious injury 20 foot drop p/hi : hi traffic, speed/shard curve, bad weather, road /many workers/ volatile equipment ii. accident: trucks pull on road, collide with traffic risk to trucks, drivers, and pedestrians ser. Inj. Heavy trucks/ fast cars p/hi : hi traffic, speed / many lg. trucks/ bad weather, road. iii.accident: debris onto rd., car collides risk to drivers, etc. serious injury fast cars/ heavy debris p/hi : hi traffic, speed / much, heavy debris in site. Low cost of avoidance Concrete barrier lo cost barrier/install, 1-time r of driver collision, but low Side entrance -lo cost, 1-time, no risk, no delay 3
truck path -lo cost, 1-time, no risk, no delay s risk argument low risk i.accid: vehicles into pit p/lo: lo traffic, speed / good weather, road/few workers / no volatile equipment ii. accid: trucks pull on road, collide: p/lo: lo traffic, speed / few, small trucks / good weather, road iii.accid: debris on rd, car collides -p/lo: lo traffic, speed / light, little debris. High cost i. concrete bar r of driver collision, hi damage ii.side entrance/truck path new risk of harm to neighbors property delay to drive extra distance iii.truck path behind barrier: new risk of accid/ slow truck turn in delay from slow turn in/out
III. RPS Substitutes: Candidates: judge made rules business safety customs safety statutes A. Judge Made Rules : Based on experience, js artic. Concrete situational rule Holmes in Goodman (driver get out of car and stop look listen) Cardozo in Pokora wont work , not effective prevailing view still rely on RPS judges standards hard to work with. B. business practice/custom if so, can work for and in trimarco (shatter proof glass custom) argues, cust = rps, deviation from custom = negligence in tj hooper (radio on a ship custom), argues custom = rps, conform to custom = rps/no negligence ** courts hold custom is not = RPS (dev. Not = neg., conf. not = due care) instead, custom some evid. of rps. Helps prove rps because custom shows what rps would know about r & c/av
custom argument is integrated into the rps/r-av argument what is custom ? safer pracice? its a minimum established by businesses to get by with the min. costs therefore, not necessarily very safe. C. Safety Standards (NPS) why stat. rules > j-made rules? institutional differences: -legislation job to make general rules/not judges job -legislative process best for general rules -leg. Has legitimacy not courts -leg. Has competency , not cts. RULE: Martin v. Herzog --- NPS -violation of stat. command is neg. per se -but only if stat meets 4 conditions -what conditions? What effects? 4 + () conditions for NPS 1. stat covers/regs defs conduct : regulates what def. doing at time 2. stat purp. safety/accid. Prevention -damage to life limb (martin), property (tedla) -but NOT conservation of econ, morals *(example of non-safety purpose 55 mph speed limit for conservation of gas purposes) *(example of non-safety purpose Platz v. City : Blue Laws say dont drive ) 3. stat. purp prevent this type of accid. -prevents the type of accident that occurs in our case examples: martin collision de haen materials fall 4. stat. purp prevent this type of victim *legislative concern type of victim in our case examples: martin: driver de haen : worker + (1/2) no excuse for violation : excuse = emergency circumstances beyond s control -impossible to comply b/c of emergency all 4 + (1/2) required or stat. inadmissible - must prove all to get stat. in - can negate any 1 to keep stat. out if all 4 and no excuse, statute admitted, as subst. for RPS. -unexcused viol = NPS , no need for r/Av - wins neg. issue
But, C/F still reqd If any NPS condition negated, or excuse: -stat. excluded COMPLETELY -sep. hearing w/out jury - can/must now argue R/AV RPS NO DUE CARE PER SE complied with statute, and 4 conditions. D/C PER SE?? -NO!! Compliance not + D/C - must respond to R/AV argument (obviously overcame No duty to get here so Negligence question must be answered).
