Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mechanics: Scalar and Vector Quantities
Hochgeladen von
Tawfik KhattabOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mechanics: Scalar and Vector Quantities
Hochgeladen von
Tawfik KhattabCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mechanics
Physics is relations between quantities o Speed = Distance / Time m/s o Energy = mC2 (m = mass, C = speed of light = 3 x 108 m/s) o F = ma (F=Force, m=mass, a=acceleration) Year 1960 : Standard International System of units (SI ) o Length meter o Area m2 o Volume m3 o Mass Kg o Time second Measurement Skills o Put so many next to each other divide total by number o Improve accuracy increase number of papers o Measure thickness of one paper: Stack n papers measure thickness of stack thickness = x / num. o Measure diameter of thread Rotate thread around pen measure width of thread on pen (x) diameter of thread = x / number of turns o Measure Periodic time of a pendulum o Time to oscillate once from right to left measure time to oscillate 20 times Time = Measure Diameter of Solid ball: put between two books measure diameter
Scalar and Vector Quantities: Scalar: magnitude only length, mass, temperature, distance, speed Vector: magnitude + direction force, velocity, acceleration, displacement If opposite directions vector will have a negative sign before magnitude o Distance vs. displacement o Speed vs. velocity o Weight vs mass: W=mg
Motion Speed = Acceleration = o o o o m/s This calculates Average constant Speed m/s2 This calculates constant acceleration (car speed will be increasing still) Decreasing acceleration: Increasing acceleration : rocket speed at launch Deceleration, increasing deceleration, decreasing deceleration.
o Determine acceleration and Deceleration on curve: ab: increases velocity from rest. (Acceleration) bc: decreases velocity to zero. (Deceleration) cd: INCREASES velocity from rest in REVERSE direction (ACCELERATION) de: DECREASES velocity to zero in REVERSE direction. (DECELERATION)
Understand Graph Shape (line or curve, up or down, U or N shape) o Straight line constant no change o Curve line increasing (curve up) or decreasing (curve down) o Horizontal straight line change = 0 Speed (displacement time graphs): Zero Speed Increasing Speed Constant increasing Speed Decreasing Speed
Velocity vs. time graph (v - t graph): o acceleration is gradient (slope) = change in velocity / change in time o distance covered = area under curve V=increasing increase A= increasing Acceleration V=constant Decrease A= constant Deceleration V = decreasing increase A = decreasing Acceleration
V=constant increasing A=constant Acceleration
Compare graphs of deceleration: Acceleration - time graph (a - t graph) o Compare graphs of acceleration: zero, constant inc, constant dec, increasing, decreasing. Free fall: o Zero initial speed o Constant acceleration = g for any kind of object
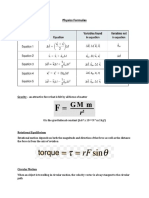
Forces: F=ma If velocity is constant a=0 F (resultant) must be 0 Types of forces: o Mass: content of matter. Scalar (Kg) o Weight: attraction force of gravity based on body mass. Vector quantity (Newtons) o Resistance Force always opposing motion. Thrust of car due to air resistance, friction and viscouse force o Stretching Force: Spring extend in length proportional to load (Hookes law) up to limit of proportionality (break) o Up thrust force: Before parachute: initial v=0, R increases with V until W=R and body does not accelerate and reach no parachute terminal velocity
o o o o
when parachute opens R>W body deaccelerate till parachute terminal velocity Reaction Force due to weight force from an object resting on a table Tension Force is pull strength of wire/rope before it break Drag Force of parachute Circular Motion: Object accelerating but speed is constant due to continuous change in direction centrifugal force is net force towards center of rotation cause successive change in direction Moment: M=F.d (d=distance) , fishing rod decrease force to catch fish
Work, Energy & Power Work is done when energy is transformed. W=Force * Distance Energy is ability to do work. o Example: Energy stored in arm to do work o Never created ONLY transformed from one form to another o Potential Energy: PE = mgh (mass, 10m/s, height) o Kinetic Energy: KE = mv2 (mass in kg, velocity) Power: o Rate of doing work P = E/t o In a car: P=Force * Velocity
