Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Higher Unit 3 Summary
Hochgeladen von
knoxmathsCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Higher Unit 3 Summary
Hochgeladen von
knoxmathsCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
hsn.uk.
net
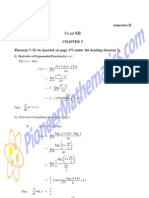
Vectors
V ectorsare nam ed usi a di ng rected lne segm ent, eg AB, or a bol l i d etter, tten by hand as u eg u, w ri a a+d d A com ponent vector i i the f sn orm u +v = b + e = b +e c f c+ f a b al know n as a col n vector so um a a d d c u v = b e = b e The m agni tude of a vector, denoted c f c f 2 2 2 AB or u , i a + b + c s BA i the negati of AB . s ve a ka 1 1 M ul plcati by a scal i k b = kb . ti i on ar s eg AB = 2 BA = 2 c kc 3 3 2 4 Thi i the sam e lne ss i If u = 4 and v = 8 then 2u = v segm ent, but i poi i the t nts n 12 6 opposi di on te recti thi m eans that u and v are paralel but s l, v i tw i as l as u s ce ong The Scalar Product
0 The zero vector i 0 s 0 1 0 0 i = 0 , j = 1 and k = 0 0 0 1
3 eg 3i + 4 j k = 4 1
Further Calculus
y = si ax n dy = a cosax dx si ax dx = 1 cosax + C n a
n
C hai R ul n e
y = (ax + b)
dy = a si ax n dx cosax dx = 1 si ax + C a n The above are gi i the exam ven n y = cosax
Higher Mathematics HSN23500
Af uncti i the f on n orm y = a x i caled an exponenti f s l al uncti on e x i caled the exponenti f s l al uncti to the base e. on x y=a l a y = x the base num ber stays the sam e, and og the other tw o term s f i over lp
Logarithms and Exponentials
dy n1 = an (ax + b) Example 3 dx y = ( x 9 + 8x ) pow er m ul ples to the f ti i ront, bracket stays the sam e, l er dy = 3 ( x 9 + 8 x )2 ( 9 x 8 + 8 ) ow the pow er by 1 and m ul pl dx ti y 2 by the deri i oft bracket vat ve he = 3 ( 9 x 8 + 8 )( x 9 + 8 x ) ( ax + b )n+1 n +C ( ax + b ) dx = a ( n + 1) R ai the pow er by 1 and di de by the new pow er se vi m ul pled by the deri ve of the bracket, pl C ti i vati us The deri ve of the bracket shoul onl ever be an vati d y 2 i nteger, eg 3 not 4x etc.
Laws of Logs
l a x + l a y = l a xy (Squash) og og og l a x l a y = l a x (Splt) og og og y i
l a x n = n l a x (Fl og og y) l a a = 1 eg l 8 8 = 1 og og l e x i the sam e as l x and i caled the naturall og s n s l ogari thm l on a cal ator stands f l 10 and l stands f l e og cul or og n or og To sol an equati w here the unknow n i a pow er, you ve on s m ust take l of both si and use the f y rul It does not ogs des l e. n f on nvol m atter i you use l 10 or l but i the equati i ves an e f og then l coul be easi n d er.
Example
( 2 x + 3 )5 ( 2 x + 3 )5 ( 2 x + 3 ) dx = +C = +C 5 2 10
4
b1 a1 a = a2 and b = b2 a3 b3 a b = a b cos (gi i the exam ) ven n R em em ber: the vectors m ust poi aw ay nt f rom the vertex, eg
a b
Unit 3
2 2
Examples
5x = 11 l 10 5x = l 10 11 og og og og x l 10 5 = l 10 11 x= l 10 11 og l 10 5 og = 1.49 (to 2 d.p.)
e x = 14 l ex = l n n14 xl e =l n n14 x=l n14 (si l e = l e e = 1) nce n og = 2.64 (to 2 d.p.)
a cosx + b si x can be expressed i the f n n orm k cos( x ) w here
The Wave Function
Position Vectors
AB = b a w here a and b are the posi on vectors of A and B. ti
k si n k = a + b and tan = k cos a cosx + b si x can al be expressed as n so k cos( x + ), k si ( x + ) or k si ( x ) but i n n f s w you have a choi k cos( x ) i al ays m ore ce, strai orw ard. ghtf a cos2 x + b si 2 x can be w ri n tten i any of the n f s;i k cos( 2 x ) etc orm e
If asked to sol an equati w hi contai ve on ch ns n ther: both a si x and a cosx , m ust use ei D oubl angl substi on (see U 2O C3), or e e tuti The w ave f uncti on The sol on m ust i ve a CAST di uti nvol agram .
