Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Graphic Isl 14 (Ray Diagram)
Hochgeladen von
Nik FakhiraOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Graphic Isl 14 (Ray Diagram)
Hochgeladen von
Nik FakhiraCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
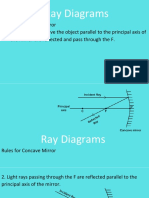
1) Ray Diagrams of concave mirror
Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will pass through the focal point upon reflection. Any incident ray passing through the focal point on the way to the mirror will travel parallel to the principal axis upon reflection.
Step-by-Step Method for Drawing Ray Diagrams :
Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the mirror. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly parallel to the principal axis.
Once these incident rays strike the mirror, reflect them according to the two rules of reflection for concave mirrors. The ray that passes through the focal point on the way to the mirror will reflect and travel parallel to the principal axis. Use a straight edge to accurately draw its path. The ray that traveled parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will reflect and travel through the focal point.
Mark the image of the top of the object. The image point of the top of the object is the point where the two reflected rays intersect. If you were to draw a third pair of incident and reflected rays, then the third reflected ray would also pass through this point. This is merely the point where all light from the top of the object would intersect upon reflecting off the mirror.
Repeat the process for the bottom of the object. The goal of a ray diagram is to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image that is formed by the concave mirror. After completing the first three steps, only the image location of the top extreme of the object has been found. Thus, the process must be repeated for the point on the bottom of the object. If the bottom of the object lies upon the principal axis (as it does in this example), then the image of this point will also lie upon the principal axis and be the same distance from the mirror as the image of the top of the object. At this point the entire image can be filled in.
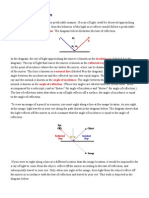
2) Methods to draw Ray Diagrams of convex mirror
Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it travels towards the focal point on the opposite side of the mirror; this ray will strike the mirror before reaching the focal point; stop the ray at the point of incidence with the mirror. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly parallel to the principal axis. Place arrowheads upon the rays to indicate their direction of travel.
Once these incident rays strike the mirror, reflect them according to the two rules of reflection for convex mirrors. The ray that travels towards the focal point will reflect and travel parallel to the principal axis. Use a straight edge to accurately draw its path. The ray that travel parallel to the principal axis on the way to the mirror will reflect and travel in a direction such that its extension passes through the focal point. Align a straight edge with the point of incidence and the focal point, and draw the second reflected ray. The two rays should be diverging upon reflection.
Locate and mark the image of the top of the object.
At this point the complete image can be filled in.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ray DiagramsDokument2 SeitenRay DiagramsIna ArdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Law of ReflectionDokument11 SeitenThe Law of ReflectionJeremy ChaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Rules of Reflection For Concave MirrorsDokument15 SeitenTwo Rules of Reflection For Concave MirrorsNiel GongoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curved Mirror Image FormationDokument13 SeitenCurved Mirror Image FormationBereket HaileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Folio Physics Chapter 5: Light: Name: Nor Nadia Mohd Azam Class: 4 Ibn Khaldun Teacher'S Name: en - Zai HousneyDokument16 SeitenFolio Physics Chapter 5: Light: Name: Nor Nadia Mohd Azam Class: 4 Ibn Khaldun Teacher'S Name: en - Zai Housneynornadeeya_94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10Dokument25 SeitenScience 10rosellmariateresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Diagrams: Drawing Ray Diagrams A Step by Step ApproachDokument3 SeitenRay Diagrams: Drawing Ray Diagrams A Step by Step ApproachLeon MathaiosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Dokument6 SeitenScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- Concave MirrorsDokument16 SeitenConcave MirrorsJian Christian FerminNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 - Plane Mirrors LessonDokument23 Seiten6 - Plane Mirrors LessondaregumacalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction Lesson 1 HandoutDokument5 SeitenRefraction Lesson 1 Handoutmarchessazarnaih061Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23 - Mirrors and LensesDokument29 SeitenChapter 23 - Mirrors and LensesrichardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics Learning Goals ReviewDokument8 SeitenOptics Learning Goals Reviewpwysz093Noch keine Bewertungen
- Opticsbasicsconcepts 170317181954Dokument189 SeitenOpticsbasicsconcepts 170317181954MAHMOUD AL-SHAIBANINoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 25 Physics 2 TatulianDokument28 SeitenChapter 25 Physics 2 TatulianKarissa JanisseNoch keine Bewertungen
- La Martiniere College, Lucknow: Digital Academic ServicesDokument18 SeitenLa Martiniere College, Lucknow: Digital Academic ServicesShreya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Formation Reflection of Light in MirrorsDokument55 SeitenImage Formation Reflection of Light in MirrorsDavidis DotaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light NotessDokument71 SeitenLight NotessShayan RasheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 17 PowerPt Notes PDFDokument5 SeitenUnit 17 PowerPt Notes PDFravilullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIRRORDokument11 SeitenMIRRORAlbenJames TabuldanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plane Mirror: Mirror Plane Light Rays Reflection Collimated Beam of Light DiffractionDokument2 SeitenPlane Mirror: Mirror Plane Light Rays Reflection Collimated Beam of Light Diffractionanon_882095709Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mirror TracingDokument7 SeitenMirror Tracingdaphnereeze100% (1)
- Optics - Reflection, Refraction and LensesDokument46 SeitenOptics - Reflection, Refraction and LensesBrianna Malcolm100% (1)
- Malabanan Matthew Sa3 Part C Phyla1Dokument6 SeitenMalabanan Matthew Sa3 Part C Phyla1Matt MalabananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection of Light 11Dokument18 SeitenReflection of Light 11Anne MalobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1cm ScaleDokument2 Seiten1cm ScaleVijay Sai Ram ParuchuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Study Reflection in Concave Mirror - Physics Astronomy Project TopicsDokument4 SeitenTo Study Reflection in Concave Mirror - Physics Astronomy Project TopicsramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Curved MirrorsDokument44 Seiten03 Curved MirrorsZeina AwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Diagramming Involving MirrorsDokument7 SeitenRay Diagramming Involving MirrorsNins SarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lens PointsDokument5 SeitenLens PointsPragati TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uri AttaacksDokument7 SeitenUri AttaacksArJitYaDavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spherical Mirrors: Symmetric About This Axis. Hence, We Can Represent A Three-Dimensional Mirror in ADokument13 SeitenSpherical Mirrors: Symmetric About This Axis. Hence, We Can Represent A Three-Dimensional Mirror in AAlankrit BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection of LightDokument34 SeitenReflection of LightTrisha Esplana Second100% (1)
- Reflection of Light 1Dokument28 SeitenReflection of Light 1Anne MalobagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mirrors: Law of ReflectionDokument4 SeitenMirrors: Law of Reflectionblackmoon_boyzNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScienceDokument10 SeitenScienceStopnaplsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric OpticsDokument8 SeitenGeometric OpticsSerge Mandhev SwamotzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02A Lesson Proper For Week 16: 4.1 Image Formation by Lenses Converging or Convex LensDokument5 Seiten02A Lesson Proper For Week 16: 4.1 Image Formation by Lenses Converging or Convex LensNanzkie Andrei SamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction by LensesDokument5 SeitenRefraction by LensesJanis Micaela EsmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mirror NotesDokument6 SeitenMirror Notesmarife gupaal100% (1)
- Course of Lectures Contemporary Physics: Part2 : Lecture 1Dokument64 SeitenCourse of Lectures Contemporary Physics: Part2 : Lecture 1Dana SatybaldyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 - LightDokument35 SeitenChapter 10 - LightMadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imaging Option CDokument47 SeitenImaging Option Clove_241100% (1)
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDokument78 SeitenThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Perspective Drawing (Cap 8)Dokument19 SeitenBasic Perspective Drawing (Cap 8)Roxana TissieresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin LensesDokument21 SeitenThin Lensesahmed mahamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curve Lens Class NotesDokument9 SeitenCurve Lens Class Noteswoman in stemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection of Light and Image FormationDokument3 SeitenReflection of Light and Image FormationDeepukavyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical PrinciplesDokument21 SeitenPhysical PrinciplesLeo CerenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Tutorial - Ray Diagrams For Spherical Mirrors Thin LensesDokument20 SeitenE-Tutorial - Ray Diagrams For Spherical Mirrors Thin LensesKar YanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMAT Reviewer Geometrical OpticsDokument37 SeitenNMAT Reviewer Geometrical Opticsmannypot83% (12)
- 3.2 LightDokument11 Seiten3.2 LightDhanBahadurNoch keine Bewertungen
- (12136) mIRRORSDokument23 Seiten(12136) mIRRORSppatsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment Reflection of LightDokument6 SeitenExperiment Reflection of Lightrizcst9759Noch keine Bewertungen
- Title: Reflection On Plane Mirrors. Objective: To Investigate The Reflection of Images of A Plane MirrorDokument8 SeitenTitle: Reflection On Plane Mirrors. Objective: To Investigate The Reflection of Images of A Plane MirrorNomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection From A Plane MirrorDokument6 SeitenReflection From A Plane MirrorHamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ray Tracing: Graphics For The Masses: SummaryDokument2 SeitenRay Tracing: Graphics For The Masses: SummaryAbdul MunimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Positional Astronomy Supported by PC Software ProgramsVon EverandElementary Positional Astronomy Supported by PC Software ProgramsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Units of MeasurementDokument5 SeitenUnits of MeasurementNik FakhiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Botanic GardensDokument10 SeitenRole of Botanic GardensNik FakhiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics in Context SC3105Dokument27 SeitenPhysics in Context SC3105Nik FakhiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Polymers: Cotton, Silk, WoolDokument28 SeitenNatural Polymers: Cotton, Silk, WoolNik Fakhira100% (4)
- Provisional Painting Part 1 and 2Dokument24 SeitenProvisional Painting Part 1 and 2Scott Grow100% (1)
- Better Homes and Other Fictions by Connie MaraanDokument13 SeitenBetter Homes and Other Fictions by Connie MaraanUST Publishing HouseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arts 6Dokument24 SeitenArts 6Levelyn De GranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossy Magazine Issue 5 PreviewDokument21 SeitenGlossy Magazine Issue 5 PreviewGlossy Magazine33% (9)
- TKR in MENDokument1 SeiteTKR in MENHotelPRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental Color Matching Instruments and Systems.Dokument15 SeitenDental Color Matching Instruments and Systems.Tudor Grou100% (2)
- Ad0200177 PDFDokument63 SeitenAd0200177 PDFali_raza117Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pigment DispersionDokument134 SeitenPigment Dispersionrajushinde_27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Boney, Elaine E - Duinesian ElegiesDokument22 SeitenBoney, Elaine E - Duinesian ElegiesmarxbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVH G215BT Quick Start GuideDokument32 SeitenAVH G215BT Quick Start GuidekevinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parminder Deo CV/Resume No AddressDokument1 SeiteParminder Deo CV/Resume No AddresspardeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describe Things ExercisesDokument2 SeitenDescribe Things ExercisesFernando QuinteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epson - X11 Review SpesifikasiDokument2 SeitenEpson - X11 Review SpesifikasiJesika Dewi MonalisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GearsjohannesDokument7 SeitenGearsjohannesapi-238276665Noch keine Bewertungen
- Allengers Venus MammoDokument3 SeitenAllengers Venus MammoThiagarajan KanagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge English Preliminary Fs Sample 5 Speaking Part 2 Candidate Booklet v2Dokument4 SeitenCambridge English Preliminary Fs Sample 5 Speaking Part 2 Candidate Booklet v2teodor0220100% (1)
- Grade 8 Mid Term TestDokument4 SeitenGrade 8 Mid Term TestShefat Phiri100% (1)
- Mini Camera User ManualDokument4 SeitenMini Camera User ManualAndronikus Marintan NapitupuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure Rumah HuniDokument2 SeitenBrochure Rumah HuniAnjas OktamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccesp 3Dokument94 SeitenCcesp 3Gabriel ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paley On Agni ParikshaDokument31 SeitenPaley On Agni ParikshaBill BenzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centre Pompidou Metz Final ReportDokument19 SeitenCentre Pompidou Metz Final Reportyarikh870% (1)
- The Three Pillars of PhotographyDokument8 SeitenThe Three Pillars of Photographyapi-273202456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prince Caspian Movie ScriptDokument53 SeitenPrince Caspian Movie ScriptVicky Larson100% (6)
- Black Box G1W User ManualDokument10 SeitenBlack Box G1W User ManualDiana BurrowsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 20 Selecting Presentation AidsDokument7 Seiten1 20 Selecting Presentation Aidsapi-255604476Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accommodation in The EyesDokument2 SeitenAccommodation in The EyesCresanelle PoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naked WomenDokument12 SeitenNaked WomenlowrypeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mura Tore 2007Dokument8 SeitenMura Tore 2007Lepaca KliffothNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of PatentDokument52 SeitenUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of PatentChoo Wei shengNoch keine Bewertungen