Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing NCP For Client With Schizophrenia
Hochgeladen von
ericjake_limOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing NCP For Client With Schizophrenia
Hochgeladen von
ericjake_limCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
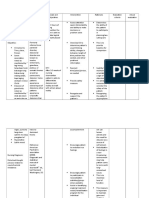
- Gross splitting of mental functions and loosing connection between these functions.
Epidemiology: - incidence (about 1% male = female) - 50% of male admitted < 25 - 30% of female admitted <25 - peak age of onset 15-25 in males. - Peak onset 25-35 in females . - Rare <10ys >50ys - Seasonality: more in winter - Suicide : 10 15 % - Substance abuse : (cigarette alcohol marijuana cocaine ) - From DSMIV Schizophrenia: Two or more of the following symptoms for at least one month a) delusions. b) hallucinations. c) disorganized speech(incoherence or derailment). d) grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior. e) negative symptoms (affective flattening, alogia ,or avolition.) - significant social/occupational dysfunction since the disorder began. positive and negative symptoms a) positive symptoms - formal thought disorder(derailment-tangential-incoherent-irrelevant answers-illogical) - bizarre behavior(in clothing appearance- social and sexual behavior-agitated or aggressive repetitive or stereotyped behavior ) - delusions - hallucinations. b) negative symptoms. - alogia(poverty of speech or contents-blocking-increased latency) - flattening of affect (poor facial expression decreased spontaneous movements and expressions-poor eye contact ) - avolition (impaired hygiene-anergia-lack of persistence at work or school) - anhedonia (decreased interests impaired intimacy-few relationships) - impaired attention (social inattentiveness- or during testing) Etiology: 1) genetic : 1st degree relatives (one parent 13% two parents 46% ) - Monozygotic twins 50% - mode of inheritance unclear 2) Neurochemistry and neuroanatomy: - low blood flow. - Low metabolism in brain cells specially in frontal cortex(PET) - Electrical activity shows hypo function. - Hypersensitivity of dopamine receptors. - Widening of ventricles. - Faulty metabolism . 3) psychosocial factors History : 1) emil kraepelin ( named it dementia praecox comes in early life with downhill course due to organic pathology , comes with hallucinations , delusions, affecting thought, speech, with poor insight and judgment, and reduced attention to outside world.). 2) bleuler : it is splitting in mind with 4 fundamental and 3 accessory behavior - fundamental: associative disturbance , autism, ambivalence , affective flattening. Accessory : delusions , hallucinations , catatonic posturing. 3) Freud : schizophrenia is reaction to frightening unbearable idea. 4) Sullivan: it is originated from impaired interpersonal relations to parents , or a significant people .
5) Schneiders: schizophrenia is syndrome characterized by(3 hallucinations audible thoughts, second person voice, third person voice, 3 thoughts insertion, withdrawal ,broadcasting, 3 made feelings , impulses ,passivity , and delusional perception. Schizophrenia subtypes: a) paranoid - client preoccupied by one or more delusions or auditory hallucinations, no disorganized speech or catatonic behavior, no flat or inappropriate affect. b) disorganized - disorganized speech or behavior , flat or inappropriate affect . - not having criteria for catatonic type. c) catatonic - motor immobility , excess motor activity not influenced by external stimuli. - Peculiarities of involuntary movement, echolalia or echopraxia. d) undifferentiated - that does not meet the criteria of the above groups. e) residual - no florid psychotic symptoms or present in attenuated form , with one or more negative symptoms . Delusional disorder Diagnostic criteria: 1- None bizarre delusions involving situation that could occur in real life such as being followed , poisoned ,infected having a disease , loved at distance , deceived , or got a message from Allah , of at least one month duration . 2- has never met a criteria a of schizophrenia for more than few hours. 3- apart from impact of delusions or its ramifications , functions are not markedly impaired , and behavior is not obviously odd or bizarre. Types: - Erotomanic: delusions that another person usually higher status is in love with the individual. - Grandiose : delusions of inflated worth, power, knowledge, identity , or special relationship with diety or famous person. - Jealous and infidelity : delusions that ones sexual partner is unfaithful. - Persecutory: delusions that one usually close to him is being malevolently treated in some way . - Somatic : delusions that one has some physical defect . - Mixed : has more than one character of the above types but none of them predominates. - Unspecified. Nursing role in management of schizophrenia: (a) assessment :collecting all medical , psychiatric, social ,and financial ,informations and needs to include them in overall coordinated plan. (b) planning :overall plan includes management, crisis intervention, service providers , to ensure continuity of care. (c) linking : helps the patients and families to get access to services required for comprehensive care (d) therapeutic care : 1) education teaching patient about his illness , how to manage stress, importance of treatment and side effects. 2) focusing on problem solving. 3) setting reasonable expectations. 4) expressing emotions. 5) crisis intervention. 6) managing dependence . 7) illness self management. 8) good selection for recreational activities e.g. art ,dance or music (e)evaluation efficacy of procedures. and outcome. Antipsychotics A- Typical antipsychotics: - e.g. Serenace (Haloperidol ), Largactil (Chlorpromazine ). - Side effects: sedation, dry mouth, urine retention, constipation and EPS EPS Extra pyramidal - Dystonias: muscle spasm.
