Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Maths 10
Hochgeladen von
Rajesh SinghOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Maths 10
Hochgeladen von
Rajesh SinghCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
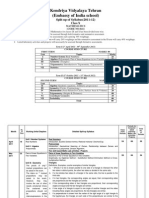
Kendriya Vidyalaya Tehran (Embassy of India school)
Split up of Syllabus(2011-12)
Class X
MATHEMATICS (CODE NO:041)
As per CCE guidelines, the syllabus of Mathematics for classes IX and X has been divided term wise. The units specified for each term shall be assessed through both formative and summative assessment. In each term, there will be two formative assessments each carrying 10% weightage. The summative assessment in the I term will carry 20% weightage and the summative assessment in the II term will carry 40% weightage. Listed laboratory activities and projects will necessarily be assessed through formative assessments. Term I (1st April 2011 - 30th September 2011) COURSE STRUCTURE FIRST TERM MARKS: 80 Unit Topics Marks Number System (Real Numbers) I 10 Algebra (Polynomials, Pair of linear Equations in two Variables) II 20 Geometry (Triangles) III 15 Trigonometry (Introduction to Trigonometry, Trigonometric V 20 Id i ) VII Statistics 15 Total 80 Term II (1st October 2011 31st March 2012) COURSE STRUCTURE SECOND TERM MARKS: 80 Unit Topics Marks Algebra (Quadratic equations, Arithmetic progressions) II 20 Geometry (Circles, Constructions.) III 16 Mensuration (Areas Related to Circles, Surface Areas & Volumes) IV 20 Trigonometry (Heights & Distances) V 08 VI Coordinate Geometry 10 VII Probability 06 Total 80
Month
No. of Days
Working Units/Chapters
Detailed Split-up Syllabus
Class room Periods
Periods for Computer aided Learning/ Maths Lab Activities Projects
Total No. of Periods
April 2011
18
Unit I: Number Systems Real Numbers Unit II : Algebra Polynomials
May 2011
22
Pairs of linear Equations in Two Variables
Unit III : Geometry The proofs of only* marked propositions can be asked in the exam. The riders on * marked propositions may be asked in the exam. However, they may involve the use of other results (Unstarred Ones) The unstarred ones propositions should not be asked riders/expressions in the exam. Triangles
Real Numbers Introduction, Euclids Division lemma. Rational Irrational Decimal Exp. Polynomials Introduction, Geometrical Meaning of Zeroes, Relationship between Zeroes and coefficient of a polynomial. Division Algorithm. Two skill based Maths Lab activities / Projects Pairs of linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions of Pair of linear Equations in two variables Graphically, by Algebraic Method : Substitution Method Elimination Method & Crossmultiplication Method. Triangles Definitions, Examples, counter examples of similar triangles. a. * (Prove) If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides ax divided in the same ratio. b. If a line divides two sides of a triangle in the same ratio, the line is parallel to the third side. c. If in two triangles, the corresponding angles are equal, their corresponding sides are proportional and the triangles are similar. d. If the corresponding sides of two triangles are proportional, their corresponding angles are equal and the two triangles are similar. e. If one angle of a triangle is equal to one angle of another triangle and the sides including these angles are proportional, the two triangles are similar. f. If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of the right angle of a right triangle to the hypotenuse, the triangle on each side of the perpendicular are similar to the whole triangle and to each other. g. * The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares on their corresponding sides. h. * In a right triangle the sq. on the hyp. is equal to the sum of the sq. the other two sides. i. * In a triangle, if the sq. On one side is equal to sum of the sq. on the other two sides the angle opposite to the first side is a right triangle. Two skill based Maths lab activities/Projects.
24
06
30
28
06
34
June 2011
19
Trigonometry
Unit VII :Statistics and Probability Statistics
Trigonometry : Introduction, Trigonometric Ratios of : Some Specific angles Acute angle of a right-angled triangle Complementary angles Proof of their existence Trigonometry identities cos2A + sin2A = 1, 1 + tan2A = sec2 A cot2 A + 1 = cosec2 A Statistics Mean, median and mode of grouped data (bimodal situation to be avoided) cumulative frequency graph. Two skill based Maths Lab Activities/Projects
30
06
36
August 2011 September 2011 October 2011
27 19 Unit II : Algebra Quadratic Equation Quadratic Equations :
Revision for Summative Test I Summative Test I
38
08
46
26 08
06
32 08
19
Standard form of quadratic Equation
Arithmetic Progression
ax + bx + c = 0 by Solution of ax2 + bx + c = 0 by (a) Factorization (b) Quadratic formula (c) Completing the squares Application of quadratic eqn. in solving words problems from different areas (Roots should be real) Arithmetic Progression Introduction to A.P. by pattern of numbers. General term of an A.P., Sum of n-terms of an A.P. Simple problems (common difference should not be irrational nos.) Two skill based Maths lab activities/projects Circles Tangents to a circle motivated by chords drawn from points coming closer and closer and closer to the points. 1. * The tangent at any point of a circle in perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact 2. * The lengths of tangents drawn from an extend points to circle are equal.
November 2011
Circles 19
20
08
28
Construction
Unit IV : Mensuration Area Related to Circles
December 2011
20
Unit IV : Mensuration Surface Area and Volumes Unit V : Trigonometry Height and Distances
January 2012
18
Unit VI : Co-ordinate Geometry Co-ordinate Geometry
Unit VII :Statistics and Probability Probability
February 2012 March 2012 12
Constructions Division of a line segment in a given ratio (internally) Tangent to a circle from a point outside it. Construction of a triangle similar to a given triangle. Area Related to Circles Motivate the area of a circle, sectors segments. Problems based on areas and perimeters/circumference Problems should be restricted to central angle of 60, 90 & 120 only. Plane Fig. involving triangles, Simple Quad. and Circle. Surface Area and Volumes Surface Area of a combination of solids, Volume of combination of solids. Conversion of solid from one shape to another. Frustum of a cone. Problems with combination of not more than two different solids taken. Applications of Trigonometry Height and Distances Simple problems on height and distances Problems should not involve more than two right triangles. Angle of elevation/depression should be only 30, 45 & 60 Co-ordinate Geometry Lines (In two-dimensions) Review the concepts of co-ordinate Geometry, Geometrical Repn. of quadratic polynomials. Distance between two points and section formula (Internal) Area of Triangle Probability Definition, related with probability in class IX, Simple problems on single event, not using set notation. Revision with study materials and sample papers and Revision for Summative Test - II Revision for Summative Test - II Summative Test - II
12
04
16
24
06
30
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Tissue Culture in A Pressure CookerDokument12 SeitenTissue Culture in A Pressure CookerRajesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus30 Class 10thengDokument20 SeitenSyllabus30 Class 10thengSANTHOSH KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Class 10 Syllabus: Course StructureDokument11 SeitenMathematics Class 10 Syllabus: Course StructureBangaru BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Class 10 SyllabusDokument5 SeitenMathematics Class 10 SyllabusBhawana thakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Class 10 - 2021-22-Term WiseDokument5 SeitenMathematics Class 10 - 2021-22-Term WiseDevansh AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Syllabus 10 MathematicsDokument5 Seiten2017 Syllabus 10 MathematicsayonavobrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math I TDokument2 SeitenMath I TAdonias Pereira da SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Syllabus for Classes 9-10Dokument7 SeitenMath Syllabus for Classes 9-10Lyngdoh DamelamanbhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10th Mathematics SyllabusDokument3 Seiten10th Mathematics SyllabusFreQuency Career InsTituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC D0 M OPSyk UEB5 LTO6 EuDokument6 SeitenPC D0 M OPSyk UEB5 LTO6 EuAtul Vikash Kumar AnshNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Syllabus For Class 10 MathsDokument4 SeitenNCERT Syllabus For Class 10 MathsPrash S100% (1)
- Course Structure Class X: First Term Marks: 90 Units MarksDokument4 SeitenCourse Structure Class X: First Term Marks: 90 Units Marksadamshareef_itNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Math Syllabus & Exam PatternDokument7 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Math Syllabus & Exam PatternDibyasha DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics SR - Sec 2020-21Dokument14 SeitenMathematics SR - Sec 2020-21Vandana GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Standard: Reduced SyllabusDokument5 SeitenMathematics Standard: Reduced SyllabusOP GAMERZ100% (2)
- Xi-Xii: Mathematics (C No. 041)Dokument6 SeitenXi-Xii: Mathematics (C No. 041)Bhatnagar Suraj MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 MathematicsDokument11 Seiten6 Mathematicsapi-352990570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: Course Structure Class - XDokument7 SeitenMathematics: Course Structure Class - XShubhm PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class - X Subject: Mathematics (Code: 041 & 241)Dokument6 SeitenTerm - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class - X Subject: Mathematics (Code: 041 & 241)Kumud KumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10th Syllabus and Marking SchemeDokument5 SeitenClass 10th Syllabus and Marking SchemeSagar ChhabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class X Math syllabus changesDokument6 SeitenClass X Math syllabus changesMrinal chakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Math Syllabus BreakdownDokument6 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Math Syllabus BreakdownShivani MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduced Syllabus: Class-IX: Mathematics: 80 Marks: 2020-2021 Deleted Portion of SyllabusDokument7 SeitenReduced Syllabus: Class-IX: Mathematics: 80 Marks: 2020-2021 Deleted Portion of Syllabusamar sarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Maths Class X SyllabusDokument4 Seiten4 Maths Class X SyllabusPolineni JayachandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Structure Class - X: Units Unit Name MarksDokument6 SeitenCourse Structure Class - X: Units Unit Name MarksGfl• TaneeshTM100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2021-22 Download Combined Curriculum in PDFDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2021-22 Download Combined Curriculum in PDFSai TanveeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 11 2021-22 Term 1 SyllabusDokument4 SeitenMathematics 11 2021-22 Term 1 SyllabusBetaBeast12Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus BreakdownDokument4 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus Breakdownराहुल रविराज100% (1)
- Curriculum & Syllabus for Math Classes XI & XIIDokument6 SeitenCurriculum & Syllabus for Math Classes XI & XIIShivamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics (Ix-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session 2021-22: ObjectivesDokument11 SeitenMathematics (Ix-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session 2021-22: ObjectivesGarima SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics (Ix-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session 2021-22: ObjectivesDokument11 SeitenMathematics (Ix-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session 2021-22: ObjectivesPalak KhatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATHEMATICS (IX) SYLLABUSDokument6 SeitenMATHEMATICS (IX) SYLLABUSAnika MohapatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 2011 Syllabus MathematicsDokument4 Seiten11 2011 Syllabus MathematicscerlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Math Eng 2018Dokument231 Seiten11 Math Eng 2018Karuna SuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term-Wise Syllabus for Class IX MathDokument5 SeitenTerm-Wise Syllabus for Class IX MathShreya JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Structure: Class IXDokument9 SeitenCourse Structure: Class IXvstifler_aroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPBOSE MATHSDokument6 SeitenHPBOSE MATHSSakshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 10 Curriculum 2016 2017 MathsDokument12 SeitenClass 9 10 Curriculum 2016 2017 MathsAbhishek PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus BreakdownDokument4 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Maths Syllabus Breakdownराहुल रविराजNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Structure Class - X: 1. Real NumberDokument5 SeitenCourse Structure Class - X: 1. Real NumbersasyedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Syllabus-Grade 10Dokument3 SeitenMath Syllabus-Grade 10Vedant KakdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Term - Wise Syllabus Session - 2021-22 Class-IX Subject: Mathematics (Code: 041)Dokument3 SeitenTerm - Wise Syllabus Session - 2021-22 Class-IX Subject: Mathematics (Code: 041)Tech 34Noch keine Bewertungen
- University of Calcutta: SyllabiDokument49 SeitenUniversity of Calcutta: SyllabiSayan SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 9 Mathematics Syllabus 2020-21Dokument6 SeitenClass 9 Mathematics Syllabus 2020-21Channappa C SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus MathsDokument24 SeitenSyllabus MathsPraveen praveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Ix, X 1Dokument5 SeitenMathematics Ix, X 1kohliuma658Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths PDFDokument3 SeitenMaths PDFGaganpreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015-16 - Senior School MathematicsDokument11 Seiten2015-16 - Senior School MathematicsJyoti BholaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths sylabbusICSE Class 10 Maths SyllabusDokument8 SeitenMaths sylabbusICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabusprash_hingeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICSE Class 10 Maths SyllabusDokument8 SeitenICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabusprash_hingeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Structure Class - X: Units Unit Name MarksDokument5 SeitenCourse Structure Class - X: Units Unit Name MarksTarun GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOLDEN CBSE Board Sample Paper 2020-2021 Mathematics-XDokument92 SeitenGOLDEN CBSE Board Sample Paper 2020-2021 Mathematics-XAnnesha MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 177 BTechMathematicsR22SyllabusDokument21 Seiten177 BTechMathematicsR22SyllabusAshish Ranjan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathematicsDokument7 SeitenMathematicsHarman VishnoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus 2019 20 PDFDokument6 SeitenCbse Class 10 Mathematics Syllabus 2019 20 PDFwhat can we do?Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revised CBSE 10th Maths Syllabus 2020-21Dokument5 SeitenRevised CBSE 10th Maths Syllabus 2020-21Kunsh WadheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabuses ADokument4 SeitenSyllabuses Aaesopp986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Maths Term-Wise Syllabus 2021-22Dokument5 SeitenClass 10 Maths Term-Wise Syllabus 2021-22Lakshay JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bana Barn PDFDokument4 SeitenBana Barn PDFRajesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vegifresh Profile Export Profile PDFDokument9 SeitenVegifresh Profile Export Profile PDFRajesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tichwcfll/Diglsf: Bamboo Cultivation - Potential and ProspectsDokument13 SeitenTichwcfll/Diglsf: Bamboo Cultivation - Potential and ProspectsRajesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse-9 SCIENCE PracticalDokument49 SeitenCbse-9 SCIENCE Practicalpace_saNoch keine Bewertungen
- KV Tehran Syllabus Class X Maths 2011-12Dokument4 SeitenKV Tehran Syllabus Class X Maths 2011-12Rajesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen