Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lab 2.8.3.2
Hochgeladen von
free334Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lab 2.8.3.2
Hochgeladen von
free334Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lab 2.8.
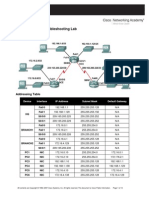
3: Troubleshooting Static Routes Topology Diagram
Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 N/A BRANCH S0/0/0 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 N/A Fa0/0 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128 N/A S0/0/0 172.20.1.2 255.255.255.128 N/A HQ S0/0/1 192.168.38.254 255.255.255.252 N/A FA0/0 192.168.39.65 255.255.255.192 N/A ISP S0/0/1 192.168.38.253 255.255.255.252 N/A PC1 NIC 172.20.1.135 255.255.255.128 172.20.1.129 PC2 NIC 172.20.0.135 255.255.255.128 172.20.0.129 Web Server NIC 192.168.39.70 255.255.255.192 192.168.39.65
Learning Objectives Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Cable a network according to the Topology Diagram. Erase the startup configuration and reload a router to the default state.
Load the routers with supplied scripts. Discover points where the network is not converged. All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 1 of 9 CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: Static Routing Lab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes
Gather information about errors in the network. Propose solutions to network errors. Implement solutions to network errors. Document the corrected network. Scenario In this lab, you will begin by loading configuration scripts on each of the routers. These scripts contain errors that will prevent end-to-end communication across the network. You will need to troubleshoot each router to determine the configuration errors, and then use the appropriate commands to correct the configurations. When you have corrected all of the configuration errors, all of the hosts on the network should be able to communicate with each other. Task 1: Cable, Erase, and Reload the Routers. Step 1: Cable a network that is similar to the one in the Topology Diagram. Step 2: Clear the configuration on each router. Clear the configuration on each of routers using the erase startup-config command and then reload the routers. Answer no if asked to save changes. Task 2: Load Routers with the Supplied Scripts. Step 1: Load the following script onto the BRANCH router:
hostname BRANCH ! no ip domain-lookup ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 172.20.1.129 255.255.255.128 duplex auto speed auto no shutdown ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 172.20.1.1 255.255.255.128 clock rate 64000 no shutdown ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.20.0.129 ! line con 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login ! end
Step 2: Load the following script onto the HQ router:
hostname HQ
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 9 CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: Static Routing Lab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes
! no ip domain-lookup ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 172.20.0.129 255.255.255.128 duplex auto speed auto no shutdown ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 172.20.1.2 255.255.255.128 no shutdown ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.38.254 255.255.255.252 clock rate 64000 no shutdown !
ip route 192.168.39.64 255.255.255.192 192.168.38.253 ! line con 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco login ! end Step 3: Load the following script onto the ISP router: hostname ISP ! no ip domain-lookup ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.39.65 255.255.255.192 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.38.253 255.255.255.252 no shutdown ! ip route 172.20.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.38.254 ! line con 0 line vty 0 4 password cisco
login ! end Task 3: Troubleshoot the BRANCH Router. Step 1: Begin troubleshooting at the host connected to the BRANCH router. From the host PC1, is it possible to ping PC2? _No______ From the host PC1, is it possible to ping the Web Server on the ISP LAN? ____NO___ From the host PC1, is it possible to ping the default gateway? ___yes____ Routing Protocols and Concepts: Static Routing Lab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes
Step 2: Examine the BRANCH router to find possible configuration errors. Begin by viewing the summary of status information for each interface on the router. Are there any problems with the status of the interfaces? no ___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________
If there are any problems with the status of the interfaces, record any commands that will be necessary to correct the configuration errors. The no shutdown command is missing from the fastethernet 0/0 interface and the subnet mask is also incorrect.
Step 3: If you have recorded any commands above, apply them to the router configuration now. Step 4: View summary of the status information. If any changes were made to the configuration in the previous step, view the summary of the status information for the router interfaces again. Does the information in the interface status summary indicate any configuration errors? _______ If the answer is yes, troubleshoot the interface status of the interfaces again. Step 5: Troubleshoot the static routing configuration on the BRANCH router. Begin by viewing the routing table. What routes are shown in the routing table? 172.20.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 172.20.1.128 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
Are there any problems with the routing table? The static default route to the HQ router is missing from the routing table because the destination address in the ip route statement is incorrect.