- Akathesia: Motor restlessness. - Drug induced parkinsonism: tremors, rigidity and akinesia. - Tardive dyskinesia: late- appearing and irreversible movements. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome A- Fatal Side effect. - Muscle rigidity. - Tremors. - Inability to talk. - Altered level of consciousness. - Hyperthermia. - Autonomic dysfunction . - Leukocytosis. B- Atypical antipsychotic: - O- lanzepine ( weight gain, DM, dyslipidemia) - Respiredal ( EPS, hyperprolactenemia) - Quetiapine ( weight gain ) - Clozapin ( weight gain, sedation, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, DM, orthostatic hypotension)
Source: http://www.nursing-lectures.com/2011/08/schizophrenia-and-nursing-care-plan.html
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Schizophrenia OverviewDokument8 SeitenSchizophrenia OverviewRiscky LauwNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 7 MseDokument20 SeitenCH 7 MseIyanna BaylonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scizophrenia NCP1Dokument13 SeitenScizophrenia NCP1Kholid Abu Mohammad AlfaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Drug Study Final Paranoid SchizophreniaDokument11 SeitenNCP Drug Study Final Paranoid SchizophreniaCherubim Lei DC FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study SchizophreniaDokument3 SeitenCase Study SchizophreniaCHRISANTO ARZANANNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care PlanDokument1 SeiteSCHIZOPHRENIA Nursing Care Planrinkai130% (1)
- Disturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Dokument3 SeitenDisturbed Thought Process NCP Gallano May 22 2018Charles Mallari ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Running Head: Comprehensive Case Study 1Dokument11 SeitenRunning Head: Comprehensive Case Study 1api-546355462Noch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvDokument8 SeitenSubmitted By: Charisa S. Simbajon BSN IvCharisa Simbajon100% (1)
- Format MSEDokument3 SeitenFormat MSESubir Banerjee0% (1)
- Psych NCPDokument1 SeitePsych NCPEliza Joy Franco RNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia Case StudyDokument13 SeitenSchizophrenia Case StudyAnonymous Hfrl594Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Status ExaminationDokument11 SeitenMental Status ExaminationIman TawasilNoch keine Bewertungen
- SchizophreniaDokument3 SeitenSchizophreniaPete Cobra Cobraiti100% (2)
- NCP SchizophreniaDokument7 SeitenNCP SchizophreniaSteffi Raye Madrid50% (2)
- Case Study 1Dokument67 SeitenCase Study 1Herbie SoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis: Acute ConfusionDokument4 SeitenNursing Diagnosis: Acute Confusionasmika danaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognitive TherapyDokument7 SeitenCognitive Therapyshivani singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Nursing - Mental Status ExaminationDokument4 SeitenPsychiatric Nursing - Mental Status ExaminationChien Lai R. BontuyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scizophrenia NCP2Dokument12 SeitenScizophrenia NCP2Kholid Abu Mohammad AlfaizinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A CASE sSTUDY OF MARY WITH MDDDokument13 SeitenA CASE sSTUDY OF MARY WITH MDDericNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paranoid Schizoprenia (Individual Case)Dokument25 SeitenParanoid Schizoprenia (Individual Case)Karla Dagdag0% (1)
- MSE Sample PDFDokument5 SeitenMSE Sample PDFSam Raven AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Psyche 1Dokument7 SeitenNCP Psyche 1Pete SkullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psych NCPDokument4 SeitenPsych NCPnoman-053Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Mental HealthDokument9 SeitenCase Study - Mental Healthapi-380891151Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument17 SeitenCase Studyapi-508597583Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Status ExaminationDokument4 SeitenMental Status ExaminationavigaeljoieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderDokument3 SeitenPathophysiology: Bipolar DisorderPae EdejerNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDokument6 SeitenCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structured Format For History and MSEDokument22 SeitenStructured Format For History and MSEfizNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardDokument9 SeitenNCP BSN 3rd Yr Psychiatric WardMary Margarett BoadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDokument26 SeitenUndifferentiated SchizophreniaVictor Shon100% (1)
