Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Questions
Hochgeladen von
Onyekachi Okafor ElishaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Questions
Hochgeladen von
Onyekachi Okafor ElishaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
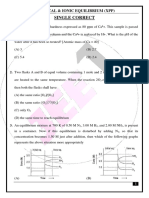
Questions 1. Which of these ionic solids decrease in solubility as temperature increases? CA (OH) 2, CASO4, COA, NACO3.
The ans=CA (OH) 2 AND CASO4 2. Which of these constraints has negligible effect on the solubility of solids and liquids? A. concentration. B. temperature. C. pressure. D. molar mass. 2C6H5OH (aq) +2NA(S) 2C6H5ONA+H2 From the above equation, phenol acts as a -------------. A. oxidizing agent. B reducing agent. C an acid. D an alcohol. 3. Why is carbon said to be tetravalent? The electrons in both 2s and 2p orbitals are equivalent. B the electrons in all the orbitals are equivalent. C the 2s and 2p orbitals are hybridized. D all atomic orbital of carbon are hybridized. 4. How many hybridized orbitals are there in the following hybrid orbitals.( A )sp3 ( B) sp2 (C) sp Solution, You have to just add one to the superscripts.eg sp3= 1+3=4 hybrid orbitals Sp2= 1=2= 3 hybrid orbitals Sp= 1+1= 2 hybrid orbitals. 5. Agcl is mostly soluble in --------. A NaNO3. B water C Nacl Hint; consider common ion effect and solubility of salts (sparingly soluble) 6. the most active carbon in the compound below is------------CH3CCH2CH. A =4. B= 3. C =2. D. =1
The ans is d because it is carbon I1 that carrys the most active carbon.i.e the carbon that is attached directly to the functional group. Please note that you ought to start assigning numbers to the carbon atoms from that which is close to the functional group (alkynes).
7. CH3CHBrCH2B
KOH
CH3CCH
The reaction above is .. A dehydrohalogenation. B halogenations. C addition reaction. D bond breakage. N.b electrophiles carries (+ve) but neucleophiles carrys (-ve) N.b it is only terminal alkynes which can react with ammoniacal copper (i) chloride or ammoniacal silver trioxonitrate (v) 9 which of these hydrogen halides undergoes anti-markovnikoffs rule? A HBr. B Hcl. C Hf. D HI N.b markovnikoffs rule states that while trying to add a hydrogen halide to an alkynes,(terminal),the halogen will always be attached to the carbon with the list number of hydrogen. This principle is only applied to alkynes. Illustration CH3CHCCH+HBr CH3CHC (Br) =CH2.
Please note that terminal alkynes are alkynes with a terminal carbon. A terminal carbon is that carbon which is directly attached to the triple bond in alkyne.any hydrogen which is attached to this carbon is strongly acidic or otherwise known as acidic hydrogen. Please n.b, unsymetric alkynes are terminal alkynes. 10. Which of these structures represents methoxyethane?
A CH3-O-CH2CH3.B CH2CH3-O-CH3 C. CH2CH3-O-CH2. D CH3-O-CH2CH3 11. X Kmno4/dilHno3 ketones. In the equation above, x is. And the reaction is called. A primary akanol, oxidation reaction. B secondary alkanol, dehydrogenation reaction. C tertiary alkanol, oxidation reaction. D secondary alkanol, oxidation reactions. Please note that primary alkanols are oxidized to aldehydes which may further be oxidized to carboxylic acids on excess us of the oxidizing agents. 12. ROH 3I2/NAOH RCOONA-+CHI3+3NAI. The reaction above is.. A oxidation. B dehydrohalogenation. C halogenation. D iodoform reaction 13. Lucas reagent can be used to test.. A amines. B alkanoic acids. C alkanols. D alkynes. Lucas reagent is a mixture of Hcl and zinc chloride. It is basically used to distinguish the three types of alkanols. (Primary, secondary and tertiary alkanols) DEHYDROGENATION OF ALKANOLS 1. Primary alkanols are dehydrogenated to aldehydes 2. Secondary alkanols are dehydrogenated to ketones(alkanones) 3. Tertiary alkanols are dehydrogenated to an alkenes. Variations in the boiling point of alkanols Primary>secondary>tertiary N.b. alkanols are polar due to hydrogen bonding.
2(C6H10O5) N+NH20 diastase n (C12H22O11).the process here is .. A fermentation. B malting. C mashing. D fractional distillation.
Which of the following is not true of benzene? A it is hexagonal or plannar in shape. B the c-c bonding distance is the same. C the c-c bond angle is the same. D it does not undergo addition reaction. E it is trigonal in shape.
T= temperature, S=entropy.H=enthalpy. Important notes 1. When G is negative, a process or a chemical reaction proceeds spontaneously in the forward direction. 2. When G is positive, the process proceeds spontaneously in the backward direction. 3. When G is zero, the process is already in equilibrium with no net change taking place over time. 4. When S of a reaction is positive and H is positive, the process is spontaneous at a high temperature. 5. When S of a reaction is negative and the H is negative, the process is spontaneous at a low temperature. 6. When S of a reaction is negative and H is positive, the process is not spontaneous at any temperature. Additional questions and solutions. If 0.4g of ethanol reacts with certain acid to produce water and an ester. If the reaction occurred between a temperature range of 298.2 and 323k.if the mass of water produced after the reaction is 100g.taking the specific heat capacity of water as 4.2jg-1k-1 Calculate the heat of combustion of ethanol. Solution Mass of ethanol that was burned in the process was 0.4g.the relative atomic mass of ethanol is 46g. The mole ratio of ethanol that was burned was 0.4/46=0.0087mol. The heat evolved in producing was is given by H=MC . M=100g of water C=4.2jg-1k-1 . = (323-298.20 H= 100x4.2x24.8=10416j The heat of combustion of ethanol in the reaction is 10416j/0.0087=1197kj. But the standard heat of combustion of ethanol in the reaction is
-1197kjmol-1 because the reaction is exothermic. 2. 11g of cacl2 dissolved in 30cm3 of water caused a rise in temperature of 34c .the heat of the reaction ,all for cacl2 in kj per mole is------------A 71.1 B 171.1 C 4.18 D 111.0
Solution The mass of cacl2 that reacted is 11g.the relative molar mass of cacl2 is 111g The mole of cacl2 that reacted is 11/111= 0.099= 0.1 mol. Note; if 1000cm3 gives 1g of water. 50cm3 will give? =50x 1/1000=0.05g. The heat evolved in the reaction is H=MC =(34-0) c =34c m=0.05g c=4.2jg-1k-1 h=0.05x 4.2x34=7.14j The heat of the reaction =7.14/0.1=71.4j .
The actual heat of the reaction is 71.4/1000=0.0714kj.so the answer is not available. 4. 0.46g of ethanol when burned, raised the temperature of 50g of water by 14.3k.calculate the heat of combustion of ethanol? Specific heat capacity of water=4.2jg-1k-1 Solution Mass of ethanol burned= 0.46g Molecular mass of ethanol =46g Mass of water evolved=50g The ambient temperature=14.3k Mole of ethanol burned =0.46/46=0.01mol Heat evolved in the reaction = H=MC . H=50X 4.2X14.3=3003J Heat of combustion of ethanol=3003/0.01=300300jmol-1 which is 300.3kjmol-1 But because the reaction is exothermic, it now becomes300.3kjmol-1. Please note, all combustion reactions are exothermic. 5. WHEN H is negative ,a reaction is said to be--a. Endothermic. B exothermic. C reversible. D ionic.
6. NH3(g)+HCL(g)
NH4CL(s)
The entropy change in the system above is-------A zero. B indeterminate. C positive. D negative. Since entropy is a measure of the disorderliness of a system. Systems in gaseous phase are the most disorderly system .when compared to a system in solid or liquid phase. Therefore in the reaction above, For the fact that there is a change in the phases of the system from gas to solid phases. It implies that there is a decrease in the disorderliness of the system (i.e. the entropy) Therefore, S products 7. C(s)+2S(g) S reactants = CS2(g) S of a system.
H =+89kjmol-1
The chemical equation above implies that. A 89kj of energy is absorbed. B each of carbon and sulphur has 89kj of energy. C both carbon and sulphur contributes 89kj of energy. D 89kj of energy is released. Explanation From the above eqation, the enthalpy of the reacting system is positive. (+89kjmol-1).this implies that the reaction is an endothermic reaction and hence heat is absorbed by the system. 8. Which of the following equations shows that a reaction is in equilibrium? A G=0. B G>0. C G<0. D G= H-T S
If the G >0,it shows that the G is positive ,therefore the reaction or the system will be spontaneous in the reverse or backward direction. But if G<0, it shows that it has a negative value, therefore the system will be spontaneous in the forward direction. But generally, when G=0, the reaction is said to be in equilibrium.
9. When dissolves in water, NAOH flakes shows.. A an exothermic change. B an endothermic change. C a rapid reaction. D a slow reaction. Clue; When oxides, and hydroxides of most reactive metals dissolves in water, a lot of energy is released and hence an exothermic reaction. 10.if an equilibrium reaction has H>0,the reaction will proceed favorably in the forward direction at A low temperature. B high temperature. C minimum temperature. D any temperature. Clue; H>0 shows a positive value. This shows that the reaction is endothermic. All endothermic reactions proceed favorably in the forward direction at a high temperature. But for exothermic reactions (-ve H) the reverse becomes the case. This implies that they can proceed in the forward direction at a low temperature. 11.if the heat of combustion of hydrogen is -285.8kj,what is the heat of formation of water?
Solution Equation for the reaction=2H2+O2 2 moles 2H20 2 moles
Since they have the same mole, their heat of combustion is the same.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chem 17 LE 1 Answers1Dokument11 SeitenChem 17 LE 1 Answers1alyssa100% (1)
- Ap Unit6 Worksheet AnswersDokument5 SeitenAp Unit6 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry For Engineers Group 17 Assignment 3Dokument5 SeitenChemistry For Engineers Group 17 Assignment 3Vỹ KhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Reaksi EksotermDokument8 SeitenSoal Reaksi EksotermJack ReacherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry, Equilibrium, Electrochemistry Review WorksheetDokument5 SeitenThermochemistry, Equilibrium, Electrochemistry Review WorksheetakshayddsbNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUTORIAL CHAPTER 1 by DR - KavirajaaDokument4 SeitenTUTORIAL CHAPTER 1 by DR - Kavirajaaathirah ashikinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Education School, KuwaitDokument6 SeitenIndian Education School, KuwaitsarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ap Unit6 WorksheetDokument4 SeitenAp Unit6 Worksheetburcak gecNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Organ PDFDokument3 Seiten16 Organ PDFAya ZhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enthalpy of A ReactionDokument3 SeitenEnthalpy of A ReactionFelicia LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 1051 Final Exam ReviewDokument17 SeitenChem 1051 Final Exam ReviewClaire Elizabeth SnowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - EquilibriumDokument5 SeitenAssignment - EquilibriumYash KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test - Solution and AmineDokument3 SeitenTest - Solution and AmineaayushhariharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsDokument17 SeitenPhysics-Third Law of ThermodynamicsShubham JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry Practice AnswersDokument3 SeitenThermochemistry Practice AnswersakshayddsbNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE1010 Tutorial Sheet 6Dokument4 SeitenCHE1010 Tutorial Sheet 6Chimuka Onson MapikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry PDFDokument13 SeitenOrganic Chemistry PDFPrem KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Shift 2 Nest 2023Dokument10 SeitenChemistry Shift 2 Nest 2023Hardik JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Final Exam - Honors ChemDokument3 SeitenReview Final Exam - Honors ChemAidan LeBlancNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Class Xii Sample Paper 01 AnswersDokument8 SeitenChemistry Class Xii Sample Paper 01 Answerssouparnikar1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Full Test 03Dokument4 SeitenFull Test 03rskr_tNoch keine Bewertungen
- Students Involved in Cheating Will Receive A Failing Grade For This TestDokument13 SeitenStudents Involved in Cheating Will Receive A Failing Grade For This TestFendy FendyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaloalkanesDokument13 SeitenHaloalkanesChingYan TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH302 Homework 2Dokument7 SeitenCH302 Homework 2Edward SpellingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examen Campinas InglesDokument7 SeitenExamen Campinas InglesSharon Laurente RamónNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsDokument29 SeitenThe Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsMinh TieuNoch keine Bewertungen
- KooferDokument9 SeitenKooferslilani_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 16 3rd Long Exam ReviewerDokument3 SeitenChem 16 3rd Long Exam Reviewerggwp21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chang Problems Chapter 4Dokument13 SeitenChang Problems Chapter 4ChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contest 26BDokument3 SeitenContest 26BChristian Joel Mawuli DonkohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- EquillibriumDokument16 SeitenEquillibriumparth ladaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 12 Chem Final ExamDokument3 SeitenGrade 12 Chem Final Examabdimoh7522Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsDokument29 SeitenThe Problem Set of The Four Rounds: ProblemsabcdefNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM102 051 Old-Exam Second-Major UnsolvedDokument5 SeitenCHEM102 051 Old-Exam Second-Major UnsolvedAbdullah AltwirqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contest 36BDokument3 SeitenContest 36BChristian Joel Mawuli DonkohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Test 3 Q 3 Gen - Chem 2 SY 2022 2023 Copy - Edited Copy - Edited.edited Copy - EditedDokument12 SeitenSummative Test 3 Q 3 Gen - Chem 2 SY 2022 2023 Copy - Edited Copy - Edited.edited Copy - EditedJV Subang PatindolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amalkebajikan - 1 TermoDokument17 SeitenAmalkebajikan - 1 TermokjjkimkmkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM011 ReviewerDokument5 SeitenCM011 ReviewerSofia Isabelle GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sydney Boys 2020 Chemistry Trials & SolutionsDokument38 SeitenSydney Boys 2020 Chemistry Trials & SolutionsNhân Lê Nguyễn ThiệnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat of NeutralizationDokument4 SeitenHeat of NeutralizationEsha ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- EquilibriumDokument9 SeitenEquilibriumKashvi DevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical EngineeringDokument5 SeitenChemical EngineeringErcille Mae Oraiz PacamoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction KineticsDokument12 SeitenReaction KineticsTheresaHangDuongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat of NeutralizationDokument8 SeitenHeat of NeutralizationMohd Hafiz AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium XPPDokument24 SeitenEquilibrium XPPruchikumari76543Noch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium Doc 2Dokument5 SeitenEquilibrium Doc 2Alex IoannouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Sets Enthaly Calorimetry Redox Gibbs EntropyDokument2 SeitenPractice Sets Enthaly Calorimetry Redox Gibbs EntropyKAYE AIRA DE LEONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsDokument120 SeitenOrganic Chemistry - Reactions and MechanismsLoveena Steadman100% (8)
- Chemistry SQPDokument4 SeitenChemistry SQPstressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical EquilibriaDokument13 SeitenChemical EquilibriaLok Jun Hao100% (1)
- DocumentDokument3 SeitenDocumentAfthirah AmiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Important QuestionsDokument4 SeitenClass 12 Important Questionsmisraadyasha6Noch keine Bewertungen
- ThermochemistryDokument31 SeitenThermochemistryDavidson ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Chemistry Revision Book 2017 2018 Chapter 7Dokument14 Seiten11 Chemistry Revision Book 2017 2018 Chapter 7Tahseen ShowkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Revision WorksheetDokument26 SeitenFinal Revision Worksheetawash0takuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical ChemistryDokument8 SeitenPhysical ChemistryFroileth PulidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee-Main - Numeric Value Questions - ChemistryyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyDokument111 SeitenJee-Main - Numeric Value Questions - ChemistryyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyySai GokulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal University of Technology, Owerri: Course RegistrationDokument1 SeiteFederal University of Technology, Owerri: Course RegistrationOnyekachi Okafor ElishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of Rice Straw Ash .Dokument20 SeitenCharacteristics of Rice Straw Ash .Onyekachi Okafor Elisha0% (1)
- Ada Straw ProdcompDokument26 SeitenAda Straw ProdcompOnyekachi Okafor ElishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contribution of Rice Husk Ash To The Properties of Mortar and Concrete: A ReviewDokument9 SeitenContribution of Rice Husk Ash To The Properties of Mortar and Concrete: A ReviewOnyekachi Okafor ElishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DedicationDokument4 SeitenDedicationOnyekachi Okafor ElishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Just Another RantDokument6 SeitenJust Another RantJuan Manuel VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSB 3441 CH 1 HallucinogensDokument2 SeitenPSB 3441 CH 1 HallucinogensAnonymous lm3GIU45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grounds of Divorce Under Hindu Religion or Hindu Law Unit-A: Chapter-IiDokument42 SeitenGrounds of Divorce Under Hindu Religion or Hindu Law Unit-A: Chapter-IiSatyam PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pentacam Four Maps RefractiveDokument4 SeitenPentacam Four Maps RefractiveSoma AlshokriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capstone-ModDokument25 SeitenCapstone-ModMohammad Ryyan PumbagulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11-15Dokument172 SeitenChapter 11-15Mansoor AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Bridge Phase Shift ConverterDokument21 SeitenFull Bridge Phase Shift ConverterMukul ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analyzing Activity and Injury: Lessons Learned From The Acute:Chronic Workload RatioDokument12 SeitenAnalyzing Activity and Injury: Lessons Learned From The Acute:Chronic Workload RatioLukas ArenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studovaný Okruh: Physical Therapist Sample Test Questions (G5+)Dokument8 SeitenStudovaný Okruh: Physical Therapist Sample Test Questions (G5+)AndreeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TC 000104 - VSL MadhavaramDokument1 SeiteTC 000104 - VSL MadhavaramMK BALANoch keine Bewertungen
- For Hand Grip Strength: NormsDokument7 SeitenFor Hand Grip Strength: NormsPraneethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCM Design and ImplementationDokument34 SeitenRCM Design and ImplementationRozi YudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIAC Experienced Associate HealthcareDokument3 SeitenDIAC Experienced Associate HealthcarecompangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wes Jackson PM PMP OhioDokument10 SeitenWes Jackson PM PMP Ohioraj jdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afforestation Powerpoint For NandniDokument9 SeitenAfforestation Powerpoint For NandniFagun Sahni100% (1)
- 2008 NOHC - JPHDSupplementDokument62 Seiten2008 NOHC - JPHDSupplementEliza DNNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Nitanshi Singh Full WorkDokument9 Seiten1 Nitanshi Singh Full WorkNitanshi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- TDS Shell Spirax s6 Gxme 75w-80Dokument2 SeitenTDS Shell Spirax s6 Gxme 75w-80rstec pyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ainsworth, The One-Year-Old Task of The Strange SituationDokument20 SeitenAinsworth, The One-Year-Old Task of The Strange SituationliliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 VGP Checklist Rev 0 - 23 - 1 - 2023 - 9 - 36 - 20Dokument10 Seiten2023 VGP Checklist Rev 0 - 23 - 1 - 2023 - 9 - 36 - 20mgalphamrn100% (1)
- Reference Document GOIDokument2 SeitenReference Document GOIPranav BadrakiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead Avr PDFDokument9 SeitenLead Avr PDFsiddharthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laughter, It Is Good For YouDokument2 SeitenLaughter, It Is Good For YouClaire B.L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Athletes Who Made Amazing Comebacks After Career-Threatening InjuriesDokument11 SeitenAthletes Who Made Amazing Comebacks After Career-Threatening InjuriesანაNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polikanov 2019-05-14 Curriculum Vitae YuryDokument6 SeitenPolikanov 2019-05-14 Curriculum Vitae Yuryapi-460295531Noch keine Bewertungen
- Generic 5S ChecklistDokument2 SeitenGeneric 5S Checklistswamireddy100% (1)
- The Chemical Composition and Organoleptic Attributes of Lesser-Known Vegetables As Consumed in Njikoka Local Government Area, Anambra State, NigeriaDokument4 SeitenThe Chemical Composition and Organoleptic Attributes of Lesser-Known Vegetables As Consumed in Njikoka Local Government Area, Anambra State, NigeriaEmri CynthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRM McDonalds ScribdDokument9 SeitenCRM McDonalds ScribdArun SanalNoch keine Bewertungen
- VOC & CO - EnglishDokument50 SeitenVOC & CO - EnglishAnandKumarPNoch keine Bewertungen