Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
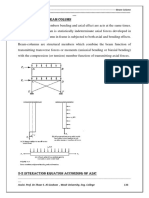
An Abuse-Free Fair Contract-Signing Protocol Based On The RSA Signature
Hochgeladen von
mahesh_kumar_mandiaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
An Abuse-Free Fair Contract-Signing Protocol Based On The RSA Signature
Hochgeladen von
mahesh_kumar_mandiaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PowerNap: An Energy Efficient MAC Layer for Random Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks
Abstract
Idle-listening is the biggest challenge for energy efficiency and longevity of multihop wireless sensor network (WSN) deployments. While existing coordinated sleep/wakeup scheduling protocols eliminate idle-listening for simple traffic patterns, they are unsuitable to handle the complex traffic patterns of the random routing protocols. We present a novel coordinated sleep/wakeup protocol POWERNAP , which avoids the overhead of distributing complex, large sleep/wakeup scheduling information to the nodes. POWERNAP piggybacks onto the relayed data packets the seed of the pseudo-random generator that encodes the scheduling information, and enables any recipient/snooper to calculate its sleep/wakeup schedule from this seed. In essence, POWERNAP trades off doing extra computation in order to avoid expensive control packet transmissions.
An Abuse-Free Fair Contract-Signing Protocol Based on the RSA Signature
Abstract
Afair contract-signing protocol allows two potentially mistrusted parities to exchange their commitments (i.e., digital signatures) to an agreed contract over the Internet in a fair way, so that either each of them obtains the others signature, or neither party does. Based on the RSA signature scheme, a new digital contract signing protocol is proposed in this paper. Like the existing RSA-based solutions for the same problem, our protocol is not only fair, but also optimistic, since the trusted third party is involved only in the situations where one party is cheating or the communication channel is interrupted. Furthermore, the proposed protocol satisfies a new property abuse-freeness. That is, if the protocol
is executed unsuccessfully, none of the two parties can show the validity of intermediate results to others. Technical details are provided to analyze the security and performance of the proposed protocol. In summary, we present the first abuse-free fair contractsigning protocol based on the RSA signature, and show that it is both secure and efficient.
On demand Temporary Route Recovery for Frequent Link Failures in Adhoc Networks
Abstract
Adhoc network is a collection of wireless mobile nodes dynamically forming a temporary network without the use of existing network infrastructure or centralized administration. Each node acts as a router by itself and forwards all the packets which it receives. There is a frequent link failure in adhoc Networks, which causes packet to be lost or packets doubt to reach destination. In this scenario a different mechanism and a scheme is proposed and implemented to make the important time critical data like real time or voice data to reach the destination without any loss. The mechanism used is a special propagation which propagates a unique kind of route discovery for real time application scenario to send the time critical data safely. The scheme used is temporary path between the nodes during link failure. The important node then forwards the buffered packets to the destination without any loss which is on-demand based on type of information a node forwards. Special buffer is allocated for the nodes marked important during special propagation.
A Secure and Power Efficient Routing Scheme for Ad Hoc Networks
ABSTRACT A recent trend in Ad Hoc network routing is the reactive on demand philosophy where routes are established only when required. Security and Power efficiency are the major concerns in this field. This paper is an effort to combine these factors of security and power to achieve more reliable routing. Most of the protocols in this category are either incorporating security features or considering power factor. In the study no existing protocol is merging the two factors to see results. The ad hoc environment is accessible to both legitimate network users and malicious attackers. The ad hoc environment has the constraint of power factor. The proposed scheme is intended to incorporate both factors on existing protocols. The study will help in making protocol more robust against attacks and implementing power factor to achieve stable routing in routing protocols
Rumor Riding: Anonymizing Unstructured Peer-to-Peer Systems
Abstract
Although anonymizing Peer-to-Peer (P2P) systems often incurs extra traffic costs, many systems try to mask the identities of their users for privacy considerations. Existing anonymity approaches are mainly path-based: peers have to pre-construct an anonymous path before transmission. The overhead of maintaining and updating such paths is significantly high. We propose Rumor Riding (RR), a lightweight and non-path-based mutual anonymity protocol for decentralized P2P systems. Employing a random walk mechanism, RR takes advantage of lower overhead by mainly using the symmetric cryptographic algorithm. We conduct comprehensive
trace-driven simulations to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of this design, and compare it with previous approaches. We also introduce some early experiences on RR implementations.
