Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cloud Computing - Prashant
Hochgeladen von
Sachin MauryaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cloud Computing - Prashant
Hochgeladen von
Sachin MauryaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cloud Computing
system networks and storage system cloud may not be reliable for data, but it scores well as far as security is concerned. In cloud computing, security is tremendously improved because of a superior technology security system, which is now easily available and affordable. Yet another important characteristic of cloud is scalability, which is achieved through server virtualization. In a nutshell, cloud computing means getting the best performing system with the best value for money. A cloud service has three distinct characteristics that differentiate it from traditional hosting. It is sold on demand, typically by the minute or the hour; it is elastic -- a user can have as much or as little of a service as they want at any given time; and the service is fully managed by the provider (the consumer needs nothing but a personal computer and Internet access). Significant innovations in virtualization and Keywords Cloud computing, Infrastructure as a service, distributed computing, as well as improved access to highPlatform as a Service, Software as a service speed Internet and a weak economy, have accelerated interest in cloud computing.
Abstract This paper describes cloud computing, a computing platform for the next generation of Internet. Cloud Computing can be described as clouds, or clusters of distributed computers, providing on-demand resources and services over a network, usually the Internet, with the scale and reliability of a data centre. It is a general term for anything that involves delivering hosted services over the Internet. Cloud computing can be called as a fifth generation of computing after Mainframe, Personal Computer, Client-Server Computing and the Web. Cloud Computing is the biggest thing since the web. Organizations and individuals can benefit from mass computing and storage, provided by large companies with stable and strong cloud architectures. On the other hand, companies that desire to build massive, scalable environments, utilizing virtualization and cloud computing will increase their future margin of success greatly.
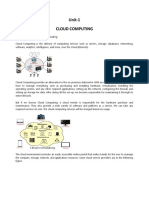
I. INTRODUCTION Cloud Computing, to put it simply, means "Internet Computing." The Internet is commonly visualized as clouds; hence the term cloud computing for computation done through the Internet. With Cloud Computing users can access database resources via the Internet from anywhere, for as long as they need, without worrying about any maintenance or management of actual resources. Besides, databases in cloud are very dynamic and scalable. The name cloud computing was inspired by the cloud symbol that's often used to represent the Internet in flow charts and diagrams. Cloud computing is unlike grid computing, utility computing, or autonomic computing. In fact, it is a very independent platform in terms of computing. The best example of cloud computing is Google Apps where any application can be accessed using a browser and it can be deployed on thousands of computer through the Internet. Cloud computing is cost-effective. Here, cost is greatly reduced as initial expense and recurring expenses are much lower than traditional computing. Maintenance cost is reduced as a third party maintains everything from running the cloud to storing data. Cloud is characterized by features such as platform, location and device independency, which make it easily adoptable for all sizes of businesses, in particular small and mid-sized. However, owing to redundancy of computer II. CLOUD COMPUTING ARCHITECTURE Cloud computing architecture, just like any other system, is categorized into two main sections: Front End and Back End. Front End can be end user or client or any application (i.e. web browser etc.) which is using cloud services. Back End is the network of servers with any computer program and data storage system. It is usually assumed that cloud contains infinite storage capacity for any software available in market. Cloud has different applications that are hosted on their own dedicated server farms. Cloud has centralized server administration system. Centralized server administers the system, balances client supply, adjusts demands, monitors traffic and avoids congestion. This server follows protocols, commonly known as middleware. Middleware controls the communication of cloud network among them. Cloud Architecture runs on a very important assumption, which is mostly true. The assumption is that the demand for resources is not always consistent from client to cloud. Because of this reason the servers of cloud are unable to run at their full capacity. To avoid this scenario, server virtualization technique is applied. In sever virtualization, all physical servers are virtualized and they run multiple servers with either same or different application. As one physical server
Fig. 1 Global Cloud exchange and market infrastructure for trading services.
acts as multiple physical servers, it curtails the need for more physical machines.
Customers use the provider's application program interface (API) to start, stop, access and configure their virtual servers and storage. Because this pay-for-what-you-use model As a matter of fact, data is the most important part of cloud resembles the way electricity, fuel and water are consumed, computing; thus, data security is the top most priority in all it's sometimes referred to as utility computing. the data operations of cloud. Here, all the data are backed up at multiple locations. This astoundingly increases the data B. Platform as a Service (PaaS) storage to multiple times in cloud compared with a regular Platform as a service in the cloud is defined as a set of system. Redundancy of data is crucial, which is a must-have software and product development tools hosted on the provider's infrastructure. attribute of cloud computing. Platform as a service (PaaS) delivers a computing platform and solution stack as a service. It facilitates III. DIFFERENT FORMS OF CLOUD COMPUTING deployment of applications without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software Cloud Computing services are broadly divided into three layers, providing all of the facilities required to support the complete life cycle of building and delivering web categories: applications and services entirely available from the Internet Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) with no software downloads or installation for developers, IT Platform as a Service (PaaS) managers or end-users. It's also known as cloudware. Software as a Service (SaaS) PaaS offerings include workflow facilities for application design, application development, testing, deployment and A. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the delivery of hosting as well as application services such as team computer infrastructure (typically a platform virtualization collaboration, web service integration and marshalling, environment) as a service. These 'virtual infrastructure stacks' database integration, security, scalability, storage, persistence, are an example of everything as a service trend and shares state management, application versioning, application many of the common characteristics. Rather than purchasing instrumentation and developer community facilitation. These servers, software, data center space or network equipment, services are provisioned as an integrated solution over the web. A second definiton of PaaS is more client oriented. PaaS clients instead buy those resources as a fully outsourced can be defined as the concept to deliver a cost-effective cloud service. The service is typically billed on a utility computing basis and amount of resources consumed (and therefore the based workspace environment the platform - to the End-user cost) will typically reflect the level of activity. It is an which integrates work/life environment and facilitates him or/her to work, communicate, interact and play (games) evolution of web hosting and virtual private server offerings. Amazon Web Services provides virtual server instances anywhere, anytime, any device in a safe manner based on the with unique IP addresses and blocks of storage on demand. roles assigned to the end-user. As such PaaS could also be
described as Datacenter Centric Client Based Utility Computing. Developers create applications on the provider's platform over the Internet. PaaS providers may use APIs, website portals or gateway software installed on the customer's computer. Force.com, (an outgrowth of Salesforce.com) and GoogleApps are examples of PaaS. Developers need to know that currently, there are no standards for interoperability or data portability in the cloud. Some providers will not allow software created by their customers to be moved off the provider's platform. C. Software as a Service (SaaS) Software as a Service (SaaS) is a model of software deployment whereby a provider licenses an application to customers for use as a service on demand. SaaS software vendors may host the application on their own web servers or download the application to the consumer device, disabling it after use or after the on-demand contract expires. The ondemand function may be handled internally to share licenses within a firm or by a third-party application service provider (ASP) sharing licenses between firms. IV. CLOUD COMPUTING APPLICATIONS The applications of cloud computing are practically limitless. With the right middleware, a cloud computing system could execute all the programs a normal computer could run. Potentially, everything from generic word processing software to customized computer programs designed for a specific company could work on a cloud computing system. A few applications are: Clients would be able to access their applications and data from anywhere at any time. They could access the cloud computing system using any computer linked to the Internet. Data wouldn't be confined to a hard drive on one user's computer or even a corporation's internal network. It could bring hardware costs down. Cloud computing systems would reduce the need for advanced hardware on the client side. Theres no need to buy the fastest computer with the most memory, because the cloud system would take care of those needs for you. Instead, an inexpensive computer terminal may be purchased. The terminal could include a monitor, input devices like a keyboard and mouse and just enough processing power to run the middleware necessary to connect to the cloud system. You wouldn't need a large hard drive because you'd store all your information on a remote computer. Corporations that rely on computers have to make sure they have the right software in place to achieve goals. Cloud computing systems give these organizations company-wide access to computer applications. The companies don't have to buy a set
of software or software licenses for every employee. Instead, the company could pay a metered fee to a cloud computing company. Servers and digital storage devices take up space. Some companies rent physical space to store servers and databases because they don't have it available on site. Cloud computing gives these companies the option of storing data on someone else's hardware, removing the need for physical space on the front end. Corporations might save money on IT support. Streamlined hardware would, in theory, have fewer problems than a network of heterogeneous machines and operating systems. If the cloud computing system's back end is a grid computing system, then the client could take advantage of the entire network's processing power. Often, scientists and researchers work with calculations so complex that it would take years for individual computers to complete them. On a grid computing system, the client could send the calculation to the cloud for processing. The cloud system would tap into the processing power of all available computers on the back end, significantly speeding up the calculation. V. EXAMPLES Industry analysts have made projections on how Cloud computing will transform the entire computing industry. According to a recent Merrill Lynch research note, Cloud computing is expected to be a $160-billion addressable market opportunity, including $95-billion in business and productivity applications, and another $65-billion in online advertising. Another research study by Morgan Stanley has also identified Cloud computing as one of the prominent technology trends. As the computing industry shifts toward providing Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS) for consumers and enterprises to access on demand regardless of time and location, there will be an increase in the number of Cloud platforms available. Recently, several academic and industrial organisations have started investigating and developing technologies and infrastructure for Cloud Computing. Academic efforts include Virtual Workspaces and OpenNebula. In this section, we compare six representative Cloud platforms with industrial linkages in Figure 2. Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) provides a virtual computing environment that enables a user to run Linux-based applications. The user can either create a new Amazon Machine Image (AMI) containing the applications, libraries, data and associated configuration settings, or select from a library of globally available AMIs. The user then needs to upload the created or selected AMIs to Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), before he can start, stop, and monitor instances of the uploaded AMIs.
Fig. 2 Comparison of some representative Cloud platforms
Amazon EC2 charges the user for the time when the instance is alive, while Amazon S3 charges for any data transfer (both upload and download). Google App Engine allows a user to run Web applications written using the Python programming language. Other than supporting the Python standard library, Google App Engine also supports Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) for the datastore, Google Accounts, URL fetch, image manipulation, and email services. Google App Engine also provides a Web-based Administration Console for the user to easily manage his running Web applications. Currently, Google App Engine is free to use with up to 500MB of storage and about 5 million page views per month.
Microsoft Live Mesh aims to provide a centralized location for a user to store applications and data that can be accessed across required devices (such as computers and mobile phones) from anywhere in the world. The user is able to access the uploaded applications and data through a Web-based Live Dekstop or his own devices with Live Mesh software installed. Each users Live Mesh is password-protected and authenticated via his Windows Live Login, while all file transfers are protected using Secure Socket Layers (SSL). Sun network.com (Sun Grid) enables the user to run Solaris OS, Java, C, C++, and FORTRAN based applications. First, the user has to build and debug his applications and runtime scripts in a local development environment that is configured to be similar to
that on the Sun Grid. Then, he needs to create a bundled zip archive (containing all the related scripts, libraries, executable binaries and input data) and upload it to Sun Grid. Finally, he can execute and monitor the application using the Sun Grid Web portal or API. After the completion of the application, the user will need to download the execution results to his local development environment for viewing. GRIDS Lab Aneka, which is being commercialized through Manjrasoft, is a .NET-based service-oriented platform for constructing enterprise Grids. It is designed to support multiple application models, persistence and security solutions, and communication protocols such that the preferred selection can be changed at anytime without affecting an existing Aneka ecosystem. To create an enterprise Grid, the service provider only needs to start an instance of the configurable Aneka container hosting required services on each selected desktop computer. The purpose of the Aneka container is to initialize services and acts as a single point for interaction with the rest of the enterprise Grid. Aneka provides SLA support such that the user can specify QoS requirements such as deadline (maximum time period which the application needs to be completed in) and budget (maximum cost that the user is willing to pay for meeting the deadline). The user can access the Aneka Enterprise Grid remotely through the Gridbus broker. The Gridbus broker also enables the user to negotiate and agree upon the QoS requirements to be provided by the service provider. VI. ADVANTAGES Agility improves with users able to rapidly and inexpensively re-provision technological infrastructure resources. The cost of overall computing is unchanged, however, and the providers will merely absorb up-front costs and spread costs over a longer period. Cost is claimed to be greatly reduced and capital expenditure is converted to operational expenditure. This ostensibly lowers barriers to entry, as infrastructure is typically provided by a third-party and does not need to be purchased for one-time or infrequent intensive computing tasks. Pricing on a utility computing basis is fine-grained with usagebased options and fewer IT skills are required for implementation (in-house). Some would argue that given the low cost of computing resources, that the IT burden merely shifts the cost from in-house to outsourced providers. Furthermore, any cost reduction benefit must be weighed against a corresponding loss of control, access and security risks. Device and location independence enable users to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they are using (e.g., PC,
mobile). As infrastructure is off-site (typically provided by a third-party) and accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere. Multi-tenancy enables sharing of resources and costs across a large pool of users thus allowing for: Centralization of infrastructure in locations with lower costs (such as real estate, electricity, etc.) Peak-load capacity increases (users need not engineer for highest possible load-levels) Utilization and efficiency improvements for systems that are often only 1020% utilized. Reliability improves through the use of multiple redundant sites, which makes cloud computing suitable for business continuity and disaster recovery. Nonetheless, many major cloud computing services have suffered outages, and IT and business managers can at times do little when they are affected. Scalability via dynamic ("ondemand") provisioning of resources on a finegrained, self-service basis near real-time, without users having to engineer for peak loads. Performance is monitored, and consistent and loosely-coupled architectures are constructed using web services as the system interface. Security typically improves due to centralization of data, increased security-focused resources, etc., but concerns can persist about loss of control over certain sensitive data, and the lack of security for stored kernels. Security is often as good as or better than under traditional systems, in part because providers are able to devote resources to solving security issues that many customers cannot afford. Providers typically log accesses, but accessing the audit logs themselves can be difficult or impossible. Sustainability comes about through improved resource utilization, more efficient systems, and carbon neutrality. Nonetheless, computers and associated infrastructure are major consumers of energy. A given (server-based) computing task will use X amount of energy whether it is on-site, or off.
VII.
DISADVANTAGES
All Requires a Constant Internet Connection Due to the need for Internet to connect to both your applications and documents, Cloud computing is, quite simply, impossible if connection to the Internet is unavailable. Doesnt Work Well with Low-Speed Connections Similarly, a low-speed Internet connection, such as that found with dial-up services, makes cloud
computing painful at best and often impossible. Webbased apps often require a lot of bandwidth to download, as do large documents. Even on a fast connection, web-based applications can sometimes be slower than accessing a similar software program on your desktop PC. Thats because everything about the program, from the interface to the document youre working on, has to be sent back and forth from your computer to the computers in the cloud. If the cloud servers happen to be backed up at that moment, or if the Internet is having a slow day, you wont get the instantaneous access youre used to with desktop apps. Features Might Be Limited This particular disadvantage is bound to change, but today many web-based applications simply arent as full-featured as their desktop-based brethren. Compare, for example, the feature set of Google Presentations with that of Microsoft PowerPoint; theres just a lot more you can do with PowerPoint than you can with Googles web-based offering. The basics are similar, but the cloud application lacks many of PowerPoints advanced features. So if youre an advanced user, you might not want to leap into the cloud computing waters just yet. That said, many web-based apps add more advanced features over time. This has certainly been the case with Google Docs and Spreadsheets, both of which started out somewhat crippled but later added many of the more niche functions found on Microsoft Word and Excel. Still, you need to look at the features before you make the move. Make sure that the cloud-based application can do everything you need it to do before you give up on your traditional software. Stored Data Might Not Be Secure With cloud computing, all your data is stored on the cloud. Thats all well and good, but how secure is the cloud? Can other, unauthorized users gain access to your confidential data? These are all important questions, and well worth further examination. To that end, read ahead to the The Security Conscious section later in this chapter, where we examine just how safe your data is in the cloud. The Risk of Losing Data Theoretically, data stored in the cloud is unusually safe, replicated across multiple machines. But on the off chance that your data does go missing, you have no physical or local backup.
VIII.
CONCLUSION
Cloud Computing is the fastest growing part of IT and has a potential to offer tremendous benefits enterprises, home users and customers of all sizes. Cloud services are simpler to acquire and scale up or down providing flexibility and feasibility under one roof. It also provides better and easier management of data security, since all the data is located on a central server, administrators can control the permissions for the other users to access the files. It could as well, provide Key opportunity for application and infrastructure vendors. Public clouds work great for some but not all applications. Private clouds offer many benefits for internal applications. Public and private clouds can also be used in combination. There are some down sides as well to cloud computing. Peripherals such as printers or scanners might have issues dealing with the fact that there is no hard drive attached to the physical, local machine. If there are machines a user uses at work that aren't their own for any reason, that require access to particular drivers or programs, it is still a struggle to get this application to know that it should be available to the user. REFERENCES
[1]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computi ng [2] IBM Available:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/web/library/wa cloudgrid/#N10121 [3] Sam Johnston s blog Available:http://samj.net/2008/09/taxonomy-6-layer-cloud-computingstack.html [4] An Oracle White Paper in Enterprise Architecture August 2009 Architectural Strategies for Cloud Computing [5] IBM Perspective on Cloud Computing [6] M. D. Dikaiakos, D. Katsaros, G. Pallis, A. Vakali, P. Mehra: Guest Editors Introduction: "Cloud Computing, IEEE Internet Computing", 12(5), Sep. 2009 Available:http://www.cs.ucy.ac.cy/~gpallis/publications/journals/
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cloud Computing DocumentationDokument11 SeitenCloud Computing DocumentationSailaja MannemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationDokument5 SeitenVirtualizing The Private Cloud For Maximum Resource UtilizationIjarcet JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iaas Paas) Saas FlowchartDokument3 SeitenIaas Paas) Saas FlowchartersharvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersDokument38 SeitenCloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersPraveen Madupu100% (1)
- Cloud ComputingDokument8 SeitenCloud ComputingAnjali SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: An Introduction to the Delivery of Computing as a ServiceDokument5 SeitenCloud Computing: An Introduction to the Delivery of Computing as a ServiceHarshvardhan SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of Cloud ComputingDokument8 SeitenEvolution of Cloud Computinghiteshsharma01abuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Is A General Term For Anything That Involves Delivering Hosted Services Over The InternetDokument14 SeitenCloud Computing Is A General Term For Anything That Involves Delivering Hosted Services Over The InternetKh Aasim BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- CloudDokument11 SeitenCloudcherry grootNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyDokument5 SeitenA Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyR Dharshini SreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Presentation-Cloud ComputingDokument14 SeitenPaper Presentation-Cloud Computingdeepakfct100% (4)
- Definition 451Dokument2 SeitenDefinition 451Ambekar NitinkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PG Cloud Computing Unit-IDokument33 SeitenPG Cloud Computing Unit-Ideepthi sanjeevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: An Overview: Charandeep Singh Bedi, Rajan SachdevaDokument10 SeitenCloud Computing: An Overview: Charandeep Singh Bedi, Rajan SachdevaCharndeep BediNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Cloud ComputingDokument6 SeitenWhat Is Cloud Computingstorm8811Noch keine Bewertungen
- CC Evolution Od CloudDokument51 SeitenCC Evolution Od CloudTushar MircheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit1 1Dokument30 SeitenUnit1 1HimajanaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zarmina DDB Ass#1Dokument13 SeitenZarmina DDB Ass#1Meena JadoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: Submitted By: Divya Khandelwal B.Tech (CSE) 7 Sem 0271352707Dokument31 SeitenCloud Computing: Submitted By: Divya Khandelwal B.Tech (CSE) 7 Sem 0271352707divya25sepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging Technology for Engineering - Cloud Computing Benefits and ServicesDokument17 SeitenEmerging Technology for Engineering - Cloud Computing Benefits and ServicesManya JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Lab FileDokument42 SeitenCC Lab FileRitika SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will LearnDokument11 SeitenCloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will Learnsangeet83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument2 SeitenCloud ComputingAnju NishadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: Presentation ByDokument20 SeitenCloud Computing: Presentation Bymahesh_mallidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Cloud ComputingDokument8 SeitenWhat Is Cloud ComputingDillip Kumar SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing EssayDokument14 SeitenCloud Computing EssayDeepak100% (2)
- Unit 5 Cloud ComputingDokument12 SeitenUnit 5 Cloud ComputingvibhamanojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar ReportDokument17 SeitenSeminar ReportJp Sahoo0% (1)
- Assignment: Q1. What Is Cloud Computing? AnsDokument8 SeitenAssignment: Q1. What Is Cloud Computing? Ansvashishttyagi91Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction to Cloud Computing Models and ServicesDokument2 SeitenAn Introduction to Cloud Computing Models and ServicesAmritendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Term PaperDokument9 SeitenCloud Computing Term PaperArvind ToorpuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument20 SeitenCloud ComputingxyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument13 SeitenUnit 1Bnod MsraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingDokument6 SeitenETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingSheshrao LandgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument11 SeitenCloud ComputingLvenkatesh VenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing 1Dokument15 SeitenCloud Computing 1Tresor DuniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Business Models in Cloud Computing": Assignment-1Dokument22 Seiten"Business Models in Cloud Computing": Assignment-1Ajay KakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Unit IDokument31 SeitenCC Unit ISuriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingDokument8 SeitenAssignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingMonir HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Architecture and SaaSDokument16 SeitenCloud Computing Architecture and SaaSvikram kumar jonnalagaddaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iaas Paas) Saas Flowchart: As A Service (Saas)Dokument4 SeitenIaas Paas) Saas Flowchart: As A Service (Saas)Soni Ashish KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Communication TechnologyDokument8 SeitenInformation Communication TechnologyMalik KhawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5Dokument24 SeitenUnit 5diwansingh29081999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: (Business Needs)Dokument38 SeitenCloud Computing: (Business Needs)starvamsi123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I Introduction To Cloud ComputingDokument36 SeitenUnit I Introduction To Cloud Computingkomalpopatshinde2345Noch keine Bewertungen
- IIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingDokument9 SeitenIIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingRohit PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument36 SeitenCloud Computingsubhayanmanna1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Security Issues in Infrastructure As A ServiceDokument7 SeitenCloud Computing Security Issues in Infrastructure As A ServiceArchanasubburamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementation of Cloud Based Query Solver System For Educational Institutes Featuring OntologyDokument7 SeitenImplementation of Cloud Based Query Solver System For Educational Institutes Featuring OntologyIjarcet JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Overview: Key Concepts and ApplicationsDokument6 SeitenCloud Computing Overview: Key Concepts and ApplicationsArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud ComputingDokument2 SeitenCloud ComputingAsha GanesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Cloud ComputingDokument17 SeitenWhat Is Cloud ComputingVictor ImarhiagbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Book (2017-Regulation) PDF-1-89 Unit - I & IIDokument89 SeitenCloud Computing Book (2017-Regulation) PDF-1-89 Unit - I & IIVishnu Kumar KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing - Quick GuideDokument25 SeitenCloud Computing - Quick GuideMadhav ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing IntroductionDokument95 SeitenCloud Computing IntroductionjanuaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- SECC - Tutorials - An Introduction To Cloud Computing ConceptsDokument19 SeitenSECC - Tutorials - An Introduction To Cloud Computing ConceptsAaron MangalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud and Network Securityt10Dokument19 SeitenCloud and Network Securityt10Md. EmdadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingVon EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionVon EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeVon EverandCloud computing: Moving IT out of the officeBCS, The Chartered Institute for ITNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diodes 1Dokument1 SeiteDiodes 1Sachin MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diff Bet Ceramic and Electrolitic CapDokument2 SeitenDiff Bet Ceramic and Electrolitic CapSachin MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SensorDokument8 SeitenSensorSachin MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepaid Energy MeterDokument12 SeitenPrepaid Energy MeterSachikanta SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigs of Rods Physics EngineDokument31 SeitenRigs of Rods Physics Engineengineer_khaula7035Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Financials Cloud Budget Import EnhancementsDokument14 SeitenOracle Financials Cloud Budget Import EnhancementsIloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accu-Chek Smart Pix Manual-EN-2.2.1Dokument190 SeitenAccu-Chek Smart Pix Manual-EN-2.2.1Laboratorium Ansari SalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 830-00742-47 ZMS Admin GuideDokument158 Seiten830-00742-47 ZMS Admin Guidepolan78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Niharika Santoshsingh Pawar ResumeDokument2 SeitenNiharika Santoshsingh Pawar Resumeshantibhushan.saleNoch keine Bewertungen
- MISRA C-Some Key Rules To Make Embedded Systems Safer PDFDokument3 SeitenMISRA C-Some Key Rules To Make Embedded Systems Safer PDFLeiser HartbeckNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0016.Dokument82 SeitenWa0016.Uchi PurnamasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esee Camera Security - Information DisclosureDokument5 SeitenEsee Camera Security - Information DisclosureOMAR ANDRES CASTANEDA LIZARAZONoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Create Badges With A Vcard QR Code Using OnMerge BarcodesDokument8 SeitenHow To Create Badges With A Vcard QR Code Using OnMerge BarcodesWAWANNoch keine Bewertungen
- PeopleSoft Technical Training - Day 1 PDFDokument249 SeitenPeopleSoft Technical Training - Day 1 PDFdwi kristiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DDR Configuration and Boot Logs on 8756 SOCDokument5 SeitenDDR Configuration and Boot Logs on 8756 SOCAnhHuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etm 120 - 301 Ethical Scenarios 1Dokument6 SeitenEtm 120 - 301 Ethical Scenarios 1api-339987800Noch keine Bewertungen
- HackDokument1 SeiteHackAliceaka Ayuwidhiastuti100% (2)
- Book of Champions 1972-1983Dokument91 SeitenBook of Champions 1972-1983Luis Rr100% (1)
- ODK TOOLKITDokument17 SeitenODK TOOLKITAbi El CakepNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual - K2Dokument31 SeitenUser Manual - K2Muhammad AdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Use The Rohde & Schwarz Labview Instrument DriverDokument10 SeitenHow To Use The Rohde & Schwarz Labview Instrument DriverjuanchitoperezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LogDokument150 SeitenLogMalivoc FenandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3PL Partner - Welcome Kit 2016 (Go/3pl-Welcome)Dokument15 Seiten3PL Partner - Welcome Kit 2016 (Go/3pl-Welcome)Tú Xike100% (2)
- Manoj Kumar UpdatedDokument2 SeitenManoj Kumar UpdatedmanojanindianNoch keine Bewertungen
- FreightVerify CarrierView User Guide - enDokument33 SeitenFreightVerify CarrierView User Guide - enjennifer becerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor LAB MANUAL Reg-2013Dokument106 SeitenMicroprocessor LAB MANUAL Reg-2013keerthi3214100% (1)
- Glitch2 ReadmeDokument3 SeitenGlitch2 ReadmeAghzuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Analyst Role Responsibilities and DutiesDokument2 SeitenApplication Analyst Role Responsibilities and DutiesAmit KhyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPAM Microsoft DocumentationDokument97 SeitenIPAM Microsoft DocumentationJoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Billing Invoice For Legal ServicesDokument6 SeitenBilling Invoice For Legal ServicesArahiwang Cipta manunggalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Service Bus 12c - Design and Integration Service (Student Guide)Dokument384 SeitenOracle Service Bus 12c - Design and Integration Service (Student Guide)Felipe Antonio Vásquez Castañeda100% (4)
- E-Zone Cart With Recommendation SystemDokument18 SeitenE-Zone Cart With Recommendation Systemdeepak chandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repro-5 User GuideDokument46 SeitenRepro-5 User GuideGraig EarleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - Storing and Processing Spatial Data With FOSS - GEOG 585 - Web MappingDokument16 SeitenLesson 3 - Storing and Processing Spatial Data With FOSS - GEOG 585 - Web MappingrokomNoch keine Bewertungen