- Mental Status ExaminationDokument8 SeitenMental Status ExaminationanisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mental Status ExaminationDokument3 SeitenMental Status ExaminationjudssalangsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Undifferentiated SchizophreniaDokument16 SeitenUndifferentiated SchizophreniavinalonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study HaldolDokument2 SeitenDrug Study HaldolGracia EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaDokument14 SeitenNursing Care Plan For A Patient With SchizophreniaMary Luz De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoloft Sertraline Drug CardDokument1 SeiteZoloft Sertraline Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Process RecordingDokument12 SeitenProcess Recordingchristian_cayle100% (1)
- Process Recording NCMHDokument15 SeitenProcess Recording NCMHJohanna Elaine Tandoc0% (2)
- Mental Status ExamDokument2 SeitenMental Status Examkristel_nicole18yahoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 2Dokument8 SeitenCase 2Kreshnik IdrizajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Dokument6 SeitenNursing Prioritization (Schizophrenia)Elaine Dionisio TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anxiety Disorder and Case PresentationDokument52 SeitenAnxiety Disorder and Case Presentationmulanako0% (1)
- Additional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaDokument26 SeitenAdditional Nursing Care Plans - SchizophreniaJasmin Jacob100% (5)
- NCP Depression1Dokument1 SeiteNCP Depression1kyreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocd PsychopathologyDokument14 SeitenOcd PsychopathologyelvinegunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPJoseph Dableo ParreñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia NCPDokument2 SeitenSchizophrenia NCPNicole cuencos100% (2)
- Unit 3 Psychotic DisorderDokument12 SeitenUnit 3 Psychotic Disorderreeta yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shizophrenia Other Psychotic Disorders: Hyacinth C. Manood, MD, DPBPDokument56 SeitenShizophrenia Other Psychotic Disorders: Hyacinth C. Manood, MD, DPBPDani NugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- KR - SchizophreniaDokument4 SeitenKR - SchizophreniaValantino RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia This OneDokument44 SeitenSchizophrenia This OneAnabelle RicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia and OtherDokument24 SeitenSchizophrenia and OtherMariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia Lecture 2010 PART 1 and 2Dokument69 SeitenSchizophrenia Lecture 2010 PART 1 and 2Rahul Kumar DiwakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic7 AbnormalPsych (Students)Dokument33 SeitenTopic7 AbnormalPsych (Students)nickpho21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neurobyology Respons Schizophrenia & Other Psychotic DisorderDokument24 SeitenNeurobyology Respons Schizophrenia & Other Psychotic DisorderquinnNoch keine Bewertungen
- S H Z P R N A: Colegio de Sta. Lourdes of Leyte Foundation, Inc. College of Nursing Tabontabon, LeyteDokument74 SeitenS H Z P R N A: Colegio de Sta. Lourdes of Leyte Foundation, Inc. College of Nursing Tabontabon, LeyteGlenn ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NS 48 Psychological Disorders II: Conversion DisorderDokument11 SeitenNS 48 Psychological Disorders II: Conversion DisordermuhammadridhwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Do A Pulse Oximetry EvaluationDokument1 SeiteB. Do A Pulse Oximetry Evaluationericjake_limNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methyldopa 250mg BIDDokument1 SeiteMethyldopa 250mg BIDericjake_limNoch keine Bewertungen
- D. Add Amlodipine To The RegimenDokument1 SeiteD. Add Amlodipine To The Regimenericjake_limNoch keine Bewertungen