Fuzzy Keyword Search over Encrypted Data in Cloud Computing
Abstract
As Cloud Computing becomes prevalent, more and more sensitive information are being centralized into the cloud. For the protection of data privacy, sensitive data usually have to be encrypted before outsourcing, which makes effective data utilization a very challenging task. Although traditional searchable encryption schemes allow a user to securely search over encrypted data through keywords and selectively retrieve files of interest, these techniques support only exact keyword search. That is, there is no tolerance of minor typos and format inconsistencies which, on the other hand, are typical user searching behavior and happen very frequently. This significant drawback makes existing techniques unsuitable in Cloud Computing as it greatly affects system usability, rendering user searching experiences very frustrating and system efficacy very low. In this paper, for the first time we formalize and solve the problem of effective fuzzy keyword search over encrypted cloud data while maintaining keyword privacy. Fuzzy keyword search greatly enhances system usability by returning the matching files when users searching inputs exactly match the predefined keywords or the closest possible matching files based on keyword similarity semantics, when exact match fails. In our solution, we exploit edit distance to quantify keywords similarity and develop an advanced technique on constructing fuzzy keyword sets, which greatly reduces the storage and representation overheads. Through rigorous security analysis, we show that our proposed solution is secure and privacy-preserving, while correctly realizing the goal of fuzzy keyword search.
Client-side Load Balancer using Cloud
ABSTRACT Web applications' traffic demand fluctuates widely and unpredictably. The common practice of provisioning a fixedcapacity would either result in unsatisfied customers (underprovision) or waste valuable capital investment (overprovision). By leveraging an infrastructure cloud's ondemand,pay-per-use capabilities, we finally can match the capacity with the demand in real time. This paper investigates how we can build a large-scale web server farm in the cloud. Our performance study shows that using existing cloud components and optimization techniques, we cannot achieve high scalability. Instead, we propose a client-side load balancing architecture, which can scale and handle failure on a milli-second time scale. We experimentally show that our architecture achieves high throughput in a cloud environment while meeting QoS requirements.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Java/J2Ee Project Abstracts: (Big Data,)Dokument2 SeitenJava/J2Ee Project Abstracts: (Big Data,)infinity InfinityNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCCT NCCT NCCT NCCT: IEEE Transaction Papers Abstract EnclosedDokument52 SeitenNCCT NCCT NCCT NCCT: IEEE Transaction Papers Abstract EnclosedPawan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network-Assisted Mobile Computing With Optimal Uplink Query ProcessingDokument16 SeitenNetwork-Assisted Mobile Computing With Optimal Uplink Query ProcessingPonnu ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy and Memory Efficient Clone Detection in WSN AbstractDokument4 SeitenEnergy and Memory Efficient Clone Detection in WSN AbstractBrightworld ProjectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term Paper Project Designing A Secure NetworkDokument7 SeitenTerm Paper Project Designing A Secure Networkeryhlxwgf100% (1)
- Student Member, Ieee, Ô Ômember, IeeeDokument3 SeitenStudent Member, Ieee, Ô Ômember, IeeeKannan VijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIKASYS Java Proj With Abstract 2011Dokument12 SeitenVIKASYS Java Proj With Abstract 2011vijayabaskar1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Sensor Networks Research Papers PDFDokument5 SeitenWireless Sensor Networks Research Papers PDFpimywinihyj3100% (1)
- Fuzzy Keyword Search Over Encrypted Data in Cloud Computing Domain Name: Cloud ComputingDokument4 SeitenFuzzy Keyword Search Over Encrypted Data in Cloud Computing Domain Name: Cloud ComputinglakcyberwayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On VPN PDFDokument10 SeitenResearch Paper On VPN PDFc9rvz6mm100% (1)
- Thesis Report On Ad Hoc NetworkDokument6 SeitenThesis Report On Ad Hoc Networkqpftgehig100% (2)
- Java Projects On 2013 Ieee PapersDokument7 SeitenJava Projects On 2013 Ieee Papersமுத்து குமார்Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resource Literature ReviewDokument5 SeitenResource Literature ReviewpriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On Aodv ProtocolDokument5 SeitenResearch Paper On Aodv Protocolgw2x60nw100% (1)