Sources of Energy: Non Renewable Sources: Oil, coal, natural gas, nuclear Renewable sources: o Hydropower station & Tidal Energy: PEKEelectric Energy o Wind: Wind energy KE electric o Wave Energy: Wave Energy Electric Energy o Solar: Heat Energy o Nuclear Energy: Fission Reactions: nucleus split in two halves release large energy Fusion Reaction: light nuclei combine together form heavy nucleus + release large energy Density: o o o Mass per unit volume (rho kgm/m3) Density never change and it is constant for every element Experiment to determine density of irregular solid Measure height of liquid put irregular body measure height of liquid V = V2 V1 Pressure: o Force on unit area o Unit: Pascal (Pa) o o o The smaller the area the larger the pressure Any height of liquid or filled object (not hollow) causes the following pressure (density, acceleration of free fall, height (v=a*h)
Atmospheric Pressure: Mercury Barometer: Patm (height=76cm) = phg = 13600 * 10 * 0.76 = 103000 Pa Any two points in a free moving liquid will have same Pressure o If vertical tube is wider mercury will have same height (due to equation above) o If vertical tube is inclined mercury will have same height Manometer: To measure pressure of compressed gas PA= PB Pgas = Pressure of mercury + Patm
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physical Quantities and Measurement TechniquesDokument19 SeitenPhysical Quantities and Measurement TechniqueslavanyagolebuissnessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics A and B Formula SheetDokument14 SeitenPhysics A and B Formula SheetEpic WinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Mechanics Revision NotesDokument5 Seiten1 - Mechanics Revision NotesHuaxiang HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid MechanicsDokument41 SeitenFluid MechanicsRian SteveNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 JC1 H2 MYE (Solution)Dokument21 Seiten2012 JC1 H2 MYE (Solution)Stella MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 5Dokument20 SeitenPhysics 5DaNy3lMatheoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips MCAT Physics ReviewDokument59 SeitenDokumen - Tips MCAT Physics ReviewJIRUT SirisounthornNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves and Oscilla-OnsDokument33 SeitenWaves and Oscilla-OnsDavid SenjayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula FizikDokument10 SeitenFormula Fiziknew_farhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formula FizikDokument9 SeitenFormula Fizikqaslun basheer100% (2)
- Form Two Summary PhysicsDokument2 SeitenForm Two Summary PhysicsFaadumomizankaahiyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics As NotesDokument28 SeitenPhysics As NotesShyam SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 General PhysicsDokument17 SeitenTopic 1 General PhysicsSashideran ThilagesuaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Notes in Physics 1Dokument13 SeitenReview Notes in Physics 1Anonymous cuVSFiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Motion PracticalDokument16 SeitenLinear Motion PracticalAlastair TavernerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid PropertiesDokument41 SeitenFluid PropertiesRamesh Kumar100% (1)
- Aerodynamics SlidesDokument205 SeitenAerodynamics SlidesAbhinil MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparatory Guide Physics PDFDokument260 SeitenPreparatory Guide Physics PDFHasan NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Physics Unit 1 Basic NotesDokument19 SeitenAs Physics Unit 1 Basic NotesA093874659927392789% (9)
- Physics Questions ImportantsDokument130 SeitenPhysics Questions Importantsblackbumber69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hooke's LawDokument19 SeitenHooke's LawWan Afiff100% (1)
