Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Edc Question Bank
Hochgeladen von
Manoj KumarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Edc Question Bank
Hochgeladen von
Manoj KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
PANIMALAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS QUESTION BANK
PART-A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Define the term transition capacitance CT of a PN diode? What is thermal runaway? What is MOSFET?Mention its types. What is a TRIAC?Draw its symbol. What are the salient features of hybrid parameters? Classify the power amplifiers based on its biasing conditions. What are the disadvantages of negative feedback? State the Barkhausen criterion? Draw the response of highpass RC circuit to a pulse input? What is the need for filters in power supplies? The reverse saturation current in a silicon diode is 100na at 27c. Find the current through the diode if the applied forward voltage is 1 volt What is the difference between DC load line and AC load line in a CE amplifier having voltage divider bias and external load resistance RL? Why FET is called voltage divider bias? What is meant by holding current in a SCR? Compare input impedance and voltage gain of CE and CC amplifiers? What is meant by crossover distortion? What are the advantages of negative feedback in amplifiers? In Weins bridge oscillator,write the expression for oscillator frequency for oscillation frequency and minimum value of gain needed for sustained oscillation. In the following circuit,find the waveform of the output voltage. Assume the diode to be ideal.
20. 21. 22. 23.
What is meant by switched mode power supplies? What is the diffusion current in PN junction diode? What is LED? Which material is used for LED? Why is collector region wider than emitter region in BJT?
24. In a BJT,the emitter current is 12mA and the emitter current is 1.02 times the collector current. Find the base current. 25. What are the special features of FET? 26. define a) Pinch off voltage b) Amplification factor in JFET. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. What is meant by Common Mode Rejection Ratio? Mention some applications of UJT? What is a multivibrator? Explain Avalanche breakdown and Zener breakdown. What is thermal runaway? How it can be avoided? Define the parameters transconductance(gm),drain resistance(rd),and amplification factor() of a JFET. Establish the reletion between them. Explain the terms a) Peak Point Voltage(VP) and b) Valley point voltage(Vv) of a UJT Compare the performance of a BJT as an amplifier in CE,CB&CC configurations. Explain cross over distortion. How it can be minimized. What are the different types of negative feedback? Explain how the input and output impedance of amplifier are affected by the different types of negative feedback State and briefly explain Barkhausen criterion for oscillation. Explain LOWER and UPPER threshold voltages in a Schmitt Trigger. Define line regulation and load regulation in a voltage regulator? Define KNEE voltage of a diode? What is peak inverse voltage? Name the operating mode of a transistor? What are hybrid parameters? Draw the high frequency model of JFET. Write the Ac input impedance of a Darlington Transistor. Mention the operating modes of MOSFET. Mention any two high frequency LC oscillators. Write the frequency equation of an Astable multivibrator. What is Schmitt trigger? State the Barkhausen criterion?
34. 35. 36.
37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50.
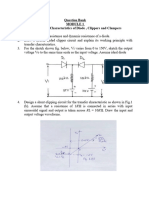
PART-B 1. Show that reverse biased PN junction can be used as a variable capacitor. 2. From the energy band diagram explain the V-I characteristics of a tunnel diode. 3. Draw the circuit diagram of NPN junction transistor CE configuration and describe the static input and output characteristics. Also define active ,saturation and cutoff regions and saturation resistance of Ce amplifier. 4. Draw a voltage divider bias circuit and derive the expression for its stability factor. 5. Assuming that the saturation drain current IDS given by the parabolic relation IDS=IDSS (1Prove that the transconductance gm is given by gm=gmo(1-
)2.
)=
DSSIPS
where gmo is the
value og gm for VGS=0 6. Explain the biasing of JFET and MOSFET with circuit diagram.
7. Describe the working principle of SCR with V-I characteristics. Explain why it is operated only in the forward biased condition. 8. Derive the equations for voltage gain,current gain,input impedance,output admittance for a BJT using low frequency h-parameters model in CE configuration. 9. A CE amplifier is driven by a voltage source of internal resistance Rs=1000 and load impedance of 1200. The h-parameters of the transistor are hie=1.2k,hre=2 x 10-4,hfe=60,hoe=25A/V. Compute the current gain(Ai),input resistance(Ri),voltage gqain(Av) and output resistance (Ro) using exact analysis. 10. Draw the circuit diagram of a class-B push-pull amplifier and explain its working. Derive the equation for efficiency. 11. Derive the equation for maximum value of efficiency of class-A transformer coupled amplifier. 12. Describe with necessary derivations the effect of negative feedback on the band width and distortion in an amplifier. 13. An amplifier with 2.5k input impedance and 50 k output impedance has a voltage gain of 100. The amplifier is now modified to provide 5% negative feedback in series with the input. Calculate a. The voltage gain b. The input resistance and c. The output resistance with feedback 14. Derive the expression for the frequency of oscillation and the minimum gain required for sustained oscillations of the rC phase shift oscillator using BJT. 15. Draw the circuit of Hartley oscillator and explain its working. Derive the expressions for frequency of oscillation and condition for starting of oscillation. 16. With the help of a neat circuit diagram and relevant waveform describe the operation of two level diagrams. 17. With a neat figure,explain the working of an astable multivibrator. Derive the expression for output frequency. On what factors does the frequency of the output wave depend?
18. Derive the expression for Rectification efficiency,Ripple factor,Transformer utilization factor,form factor & peak factor of a full wave rectifier with a resistive load. 19. Compare the linear and switched mode power supplies. Explain the operation of a switched mode power supply in detail with a neat block diagram. 20. Draw the two transistor modes of SCR and explain its breakdown operation. Explain how triggering of the SCR can be controlled by gate signal supplied? 21. Explain the working of FWR with centre tap transformer. Also derive the following for this transformer. i. Dc output voltage ii. Dc output current iii. RMS output voltage 22. Explain the following regulator circuits i. Transistorized shunt regulator ii. Zener diode shunt regulator. 23. Describe the static input & output characteristic of a CB transistor with neat circuit diagram. 24. Derive the expression for current gain,input impedance and voltage gain of a CE Transistor Amplifier. 25. Explain the construction of N channel JFET. Also explain the drain and transfer characteristics of the same. 26. Describe the operation of common drain FET amplifier and derive the equation for voltage gain.(12) 27. In the common drain FET amplifier of above Let Rs=4k:=50;rd=35k. evaluate the voltage gain Av.(4) 28. Derive the equation for differential mode gain and common mode gain pf a differential amplifier. 29. Draw and explain the operation of a Hartley oscillator. Derive the equation for fr and hfe 30. Explain the working of UJT as a relaxation oscillator with necessary waveforms and equations. 31. Draw the circuit of a monostable multivibrator and explain.(14) 32. What are the applications of monostable multivibrator(2) 33. Draw and explain the VI characteristics of a PN junction diode(6) 34. Explain the operation of a FULL wave rectifier & derive its Ripple factor.(10) 35. Explain the working of a zener diode as a regulator(8) 36. Discuss the working principle,characteristics and applications of LED in detail.(8) 37. Draw and explain the input and output characteristics of a BJT in CE configuration. 38. Draw the Hybrid model of CE configuration and also derive the expressions for its Input and output Impedance current and voltage gain 39. Write a note on optocouplers(4) 40. Explain the switching characteristics of a transistor(4) 41. Explain in detail about the construction,working principle of depletion MOSFET. Also explain how DEPLETION MOSFET acts both in enhancement and depletion mode. 42. With a neat circuit diagram explain the operation of a common source amplifier(6)
43. From the low frequency model,determine the input and output impedances and the voltage gain of a JFET. 44. Discuss the various topologies of feed back amplifier 45. Discuss the operation of a Colpitts oscillator in detail 46. Explain the effects of negative feed back in amplifiers 47. Describe the operation of a typical voltage shunt feedback amplifier 48. What is a clipper and clamper? Explain the concept of a positive clipper and a clamper 49. Distinguish between astable and bistable multivibrators. Mention some applications 50. What is Schmitt Trigger? Discuss any two applications of Schmitt Trigger 51. Explain the application of UJT as a Sawtooth oscillator 52. Explain the capacitance in diode under forward biased and revaerse bias condition. 53. Describe the V-I characteristics of Schottky diode 54. In the following circuit shown in diagram. Find the values of IBQ,ICQ and VCEQ.. Also draw the DC load line and AC load line for the circuit
55. Draw the V-I characteristics of Zener diode and explain its operation 56. With neat circuit diagram and characteristics ,explain the operation of Varactor Diode. 57. Draw the collector to base bias circuit of a transistor and derive an expression for the stability factor. 58. Explain the construction and operation of N-channel JFET with its characteristics 59. Briefly explain the construction of DC and Ac load lines on the output characteristics of the CE transistor amplifier. 60. Define the characteristic parameters of the JFET and derive the relation ship among them 61. Describe the working principle of an SCR with V-I characteristics 62. Draw the V-I characteristics of a DIAC and explain its working. 63. Derive the equation for power output and maximum conversion efficiency of class A series fed amplifier. 64. Explain the operation of class-B complementary symmetry push-pull amplifiers. State its advantages and disadvantages. 65. Derive the expression for Input and Output resistances of a voltage series negative feedback amplifier. 66. Voltage-series negative feedback amplifier has a voltage gain without feedback of A=500,input resistance(Ri)=3K.Output resistance R=20 K and feedback ratio()=0.01. calculate the voltage gain AF,input impedance(Rif) and output resistance (Rof) of amplifier with feedback.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- What Do You Mean by Transistor BiasingDokument4 SeitenWhat Do You Mean by Transistor BiasinganupvasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edctutorial BctII IDokument3 SeitenEdctutorial BctII INeelesh MrzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beee Important QuestionsDokument5 SeitenBeee Important Questionssai pranayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edc - Assignment Questions - NbaDokument5 SeitenEdc - Assignment Questions - Nbagunda manasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Frequency Work SheetDokument2 SeitenRadio Frequency Work Sheetabazer ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC - Question BankDokument7 SeitenEDC - Question BankSwaum KisNoch keine Bewertungen
- EdcDokument3 SeitenEdcSandy RonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC Question BankDokument13 SeitenEDC Question BankvenzkrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank BEC1Dokument2 SeitenQuestion Bank BEC1ARYAN MOHADENoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject:EDC (EC0116) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Dokument4 SeitenSubject:EDC (EC0116) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9Mihir JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC6202 Electronic Devices and Circuits NotesDokument6 SeitenEC6202 Electronic Devices and Circuits NotesrejinpaulpaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics CircuitDokument4 SeitenElectronics CircuitSuresh PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edc Question BankDokument4 SeitenEdc Question BanksanthoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback Amplifiers and Multistage AmplifiersDokument43 SeitenFeedback Amplifiers and Multistage Amplifiersjanardhan chNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ty PeDokument3 SeitenTy Pepankaj mobile zoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic CircuitsDokument18 SeitenElectronic CircuitsMythily VedhagiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEEE-Question Bank 2023Dokument5 SeitenBEEE-Question Bank 2023peoplewatching41Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee-304 Analog Electronics 75 QuestionsDokument5 SeitenEe-304 Analog Electronics 75 QuestionsnaactitexcellenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Dokument7 SeitenPower Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Herbert DeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maharaja Institute of Technology Mysore Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDokument2 SeitenMaharaja Institute of Technology Mysore Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDhanush Gowda D TNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2EC6304 Electronic Circuits I QBDokument7 Seiten2EC6304 Electronic Circuits I QBRaji SharmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro 4Dokument5 SeitenElectro 4karthiksvr26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank: Unit I Part ADokument4 SeitenQuestion Bank: Unit I Part Asamsath10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFDokument8 SeitenElectronic Devices and Circuits Question Bank PDFVenkata SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE2301 Power ElectronicsDokument12 SeitenEE2301 Power ElectronicsMuniyasamy BalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Concept in Power SystemsDokument9 SeitenPower Electronics Concept in Power SystemsT.l. SelvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE%20blueprint%20SemDokument4 SeitenPE%20blueprint%20Semsparkle courageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-Wise Eln QBDokument5 SeitenModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument3 SeitenQuestion BankthakkannavarnaveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Electronics Devices and Controlled RectifiersDokument7 SeitenPower Electronics Devices and Controlled Rectifierssushil4056Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ece Vii Power Electronics (10ec73) AssignmentDokument6 SeitenEce Vii Power Electronics (10ec73) AssignmentThomas PriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2-QB-BJT Applic & Feedback AmplisDokument2 SeitenChapter 2-QB-BJT Applic & Feedback AmplisRamyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics (BBEE103/BBEE203) - Question Bank - VTUDokument11 SeitenBasic Electronics (BBEE103/BBEE203) - Question Bank - VTUShrishail Bhat100% (1)
- Ec2205 Electronic Circuits IDokument5 SeitenEc2205 Electronic Circuits Isudha_monisha16Noch keine Bewertungen
- EC2Dokument12 SeitenEC2ankurwidguitarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 1Dokument1 SeiteEc 1Rengaprabhu SPNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHM604 QB 2019 PDFDokument5 SeitenPHM604 QB 2019 PDFAbhishek Yadav100% (1)
- Pe Course File 9 198Dokument190 SeitenPe Course File 9 198Dr ADITYA VORANoch keine Bewertungen
- Edec Question Paper-IDokument8 SeitenEdec Question Paper-IarunfriendsNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE1152- Circuits & ElectronicsDokument5 SeitenEE1152- Circuits & ElectronicsSaranya PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC6202-Electronics Devices and CircuitsDokument6 SeitenEC6202-Electronics Devices and Circuitssaravananvaratharajan4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Important QuestionsDokument2 SeitenImportant Questionsramjidr0% (1)
- EE2301 Power Electronics Question BankDokument11 SeitenEE2301 Power Electronics Question Bankvenkatesh_paboluNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC Question BankDokument6 SeitenEDC Question BankSudershan DolliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics Model Paper 2nd YearDokument38 SeitenElectronics Model Paper 2nd Yearbhaivarun65Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ece-Vii-Power Electronics (10ec73) - Assignment PDFDokument6 SeitenEce-Vii-Power Electronics (10ec73) - Assignment PDFAdarsh S Shettigar100% (1)
- 08.304 Electronic Circuits (R F) : C (Sat)Dokument2 Seiten08.304 Electronic Circuits (R F) : C (Sat)akhilarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectifiers&filters NOTESDokument50 SeitenRectifiers&filters NOTESMake the Best with SunithaGuganNoch keine Bewertungen
- EdcqbDokument10 SeitenEdcqbPranveer Singh PariharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vtu B Ele 1,2Dokument1 SeiteVtu B Ele 1,2syed irfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AsdaDokument1 SeiteAsdarrkeerthanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSTU EEE Power Electronics Assignment QuestionsDokument6 SeitenNSTU EEE Power Electronics Assignment QuestionsSalma AkterNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDC EC8353 QuestionsDokument5 SeitenEDC EC8353 QuestionsBalaji PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Signal Amplifiers Midband AnalysisDokument10 SeitenSmall Signal Amplifiers Midband AnalysishanifathariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec3353 QBDokument11 SeitenEc3353 QBrajasncetsbcNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC I EC2205 University Ques BankDokument14 SeitenEC I EC2205 University Ques Bankkamalsrec78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Analog Electronics Model Question CollegeDokument5 SeitenAnalog Electronics Model Question Collegenodov66591Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 