- Discussions, Conclusion and Further ExtensionDokument3 SeitenDiscussions, Conclusion and Further ExtensionMin Nyi That TantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year Project - (NS2-Networking-Network Security-MANET-VANET-WSN-AdHoc Network) IEEE 2016-17 Project ListDokument19 SeitenFinal Year Project - (NS2-Networking-Network Security-MANET-VANET-WSN-AdHoc Network) IEEE 2016-17 Project ListSPECTRUM SOLUTIONSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secure and Policy-Compliant Source RoutingDokument37 SeitenSecure and Policy-Compliant Source RoutingSuresh PoosapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qos in Manets ThesisDokument5 SeitenQos in Manets Thesisppxohvhkd100% (2)
- Cloud Computing:: WWW - Globalsoftsolutions.inDokument8 SeitenCloud Computing:: WWW - Globalsoftsolutions.inAntony Joseph SelvarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.Eng-Trace Back Mechanism For Rectified-Anil VDokument6 Seiten10.Eng-Trace Back Mechanism For Rectified-Anil VImpact JournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- FT AlertDokument4 SeitenFT AlertahmedbaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projects On Dot Net (IEEE 2010)Dokument31 SeitenProjects On Dot Net (IEEE 2010)Ram MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Queue-Aware Adaptive Resource Allocation For OFDMA Systems Supporting Mixed ServicesDokument7 SeitenQueue-Aware Adaptive Resource Allocation For OFDMA Systems Supporting Mixed ServicesSameer SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rumor Riding: Anonymizing Unstructured Peer-to-Peer SystemsDokument31 SeitenRumor Riding: Anonymizing Unstructured Peer-to-Peer SystemsKarthi KeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Wireless Peer-To-Peer Network With Higher End-To-End Throughput and Lower End-To-End DelayDokument14 SeitenMobile Wireless Peer-To-Peer Network With Higher End-To-End Throughput and Lower End-To-End DelayAJER JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementation of A Company Network Scenario Module by Using Cisco Packet Tracer Simulation SoftwareDokument8 SeitenImplementation of A Company Network Scenario Module by Using Cisco Packet Tracer Simulation SoftwareAbdurahman awilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technology: Java Domain: Ieee Transactions On Networking S.No Project Code Project Titles DescriptionDokument6 SeitenTechnology: Java Domain: Ieee Transactions On Networking S.No Project Code Project Titles DescriptionParameshwargoud LavvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Thesis On Wireless Sensor NetworksDokument4 SeitenResearch Thesis On Wireless Sensor Networkscaitlinwilsonsavannah100% (2)
- Research Paper On DSR ProtocolDokument4 SeitenResearch Paper On DSR Protocolafnhemzabfueaa100% (1)
- Literature Review of Wireless Mesh NetworkDokument8 SeitenLiterature Review of Wireless Mesh Networkaflskkcez100% (1)
- Assignment: Submitted ToDokument11 SeitenAssignment: Submitted ToMuqaddas FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SynopsisDokument5 SeitenSynopsisDivya LunawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review On Leach ProtocolDokument7 SeitenLiterature Review On Leach Protocolewhknurif100% (1)
- Research Paper On Wireless Sensor Network 2014Dokument6 SeitenResearch Paper On Wireless Sensor Network 2014vguomivnd100% (1)
- Secure Cooperative Caching in Wireless P2P NetworksDokument5 SeitenSecure Cooperative Caching in Wireless P2P NetworksIJERDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elysium Technologies Private Limited: Churn-Resilient Protocol For Massive Data Dissemination in P2P NetworksDokument35 SeitenElysium Technologies Private Limited: Churn-Resilient Protocol For Massive Data Dissemination in P2P Networkssunda_passNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report SampleDokument61 SeitenProject Report SampleVIMALNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Secure Hierarchical Protocol For Wireless Sensor NetworksDokument13 SeitenA Secure Hierarchical Protocol For Wireless Sensor NetworksAJER JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java IEEE AbstractsDokument24 SeitenJava IEEE AbstractsMinister ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enhanced Secure and Reliable Routing Protocols For Heterogeneous Multihop Wireless Networks Using QosDokument5 SeitenEnhanced Secure and Reliable Routing Protocols For Heterogeneous Multihop Wireless Networks Using QosEditor InsideJournalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ieee 2010 Titles: Data Alcott Systems (0) 9600095047Dokument6 SeitenIeee 2010 Titles: Data Alcott Systems (0) 9600095047Sudharsan_Kuma_8469Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Evaluation of AODV, DSDV & DSR Routing Protocol in Grid EnvironmentDokument8 SeitenPerformance Evaluation of AODV, DSDV & DSR Routing Protocol in Grid EnvironmentkanjaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Enhancement of A DSR Protocol With Self Healing Optimizing TechniqueDokument8 SeitenAnalysis and Enhancement of A DSR Protocol With Self Healing Optimizing TechniqueRakeshconclaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract: Due To Significant Advances in Wireless Modulation Technologies, Some MAC Standards Such As 802.11aDokument6 SeitenAbstract: Due To Significant Advances in Wireless Modulation Technologies, Some MAC Standards Such As 802.11aVidvek InfoTechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis On Ad Hoc NetworkDokument7 SeitenThesis On Ad Hoc Networkbk4p4b1c100% (2)