- AE3010 Aerodynamics and Propulsion: Dr. Peter Barrington RV219 P.barrington@kingston - Ac.ukDokument55 SeitenAE3010 Aerodynamics and Propulsion: Dr. Peter Barrington RV219 P.barrington@kingston - Ac.ukSabine BroschNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws of MotionDokument29 SeitenNewton's Laws of MotionAbe FreedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives - Unit 1 OCR Physics A-LevelDokument7 SeitenLearning Objectives - Unit 1 OCR Physics A-Leveleugene_970418755Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Chapter 12Dokument26 SeitenDynamics Chapter 12Sudarshan KambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMB222 - KinematicsParticles-01-OneDimension Lecture 1Dokument27 SeitenMMB222 - KinematicsParticles-01-OneDimension Lecture 1Olefile Mark MolokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Equation List PhysicsDokument5 SeitenIGCSE Equation List PhysicsJoseLinNoch keine Bewertungen
- VCE Physics - Yr 11 Essays and Projects 6285Dokument9 SeitenVCE Physics - Yr 11 Essays and Projects 6285TimNguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2. Kinematics in One DimensionDokument74 SeitenChapter 2. Kinematics in One DimensionMaggie WestbrookNoch keine Bewertungen
- A V V T V T A Average Acceleration V Finalvelocit V Initial Velocity T TimeDokument3 SeitenA V V T V T A Average Acceleration V Finalvelocit V Initial Velocity T TimeKing OsumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Last Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014Dokument13 SeitenLast Name: - : University of Waterloo Final Examination Fall 2014YuChenQianNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics ReviewerDokument8 SeitenGeneral Physics ReviewerXyrell Claude Monta100% (1)
- 1.4 What Is Cfd?: M M ⟹ Ρva Dm Dt ∑F ⟹ F=Ma, M=Mv, Dm Dt D (Mv) DtDokument43 Seiten1.4 What Is Cfd?: M M ⟹ Ρva Dm Dt ∑F ⟹ F=Ma, M=Mv, Dm Dt D (Mv) DtTeh Boon SiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (10)
- CONCISEFORMULASandPRACTICAL PDFDokument5 SeitenCONCISEFORMULASandPRACTICAL PDFEmilyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drag Coeffecient LabDokument5 SeitenDrag Coeffecient LabYassir HindiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1 EncDokument84 SeitenPhysics 1 EncMhelveneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics FormulasDokument20 SeitenPhysics Formulasbrandon100% (1)
- Mech 2Dokument71 SeitenMech 2Gino Mandado0% (1)
- Engineering Dynamics Lecture 3Dokument30 SeitenEngineering Dynamics Lecture 3Anokha LadlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KinematicsDokument72 SeitenKinematicsRenerio P. Gentallan Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nouveau Microsoft Word DocumentDokument7 SeitenNouveau Microsoft Word DocumentRIDA shopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Forces and EnergyDokument47 SeitenUnit 3 Forces and Energy4w7b9kkyp8Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3. MechanicsDokument12 Seiten1.3. MechanicsLiang LuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Experiment 1-4Dokument8 SeitenPhysics Experiment 1-4SummaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- w14d2 Class 35Dokument72 Seitenw14d2 Class 35eviroyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- FN MKGGMS: Experiment 2.acceleration of GravityDokument8 SeitenFN MKGGMS: Experiment 2.acceleration of GravityJessica RossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Forces and EnergyDokument13 SeitenMotion Forces and EnergyAbid KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP 2012 Physics B Free Response QuestionsDokument12 SeitenAP 2012 Physics B Free Response QuestionsAlan G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Circular MotionDokument3 SeitenApplications of Circular Motionmonkey2rockz100% (2)
- Section 1 - Introduction To Applied MechanisDokument10 SeitenSection 1 - Introduction To Applied MechanisAfhnan TemiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Derived Quantities?: Part - ADokument8 SeitenWhat Are Derived Quantities?: Part - AGirish BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect1 DynamicsDokument28 SeitenLect1 Dynamicsأميرول فاروقاNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: Continuous Motion: Today's ObjectivesDokument17 SeitenIntroduction & Rectilinear Kinematics: Continuous Motion: Today's Objectivesجعفر السلطانNoch keine Bewertungen