IV. Proof of Negligence: Res Ipsa Loquitor (RIL) So far, proving the standard- what would rp do? What is the sdha? Now: Proving the Breach - What did do? What was the did ? Problem of Evidence -how much needed ? -what kinds of evidence? Stop & shop outcome versus Gordon need more the spec.(speculation) ex- evidence-surveillance camera, employee testimony If No Evidence: Byrne v. Boedle what did do? Cant be proven. Rule of RIL : 3 conds 1) Prob. Of someones neg. acc. Like this dont happ. Unless someone neg. based on the type of acc. (ie. Wayward wheel cases) Using precedent. Scenarios Neg / Innocent Scenarios > imagined innocent ways this type of acc. happen 2) s exclusive control of instrum. usually many hands touch the accident negating mult. Control which party had the greatest degree of involvement at most of the times when negligence was most likely to occur? -elimination -dominion -majority -combo
3) No participation -must look to the facts must prove all 3. can negate 1 to throw out RIL, back to the RPS. effect of ril: alt. to proving did case to jury only if 3 conds proven -with instruction - > you can find n. on ril alone s options: challenge each part -reput inference with d/c evidence, but ???*** [but what?] and can argue specific evid. in alt??
Example of Scenario Argument : Abbot v. Page - airplane crash I. Neg No Neg Pilot error birds flew in Mechanic goofed bad weather tornado Bad weather flew anyway Ran out of fuel Sabotage Air control mistake Stupid passenger Wing fell off II. Negating Multiple Control (requires only one person had control vs. 4 different possible causes) Air traffic - elim Manufacturer - elim Pilot --------- Dominion Passenger ^ Mechanic ^ Security ^ * Elimination no neg Dominion show control over other actors *? Majority - most of the time it is pilot/pass/mech that causes this type of accident? III. No involvement.
V. Cause in Fact: concepts/evidence/proof standards A. Concept : Necy link in chain But-For x, No Harm.
B. Test: Hypo. Alt. imagine situation w/out x: would harm still happen? -If no, then x = necy c/f -if yes, then x not necy, not c/f C. Arguments: Both Sides argues: - but for s bad conduct, No Injury. - Imagine acted diff/ok , No Injury. So, s conduct made the difference = C/F argues: - even if no bad conduct, injury anyway -imagine acted different/ok still injury - so s condition made no difference, not C/F D. Types of Evidence : -testimonial -direct/physical -expert -circumstantial **? -statistical BURDEN on : >50% prop. to get to the jury (Stubbs contaminated drinking water caseshigh hurdle to keep from jury ) C/F special rules: Statistical Evidence -most courts : admissible but addl individuating evid. necy -some courts: s/ev alone sufficient, if proves > 50% prob. c/f -prob of over/under deter/compensation (comp -potl sol.(potential solution) : RPP recov. Prop. to proof. Example: Zuchowicz In 1000 cases with similar accidents, 750 caused by drug O.D. 3 problems with statistical evidence : 1) confuse/intimidate jury 2) stat. evid. asks to conclude individual from group 3) stats prove too much 1000 exposed cancer rate before: 20/1,000 after: 50/1,000 S0, 30 got cancer from leak, 20 would have gotten anyway. -stat alone, all get paid, meaning 20 people get paid for nothing. OVERDETER/bad for s most courts require additional individuating evidence -no stat, none get paid, unfair to s
corrective justice theory of tort law a bad act cant be corrected by making a new one (two wrongs dont make a right) Possible Solution : RPP schwartz rule accident but limit recovery to % increase. Ie. In cancer example, 60% increase, so each gets 60%. C/F special rules : LOST CHANCE Conditions: med. mal. Only stat. evid. = survival /success rate change recov < 50% (meaning <50% stat. prop c/f) Effect: RPP: Recov. Prop. to chance lost (meaning stat. prop. c/f) Limit: chance/prob > 50%, full recov, not RPP. RPP - % C/F -> % recovery Lost chance is RPP w/ less than preponderance of the evidence. A way to pin the tail on the donkey. ? Is this Honest? Examples/Application : 1-NO lost chance, pay 100%, preponderance w/ 75% survival rate 1000 cases w/ negligence + injury 750, injury due to negligence 250, die/lose limb anyway. 2-LOST CHANCE, RPP, pay 25% w/ 25% success rate 1000 cases w/ n + injury only 250, inj. Due to n 750 die/lose limb anyway Lost Chance turns torts into an insurance scheme. Why do we give up the preponderance rule for L/C? <50% rate allows for some compensation >50% allows for full recovery Why med and not toxic leaker? Then, dont want Enormous Scope. It cant be logically contained. It fits with natural human thought around med ie. Chance of recovery intrinsic way of talking about med inj. L/C is trick language. C/F Special Rules: Summers v. Tice (neither can expulpate, Drag Net rule) Conditions:
