Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Project Risk Management
Hochgeladen von
Pragya GoelOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Project Risk Management
Hochgeladen von
Pragya GoelCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Facebook Project Management Plan Managing Projects
Project Members:
GOKUL Basker GOPI Vinu Kirthey GOEL Pragya HAN Limin SA Jingpeng
Project Risk Management
Risk is an event that delays or destroys the project, thus affecting the cost. Planning and managing the risks are intended to help a team to understand and manage the uncertainty during the development process. Thus plans are made not only to understand the risk uncertainty but also to minimize the impact when things go wrong. Risk management is one of the most critical project management practices to ensure a project be successfully completed (Ref: E.g. Turner, J.R., 1999, Chapman, C., 1997). Royer (Ref: Royer, P.S., 2000) stated: Experience has shown that risk management must be of critical concern to project managers, as unmanaged or unmitigated risks are one of the primary causes of project failure. Risk management is thus in direct relation to the successful project completion. Steps involved in risk management are: 1) Risk identification to determine what events are risks to the project 2) Assessment to analysing and assess the risk and determine its impact on the project 3) Prioritization - Ranking the risk according to the probability of occurrence and impact i.e. determining in which order the risks will be addressed 4) Monitor and report - watch and report on the effectiveness of the risk mitigation The work product of Risk management is called as Risk mitigation, Monitoring and Management plan (RMMM). Risk Categories: Categories represent a structure that ensures a comprehensive process of systematically identifying risks to a consistent level and value.
Category Technical Sub-category Scope Definition/Objective, Requirement Definition, Technical Process, Technology, Technical User/Interfaces, Technology Scaling, Performance, Reliability/Safety/Security, Testing Project Management, Resources, Communication, Interdependencies Culture, Sponsorship, Business Process, Acceptance, Supportability Contractual Terms and Conditions, Funding/Financial, Vendor Stability, Internal Procurement, Subcontractors, Applicable Laws, Contractor Experience Legislative/Regulatory, Political, Pressure Groups, Weather, Force Majeure
Management Organizational Commercial
External
Risk Probability and Impact: values and calculations to be used to quantify risk exposure. The probability and impact of risks to the project will be quantified according to the risk value in the table. The combination of the impact and probability will determine the risk value. Item Probability Definition The probability of occurrence Risk Value 1, 2 or 3 (1 Unlikely to occur - L 2 May or may not occur - M 3 Likely to occur - H) Impact The impact to the project objectives if the risk 1, 2 or 3 occurs. Refer to the Project Management Body of (1 Minimal impact - L Knowledge, Section 11.1.3 for additional examples 2 Moderate impact - M of impact definitions. 3 Significant impact - H) The calculation of Probability times Impact Impact = H Likelihood = H Likelihood = M Likelihood = L Priority = 1 Priority = 1 Priority = 2 Impact = M Priority = 1 Priority = 1 Priority = 2 1 through 9 Impact = L Priority = 2 Priority = 2 Priority = 3
Total Risk
Total Risk of 1-3 is low or green. Total Risk of 4-6 is medium or yellow. Total Risk of 7-9 is high or red.
