Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Psychology Study Guide 1
Hochgeladen von
Nicole WolfOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Psychology Study Guide 1
Hochgeladen von
Nicole WolfCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Psychology Study Guide 1
Vocabulary:
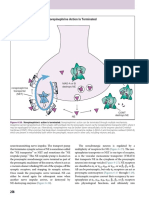
1. Acetylcholine: neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contraction through the release of sodium ions 2. Action Potential: spike of an electrical charge that travels along the membranes of a cell, used by neurotransmitters to communicate between neurons and other body tissues 3. Adaptation: trait of an organism that has been favored by natural selection 4. Applied Psychologist: the use of psychological principles and theories to overcome problems in other areas, such as mental health, business management, education, health, product design, ergonomics, and law. Applied psychology includes the areas of clinical psychology, industrial/organizational psychology, human factors, forensic psychology, engineering psychology, as well as many other areas such as school psychology, sports psychology and community psychology. In addition, a number of specialized areas in the general field of psychology have applied branches (e.g., applied social psychology, applied cognitive psychology). 5. Autonomic System: system that operates and serves its purpose by managing its self without external intervention even in the event of environmental changes 6. Axon: long, slender projection of a nerve cell that conducts electrical impulses away from the neurons cell body (soma) 7. Behavior: actions or reactions of an organism, usually in response to the environment 8. Behaviorism: (also called learning perspective) is a philosophy of psychology based on the proposition that all things which organisms do including acting, thinking and feelingcan and should be regarded as behaviors. The school of psychology maintains that behaviors as such can be described scientifically without recourse either to internal physiological events or to hypothetical constructs such as the mind. Behaviorism comprises the position that all theories should have observational correlates but that there are no philosophical differences between publicly observable processes (such as actions) and privately observable processes (such as thinking and feeling). (Skinner) 9. Case Study: in-depth study of a single incident/person (case) 10. Central Nervous System: largest part of the nervous system, includes the brain and spinal cord controls actions 11. Cerebellum: region of the brain that plays an important role in the integration of sensory perception and motor output 12. Cerebral cortex: brain-memory, attention , language, perceptual awareness, consciousness 13. Clinical Psychologist: the scientific study and application of psychology for the purpose of understanding, preventing, and relieving psychologically-based distress or dysfunction and to promote subjective well-being and personal development (Wundt)
14. Cognitive revolution: combination of psychology, anthropology and linguistics with approaches to neuroscience, artificial intelligence, and computer science 15. Computerized tomography scan (CT scan): medical imaging method employing tomography where digital geometry processing is used to produce a 3D image. 16. Confidentiality: ensuring that information is only available to those authorized to have access 17. Confounding variable: variable that should but has not been controlled in an experiment, can lead to false results and an indirect relationship 18. Corpus callosum: thing that connects the 2 hemispheres of the brain and allows them to transmit information 19. Correlation:
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Human Biology NotesDokument30 SeitenHuman Biology Notesdanlayton100% (5)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesDokument130 SeitenThe Muscular System: Powerpoint Lecture SlidesTricia Mae CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System NotesDokument25 SeitenNervous System NotesRhey BascosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psyc 100 NotesDokument157 SeitenPsyc 100 NotesJi Wook HwangNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nervous SystemDokument110 SeitenThe Nervous SystemZeren Joy C. AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEG Signal Analysis and Classification: Siuly Siuly Yan Li Yanchun ZhangDokument257 SeitenEEG Signal Analysis and Classification: Siuly Siuly Yan Li Yanchun ZhangarjetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insecticide Mode of ActionDokument76 SeitenInsecticide Mode of ActionPheromonalNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Major Conservative and Libertarian Thinkers) Adam James Tebble, John Meadowcroft-F.a. Hayek-Bloomsbury Academic (2010)Dokument175 Seiten(Major Conservative and Libertarian Thinkers) Adam James Tebble, John Meadowcroft-F.a. Hayek-Bloomsbury Academic (2010)Patrick100% (1)
- Stahl' Essential Psychopharmacology 276 PDFDokument1 SeiteStahl' Essential Psychopharmacology 276 PDFMuhammad AzkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.00 Exam 1 Notes: KOSSLYN CHAPTER 2 - The Biology of Mind and Behavior: The Brain in ActionDokument12 Seiten9.00 Exam 1 Notes: KOSSLYN CHAPTER 2 - The Biology of Mind and Behavior: The Brain in ActiondreamanujNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A NeuronDokument5 SeitenWhat Is A NeuronJason StevetimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain DevelopmentDokument13 SeitenBrain DevelopmentSumitha Mathivallan100% (1)
- Science Reviewer For Science Quiz Elementary: MatterDokument30 SeitenScience Reviewer For Science Quiz Elementary: MatterIan BelgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meeting 1 - NounsDokument5 SeitenMeeting 1 - NounsMalasari Lala0% (1)
- DEA 1500 NotesDokument2 SeitenDEA 1500 NotesJean KwonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - F5 - Coordination and ResponseDokument22 SeitenChapter 3 - F5 - Coordination and ResponseWen Shan ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACTIVITY #4G10 Feb 27Dokument2 SeitenACTIVITY #4G10 Feb 27Real Mae DayacusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwnload Full Essentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition Feldman Test Bank PDFDokument25 SeitenDwnload Full Essentials of Understanding Psychology Canadian 5th Edition Feldman Test Bank PDFlogosdeviatorjx3b7i100% (9)
- Week 5-Earth-and-Life-ScienceDokument80 SeitenWeek 5-Earth-and-Life-ScienceChaeyoung ParkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alzheimer Disease EngDokument35 SeitenAlzheimer Disease EngAna IantucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 Quarter 3 Module 3Dokument15 SeitenScience 10 Quarter 3 Module 3Zahra Alexä DavidsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Spychology Exam 1Dokument24 SeitenIntro Spychology Exam 1talk2ajalatundeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 004 Animal-Nervous-SystemDokument8 SeitenWeek 004 Animal-Nervous-SystemMark Lorens StaanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Sc. Psychology SyllabusDokument37 SeitenB.Sc. Psychology SyllabusDharshenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioelectric PhenomenonaDokument18 SeitenBioelectric PhenomenonaShibli Shadik100% (1)
- ClassificationDokument32 SeitenClassificationGauravSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly AssignmentDokument7 SeitenWeekly AssignmentBajwa AyeshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022Dokument16 SeitenSHENIBLOG-Class 10 Biology Focus Area Covered Notes (Eng Med) All Chapters 2022kailaskrishnaushusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staying Sharp Puzzle SeriesDokument18 SeitenStaying Sharp Puzzle Seriesmaureenles100% (1)
- Module 1.1 - Introduction To Biological Psychology and The Nerve CellsDokument8 SeitenModule 1.1 - Introduction To Biological Psychology and The Nerve CellsJoselitz Reyes TumulakNoch keine Bewertungen