>1 poss. c/f, must be 1, cant ID which all poss. c/f neg. innocent all poss./cfs sued, in court Effect: switch burden of proof (s only people with the access to the needed information/evidence) actually: proves c/f, and jt. Sev. Liabl. JSL- may recover from any of the Ds, 100% ( can sue other for share) C/F Special Rules: Concert of Action (c/a) Conditions: >1 poss. c/f engaged in joint activity with mutual encouragement, tacit or explicit (all in court?) **** Effect: JSL, bec. all responsible (if any pulls out, no c/a) drag race is the clearest example C/F Special Rules: Mkt. Share Liabil (Sindell) no collective action Conditions: >1 poss. c/f, must be 1, cant id which (fungible product) all poss./cfs neg. inn. sues producers resp. for substl share of total mkt. sales Effect: RPP (w/ stat. evid. of mkt. share) liabil. of each p/cf ltd. To mkt. share Could this extend RPP beyond Med. Mal. ? Reasons for Mkt. Share Rule: 1-inn. Victim w/ neg. tort feasor, tortfeasor should pay 2-s are better able to bear the expense - manufacturer best able to control quality of the goods Policy: Deterrance / Social Welfare / Providing Compensation
Example: A basis C/F argument the snow man hypo s argument against Dillons (storefront with flag) But For s Neg -> too big /too heavy a. no flag fall ev- the length of the flag shorter, snowhead wouldnt have hit the flag. b. no horse run the head crash wouldnt have caused the horse to run because the explosion already happened -evidence : composure of the horse- this horse is very calm, only the big flag would have scared her. s argument: even if non-neg -> flag small
10
a. flag fallen anyway ev-horse of the crash was huge b. horse wouldve run anyway no composure c. external 3rd cause bitten by a snake or bee. s argument against the bank: but for your poor maintenance/care a. no exploding head/ flying head b. no flying head, no falling flag ev-cracking sound , head bounce **? even if no neg proper care -> no explosion a. flag wouldve fallen anyway ev cracking siding 1. basic case neg +cause in fact 2. reactive defenses even if I wasnt negligent VI. Proximate Cause: neg assumed, c/f assumed . for the jury OK my conduct was bad, but, -> n + cf no liability s argument I was not a proximate cause. 1- 3 party intervener - 3p I/v cause 2- unforeseeable even tho def. = N & C/F, no liabil if no prox. Cause superceding interv. Cause (sic) unforeseeable type of harm (ufto) unforeseeable victim (rem. In t/sp) but uf amount/ext. dam irrelevant (t-skulled plaintiff rule u still have to pay for thin skulled peoples damages) 1. SIC (polemis) -conditions (for no prox/cause) 3p intervenors cond. = rless or delib. AND 3ps r/d conduct = UF to def. Effect: origl actor free of liabil. Only sic pays Burden of Proof: on the to prove the fability of the I/V In Doe (rape) insuffic. Ev. From to show the could have foreseen (neighborhood crime statistics et al. )
2. UFTO (Wagon Mound) -conditions (for no prox/cause) First, evidence of Unforseeability (scientific, expert testimony) actual acc./occur. UF per se
11
(as factual matter, given evidence) AND actual acc./occ. Diff in kind/char. From FHOs TEST: are forces behind acc. Subject to the same controls as forces behind FHOs? if yes, not UFTO: if no, UFTO Effect: Def. free of liabil, NO ONE PAYS 3. UFP/V (Palsgraf) or Remness T/SP even if occur. = fo p/v unforeseeable - given facts/ circumstance of case - purely factual argument ? ****so: in WM jurisd. first argue UFTO if FTO, argue UFP/V or rem. In t/sp in polemis jur: remness t/space In a WM Jurisdiction all 3 arguments made SIC, UFTO, UFP/V In Polemis Jurisdiction SiC + UFP/V(Remness T/Sp) VII. DUTY / No Duty like proximate cause s issue -so makes no duty argument , must anticipate and parry
NO DUTY more powerful than no p/c -no p/c : for jury, during trial no duty: for court, blocks trial if raised on summary jmt. , m/dismiss n/d = no trial ** Six No Duty Arguments*** 1) n/d for nonfeas 2) n/d for policy/neg.econ.impact 3) ltd. n/d for premises injury 4) n/d for social host 5) n/d for govt discr/policy 6) n/d for neg. emotl distress 1. N/D --- NON FEASANCE Feas/nonfeas = RIB v. RNB
12
no duty / no trial for RNB bec. of autonomy/liberty policy interests. if adds any new risk = RIB, inquiry ok, trial ok. types of RIB argument: A. specific affirmative conduct B. initiation of special relshp -argue one or both, but separately. A. Feasance/RIB by aff. Conduct i. direct imposition by D. (move body) (or) ii. indirect impos. By D inducing reliance by V or 3P (stop, start to help, retreat) -key: show exactly where new risk added just show changing of the risk profile ie. Taking a drunk and putting him in a police car adds new risk (of a car accident) OR B. Feas/RIB by initiat. Spec rel. -must argue type of relshp (L/ten-landlord-tenant, dr./pat., t/stud) not specific parties to the case. -two types: Control or Protection -address one or both but separately i. Control Relship - and 3P injurer are in type of relshp in which D-Role becomes controller of 3P role -prove by precedent or factors -FACTORS: D Role has abil. To predict the need for control D Role has abil. To exercise control D role takes charge, 3P role submits (or) ii.protection relshp Posecai- Protection relship btw. Cust. And WalMart? - and V are in type of relshp in which d-role becomes protector of V-role -prove by precedent or factors -factors: d role has abil. To predict need for protection d role has ability to provide protection v role surrenders self/prot. Abil. D role takes under wing
2. N/D : Policy / Neg. Econ. Impact clearly feasance, but policy dictates no trial /inquiry -bec. of neg. econ. Impact of costs of trial/liabil.
13
-applicable in public utility (pub. Util.) and other cases -only where class of Vs is large and undefd. (strauss v. coned during blackout) policy concerns: social justice imposing high costs of doing business excludes poor people from basic services public order escalation of arms, police not as powerful (posecai no duty to have armed guards)
3. N/D Premises Liability Framework: types of Vs invitee: bus. visitor, comes for matter/econ. Ben. of D (business economic benefit) duty = rble care to discover/fix dangerous conds (hidden) and the open and obvious. licensee: socl guest, comes for social contact, w/ permission duty = warn of dang. Conds known to D that are hidden from LIC. N/D to fix open and obvious danger. trespasser: intrudes w/o perm. (permission) duty = avoid traps, extreme rless (reckless) inj. Duty for - wilful or wanton conduct. (Or) s/std mod. duty- r/care for all (licensee/invitee/trespasser) although-in some jur., not for T. (trespasser) why ltd. duty in trad. categ. ? - policy goals justify ltd. duty/inq. - autonomy/liberty (if not invitee ) - Neg. econ. Impact - Social relations / civility Under Licensee category ltd. scope, ltd. duty of trial : 1) did the know? 2) If so, did they warn? 3) Did notice the danger? 4. N/D gov/tal immunity No duty for govtal acts (leg/exec. Decisions on $ cant be questioned) govt act / discretionary act -incls any decis. (decisions) on resource allocation (res. Alloc.)
14
Why no duty ? What policy? -separation of powers -neg. econ. Impact But, DUTY for acts of gov. offl if: -proprietary, ministerial, ordinary -meaning : executing policy -so: making policy - > no duty / inq. -but, carrying out policy - > duty/ inq. And DUTY if: -affirmative undertaking 5. N/D for E/D (emotional distress) N/D for E/D unless 1) Zone of Danger actions threaten imminent bodily injury (or ) 2) shocking situation - > death of a loved one (or misdiagnosis of fatal disease) (or) 3) made V witness to 3PH (3rd party harm) NY- NO DUTY FOR Witness to 3PH factors: (dillon case) FACTORS (CALI) close relationship observation w. their own senses observ. Contemp w/ accid (at the time) conditions: (portee) ELEMENTS (must be met specifically) - NJ marital/intim. observ at scene D/serious bodily injury severe e/d (or) Tobin- N/D for witness to 3ph 6- N/D Social Host no liabil. of s/host for acts of drunken guest policy bases : neg. econ. Impact social relations civility usually stated as no p/cause as matter of law why? interference w/ consortium spouse sues for damage to the household
15
- replacement cost household duties. statutory recovery for survival actions/executor sues for pre-death costs. -usually not recoverable for kids/elderly. s Case N std. quals (qualifications) -R-AV -NPS Proof RIL CF - But-For - Stat - Spl Rules PC -SIC -UFTO -UFP (rem. t/sp) D -N-Feas -econ pol -prems (2) -s/host -?? WM? -N E/D Dam -compens -P +S (pain & suffering) -w/d -l/c VIII. Defenses: Contrib. Neg. & Assumption of Risk Affirm Defenses focus on s conduct When? if n/cf/pc etc. if no N, no D - > no need for aff. Basic Overview: CN-(contrib neg) AR -(Ass. Of risk) A. CN elements- mirror s arg. But argue s neg. R-AV NPS CF P/C
16