The Risk Register captures the results of a qualitative and quantitative risk analysis and the results of planning for response. Risk ID No. Description Cause, Event, Effect statement Category Technical, Management, Organizational Commercial, External 1 2 Probability 1 - Unlikely Impact 1-Minimal Score Risk Response Status Open, In Progress, Resolved, Closed Owner Team Member
2 May or 2-Moderate may not 3- Significant occur 3 Likely to occur
Product of Watch, Probability x Accept, Impact Transfer, 1-3 Green 4-6 Yellow 7-9 - Red Mitigate, Avoid
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Swiss FCM Ordinance - EuPIA QDokument6 SeitenSwiss FCM Ordinance - EuPIA Qiz_nazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yama Buggy 400cc Parts List and SchematicsDokument50 SeitenYama Buggy 400cc Parts List and Schematicsgeorgemesfin@gmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drainage CapacityDokument33 SeitenDrainage Capacityfan_luc89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Petroleum Engineering BookDokument10 SeitenFundamentals of Petroleum Engineering BookRizwan FaridNoch keine Bewertungen
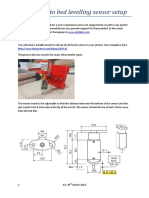
- BLTouch Setup ManualDokument7 SeitenBLTouch Setup ManualBobbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasafe AESDokument7 SeitenUltrasafe AEShuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- XPath PresentationDokument14 SeitenXPath PresentationJantrik ShopnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akta Satelit On Astra 4A at 4Dokument6 SeitenAkta Satelit On Astra 4A at 4Amirul AsyrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIS2116 ManualDokument88 SeitenDIS2116 ManualHưng Tự Động HoáNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASTM Pumping TestDokument125 SeitenASTM Pumping TestErnesto Heinze100% (1)
- Epicor ERP Embedded Courses A4 FS ENSDokument2 SeitenEpicor ERP Embedded Courses A4 FS ENSHuong NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- P287 SCIL Programming BasicsDokument78 SeitenP287 SCIL Programming BasicsOscar GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscilloscope Lab Manual11Dokument16 SeitenOscilloscope Lab Manual11DM RafiunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erita Astrid - UPBDokument25 SeitenErita Astrid - UPBmas_kinooooNoch keine Bewertungen
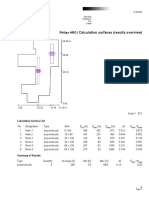
- Calculation Surfaces (Results Overview) : Philips HRODokument4 SeitenCalculation Surfaces (Results Overview) : Philips HROsanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- D20S-7 Sb1159e01 PDFDokument678 SeitenD20S-7 Sb1159e01 PDFGORDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emd-Mi928 Sistema de LubricacionDokument6 SeitenEmd-Mi928 Sistema de LubricacionVictor Raul Tobosque Muñoz100% (1)
- 4 10 59 08 Juni 2023Dokument5 Seiten4 10 59 08 Juni 2023ihor.vezhninNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ricardo R4105ZD-61kW Genset Spec SheetDokument2 SeitenRicardo R4105ZD-61kW Genset Spec SheetRonald Booc100% (3)
- StetindDokument6 SeitenStetindGiovanniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lewmar Marine Equipment Guide Ed 14Dokument224 SeitenLewmar Marine Equipment Guide Ed 14Renato Fonseca100% (1)
- The Mpeg Dash StandardDokument6 SeitenThe Mpeg Dash Standard9716755397Noch keine Bewertungen
- KampasDokument1 SeiteKampasSamer aneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas Bradford (Ver03-Apr05)Dokument8 SeitenAtlas Bradford (Ver03-Apr05)Gabriel IbarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Texture Formats Used by CFS3Dokument2 SeitenTexture Formats Used by CFS3Hillmen HussinNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEO ExPro V11i6Dokument104 SeitenGEO ExPro V11i6OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RedBull MediaHouseDokument15 SeitenRedBull MediaHousedr989981Noch keine Bewertungen
- ERPtips SAP Training Manual SAMPLE CHAPTER From Basic PayrollDokument20 SeitenERPtips SAP Training Manual SAMPLE CHAPTER From Basic Payrollravibabu1620Noch keine Bewertungen
- Building A Gate Way Service Using A SEGW TransactionDokument10 SeitenBuilding A Gate Way Service Using A SEGW Transactionswamy_yalamanchiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software: Measurlink Is An Easy-To-Use, Windows-Based Family of Quality Data Management Software ApplicationsDokument8 SeitenSoftware: Measurlink Is An Easy-To-Use, Windows-Based Family of Quality Data Management Software ApplicationsBrandi DaleNoch keine Bewertungen