Experimental Data
Collinearity
If AB = k BC, w here k i a scal then s ar, AB i paralelto BC . If B i a com m on s l s poi then A, B and C are coli nt lnear. To f nd the coordi i nates of a poi B nt n o 3, w hi di des AC i the rati 2: use ch vi AB 2 = BC 3
a b = a1b1 + a2b2 + a3b3 (gi i the exam ) ven n
M ust use the l s of l to w ri i the f aw ogs te n orm y = m x + c . See the notes f m ore detai. or l
cos =
cos =
ab ab
Example Express 3cosx + 4 si x i the form k cos( x ) n n
k cos( x ) = k cosx cos + k si x si n n = k cos cosx + k si si x n n k cos = 3 k = 32 + 4 2 k si = 4 n = 25 S A =5 T C H ence i i the sn f rst quadrant i k si n k cos
a1b1 + a2b2 + a3b3 a b
tan =
If a and b are perpendi ar then cul a b = 0 si cos90 = 0 nce
a b = b a and a ( b + c) = a b + a c
4 =3
= 53.1
So 3cosx + 4 si x = 5cos( x 53.1) n
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Solution Manual For A First Course in Abstract Algebra 8th Edition John B Fraleigh Neal Brand 2Dokument38 SeitenSolution Manual For A First Course in Abstract Algebra 8th Edition John B Fraleigh Neal Brand 2sennitgladwyn17p68o100% (11)
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDokument9 SeitenFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- O Level Trigonometry: Pythagoras TheoremDokument5 SeitenO Level Trigonometry: Pythagoras TheoremBurhan Azhar100% (2)
- Form 5 Additional Maths NoteDokument10 SeitenForm 5 Additional Maths NoteEric WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDokument5 SeitenCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralsapi-322359712Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Calculus Solution ManualDokument29 SeitenVector Calculus Solution Manualtjohnson93100% (7)
- Linear Combinations and Vector SpacesDokument6 SeitenLinear Combinations and Vector SpacesshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Quadratic Equation Part 1 of 2Dokument17 Seiten4 Quadratic Equation Part 1 of 2Abdul HudaifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths QE Teacher NotesDokument19 SeitenMaths QE Teacher NotessashaankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euler's Double Demonstration of Newton's Theorem Relating Coefficients and RootsDokument9 SeitenEuler's Double Demonstration of Newton's Theorem Relating Coefficients and RootsknuthfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curve FittingDokument37 SeitenCurve FittingToddharris100% (4)
- NUST Computer Science 2Dokument29 SeitenNUST Computer Science 2jaredleto688Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Dokument13 SeitenMaths Model Test Paper For Summative Assessment - 1Apex InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Quadratic Equation Part 1 of 2 - 2Dokument17 Seiten4 Quadratic Equation Part 1 of 2 - 2Mohit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE X MathematicsDokument8 SeitenCBSE X MathematicsmicrodotcdmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free-Mathematics-Ebook-for-JEE-Main - Short Cuts PDFDokument22 SeitenFree-Mathematics-Ebook-for-JEE-Main - Short Cuts PDFAjayMandapati100% (1)
- 12th NCERTwDokument9 Seiten12th NCERTwNcnagesh PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Question Paper Subject: Mathematics Class: Senior Secondary Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100Dokument22 SeitenSample Question Paper Subject: Mathematics Class: Senior Secondary Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100Aathira GopiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDokument9 SeitenNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometrySharmini RajagopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MI Chapt01 PDFDokument11 SeitenMI Chapt01 PDFHary KrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE CLass 10 Mathematics Standard Question Paper 2023 Set 1 30 2 1Dokument28 SeitenCBSE CLass 10 Mathematics Standard Question Paper 2023 Set 1 30 2 1yashpawar4324Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 SummaryDokument1 SeiteUnit 2 SummaryknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hein Solution BookDokument82 SeitenHein Solution Bookktokto666Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Conjencture On The Forms of The Roots of Equations Leonard EulerDokument16 SeitenA Conjencture On The Forms of The Roots of Equations Leonard Eulercoucou8949Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Amusing Sequence of Trigonometrical IntegralsDokument6 SeitenAn Amusing Sequence of Trigonometrical Integralsx100% (1)
- 14 DETEMINANTS & MATRICES PART 3 of 6 PDFDokument10 Seiten14 DETEMINANTS & MATRICES PART 3 of 6 PDFsabhari_ramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Index Gymnastics and Einstein Convention: Part (V)Dokument6 Seiten1 Index Gymnastics and Einstein Convention: Part (V)robotsheepboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAT Subject Math Level 2 FactsDokument11 SeitenSAT Subject Math Level 2 FactsSalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex NumbersDokument12 SeitenComplex NumbersHoria HamoucheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Pre Found. DPPSDokument33 SeitenMaths Pre Found. DPPSmanishphyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cubic Spline Tutorial v3Dokument10 SeitenCubic Spline Tutorial v3Sumitra ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Mathematics CompendiumDokument16 SeitenClass 10 Mathematics CompendiumApex Institute100% (1)
- Quant FormulaeDokument8 SeitenQuant Formulaeapi-3764413Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quant (Math) - Points 2 RememberDokument8 SeitenQuant (Math) - Points 2 Rememberharish.prasanna100% (2)
- Section - 1 Introduction To Quadratic Expressions: Locus Locus Locus Locus LocusDokument58 SeitenSection - 1 Introduction To Quadratic Expressions: Locus Locus Locus Locus LocusNíkhíl Bansal100% (1)
- NUST Computer Science 2 PLSPOTDokument29 SeitenNUST Computer Science 2 PLSPOTGhufran MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Von EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Von EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- S2 3f HomeworkDokument22 SeitenS2 3f HomeworkknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- S2 3d HomeworkDokument22 SeitenS2 3d HomeworkknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16+ EventDokument1 Seite16+ EventknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zot VacDokument1 SeiteZot VacknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Initial Letter To Parents June 2012Dokument2 SeitenInitial Letter To Parents June 2012knoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recruitment Poster EdinurghDokument1 SeiteRecruitment Poster EdinurghknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technicians AdvertDokument1 SeiteTechnicians AdvertknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- S2 2 - 3c HomeworkDokument20 SeitenS2 2 - 3c HomeworkknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A5 Summer School 2012 3 FlyerDokument2 SeitenA5 Summer School 2012 3 FlyerknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A5 Summer School 2012 3 FlyerDokument2 SeitenA5 Summer School 2012 3 FlyerknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zot VacDokument1 SeiteZot VacknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zot VacDokument1 SeiteZot VacknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16+ EventDokument1 Seite16+ EventknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muirfield VacDokument1 SeiteMuirfield VacknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Integration Examination Questions CALDokument4 SeitenUnit 2 Integration Examination Questions CALknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- U2 Trigonometric Formulae and EquationsDokument4 SeitenU2 Trigonometric Formulae and EquationsknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- U2 Factors and Quadratic TheoryDokument3 SeitenU2 Factors and Quadratic TheoryknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- S3 General Revision - MayDokument6 SeitenS3 General Revision - MayknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- U2 Equation of CircleDokument7 SeitenU2 Equation of CircleknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Straight Line Exam Questions CALDokument3 SeitenUnit 1 Straight Line Exam Questions CALknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit RevisionDokument7 SeitenUnit RevisionknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Recurrence Relation Examination Questions CALDokument4 SeitenUnit 2 Recurrence Relation Examination Questions CALknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit1 SummaryDokument1 SeiteUnit1 SummaryknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- U1 Graphs and FunctionsDokument4 SeitenU1 Graphs and FunctionsknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 SummaryDokument1 SeiteUnit 2 SummaryknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Integrals Formulae 1Dokument1 SeiteStandard Integrals Formulae 1knoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Differentiation Examination Questions CALDokument6 SeitenUnit 1 Differentiation Examination Questions CALknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesDokument5 SeitenAdvanced Higher Maths: Formulae: Essential Trigonometric IdentitiesknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation FormulaeDokument3 SeitenDifferentiation FormulaeknoxmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logs and ExponentsDokument20 SeitenLogs and ExponentsDondon TayabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUG243 - Cartography - Proportional SymbolDokument2 SeitenSUG243 - Cartography - Proportional SymbolmruzainimfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperbolic Functions 1 of 5 Hyperbolic Functions in Algebra and CalculusDokument5 SeitenHyperbolic Functions 1 of 5 Hyperbolic Functions in Algebra and CalculusNelsonMoseMNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE543 - M3 - Plane TrigonometryDokument4 SeitenCE543 - M3 - Plane TrigonometryMatt Julius CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radians and DegreesDokument19 SeitenRadians and DegreesBassem KhalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 6 Solving Sss TrianglesDokument5 Seiten16 6 Solving Sss Trianglesapi-299265916Noch keine Bewertungen
- CALCULUS 2 - MODULE 2 - Lessons 12 16Dokument48 SeitenCALCULUS 2 - MODULE 2 - Lessons 12 16Kim OpenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3 - Logarithmic Functions (PDFDrive)Dokument130 Seiten4.3 - Logarithmic Functions (PDFDrive)Anderson AlfredNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Advanced Factoring Techniques PDFDokument3 Seiten2 - Advanced Factoring Techniques PDFVasile NicoletaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17Dokument79 SeitenChapter 17api-408490857Noch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Unit Circle and Circular FunctionsDokument21 Seiten01 Unit Circle and Circular FunctionsJoseph Christopher ButaslacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logarithms and exponentials word problemsDokument2 SeitenLogarithms and exponentials word problemsKanak AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 9-Q4-Module-1Dokument18 SeitenMath 9-Q4-Module-1An Neh Gyn100% (2)
- Sathyabama University: Register NumberDokument3 SeitenSathyabama University: Register NumberAdarsh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratio (Level)Dokument9 SeitenTrigonometric Ratio (Level)Shehbaz ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Sheet-Theorems On Inscribed AnglesDokument6 SeitenActivity Sheet-Theorems On Inscribed AnglesBecky May SajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BK Chap13Dokument74 SeitenBK Chap13Jasmina Angelevska KostadinoskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits of Transcendental FunctionsDokument16 SeitenLimits of Transcendental FunctionsSarah BeloroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios of Multiple Angles: Coa S N NDokument6 SeitenTrigonometric Ratios of Multiple Angles: Coa S N NJaishree RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit Pada Ketakhinggaan-1 PDFDokument4 SeitenLimit Pada Ketakhinggaan-1 PDFysf ysfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taylors and Maclaurins SeriesDokument19 SeitenTaylors and Maclaurins Serieshimanshumal75% (16)
- Trigonometry - Circles, Arcs & Sectors: IB Mathematics: Analysis & ApproachesDokument3 SeitenTrigonometry - Circles, Arcs & Sectors: IB Mathematics: Analysis & Approachesbobby213Noch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of DifferentiationDokument13 SeitenMethods of DifferentiationVishruth Reddy BuruguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel IAL P2 Chapter Review 3 (Solution)Dokument3 SeitenEdexcel IAL P2 Chapter Review 3 (Solution)Kaif HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Calculus SyllabusDokument2 SeitenPre Calculus Syllabuszoheb khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 DM025 202021Dokument16 SeitenTopic 3 DM025 202021Daeyanna SamsudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Numbers WorksheetDokument4 SeitenComplex Numbers WorksheetSoundarya SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Preparation For Honors Precalculus Final ExamDokument1 SeiteTest Preparation For Honors Precalculus Final ExamPegsNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Stem - Pc11T-Iie-1) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 5Dokument7 Seiten(Stem - Pc11T-Iie-1) : Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) 5Naddy RetxedNoch keine Bewertungen