If there are any problems with the routing table, record any commands that will be necessary to correct the configuration errors. BRANCH(config)# no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.20.0.129 BRANCH(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.20.1.2
CCNA Exploration Routing Protocols and Concepts: Static Routing Lab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes
Step 6: If you have recorded any commands above, apply them to the router configuration now. Step 7: View routing information. If any changes were made to the configuration in the previous step, view routing table again. Does the information in the routing table indicate any configuration errors? no If the answer is yes, troubleshoot the routing table again. Step 8: Attempt to ping between the hosts again. From the host PC1, is it possible to ping PC2? no From the host PC1, is it possible to ping the web server on the ISP LAN? no From the host PC1, is it possible to ping the Serial 0/0/0 interface of HQ? yes Task 4: Troubleshoot the HQ Router. Step 1: Begin troubleshooting at the host connected to the HQ router. From the host PC2, is it possible to ping PC1? no From the host PC2, is it possible to ping the Web Server on the ISP LAN? no From the host PC2, is it possible to ping the default gateway? yes Step 2: Examine the HQ router to find possible configuration errors. Begin by viewing the summary of status information for each interface on the router. Are there any problems with the status of the interfaces? Yes, the interface status and the protocol on Serial 0/0/1 are both down If there are any problems with the status of the interfaces, record any commands that will be necessary to correct the configuration errors. HQ(config)# interface Serial0/0/1 HQ(config-if)# clock rate 64000 Step 3: If you have recorded any commands above, apply them to the router configuration now. Step 4: View summary of the status information. If any changes were made to the configuration in the previous step, view the summary of the status information for the router interfaces again.
Does the information in the interface status summary indicate any configuration errors? no If the answer is yes, troubleshoot the interface status of the interfaces again.
Step 5: Troubleshoot the static routing configuration on the HQ router. Begin by viewing the routing table. What routes are shown in the routing table? 172.20.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 192.168.38.252 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 Are there any problems with the routing table? The route for the BRANCH LAN, 172.20.1.128/25, is missing from the routing table If there are any problems with the routing table, record any commands that will be necessary to correct the configuration errors. HQ(config)# ip route 172.20.1.128 255.255.255.128 172.20.1.1 Step 6: If you have recorded any commands above, apply them to the router configuration now. Step 7: View routing information. If any changes were made to the configuration in the previous step, view the routing table again. Does the information in the routing table indicate any configuration errors? no If the answer is yes, troubleshoot the routing table again. Step 8: Attempt to ping between the hosts again. From the host PC2, is it possible to ping PC1? yes From the host PC2, is it possible to ping the Serial 0/0/1 interface of the ISP router? yes From the host PC1, is it possible to ping the Web Server on the ISP LAN? no Task 5: Troubleshoot the ISP Router. Step 1: Begin troubleshooting at the host connected to the ISP router.
From the Web Server on the ISP LAN, is it possible to ping PC1? no From the Web Server on the ISP LAN, is it possible to ping PC2? no From the Web Server on the ISP LAN, is it possible to ping the default gateway? yes Step 2: Examine the ISP router to find possible configuration errors. Begin by viewing the summary of status information for each interface on the router. Are there any problems with the status of the interfaces? The FastEthernet 0/0 interface is administratively down
If there are any problems with the status of the interfaces, record any commands that will be necessary to correct the configuration errors. ISP(config)# interface FastEthernet0/0 ISP(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 3: If you have recorded any commands above, apply them to the router configuration now. Step 4: View summary of status information. If any changes were made to the configuration in the previous step, view the summary of the status information for the router interfaces again. Does the information in the interface status summary indicate any configuration errors? no If the answer is yes, troubleshoot the interface status of the interfaces again. Step 5: Troubleshoot the static routing configuration on the ISP router. Begin by viewing the routing table. What routes are shown in the routing table? 172.20.0.0 [1/0] via 192.168.38.254 192.168.38.252 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 192.168.39.64 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
Are there any problems with the routing table? The wrong subnet mask is used in the ip route statement for the 172.0.0.0 network. If there are any problems with the routing table, record any commands that will be necessary to correct the configuration errors. ISP(config)# no ip route 172.20.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.38.254 ISP(config)# ip route 172.20.0.0 255.255.254.0 192.168.38.254 Step 6: If you have recorded any commands above, apply them to the router configuration now. Step 7: View routing information. If any changes were made to the configuration in the previous step, view the routing table again.