CN weakened/diluted highly limited b.c ppl dont want to get hurt -> they want to take care of themselves. victims bad conduct assessed much lower than -> more lenient in judging v neg. traditional view CN bar to recovery but since jury decides, CN often dissappears (ie. already shown case) B. Assumption of risk 2 kinds of VAR EAR : express & IAR : implied both: k/agreement of risk of negligence IAR-conduct implies A/R Cardozo in the flopper case-No Neg risk low, CAv high Posecai & baseball screens allow for categorical no neg. for policy reasons (to avoid chilling effect) social harmony policy (like no duty for social host liabil.) recklessness - C/N irrelevant recklessness total bar to recovery courts beginning to stretch liability even under EAR Comp Fault: aff (CN or A/R) Does not completely bar recovery , reduces damages Neg/reckless / - characterize by degree of badness CN- neg A/R recklessness
IX. Strict Liability (s arg.) Rest. 1 UHA conditions for S/L (no consideration of societal value) 1) Hi Non-Elim Risk (NER) 2) Not Common ( arg.) Rest 2- ADA SL 1) hi prob of harm ^ Risk 2) great harm if it happens ^ 3) non-elim risk (ner) ^ 4) not common ^ 5) inapprop. loc. ----- Cav low 6) Low societal value -----Is this is a neg argument then? R > Cav = N? Factors: How? (class r analysis) Where? (do it elsewhere?) Whether? (worthwhile)
17
Hypo: Transporting a caustic substance = NO ADA SL 1) hi prob of harm 2) great harm 3) ner 4) uncommon 5) inappropriate location? ---NO this is the best way to do it 6) low societal - -- NO ---- this is high value (need the substance) So, Risk High, but Cav is even higher NO SL Or viol. ADA conds 5-6
18
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Florida Real Estate Exam Prep: Everything You Need to Know to PassVon EverandFlorida Real Estate Exam Prep: Everything You Need to Know to PassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bush Torts BriefsDokument73 SeitenBush Torts BriefsChristine YuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Civil Procedure OverviewDokument16 SeitenFederal Civil Procedure OverviewStacy OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pennsylvania Railroad v. ChamberlainDokument1 SeitePennsylvania Railroad v. Chamberlaincrlstinaaa100% (2)
- LSL Torts HandoutDokument15 SeitenLSL Torts HandoutJon HimesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil ProcedureDokument2 SeitenCivil ProceduretylerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Property Case OutlineDokument66 SeitenProperty Case OutlineMissy MeyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Civil Procedure: A. Benjamin SpencerDokument10 SeitenFederal Civil Procedure: A. Benjamin Spencermarkarmstrong42Noch keine Bewertungen
- LBH Spring17 FinalDokument16 SeitenLBH Spring17 Finalapi-240547583Noch keine Bewertungen
- $6Wxghqw V Xlghwr&Dvh%Ulhilqj: The Case Method: in First-Year Law Courses, Professors Typically DoDokument4 Seiten$6Wxghqw V Xlghwr&Dvh%Ulhilqj: The Case Method: in First-Year Law Courses, Professors Typically DoLeizza Ni Gui Dula100% (1)
- Torts OutlineDokument23 SeitenTorts OutlineRichard SebestianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honors A Outline CPDokument27 SeitenHonors A Outline CPBranden LaxnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- NY Mini ReviewDokument32 SeitenNY Mini Reviewlaurabayne17501Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Essay Questions With AnswersDokument13 SeitenSample Essay Questions With AnswersMarlin PohlmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CivPro-McCormick v. KopmannDokument3 SeitenCivPro-McCormick v. KopmannBrian Stephen SchererNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm PracticeDokument18 SeitenMidterm PracticeJulia MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constituional LawDokument8 SeitenConstituional LawQuiana MontgomeryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civ Pro Spring 2014Dokument23 SeitenCiv Pro Spring 2014Zachary Figueroa100% (1)
