Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Breakwat Folder
Hochgeladen von
Vangjush MbriceOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Breakwat Folder
Hochgeladen von
Vangjush MbriceCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
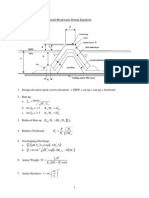
Design tool for coastal structures
Breakwat
Breakwat
Design tool for coastal structures
General Breakwat is a conceptual design tool for several types of coastal structures under wave loading. Rubble mound breakwaters with
Breakwat is useful for everyone who, even if occasional, is involved in the conceptual design of coastal structures, for example by teaching (universities), designing (consultants), testing
armour layers of rock material or concrete units, berm breakwaters, vertical caisson structures, reef type structures and near-bed structures can be designed using Breakwat up to a conceptual design stage. The first version of Breakwat has been released by WL|Delft Hydraulics (the predecessor of Deltares) at the end of the 1980s. Since then Breakwat has been widely used by a large group of users at contractors, engineering companies, universities, research institutes, etc. throughout the world. New developments in the design of coastal structures, as well as software developments in general have been incorporated in Breakwat In the future, Breakwat will be updated with new design formulae based on recent and future laboratory and field research. Breakwat uses state-of-the-art design formulae to perform calculations of the hydraulic response: wave height distribution wave run-up wave overtopping (empirical formulae and neural network) wave transmission wave reflection and of the structural response: stability of main armour layer of rock material stability of main armour layer of concrete units stability of rear side (with and without crest elements) stability of toe berm wave forces on caisson structures of several types of structures: rubble mound breakwaters berm breakwaters (profile development) low crested structures reef type structures and near-bed structures vertical (caisson) breakwaters
(research institutes) or constructing (contractors). Breakwat is an ideal tool for those who wish to apply the results of the latest research and development and wish to do this quickly and efficiently.
Photo by: BeeldbankVenW.nl, Rijkswaterstaat
General features of Breakwat Breakwat is a Microsoft Windows based product. The general features of Breakwat are: flexible set-up, easy to specify input parameters and easy view of numerical and graphical results report-ready graphical presentation of results input and output files in ASCII format possibility to calculate and compare several calculation scenarios possibility to copy data to and from clipboard export options to text editor or Microsoft Excel hard and soft limits for validity of design formulae extensive digital help function (user manual and technical background) Appearance of Breakwat The program starts by displaying the window in Figure 1. Hydraulic and structural responses can be calculated for several types of coastal structures. These structure types are a subdivision of the main classifications in the program structure, which are rubble mound structures and vertical (caisson) structures. To support the user, a calculator which can be used to determine simple parameters such as the wave steepness, the relation between volumes and masses and the relation between the several wave periods (Tp, Tm, Tm-1.0) is available as well.
Figure 1 Start window of Breakwat with overview window
Figure 4
Example of an output window where two methods are compared
existing graph, see Figure 4, and the appearance of a graph can be adjusted with a graphical editor. It is also possible to compare the output of several cases with drag-and-drop facilities.
Figure 2 Example of an input / output window and a definition sketch
Furthermore, cases can be compared numerically, see Figure 5. The results of calculations can be saved in ASCII format for future
After selecting a certain hydraulic or structural response, an input/output window and a definition sketch appears. An example is given in Figure 2. For several cases it is possible to choose between several conceptual design formulae to perform the calculation. Besides design formulae also a Neural Network is incorporated to predict wave overtopping. Once the required input for the calculations, consisting of values for the various input parameters, is specified, the output is directly calculated and presented. In some cases it is possible to specify a range of values for certain input parameters in input tables, see Figure 3. The output consists of values for several output parameters, a range of values for certain parameters or a graph. If input parameters are specified with input tables, the output can be displayed in a graph. Other output ranges can be added to an
use. It is also possible to print the results to a text editor or to Microsoft Excel to further process the data.
Figure 5
Comparison of different design formulae to calculate wave overtopping
Manual The help function can be activated at any time in Breakwat. The help function gives access to a digital document in PDF format, which consists of an extensive user and technical manual. The document includes hyperlinks to enhance the efficiency. The user manual supports more experienced users of Breakwat, as well as first-time users. In this manual some program-specific terms are defined, such as the program structure, the general screen layout, the graphical capabilities and the I/O procedures. An example calculation is also given, including a tailor-made graphical presentation of the results. The technical manual describes the technical background of all the items included in Breakwat and provides guidance on the use
Figure 3 Example of an input/output window where input is specified in an input table
of the design formulae.
System requirements Breakwat is supported on Microsoft Windows XP or higher. The advised minimum requirements are a configuration consisting of: Minimal Processor Memory (RAM) Disk free 1 GHz 1 GB 1 GB
On-line software Since 2011 the Neural Network Overtopping tool is freely accessible through the Deltares website: http://nnovertopping.deltares.nl
References
Battjes, J.A. and Groenendijk, H.W. (2000). Wave height distributions on shallow foreshores. Coastal Engineering, 40. p. 161-182. CIRIA; CUR; CETMEF (2007). The Rock Manual. The use of rock in hydraulic engineering (2nd edition), C683, CIRIA, London EA; ENW; KFKI (2007). EurOtop Manual, Wave Overtopping of Sea Defences and Related Structures: Assessment Manual Goda, Y. (2000) Random seas and design of maritime structures (2nd edition), Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering, Volume 15, world Scientific Groenendijk, H.W. and Van Gent, M.R.A. (1999). Shallow foreshore wave height statistics : a predictive model for the probability of exceedance of wave heights. Also: WL | Delft Hydraulics Report No. H3351 Van der Meer, J.W., 1988. Rock slopes and gravel beaches under wave attack. PhD Thesis. Delft University of Technology. Also: WL | Delft Hydraulics Communication No.396. Van Gent, M.R.A., H.F.P. van den Boogaard, B. Pozueta and J.R. Medina, Neural network modelling of wave overtopping at coastal structures. Elsevier, Coastal Engineering, 2007.
License For this software package, node locked and floating licences can be issued. For more information on how to purchase this package please contact: delftchess.info@deltares.nl or visit our web site: www.deltaressystems.nl
Support Deltares systems tools are supported by Deltares. A group of 70 people in software development ensures continuous research and development. Support is provided by the developers and if necessary by the appropriate Deltares experts. These experts can provide consultancy backup as well.
Photo by: https://beeldbank.rws.nl, Rijkswaterstaat / Multimedia, Rijkswaterstaat
PO Box 177 2600 MH Delft Rotterdamseweg 185 2629 HD Delft The Netherlands
+31 (0)88 335 83 00 delftchess.info@deltares.nl www.deltaressystems.nl
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- STAAD - Pro Advanced Training ManualDokument126 SeitenSTAAD - Pro Advanced Training ManualShaiju Pv100% (16)
- Tech Roles and Skills Guide for RecruitersDokument20 SeitenTech Roles and Skills Guide for RecruitersVladicia Bulhac100% (2)
- 04 BreakwaterDokument263 Seiten04 BreakwaterMd Izzuddin OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BreakwatDokument4 SeitenBreakwatberrougNoch keine Bewertungen
- Van Der Meer - Application and Stability Criteria For Rock and Artificial UnitsDokument24 SeitenVan Der Meer - Application and Stability Criteria For Rock and Artificial Unitsapi-3709579100% (1)
- STAAD Pro Advanced Training ManualDokument126 SeitenSTAAD Pro Advanced Training ManualPrantik Adhar SamantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 246 Guidance Notes On Geotechnical Performance of Spudcan Formations GN E-Jan18Dokument55 Seiten246 Guidance Notes On Geotechnical Performance of Spudcan Formations GN E-Jan18Arpit Parikh100% (1)
- Wave Runup and Overtopping HazardsDokument25 SeitenWave Runup and Overtopping Hazards허윤호Noch keine Bewertungen
- APPENDIX C Worked ExampleDokument20 SeitenAPPENDIX C Worked Examplenorsam1511Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quay Wall Bottom Protection PDFDokument12 SeitenQuay Wall Bottom Protection PDFdndudcNoch keine Bewertungen
- JRCP - Parking Yard Calc R1Dokument8 SeitenJRCP - Parking Yard Calc R1Pieter HarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tripod Support Structure: Pre-Design and Natural Frequency Assessment For The 6 MW DOWECDokument21 SeitenTripod Support Structure: Pre-Design and Natural Frequency Assessment For The 6 MW DOWECGuillermoNoch keine Bewertungen
- @ - Rubble Mound Structure DesignDokument24 Seiten@ - Rubble Mound Structure Designapi-3709579100% (1)
- Breakwater DesignDokument3 SeitenBreakwater DesignDavid ThomsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part VI Chap 5 PDFDokument378 SeitenPart VI Chap 5 PDFFrank RmDettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Pile API (LRFD) - Primary DesignDokument2 SeitenSteel Pile API (LRFD) - Primary Designbhavdip_shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Impact Loads - Pressures and ForcesDokument46 SeitenWave Impact Loads - Pressures and ForcesDonald HamiltonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scour Around Coastal StructuresDokument38 SeitenScour Around Coastal StructuresJesus Campo100% (1)
- Van Der Meer - Geometrical Design of Coastal StructuresDokument16 SeitenVan Der Meer - Geometrical Design of Coastal Structuresapi-3709579Noch keine Bewertungen
- An M.Sc. Thesis On Bangladeshi Embankment Design PDFDokument246 SeitenAn M.Sc. Thesis On Bangladeshi Embankment Design PDFMd. Yeasin MostafizNoch keine Bewertungen
- MooringSystemforVeryLargeShipsatBerth Paper ApurvaKudaleDokument10 SeitenMooringSystemforVeryLargeShipsatBerth Paper ApurvaKudaleAndreManhaesNoch keine Bewertungen
- @ - Breakwater Foundation StabilityDokument9 Seiten@ - Breakwater Foundation Stabilityapi-3709579100% (1)
- EM 1110-2-1614 Design of Coastal Revetments, Seawals, and BulkheadsDokument110 SeitenEM 1110-2-1614 Design of Coastal Revetments, Seawals, and BulkheadsengineerhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bentley Sacs BrochureDokument8 SeitenBentley Sacs BrochureIgnatius SamrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quay Walls DesignDokument12 SeitenQuay Walls DesignAdrian Frantescu100% (1)
- Introduction To Highway HygraulicsDokument218 SeitenIntroduction To Highway HygraulicsVangjush Mbrice100% (1)
- Investigation of the Chirajara Bridge CollapseVon EverandInvestigation of the Chirajara Bridge CollapseNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIANCwg 28 MainDokument87 SeitenPIANCwg 28 Mainapi-370957950% (2)
- Rubble-Mound BreakwaterDokument1 SeiteRubble-Mound BreakwaterlocasNoch keine Bewertungen
- BREAKWAT 3.3, March 2010: User & Technical ManualDokument160 SeitenBREAKWAT 3.3, March 2010: User & Technical ManualAmara Krishna KishorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial SN B C e Log W18 W18 Million Subgrade (sn3) Subbase (sn2) Base (sn1)Dokument2 SeitenTrial SN B C e Log W18 W18 Million Subgrade (sn3) Subbase (sn2) Base (sn1)Abdullah MansoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsVon EverandOffshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Models for Submerged Breakwaters: Coastal Hydrodynamics and MorphodynamicsVon EverandNumerical Models for Submerged Breakwaters: Coastal Hydrodynamics and MorphodynamicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- WDC Version 4.0Dokument95 SeitenWDC Version 4.0Ronnie oliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mooring OverviewDokument36 SeitenMooring OverviewRAUL GALDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Construction of Mounds for Breakwaters and Coastal ProtectionVon EverandDesign and Construction of Mounds for Breakwaters and Coastal ProtectionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Wave Reflection by Submerged Vertical and Semicircular BreakwatersDokument8 SeitenWave Reflection by Submerged Vertical and Semicircular BreakwatersJohn Paul Abad100% (1)
- Breakwaters DeSmet2016 PDFDokument191 SeitenBreakwaters DeSmet2016 PDFMahdi FekiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrelleborgDokument10 SeitenTrelleborgrofiqq4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Coastal Engineering ManualDokument5 SeitenIntroduction to Coastal Engineering ManualIgnatius SamrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCROPODE™ II - Design - Table - 2012Dokument4 SeitenACCROPODE™ II - Design - Table - 2012Tarun KawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conceptual Design For The Breakwater SystemDokument16 SeitenConceptual Design For The Breakwater SystemKremen Mitov100% (1)
- Flexi Lite Quick Guide-0900d80580a0ba9f PDFDokument12 SeitenFlexi Lite Quick Guide-0900d80580a0ba9f PDFAlex Enrique Chavez GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quay Walls - Combined - Wall - Buckling - TubesDokument12 SeitenQuay Walls - Combined - Wall - Buckling - TubesHugo LeiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beca Carter Hollings & Ferner LTD: Seismic Horizontal Forces Include Structure MassDokument1 SeiteBeca Carter Hollings & Ferner LTD: Seismic Horizontal Forces Include Structure MassSharyn PolleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TAW TRRunupOvertoppingDokument50 SeitenTAW TRRunupOvertoppingnguyenvanduyetNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIANC Seismic DesignDokument14 SeitenPIANC Seismic DesignMMexpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation Solutions For Projects: Harbour ConstructionDokument138 SeitenFoundation Solutions For Projects: Harbour ConstructionAnonymous U353mI1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lista 04-09-19Dokument6 SeitenLista 04-09-19comunik1977Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final - Report - Part - 2 Breakwater EngineeringDokument76 SeitenFinal - Report - Part - 2 Breakwater EngineeringBinSayeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Port Works ManualDokument191 SeitenPort Works ManualchouszeszeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CombiwallDokument20 SeitenCombiwallPeyman MznNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bridge Manual Retaining Walls - Section 3.62 Page 3.2-2Dokument1 SeiteBridge Manual Retaining Walls - Section 3.62 Page 3.2-2lomoscribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIKE21Dokument16 SeitenMIKE21Defza HuristuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coffs Harbour Coastal Processes and Hazards Definition Study Final Draft Report - September 2010Dokument204 SeitenCoffs Harbour Coastal Processes and Hazards Definition Study Final Draft Report - September 2010clarencegirl100% (1)
- IS 4651 (Part 2) Ports & Harbours (For Earth Pressure Coefficients) PDFDokument12 SeitenIS 4651 (Part 2) Ports & Harbours (For Earth Pressure Coefficients) PDFRoshanRSVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Vertical Wall Caisson BreakwatersDokument14 SeitenDesign of Vertical Wall Caisson BreakwatersHRCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Looe Marina Presentation GROUP 2Dokument33 SeitenLooe Marina Presentation GROUP 2Thomas ClarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Height Distributions in Shallow Waters: A Test of Battjes-Groenendijk ParameterizationDokument6 SeitenWave Height Distributions in Shallow Waters: A Test of Battjes-Groenendijk ParameterizationlollazzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GMB Sor Effect 11112013 Notifications PDFDokument243 SeitenGMB Sor Effect 11112013 Notifications PDFJalpesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Structures: LocksDokument150 SeitenHydraulic Structures: LocksAnand JadoenathmisierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Solutions Together 2012Dokument8 SeitenCreating Solutions Together 2012Vangjush MbriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infra-Gravity Wave Input Toolbox (IGWT) : User's GuideDokument11 SeitenInfra-Gravity Wave Input Toolbox (IGWT) : User's GuideVangjush MbriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH Girocastro Tepelene ROAD ENGDokument2 SeitenCH Girocastro Tepelene ROAD ENGVangjush MbriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- 31 PDFDokument4.999 Seiten31 PDFSmruti Ranjan Behera100% (1)
- Stocktacking Barat AprilDokument2 SeitenStocktacking Barat AprilBaginda P Siregar NamoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotics Lab Session Covers Drive Mechanisms, Payloads, Sensors (MECH 4002YDokument12 SeitenRobotics Lab Session Covers Drive Mechanisms, Payloads, Sensors (MECH 4002Ysanjiv0909Noch keine Bewertungen
- Demo guide contains setup, scripts and troubleshootingDokument24 SeitenDemo guide contains setup, scripts and troubleshootingAbdelgader MAhmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claim Form: TERABAND SMART SOLUTION SDN BHD (2021010083320) (1408631-K)Dokument200 SeitenClaim Form: TERABAND SMART SOLUTION SDN BHD (2021010083320) (1408631-K)muhammad amirul mukmininNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT9080Dokument14 SeitenRT9080TestronicpartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- KENWOOD TM 733 User Manual - Password - RemovedDokument87 SeitenKENWOOD TM 733 User Manual - Password - RemovedarrysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winpep 7 User Guide PDFDokument170 SeitenWinpep 7 User Guide PDFcesarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Fire Alarm Circuit GuideDokument14 SeitenSimple Fire Alarm Circuit GuideBRAHMA AAKUMAIIA0% (1)
- Mutillidae Installation On Xampp Win7Dokument12 SeitenMutillidae Installation On Xampp Win7Álvaro Riobóo de Larriva100% (1)
- Altec: Instruction ManualDokument33 SeitenAltec: Instruction Manualfrankie35Noch keine Bewertungen
- 228 Specificationofworks Annexure AFinalDokument19 Seiten228 Specificationofworks Annexure AFinalRoshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Practices To Execute WebSphere ILOG JRules Decision ServicesDokument37 SeitenBest Practices To Execute WebSphere ILOG JRules Decision ServicesClaudio BagnoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grebe - Capacitor Switching and Its Impact On Power Quality Draft Paper 0000 PDFDokument7 SeitenGrebe - Capacitor Switching and Its Impact On Power Quality Draft Paper 0000 PDFrmendozaing100% (1)
- 1493317093110Dokument106 Seiten1493317093110BluydeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sacombank Success Story Dcc3354 SacomBank CS v4Dokument2 SeitenSacombank Success Story Dcc3354 SacomBank CS v4thanh-truong-8011Noch keine Bewertungen
- NetworkingDokument27 SeitenNetworkingRejithaVijayachandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Lab Equipment List PDFDokument2 SeitenCCNA Lab Equipment List PDFJalal MapkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1756 pp015 - en P PDFDokument1 Seite1756 pp015 - en P PDFtrandanhhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programming 2011-2012 PDFDokument9 SeitenProgramming 2011-2012 PDFAizzat ArfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThinkPad T580 SpecDokument1 SeiteThinkPad T580 SpecTest TestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Protection and Management Participant Guide 1 PDFDokument610 SeitenData Protection and Management Participant Guide 1 PDFKevin YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osisense XC Xckj10543Dokument7 SeitenOsisense XC Xckj10543foxmancementNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLASHBACK TECHNOLOGY EXAMPLES IN 10g PDFDokument20 SeitenFLASHBACK TECHNOLOGY EXAMPLES IN 10g PDFG.R.THIYAGU ; Oracle DBA100% (2)
- MacroDokument48 SeitenMacronadar uthayakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TITLE BL-ER Ethernet Radio SpecsDokument2 SeitenTITLE BL-ER Ethernet Radio SpecsHamat AfinNoch keine Bewertungen