- 17 Implementation of A Company Network ScenarioDokument7 Seiten17 Implementation of A Company Network ScenarioVina UntalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Analysis of Handover Key Management in 4G LTE/SAE NetworksDokument4 SeitenSecurity Analysis of Handover Key Management in 4G LTE/SAE NetworksadredNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.Phil Computer Science Wireless Communication ProjectsDokument8 SeitenM.Phil Computer Science Wireless Communication ProjectskasanproNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Survey On Trust Computation Model For Multi Agent SystemDokument4 SeitenA Survey On Trust Computation Model For Multi Agent SystemijsretNoch keine Bewertungen
- M.E Computer Science Wireless Communication ProjectsDokument8 SeitenM.E Computer Science Wireless Communication ProjectskasanproNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING PAPER ON ALLOCATED BEST-EFFORT PACKET DELIVERYDokument12 SeitenIEEE/ACM TRANSACTIONS ON NETWORKING PAPER ON ALLOCATED BEST-EFFORT PACKET DELIVERYKhalid SaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ieee Research Papers On Wireless Network SecurityDokument6 SeitenIeee Research Papers On Wireless Network SecuritynepwuhrhfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Lan Security Research PaperDokument6 SeitenWireless Lan Security Research Paperlxeikcvnd100% (1)
- An Efficient Routing Protocol For Mobile Ad Hoc Network For Secured Communication and Minimized Power ConsumptionDokument8 SeitenAn Efficient Routing Protocol For Mobile Ad Hoc Network For Secured Communication and Minimized Power ConsumptionijansjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Thesis Implementation and Simulation of Routing ProtocolsDokument4 SeitenMaster Thesis Implementation and Simulation of Routing ProtocolsCustomWrittenPaperLittleRock100% (2)
- Self Chord-Achieving Load Balancing in Peer To Peer Network: M.Divya B.SaranyaDokument5 SeitenSelf Chord-Achieving Load Balancing in Peer To Peer Network: M.Divya B.Saranyawww.irjes.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On Wireless Sensor Network 2011Dokument5 SeitenResearch Paper On Wireless Sensor Network 2011mgojgerif100% (1)
- Aodv Protocol ThesisDokument4 SeitenAodv Protocol ThesisSarah MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deploying MPLS and DiffServDokument7 SeitenDeploying MPLS and DiffServMohammed MarouanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CodeDokument9 SeitenCodemahesh_kumar_mandiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 Project ListDokument1 Seite2011 Project Listmahesh_kumar_mandiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zener DiodeDokument2 SeitenZener Diodemahesh_kumar_mandiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irrigation Department: Cover Channnel by R.C.C. PipesDokument2 SeitenIrrigation Department: Cover Channnel by R.C.C. Pipesmahesh_kumar_mandiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VL AbstractDokument2 SeitenVL Abstractmahesh_kumar_mandiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRI PumpsDokument13 SeitenCRI Pumpscrigroups0% (1)
- Quality Criterion of Road Lighting Measurement and ExploringDokument96 SeitenQuality Criterion of Road Lighting Measurement and ExploringNitin UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBM and PBZ Crown Techniques ComparedDokument6 SeitenPBM and PBZ Crown Techniques ComparedDonanguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic AlgorithmDokument46 SeitenGenetic AlgorithmJerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Rolling Bridge, Scientific American 24 August 1889 p120Dokument2 SeitenElectric Rolling Bridge, Scientific American 24 August 1889 p120Rm1262Noch keine Bewertungen
- CoP Fo Petroleum Road Tanker Vapour Collection Systems and Equipment Used in Unloading OperationsDokument29 SeitenCoP Fo Petroleum Road Tanker Vapour Collection Systems and Equipment Used in Unloading OperationsMuhammad Ibad AlamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel U3 - Alcatel U3 User GuideDokument53 SeitenAlcatel U3 - Alcatel U3 User Guideoswaldomarangoni5295100% (11)
- Active Front EndDokument5 SeitenActive Front EndDaleel LillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil-Vii-Air Pollution and Control (10cv765) - Question PaperDokument4 SeitenCivil-Vii-Air Pollution and Control (10cv765) - Question PaperSathya MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column and Wall Load Take Down Spreadsheet v1.0 - CLDokument28 SeitenColumn and Wall Load Take Down Spreadsheet v1.0 - CLBilal KhattabNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAE StandardDokument28 SeitenSAE Standardwei foo83% (6)