- Enviro OutlineDokument9 SeitenEnviro OutlineWade FellinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Analysis Balmer Vs ElanDokument1 SeiteCase Analysis Balmer Vs ElanTosha BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remedies 2002 Model AnswersDokument9 SeitenRemedies 2002 Model AnswersKeenan SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline Shell Midterm TortsDokument11 SeitenOutline Shell Midterm Tortsexner2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Present Estates and Future InterestsDokument46 SeitenPresent Estates and Future InterestsFacu BernardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talmage v. SmithDokument1 SeiteTalmage v. SmithKhalil Hassan QuinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CharacterDokument15 SeitenCharacterZarah TrinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rezoning MemoDokument4 SeitenRezoning MemoSara MessinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appellant Brief Johnson V Laurels and Oak Health CareDokument61 SeitenAppellant Brief Johnson V Laurels and Oak Health CareKenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CivPro OutlineDokument238 SeitenCivPro OutlineNoam LiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief PropertyDokument4 SeitenBrief Propertyshakinmakin84Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2195 Crim Pro I OutlineDokument101 Seiten2195 Crim Pro I OutlineMariam BabayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Northbrook Court Redevelopment Preliminary Review 9-25-18Dokument29 SeitenNorthbrook Court Redevelopment Preliminary Review 9-25-18Jonah MeadowsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trademarks Tushnet Fall-2015 OutlineDokument102 SeitenTrademarks Tushnet Fall-2015 Outlinea thayn100% (1)
- Case ListDokument12 SeitenCase ListLaura HoeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objection 20handbookDokument26 SeitenObjection 20handbookDolićanin N. SanelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 62 Question Test Answer SheetDokument1 Seite62 Question Test Answer SheetzumiebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Head Civ ProDokument55 SeitenBig Head Civ ProSucolTeam6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civ Pro Essay FormatDokument1 SeiteCiv Pro Essay FormatMolly EnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crim. Law ATTACK Outline - Alschuler - Spring 2009 ChecklistDokument8 SeitenCrim. Law ATTACK Outline - Alschuler - Spring 2009 ChecklistDaniel BarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result: Factual CausationDokument4 SeitenResult: Factual CausationNawazish AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ny All LocationsDokument1 SeiteNy All LocationsHarpott GhantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIRACDokument1 SeiteCIRACJeremiahgibsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antitrust Casebook NotesDokument24 SeitenAntitrust Casebook NotesJenny QiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organize by Headings & Subheadings, Use Paragraphs: Statutory Construction ChecklistDokument4 SeitenOrganize by Headings & Subheadings, Use Paragraphs: Statutory Construction ChecklistHeidi Katherine RuckriegleNoch keine Bewertungen
- conversion/tmp/activity - Task - Scratch/541632757.docx Last Saved: 0/0/0000 0:00:00 AMDokument147 Seitenconversion/tmp/activity - Task - Scratch/541632757.docx Last Saved: 0/0/0000 0:00:00 AMAndrew FergusonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1 Partnership MM oDokument4 SeitenCH 1 Partnership MM osomeguy813Noch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Procedure Checklist - NoticeDokument7 SeitenCivil Procedure Checklist - Noticeharrier666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Con Law Outline 2009Dokument36 SeitenComparative Con Law Outline 2009The LawbraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing SkillsDokument10 SeitenWriting Skillsca1robby15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mpre Ope 1Dokument62 SeitenMpre Ope 1Julie DnqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mon FallaciesDokument4 SeitenMon FallaciesPaul WigginsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intentional Torts Intentional Torts D Case Law: Efinition ElementsDokument12 SeitenIntentional Torts Intentional Torts D Case Law: Efinition ElementsjaredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therefore ASAHI S.O.C.: Cts Use This Analysis When Dealing With Products. Product CanDokument2 SeitenTherefore ASAHI S.O.C.: Cts Use This Analysis When Dealing With Products. Product CanCory BakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snow Ip 2016Dokument2 SeitenSnow Ip 2016api-240547583Noch keine Bewertungen
- Supreme Court IdeologyDokument4 SeitenSupreme Court IdeologyJaycee Keller NormanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hls LRW Fall 2016 Week 2Dokument14 SeitenHls LRW Fall 2016 Week 2Alex KozinskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Great Bar Exam Game PlanDokument5 SeitenThe Great Bar Exam Game PlanJastin GalariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompGuide2020 021820 Online FinalDokument72 SeitenCompGuide2020 021820 Online FinalZairaYazminGarcia100% (1)
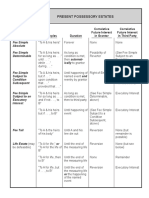
- Present Possessory Estates PDFDokument1 SeitePresent Possessory Estates PDFflorinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Professional Resp ExamDokument5 SeitenProfessional Resp ExamMaybach Murtaza100% (1)
- TFT AssignmentDokument2 SeitenTFT Assignmentpranav pomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro 11111Dokument8 SeitenIntro 11111aldric taclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Law Enforcement ReportDokument2 SeitenTraffic Law Enforcement ReportAngel TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart 3Dokument1 SeiteChart 3SravanPolepalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Traffic Problems in IndiaDokument25 SeitenUrban Traffic Problems in IndiaSunakshi MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Plant LayoutDokument18 SeitenIndustrial Plant Layoutamit singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 機車情境式題目 英文Dokument60 Seiten機車情境式題目 英文Sam SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCTV Case StudyDokument23 SeitenCCTV Case Studycarrie navaNoch keine Bewertungen
- North Perimeter Highway Public Engagement PresentationDokument22 SeitenNorth Perimeter Highway Public Engagement PresentationChrisDcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMDTINST M16672.2 Navigation Rules International InlandDokument220 SeitenCOMDTINST M16672.2 Navigation Rules International Inlandeckster16Noch keine Bewertungen
- 04 POSSIBLECAUSESANDSOLUTIONS-MD RomanSarkarDokument17 Seiten04 POSSIBLECAUSESANDSOLUTIONS-MD RomanSarkarakanksha.nijaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Zone Traffic Management Guide Version 1.2 - November 2015 IrfanDokument26 SeitenWork Zone Traffic Management Guide Version 1.2 - November 2015 IrfansamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed Construction of A Three-Storey Pay ParkingDokument134 SeitenProposed Construction of A Three-Storey Pay ParkingJan Angelo CiudadanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civl 340 - Review-2023Dokument27 SeitenCivl 340 - Review-2023justinkarlpolicarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greenstar 3 2630Dokument402 SeitenGreenstar 3 2630Jonathan Willian TozzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic SafetyDokument2 SeitenTraffic SafetyIoana UrsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Rules and RegulationsDokument11 SeitenTraffic Rules and RegulationsRashid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligent Transportation Systems and Parking Management: Implementation Potential in A Brazilian CityDokument12 SeitenIntelligent Transportation Systems and Parking Management: Implementation Potential in A Brazilian CityfahmiamroziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Development of Functional Requirements and Evaluation of Adaptive Traffic Control SystemsDokument13 SeitenGuidelines For Development of Functional Requirements and Evaluation of Adaptive Traffic Control SystemsDaniel GhitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAST Diagram: Project TitleDokument10 SeitenFAST Diagram: Project TitletechnicalvijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The - Road - Traffic Act CAP 168Dokument71 SeitenThe - Road - Traffic Act CAP 168Francisco Hagai GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A48 Bonvilston - Speeding Traffic - 040618Dokument2 SeitenA48 Bonvilston - Speeding Traffic - 040618api-281399735Noch keine Bewertungen
- InfoVista Live Small Cell Planning For Ericsson LTEDokument22 SeitenInfoVista Live Small Cell Planning For Ericsson LTEMiguel Andres Vanegas GNoch keine Bewertungen
- COP Vehicles Parking ProvisionDokument80 SeitenCOP Vehicles Parking ProvisionAden Foo100% (1)
- Proposal To Overhaul The Intersection of Yellowstone Boulevard and Austin StreetDokument15 SeitenProposal To Overhaul The Intersection of Yellowstone Boulevard and Austin StreetDNAinfoNewYorkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Final DependDokument14 SeitenThesis Final DependLeia Grace Elaine100% (6)
- Mtt29 MG Files 2015Dokument28 SeitenMtt29 MG Files 2015newspubincNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification For Onshore PipelinesDokument737 SeitenSpecification For Onshore PipelinesKarun Das75% (4)
- Lbzala STTP AditDokument77 SeitenLbzala STTP AditKRUTI DESAI100% (1)
- Accepted Safety Barriers V2 PDFDokument20 SeitenAccepted Safety Barriers V2 PDFRichu PaliNoch keine Bewertungen