- C. Discontinue The Amlodipine and Continue To Monitor BPDokument1 SeiteC. Discontinue The Amlodipine and Continue To Monitor BPericjake_limNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corollary RecommendationDokument1 SeiteCorollary Recommendationericjake_limNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement 6:: Immediate Cardiac Risk Stratification Based On HX, PE, and Trop I To Be DoneDokument2 SeitenStatement 6:: Immediate Cardiac Risk Stratification Based On HX, PE, and Trop I To Be Doneericjake_limNoch keine Bewertungen
- D. Administer O2 Immediately: PHA CPG For The Management of Patient With STEMIDokument1 SeiteD. Administer O2 Immediately: PHA CPG For The Management of Patient With STEMIericjake_limNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric RationaleDokument13 SeitenPsychiatric RationaleJohn Derama SagapsapanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Nursing 7th Edition Keltner Test BankDokument10 SeitenPsychiatric Nursing 7th Edition Keltner Test BankCynthiaJordanMDtwqra100% (12)
- SET 2 Oct 27 TRUE KEY ANSWERDokument16 SeitenSET 2 Oct 27 TRUE KEY ANSWERJayrald CruzadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Psychiatric Drugs 08 PDFDokument275 SeitenHandbook of Psychiatric Drugs 08 PDFlucian_vatamanu100% (3)
- Case Presentation Bipolar 1 Manic TypeDokument18 SeitenCase Presentation Bipolar 1 Manic Typenailed_heart0% (1)
- Free Nclex RN Study GuideDokument25 SeitenFree Nclex RN Study GuideKatie Shortt100% (11)
- HALOPERIDOLDokument1 SeiteHALOPERIDOLAlyxen Pelingen75% (4)
- Anti PsychotisDokument21 SeitenAnti Psychotissuresh sataguniNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaldolDokument2 SeitenHaldolKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Delirium Power Point PresentationDokument15 SeitenDelirium Power Point Presentationfrancis00090100% (1)
- Mental Health Practice Test QuestionsDokument11 SeitenMental Health Practice Test QuestionsHisabu MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delirium Answers 2Dokument3 SeitenDelirium Answers 2ibrahim muashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Critical Care Nursing PDFDokument124 SeitenAdvanced Critical Care Nursing PDFnandar wirawan100% (2)
- Psychiatry (Adult and Child)Dokument102 SeitenPsychiatry (Adult and Child)teena6506763Noch keine Bewertungen
- High Yield Psychiatry: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday RamahiDokument43 SeitenHigh Yield Psychiatry: Shelf Exam Review Emma Holliday Ramahigreg100% (1)
- Psych Meds Booster Nov 2022 PnleDokument11 SeitenPsych Meds Booster Nov 2022 PnleDarwin DerracoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Mental Health Comprehensive Case StudyDokument12 SeitenPsychiatric Mental Health Comprehensive Case Studyapi-508432180Noch keine Bewertungen
- PKM1 - Perhitungan Persediaan Puskesmas Tahun 2020 RevisiDokument1.059 SeitenPKM1 - Perhitungan Persediaan Puskesmas Tahun 2020 Revisiabdulkahar pkmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Nursing Mastery Test Part 2Dokument16 SeitenPsychiatric Nursing Mastery Test Part 2Rika MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aas 13501Dokument13 SeitenAas 13501Felipe FernandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consultation Liaison PsychiatryDokument57 SeitenConsultation Liaison PsychiatryPriyash Jain100% (2)
- Pre-Test Psychiatric NursingDokument17 SeitenPre-Test Psychiatric NursingDefensor Pison Gringgo100% (1)
- Laporan Kasus Skizofrenia ParanoidDokument63 SeitenLaporan Kasus Skizofrenia ParanoidMichi Mich100% (1)
- 2018 Article 1999 PDFDokument8 Seiten2018 Article 1999 PDFyusma haranisNoch keine Bewertungen
- G3 Schizo Psychiatric WardDokument18 SeitenG3 Schizo Psychiatric Wardmark OrpillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLE PRE-TEST Q Only 150 ITEMS (The Nurse Is Caring... ) - Refresher Nov 2021Dokument11 SeitenNLE PRE-TEST Q Only 150 ITEMS (The Nurse Is Caring... ) - Refresher Nov 2021Epaphras Joel MilitarNoch keine Bewertungen
- T 2 - Unit Test 2 - Psych & PediaDokument8 SeitenT 2 - Unit Test 2 - Psych & PediaenzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Test 2 RationalesDokument11 SeitenPost Test 2 Rationalesrhymes2u100% (2)
- 109 Questions and Rationale On Psychotic Disorders IIIDokument32 Seiten109 Questions and Rationale On Psychotic Disorders IIIChaelo SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDrug StudyLouise Adrene SevillaNoch keine Bewertungen