Does the information in the routing table indicate any configuration errors? no If the answer is yes, troubleshoot the routing table again. Step 8: Attempt to ping between the hosts again. From the Web Server on the ISP LAN, is it possible to ping PC1? yes From the Web Server on the ISP LAN, is it possible to ping PC2? yes From the Web Server on the ISP LAN, is it possible to the WAN interface of the BRANCH router? yes Task 6: Reflection There were a number of configuration errors in the scripts that were provided for this lab. Use the space below to write a brief description of the errors that you found.
Task 7: Documentation On each router, capture the following command output to a text (.txt) file and save for future reference. show running-config
show ip route show ip interface brief If you need to review the procedures for capturing command output, see Lab 1.5.1, Cabling a Network and Basic Router Configuration. All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 9 of 9
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ARC2 1.1 Jun12 StudentWorkbookDokument393 SeitenARC2 1.1 Jun12 StudentWorkbookgi921120100% (2)
- E2 Lab 11 6 3Dokument10 SeitenE2 Lab 11 6 3Ninja NuggetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interas Mpls VPNDokument34 SeitenInteras Mpls VPNAmit Baran ChatterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offensive Security: Penetration Test Report For OSCP ExamDokument17 SeitenOffensive Security: Penetration Test Report For OSCP ExamBlack BoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Romance Scammers in Dating Apps and Sites.: Hatim Madkhali Kentucky State University, USADokument11 SeitenRomance Scammers in Dating Apps and Sites.: Hatim Madkhali Kentucky State University, USAAnonymous fyU9mDk6A100% (1)
- Rfid ProjectDokument27 SeitenRfid ProjectVinay Krishna VadlamudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Carrier Ethernet Services Using Cisco Ethernet Virtual Circuits (EVC)Dokument45 SeitenBuilding Carrier Ethernet Services Using Cisco Ethernet Virtual Circuits (EVC)Daniel VieceliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsVon EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3gpp Charging PrinciplesDokument65 Seiten3gpp Charging Principlesjackw11100% (1)
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsVon EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- 4.2.2.7 Lab - Building An Ethernet Crossover CableDokument6 Seiten4.2.2.7 Lab - Building An Ethernet Crossover Cablerezhablo100% (2)
- E2 Lab 1 5 3Dokument4 SeitenE2 Lab 1 5 3jocko18100% (1)
- ICND120LGDokument262 SeitenICND120LGbetofranco530100% (1)
- Final Skills InstructionsDokument5 SeitenFinal Skills InstructionsEvren Asli Akçay0% (2)
- Advanced Internetworking Lab 2 - Dynamic RoutingDokument12 SeitenAdvanced Internetworking Lab 2 - Dynamic Routingmatale50% (1)
- Alcatellucentingns3 150105182641 Conversion Gate01Dokument6 SeitenAlcatellucentingns3 150105182641 Conversion Gate01parthieeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel-Lucent 5620 SAM (Service Avare Manager) - WWW - IpciscoDokument12 SeitenAlcatel-Lucent 5620 SAM (Service Avare Manager) - WWW - IpciscoJesus RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure network access lists Lab 2Dokument3 SeitenConfigure network access lists Lab 2Johann NeethlingNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECS Administration GuideDokument128 SeitenECS Administration GuidejestinvjNoch keine Bewertungen
- MNS - EOI MP Circle Rev PDFDokument77 SeitenMNS - EOI MP Circle Rev PDFkumaraiesecadityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Questions - Chapter 11-Voice - Data Delivery NetworksDokument2 SeitenReview Questions - Chapter 11-Voice - Data Delivery NetworksTrent Branch100% (1)