- F - (Volume × Density × G)Dokument11 SeitenF - (Volume × Density × G)Gaurav ShekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsVon EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 ReportDokument11 SeitenLab 1 ReportangelosoutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abb Switchgear ManualDokument7 SeitenAbb Switchgear ManualEasy Energy SACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boundary Layer and WakeDokument20 SeitenBoundary Layer and WakeXet FatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics Bes 117Dokument6 SeitenElectrostatics Bes 117Joyjoy C LbanezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochures - FRENIC-Ace For Solar PumpingDokument2 SeitenBrochures - FRENIC-Ace For Solar PumpingSINES FranceNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM2596 3.0 A, Step-Down Switching Regulator: TO 220 TV Suffix CASE 314BDokument27 SeitenLM2596 3.0 A, Step-Down Switching Regulator: TO 220 TV Suffix CASE 314BHafizh Yudha MahestraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Permanent Magnet DC MotorDokument4 SeitenPermanent Magnet DC MotorSourav Kumar100% (1)
- 55 W Kit Coleman ManualDokument14 Seiten55 W Kit Coleman ManualCésar Gerardo López DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Physics F6 Second Term 2018Dokument8 SeitenRPT Physics F6 Second Term 2018norhazli ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fermator Operation Manual PDFDokument8 SeitenFermator Operation Manual PDFMuhammad Dzulfiqar100% (1)
- CBR English Kelompok 9Dokument4 SeitenCBR English Kelompok 9Devi TariganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 1.6 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet: Min MaxDokument3 SeitenLab 1 1.6 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet: Min MaxJesusa VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- swk10d4 EnergyDokument21 Seitenswk10d4 EnergyErayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber Notes (Jan-2022)Dokument10 SeitenOptical Fiber Notes (Jan-2022)mandar desurkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP 2 DiodeDokument6 SeitenIP 2 DiodeRifky OfficialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bse8klna en v220413Dokument2 SeitenBse8klna en v220413danilo Mendoza0% (1)
- Phyc 121 Second Quarter Exam 50Dokument12 SeitenPhyc 121 Second Quarter Exam 50EyelessJean12Noch keine Bewertungen
- COOPER Price List Full Range - April 2013 r2Dokument20 SeitenCOOPER Price List Full Range - April 2013 r2Chinna ThambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (L6) - (JLD 3.0) - NLM - 22nd June.Dokument63 Seiten(L6) - (JLD 3.0) - NLM - 22nd June.Aditya BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Test (Electricity)Dokument5 SeitenScience Test (Electricity)Apoorv ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Simulation of PFC ConvertersDokument93 SeitenModeling and Simulation of PFC ConvertersSanjeev Singh100% (1)
- BM - Lec 4 - Conservation of Angular Momentum and Projectile MotionDokument50 SeitenBM - Lec 4 - Conservation of Angular Momentum and Projectile MotionBhavya PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMR and GMR Heads Increase Hard Drive Capacity in Western Digital DrivesDokument5 SeitenAMR and GMR Heads Increase Hard Drive Capacity in Western Digital DrivesTarak BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanic of Material Lab ReportDokument28 SeitenMechanic of Material Lab ReportMuhd Farhan Bin Ibrahim50% (2)
- GES 104 SummaryDokument64 SeitenGES 104 SummaryVictor OlawaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC BHUJ FinalDokument15 SeitenGOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC BHUJ FinalManan ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BB101Dokument127 SeitenBB101Fly WithmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2-211 - 2018 Interpretation of The LF Resonance in Frequency Response Analysis of Transformer Windings PDFDokument10 SeitenA2-211 - 2018 Interpretation of The LF Resonance in Frequency Response Analysis of Transformer Windings PDFNamLeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2845 Classic Collection TR-TN Estes Tech ReportsDokument46 Seiten2845 Classic Collection TR-TN Estes Tech Reportsns4gguyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Cable Models For Time Domain SimulationsDokument5 SeitenComparison of Cable Models For Time Domain SimulationsGokul VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen