Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Stemi Study Guide
Hochgeladen von
Nicholas EstradaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Stemi Study Guide
Hochgeladen von
Nicholas EstradaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
STEMI STUDY GUIDE
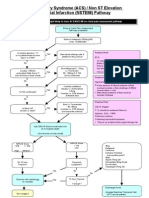
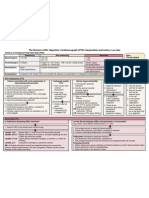
1. STEMI characteristics a. +/- Chest pain b. ECG Changes: ST elevation c. Biomarkers: Elevated cardiac enzymes 2. Cardiac Biomarkers a. Peak sensitivity at 8-12 hours b. Elevation may persist for 5-7 days c. Troponin I level i. <0.01 = Normal ii. 0.01-0.12 Troponin leak iii. >0.12 = Positive for MI 3. Diagnosis a. ST segment elevation on EKG b. Positive biomarkers of necrosis c. Symptoms same as UA/NSTEMI i. Only way to differentiate NSTEMI and STEMI is look at EKG for ST elevation 4. Reperfusion Therapy a. Goals i. Minimize ischemic time to <120 minutes (ideally <60 minutes) ii. PCI capable hospital: <90 minutes from 1st medical contact to balloon iii. Non-PCI capable hospital: 1. Transfer to PCI hospital and PCI <90 minutes from EMS to balloon 2. fibrinolytics administered <30 minutes from EMS contact iv. If a PCI cannot be performed in <90 minutes from 1st medical contact, administer fibrinolytic therapy <30 minutes from EMS contact b. Fibrinolytics i. Timing 1. <12 hrs (Class I evidence) (Max benefit <3 hrs) 2. 12-24 hrs (Class IIa evidence) 3. >24 hrs DO NOT GIVE! (Class III) ii. Agents 1. Alteplase a. 15 mg IV bolus, infuse 0.75mg/kg x 30 min (max 50mg), then 0.5mg/kg x 60 min (max 35mg) (total max 100mg in 90 min) 2. Tenecteplase a. IV Bolus over 5 seconds, 30mg if <60kg, 35mg if 60-69kg, 40 mg if 70-79kg, 45mg if 80-89kg, 50mg if >90kg iii. Contraindications 1. Absolute a. Previous intracranial hemorrhage
b. Known intracranial lesion/neoplasm c. Ischemic stroke within 3 months unless within past 3 hours d. Aortic dissection e. Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis f. Significant closed head trauma within 3 months 2. Relative a. Severe, poorly controlled, chronic hypertension b. Presentation with uncontrolled SBP > 180 mmHg or DPB > 110 mmHg c. History of prior ischemic stroke or other intracranial pathology d. Traumatic or prolonged CPR (>10 min) e. Major surgery within 3 weeks f. Internal bleeding within 2-4 weeks g. Noncompressible vascular punctures h. Pregnancy i. Active peptic ulcer j. Current anticoagulation i. The higher the INR, the higher the risk of bleeding iv. Monitoring 1. Efficacy a. Relief of symptoms b. Improvement in hemodynamic parameters c. Washout of cardiac biomarkers d. Improvement in electrical rhythm i. Reduction of ST elevation >50% within 90 minutes after reperfusion 1. If not, rescue PCI 2. Safety a. Bleeding i. Intracranial hemorrhage v. When preferred 1. Interventional strategy not available 2. Early presentation (<3 hrs) and delay in PCI (door to balloon >90 min) 3. Delay to invasive strategy c. PCI i. When preferred 1. Onset >3 hrs 2. Contraindications to fibrinolysis 3. High Risk STEMI a. Cardiogenic shock b. Killip class III or IV 4. Dx of STEMI in doubt
5. STEMI Treatment a. MONA i. Morphine 2-4 mg IV in 2 mg increments up to 8mg q 5-15 min ii. Oxygen 1. if Sa02>90% (Class I) 2. All patients during initial 6 hours (Class IIa) iii. Nitroglycerin SL x 3, IV if needed iv. Aspirin 162-325 mg chewed b. Intensive glucose control i. Maintain BG <180mg/dl while avoiding hypoglycemia c. Beta blockers i. Start ORAL within first 24 hrs unless: 1. Clinical signs of HF 2. Evidence of low output state 3. Increased risk for cardiogenic shock a. Age > 70, SBP < 120 mm Hg, sinus tachycardia > 110 or HR < 60, increased time since onset of symptoms of UA/NSTEMI 4. PR interval > 0.24 ms 5. 2nd/3rd degree AV block without pacemaker 6. Active asthma or reactive airway disease ii. If early contraindications, reevaluate for secondary prevention iii. Start IV if pt hypertensive on presentation d. ACE Inhibitors i. Prescribe at discharge if no contraindications ii. Use ARB if ACEI intolerant and pt has HF with LVEF <40% e. Aldosterone Antagonists i. Give if LVEF <40% and either HF or diabetes who are receiving and ACEI ii. Do not give if renal dysfunction or hyperkalemia iii. Spironolactone 12.5mg qday initially then 25-50 qday max iv. Eplerenone 25mg qday initially then 50mg qday f. Anticoagulants i. Enoxaparin 1. Dosing a. 30mg IV bolus b. 1mg/kg SC q 12h maintenance c. If CrCl <30ml/min, 1mg/kg sc q 24h d. PCI only i. If <8 hrs from last dose none needed ii. If >8hrs from last dose 0.3mg/kg IV iii. If no UFH/LMWH initiated 0.5-0.75mg/kg IV 2. Monitoring a. Anti-Xa = 0.6 1.0U/ml (not required in most cases)
b. Timing: If significant change in clinical status or 4 hrs after dose ii. Fondaparinux 1. Dosing a. 2.5mg SQ q day b. Avoid for CrCl < 30ml/min c. PCI only Add UFH 50-60 units/kg IV bolus 2. Monitoring a. Hg, Hct, SCr, BUN, Bleeding iii. UFH g. Clopidogrel i. ALL STEMI PTS 1. 300mg PO x 1 (no data if non-PCI and age>75 hrs), then 75 mg PO qday ii. Duration 1. PCI 1 yr 2. No PCI a. >14 days (Class I) b. >1 year (Class IIa) h. Statins i. LDL Goal <100mg/dl (Class I), <70mg/dl (Class IIa) ii. All pts should receive be discharged with statin unless they have a contraindications i. Secondary Prevention i. Smoking cessation ii. Blood pressure control iii. Lipid management iv. Diabetes management v. Weight management vi. Physical activity vii. Annual influenza vaccine
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NAPLEX Practice Question Workbook: 1,000+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)Von EverandNAPLEX Practice Question Workbook: 1,000+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Samson Handbook of PLAB 2 and Clinical AssessmentVon EverandSamson Handbook of PLAB 2 and Clinical AssessmentBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (8)
- Severe Sepsis Screening Tool NhsDokument2 SeitenSevere Sepsis Screening Tool NhsDavide Antonelli LaghiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NClex Facts To KnowDokument34 SeitenNClex Facts To KnowTcancam96% (48)
- Natural Healing Through MacrobioticDokument189 SeitenNatural Healing Through MacrobioticFady Nassar100% (9)
- Paramedic MegacodesDokument7 SeitenParamedic MegacodesAnonymous wu6RXuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersDokument91 SeitenPart III Internal Medicine Examination AnswersFırat GüllüNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petcare Power of AttorneyDokument4 SeitenPetcare Power of AttorneyLisaHospetsNoch keine Bewertungen
- O&G Off-Tag Assesment Logbook: Traces-Pdf-248732173Dokument9 SeitenO&G Off-Tag Assesment Logbook: Traces-Pdf-248732173niwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ho Notes Part 1 - Medical Emergencies Notes 2.0Dokument7 SeitenHo Notes Part 1 - Medical Emergencies Notes 2.0Amin MasromNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine ManagementsDokument87 SeitenMedicine ManagementsMohamed LibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventura County Medical Center: Mi Thrombolysis, Management ofDokument3 SeitenVentura County Medical Center: Mi Thrombolysis, Management ofblackcat657Noch keine Bewertungen
- Severe TBI 2017Dokument18 SeitenSevere TBI 2017DM internaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pembimbing: Dr. Ali Haedar, SP - EM: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas BrawijayaDokument26 SeitenPembimbing: Dr. Ali Haedar, SP - EM: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Brawijayanoval hlfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Heart Failure SyndromeDokument1 SeiteAcute Heart Failure SyndromeIndra WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 - Fahad Class 6 Cardiac AnesthesiaDokument18 Seiten6 - Fahad Class 6 Cardiac AnesthesiaOne ClickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dangarad OSCE ManagementsDokument87 SeitenDangarad OSCE ManagementsMahad IbrahemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dangarad OSCE Managements PDFDokument87 SeitenDangarad OSCE Managements PDFMohamed Liban100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Case: Presented By: Dr. SyahrianiDokument30 SeitenCardiovascular Case: Presented By: Dr. SyahrianiAkbar IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Acut StrokeDokument42 SeitenManagement Acut StrokeRizal AlwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS NSTEMI Clinical PathwayDokument3 SeitenACS NSTEMI Clinical PathwayXtiaRNoch keine Bewertungen
- A House Officer's Approach To DengueDokument9 SeitenA House Officer's Approach To DengueBaihaqi SaharunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tatalaksana STEMI: Rizky Ramadhan N, DR RS Jampang KulonDokument17 SeitenTatalaksana STEMI: Rizky Ramadhan N, DR RS Jampang KulonRizky Ramadhan NuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Ws I Perki 2019Dokument70 SeitenCase Study Ws I Perki 2019Luh Leni AriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acs Nstemi PathwayDokument3 SeitenAcs Nstemi PathwayAliey's SKeplek NgeNersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Op CABG OrdersDokument4 SeitenPost Op CABG OrdersMaria Nadia MihalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Updated ACLS HandoutsDokument24 Seiten2016 Updated ACLS Handoutskarenjlazarus86% (14)
- Nclex Ultimate Study GuideDokument87 SeitenNclex Ultimate Study GuideJeremy Christmann100% (1)
- Chest Pain ProtocolDokument4 SeitenChest Pain ProtocolArul ShanmugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1614978209sampleDokument9 Seiten1614978209sampleReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnestesiDokument61 SeitenAnestesiJack Kings QueenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest Pain Protocol in EDDokument3 SeitenChest Pain Protocol in EDshahidchaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLS Study Guide JULY 2021 UPDATEDokument3 SeitenACLS Study Guide JULY 2021 UPDATENina Morada100% (2)
- ASA Physical Status ClassificationDokument5 SeitenASA Physical Status Classificationpolushky100% (1)
- Accaha Guidelines For The Management of Patients With St1510Dokument40 SeitenAccaha Guidelines For The Management of Patients With St1510gaby andreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 EclampsiaDokument17 Seiten2 EclampsiaDrMohammad KhadrawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traumatic Brain Injury 2023Dokument17 SeitenTraumatic Brain Injury 2023Fernando Martinez AguilarNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEMI Extensive Anterior Wall Onset 4 Hours Killip I TIMI Score 3-14Dokument28 SeitenSTEMI Extensive Anterior Wall Onset 4 Hours Killip I TIMI Score 3-14Akbar IskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Stroke ManagementDokument8 SeitenAcute Stroke ManagementГурам ЧахвадзеNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAL COVID19 1 April 2021Dokument14 SeitenFINAL COVID19 1 April 2021Wleed KhledNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACS ManagementDokument24 SeitenACS ManagementkalfNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Admission:: STROKE MANAGEMENT (Beaumont Hospital)Dokument3 SeitenOn Admission:: STROKE MANAGEMENT (Beaumont Hospital)Nadia SalwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- BHS Inggris 3 - 1Dokument13 SeitenBHS Inggris 3 - 1191151023.studentNoch keine Bewertungen
- COVID-19 Protocol KGMU Version 6.0 17-4-21Dokument34 SeitenCOVID-19 Protocol KGMU Version 6.0 17-4-21Kirtivaan MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Clinical Strategies: Handbook of AnesthesiologyDokument180 SeitenCurrent Clinical Strategies: Handbook of AnesthesiologydramaganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Management of LabourDokument4 SeitenActive Management of LabourHytham AtiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penatalaksanaan StrokeDokument15 SeitenPenatalaksanaan StrokerizeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sepsis Flow Chart FinalDokument2 SeitenSepsis Flow Chart FinalDevindraPrptNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Aug IMG Poster 165760a SepsisDokument1 Seite2012 Aug IMG Poster 165760a SepsisTeng Huei LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Status Epilepticus CPGDokument3 SeitenPediatric Status Epilepticus CPGAlex GasnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Perioperative ManagementDokument14 SeitenChapter 3: Perioperative ManagementpoddataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pointers To Review Updated 2016Dokument18 SeitenPointers To Review Updated 2016Rubelyn Arriola Nioko100% (1)
- CCU HandoverDokument9 SeitenCCU Handoverapi-192342497Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gynecology All 2Dokument71 SeitenGynecology All 2Hikufe JesayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eclampsia and Severe Preeclampsia - 2019 (2302) - Edited - TaggedDokument43 SeitenEclampsia and Severe Preeclampsia - 2019 (2302) - Edited - TaggedCharlizeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Acute Asthma Pathway - Inpatient Care: Inpatient Assessment Score (Modified PRAM)Dokument2 SeitenPediatric Acute Asthma Pathway - Inpatient Care: Inpatient Assessment Score (Modified PRAM)Iswa AsyharNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTG Algorithm 3jan08Dokument1 SeiteCTG Algorithm 3jan08TunnelssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Operational Procedure PreeeclamsiaDokument4 SeitenStandard Operational Procedure PreeeclamsiaDEBY SHINTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine Test On CVS Respiratory EndocrinologyDokument10 SeitenMedicine Test On CVS Respiratory EndocrinologyNavid BabluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of StemisDokument20 SeitenManagement of Stemisapi-269001337Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acl - Rehab - Protocol After Knee OperationDokument37 SeitenAcl - Rehab - Protocol After Knee OperationGinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCB Surgical Technique - 2022 Update v3Dokument24 SeitenLCB Surgical Technique - 2022 Update v3Samuel SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Printing Biology Oral PresentationDokument15 SeitenBio Printing Biology Oral PresentationVanessa Carmody100% (1)
- A To Z Orthodontics - Vol 9 - Preventive and Interceptive OrthodonticsDokument37 SeitenA To Z Orthodontics - Vol 9 - Preventive and Interceptive OrthodonticsĐạt HuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fortify Your Knowledge About Vitamins PDFDokument3 SeitenFortify Your Knowledge About Vitamins PDFpgomperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Drug Action-1Dokument46 SeitenMechanism of Drug Action-1Sameer HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Situation Analysis of Children in Timor-LesteDokument194 SeitenSituation Analysis of Children in Timor-LesteBunga P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summer 2122 Aubf Lab Periodical Test 2Dokument38 SeitenSummer 2122 Aubf Lab Periodical Test 2RuchieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgical Catalogue PDFDokument690 SeitenSurgical Catalogue PDFSazzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Description Occupational Health and Safety SpecialistsDokument3 SeitenJob Description Occupational Health and Safety SpecialistsMala MinnieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Cardiac ArrestDokument10 SeitenManagement of Cardiac ArrestAhmed VelićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 11 Introduction To EpidemiologyDokument38 SeitenUnit 11 Introduction To EpidemiologyhumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision 1 English Open LetterDokument9 SeitenRevision 1 English Open Letterapi-441660843Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final PaperDokument58 SeitenFinal PaperAngeline MirasolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ulibas V Republic - DigestDokument2 SeitenUlibas V Republic - DigesttheamorerosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logiq E10: Empowering You To Make A DifferenceDokument5 SeitenLogiq E10: Empowering You To Make A DifferenceMadalina C0% (1)
- Dr. Ralph Moss Interview: Medical Writer, Author, and FilmmakerDokument27 SeitenDr. Ralph Moss Interview: Medical Writer, Author, and FilmmakerRosa AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 - Mycotoxin Analysis - KKDokument2 Seiten2015 - Mycotoxin Analysis - KKKai-J. Kühlmann100% (1)
- Headache and Joint PainDokument13 SeitenHeadache and Joint PainJosiah Noella BrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imp-Mediclaim & Accidental Insurance - DataDokument16 SeitenImp-Mediclaim & Accidental Insurance - DataAnup BhutadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHN ExamDokument30 SeitenCHN ExamKhei Laqui SN100% (3)
- Lifespan: Why We Age - and Why We Don't Have To - DR David A. SinclairDokument5 SeitenLifespan: Why We Age - and Why We Don't Have To - DR David A. Sinclairtidasesu0% (1)
- Bangladesh Seed Production PDFDokument125 SeitenBangladesh Seed Production PDFYanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head Trauma Brain InjuryDokument54 SeitenHead Trauma Brain Injurymirzabb1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atrium Symposium LINC 2012 Dr. GoverdeDokument45 SeitenAtrium Symposium LINC 2012 Dr. GoverdegodefroyciosiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dos 773 Csi Plan Study-1Dokument7 SeitenDos 773 Csi Plan Study-1api-504593245Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cocaine and HeroinDokument48 SeitenCocaine and Heroinzio riaNoch keine Bewertungen