6503Dokument2 SeitenEe 6503Attagasam ArjunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsVon EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24V 1A dual audio equipment power supply circuit using LM7824 ICDokument2 Seiten24V 1A dual audio equipment power supply circuit using LM7824 ICjankhristel23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ardunio Based Home Kitchen Air Monitoring Systm: Presented byDokument25 SeitenArdunio Based Home Kitchen Air Monitoring Systm: Presented byManik SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Man GRT7-TH4 R2Dokument18 SeitenMan GRT7-TH4 R2Jaime GanozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FSDL0365RN, FSDM0365RN: Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Dokument20 SeitenFSDL0365RN, FSDM0365RN: Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Andi Awal JanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accident Alert System Using Gps and GSMDokument19 SeitenAccident Alert System Using Gps and GSMshobhitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 800reozm 0318Dokument3 Seiten800reozm 0318Xuân Huy NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zener DiodeDokument19 SeitenZener DiodeHieu DinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Mode Power Switch FSDH321, FSDL321: DescriptionDokument16 SeitenGreen Mode Power Switch FSDH321, FSDL321: DescriptionJosue Rafael BorjasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programmable Electronic DetonatorDokument16 SeitenProgrammable Electronic Detonatorpartha das sharma100% (3)
- Es48 150 Uqa02Dokument2 SeitenEs48 150 Uqa02doug_nguyen7864Noch keine Bewertungen
- AME1117Dokument16 SeitenAME1117Jorge AdrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harvesting Energy With Hand-Crank Generators To Support Dismounted Soldier MissionsDokument9 SeitenHarvesting Energy With Hand-Crank Generators To Support Dismounted Soldier MissionsAlexander J RokowetzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12V 24V Boost Converter PDFDokument5 Seiten12V 24V Boost Converter PDFIonescu ViorelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project ReportDokument8 SeitenMini Project ReportSrikanth SriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICA Notes: Operational Amplifier FundamentalsDokument154 SeitenICA Notes: Operational Amplifier FundamentalsxxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transistor Series Voltage RegulatorDokument4 SeitenTransistor Series Voltage RegulatorM Lakshmi NarayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AN-1149 Switching Power Supplies Guidelines PDFDokument3 SeitenAN-1149 Switching Power Supplies Guidelines PDFingenierosunidosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naval Headquarters Directorate of Electrical EngineeringDokument50 SeitenNaval Headquarters Directorate of Electrical EngineeringAjin ShaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVR Manual Senr5833-06Dokument68 SeitenDVR Manual Senr5833-06Sayed Younis Sadaat75% (4)
- LP38690 LP38692 1A Low Dropout CMOS Linear Regulators: Stable With Ceramic Output CapacitorsDokument28 SeitenLP38690 LP38692 1A Low Dropout CMOS Linear Regulators: Stable With Ceramic Output CapacitorsNguyễn Văn QHuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- MONITORING RELAYS. W VOLTAGE MONITORING RELAY UR5U1011. W SCHRACK-INFO. W TECHNICAL DATA PDFDokument34 SeitenMONITORING RELAYS. W VOLTAGE MONITORING RELAY UR5U1011. W SCHRACK-INFO. W TECHNICAL DATA PDFovidiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top209 PDFDokument17 SeitenTop209 PDFguiodanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBO240 Product BulletinDokument8 SeitenSBO240 Product BulletinMarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BJT vs FET: Key Differences Between the Two Transistor TypesDokument13 SeitenBJT vs FET: Key Differences Between the Two Transistor TypesSivarajanRajendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Werna: WR274C - Technical Data SheetDokument8 SeitenWerna: WR274C - Technical Data SheetAbeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6) 4H.1380.02.0.PR - Installation Service & Maintenance Manual For Ac Kirloskar Green Ac LS GeneratorDokument27 Seiten6) 4H.1380.02.0.PR - Installation Service & Maintenance Manual For Ac Kirloskar Green Ac LS GeneratorAlfiya AnamNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make A Digital SynthesizeDokument32 SeitenHow To Make A Digital Synthesizewaketek100% (1)
- Dstatcom Project ReportDokument43 SeitenDstatcom Project ReportMahendar Mahe100% (3)
- TAS5624A Class-D Audio Amplifier OverviewDokument5 SeitenTAS5624A Class-D Audio Amplifier OverviewbeetorNoch keine Bewertungen