- 2SC1344, 2SC1345: Silicon NPN EpitaxialDokument9 Seiten2SC1344, 2SC1345: Silicon NPN EpitaxialrolandseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Çimsa Eco White TDS (EN)Dokument1 SeiteÇimsa Eco White TDS (EN)Babu NysemereNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Heat ExchangersDokument88 Seiten02 - Heat ExchangerssanjaysyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assist. Prof. DR - Thaar S. Al-Gasham, Wasit University, Eng. College 136Dokument49 SeitenAssist. Prof. DR - Thaar S. Al-Gasham, Wasit University, Eng. College 136Hundee HundumaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic Sub Pumps Catalog 60Hz - USDokument44 SeitenPlastic Sub Pumps Catalog 60Hz - UScarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inductance Measurements For Synchronous MachinesDokument2 SeitenInductance Measurements For Synchronous MachinesYusuf YaşaNoch keine Bewertungen
- G100-G102-Chassis-Manual #1Dokument151 SeitenG100-G102-Chassis-Manual #1Daihatsu Charade BanjarnegaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection Checklist For Lifting Tools & TacklesDokument2 SeitenInspection Checklist For Lifting Tools & Tacklesnil thaeu100% (1)
- Psan en Tcd210185ab 20220523 Inst WDokument2 SeitenPsan en Tcd210185ab 20220523 Inst Wsinar automationNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHIP HANDLING WITH ESCORT TUGS A REFERENCE MANUAL FOR MASTERS PILOTS GIANO Tug SpecsDokument8 SeitenSHIP HANDLING WITH ESCORT TUGS A REFERENCE MANUAL FOR MASTERS PILOTS GIANO Tug SpecsMahmoud ElsherifNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Software Engineer Sarika DhingraDokument2 SeitenCV Software Engineer Sarika DhingravirenderbishnoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premiertrak 1100x650 Parts ENGDokument276 SeitenPremiertrak 1100x650 Parts ENGarttv44100% (1)
- University Institute of Information Technology: Ouick Learn - MCQDokument53 SeitenUniversity Institute of Information Technology: Ouick Learn - MCQvimalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asphalt Institute PresentationDokument43 SeitenAsphalt Institute PresentationMax Cedeño De LeónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nba Sar B.tech. Electronics UgDokument171 SeitenNba Sar B.tech. Electronics UgSaurabh BhiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remeha Gas 310 ECO: Technical InformationDokument59 SeitenRemeha Gas 310 ECO: Technical InformationAdrian Blazquez MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iec 62097-2009Dokument170 SeitenIec 62097-2009luis.alvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PuleyDokument9 SeitenPuleynicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coal Drying Technology and Plant DesignDokument12 SeitenCoal Drying Technology and Plant DesignJigar M. UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireVon EverandThe Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationVon EverandCCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionVon EverandCEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsVon EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionVon EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityVon EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Von EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (4)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersVon EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamVon EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxVon EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (67)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsVon EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CompTIA Network+ Computing Technology Industry Association Certification N10-008 Study Guide: Hi-Tech Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the Exam with Confidence - Practice Test with AnswersVon EverandThe CompTIA Network+ Computing Technology Industry Association Certification N10-008 Study Guide: Hi-Tech Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the Exam with Confidence - Practice Test with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideVon EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Von EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Guide to Understanding Wireless Technology, Network Security, Computer Architecture and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCNA and CCENT)Noch keine Bewertungen
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamVon EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL 4: Create, Deliver and Support: Reference and study guideVon EverandITIL 4: Create, Deliver and Support: Reference and study guideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL® 4 Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and Strategic Leader DPI certificationVon EverandITIL® 4 Direct, Plan and Improve (DPI): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional and Strategic Leader DPI certificationNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationVon EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Cyber-Warfare: A Multidisciplinary ApproachVon EverandIntroduction to Cyber-Warfare: A Multidisciplinary ApproachBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamVon EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL 4: Direct, plan and improve: Reference and study guideVon EverandITIL 4: Direct, plan and improve: Reference and study guideNoch keine Bewertungen