- Service Provider IPv6 Deployment PDFDokument79 SeitenService Provider IPv6 Deployment PDFDaniel VieceliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP 2013 All-in-One Video Boot Camp With Chris Bryant by Chris Bryant - UdemyDokument12 SeitenCCNP 2013 All-in-One Video Boot Camp With Chris Bryant by Chris Bryant - UdemyMichael DeesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco IOS Error MSGDokument764 SeitenCisco IOS Error MSGMahmoud Al RifaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- E1 Lab 11 5 5Dokument19 SeitenE1 Lab 11 5 5Chris LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interview QuestDokument7 SeitenInterview QuestNaresh ErukullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps, How To Setup Your New VM With Iou-Web: Written by UldisdDokument11 SeitenSteps, How To Setup Your New VM With Iou-Web: Written by Uldisdlululyly100% (1)
- CISCO IOU InstallationDokument3 SeitenCISCO IOU InstallationtanzimshamsuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge PDFDokument4 Seiten11.4.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge PDFMpaphi Map'z DambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna 2 Module 4Dokument6 SeitenCcna 2 Module 4shkarkoddl83% (6)
- Alcatel BTS Presentation Using B10Dokument54 SeitenAlcatel BTS Presentation Using B10Sibte HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report - Cisco Router ConfigurationDokument20 SeitenLab Report - Cisco Router ConfigurationfelipebrazilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ospf StatesDokument9 SeitenOspf StatesnextinnovationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel - LucentDokument5 SeitenAlcatel - LucentndirangjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei Switch s9303Dokument16 SeitenHuawei Switch s9303jeffreyfloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas Internal 1Dokument216 SeitenAtlas Internal 1Sivaraman AlagappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background Information GGSN Behavior Cause Code 192 Error Example ScenariosDokument5 SeitenBackground Information GGSN Behavior Cause Code 192 Error Example Scenariosradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eigrp Practice Skills Exam Ccna3Dokument47 SeitenEigrp Practice Skills Exam Ccna3Sándor PetrócziNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Security Packet Tracer Practice SBADokument11 SeitenCCNA Security Packet Tracer Practice SBAOudome Thavong80% (5)
- 3.EBGP MultihopDokument10 Seiten3.EBGP MultihopAakash GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icnd Part 1, Vol 1Dokument367 SeitenIcnd Part 1, Vol 1Tin Myo Thaw100% (1)
- Cisco CCNP Routing and Switching 300-115 SWITCH (2019) Exam Dumps Are Out - Download and PrepareDokument5 SeitenCisco CCNP Routing and Switching 300-115 SWITCH (2019) Exam Dumps Are Out - Download and PrepareDavidEButlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Descriptors, 2nd EditionDokument99 SeitenPython Descriptors, 2nd EditionalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Route Policy RPL XRDokument1 SeiteRoute Policy RPL XRHarjanto Handi KusumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packet TracerDokument77 SeitenPacket TracerTanveer ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mpls 775023062009Dokument62 SeitenMpls 775023062009Anonymous 97rmXnVXMNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICND120SG Vol2Dokument138 SeitenICND120SG Vol2Phuoc Trinh100% (1)
- CCNA R&S-Routing and Switching EssentialsDokument1 SeiteCCNA R&S-Routing and Switching Essentialsilirgjikaj73Noch keine Bewertungen
- MX Fabric Troubleshooting GuideDokument15 SeitenMX Fabric Troubleshooting GuideSivaraman AlagappanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jncia Lab GuideDokument18 SeitenJncia Lab GuideKhiem BuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Halabi Bgp4 Case Studies TutorialDokument100 SeitenHalabi Bgp4 Case Studies Tutorialjanaksundhar85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Using Networking and Communications Software in BusinessVon EverandUsing Networking and Communications Software in BusinessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 7.5.3Dokument12 SeitenLab 7.5.3Jamesx XNguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 7.5.3Dokument13 SeitenLab - Activity CCNA 2 Exp: 7.5.3Rico Agung FirmansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes Topology Diagram: Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayDokument9 SeitenLab 2.8.3: Troubleshooting Static Routes Topology Diagram: Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayMartin O'grady0% (1)
- Tarea 3Dokument7 SeitenTarea 3Ricardo GrijalvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology DiagramDokument4 SeitenLab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology DiagramazitaggNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - Swinburne - V1.0Dokument7 Seiten2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - Swinburne - V1.0Basit KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless LAN DesiginDokument5 SeitenCCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless LAN DesiginKIERYENoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDokument4 SeitenLab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramAnjasa Keisar EtienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lista de Acrónimos de TelecomunicacionesDokument2 SeitenLista de Acrónimos de TelecomunicacionesPaiio CarrascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEO GuideDokument3 SeitenSEO GuideHimal GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahasa Inggris 3 Berbicara 2A Dan 2B BA: The AnswersDokument2 SeitenBahasa Inggris 3 Berbicara 2A Dan 2B BA: The AnswersEmi DestianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- XP Tricks & Tips-IIDokument29 SeitenXP Tricks & Tips-IIMd Raisul Islam100% (1)
- Error PDF Structure 40 Insufficient MemoryDokument2 SeitenError PDF Structure 40 Insufficient MemoryDezzNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATM Physical LayerDokument13 SeitenATM Physical Layeroureducation.in100% (1)
- Distributed System Practical FileDokument21 SeitenDistributed System Practical FileSagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flare August September 09Dokument102 SeitenFlare August September 09rizwan4everyoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Design Quote FormDokument3 SeitenWeb Design Quote FormayushNoch keine Bewertungen
- File Attachment in PeoplesoftDokument19 SeitenFile Attachment in PeoplesoftAlexvalenciaayolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fundamentals of Network CommunicationDokument38 SeitenThe Fundamentals of Network CommunicationBenedictNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Task 2 - Writing Task ForumDokument5 SeitenUnit 1 - Task 2 - Writing Task ForumMarly Yulieth NuñezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orange - Hikari No Hahen Chords by Misc Cartoons Tabs at Ultimate Guitar ArchiveDokument2 SeitenOrange - Hikari No Hahen Chords by Misc Cartoons Tabs at Ultimate Guitar ArchiveGilang TFNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS 7090 2 Cem 74C0087Dokument4 SeitenDS 7090 2 Cem 74C0087Ehsan RohaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finding A FamilyDokument4 SeitenFinding A FamilyDaniela De Alba StevensonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crossing The Line: Self-Esteem Lesson PlanDokument9 SeitenCrossing The Line: Self-Esteem Lesson PlanAlexander RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Evolution of Cybersecurity - Sandbox QuizDokument2 SeitenThe Evolution of Cybersecurity - Sandbox Quizchhun50% (4)
- 1 Isp Network Design PDFDokument97 Seiten1 Isp Network Design PDFSourav SatpathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Easy Steps To Create The "Classic" Princess Seams Bodice: Sign Up For The Isn'T That Sew EmailerDokument1 Seite10 Easy Steps To Create The "Classic" Princess Seams Bodice: Sign Up For The Isn'T That Sew EmailerAmanie Usman Amanoddin0% (1)
- Wearable ComputersDokument3 SeitenWearable Computersgovindeep88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Benefits of Social MediaDokument2 SeitenBenefits of Social MediaJessa Mae CacNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP-WPWE-85M User ManualDokument27 SeitenIP-WPWE-85M User ManualMauro SergioNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS11Dokument3 SeitenCSS11ROSE OPEL ASPILLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Itproj - SRS1Dokument9 SeitenItproj - SRS1John Paul BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chitra, A Play in One Act by Tagore, Rabindranath, 1861-1941Dokument25 SeitenChitra, A Play in One Act by Tagore, Rabindranath, 1861-1941Gutenberg.orgNoch keine Bewertungen