Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Combination Generator in Java
Hochgeladen von
Liang WuOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Combination Generator in Java
Hochgeladen von
Liang WuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
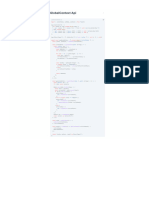
package Combinations; import import import import java.util.ArrayList; java.util.Collection; java.util.Collections; java.util.
List;
/** * * @author Liang_2 * * @param <T> */ public class CombinationGenerator<T extends Comparable<T>> implements Combinatio n<T> { protected int[] iterators; //iterators represent an index value within a n array of booleans. Values pointed to by the index are true, whilst other value s are false. //false values are items that have not been chosen. protected int k; protected int n; private boolean hasNext; List<T> items; Factory Factory = new Factory(); class Factory{ private List<T> someList(){ return new ArrayList<T>(); } private List<T> someList(Collection<T> items){ return new ArrayList<T>(items); } } public CombinationGenerator(){//must use the initialise method if this c onstructor is used } public CombinationGenerator(Collection<T> collection, int choices){ this.items = Factory.someList(collection); this.k = choices; this.n = items.size(); if( n < 1 || k < 1 || k > n){ //invariant condition should cause an exception TODO, n and k are set to be 1 or greater, since returning an empty collection could cause problems. this.hasNext = false; } else{ this.hasNext = true; } this.iterators = new int[k]; Collections.sort(items); for( int i = k - 1 ; i >= 0; i--){ this.iterators[ i ] = n-i-1; }
} public void initialise(Collection<T> collection, int choices){ this.items = Factory.someList(collection); this.k = choices; this.n = items.size(); if( n < 0 || k < 0 || k > n){ //invariant condition should cause an exception TODO this.hasNext = false; } else{ this.hasNext = true; } this.iterators = new int[k]; Collections.sort(items); for( int i = k - 1 ; i >= 0; i--){ this.iterators[ i ] = n-i-1; } } private void generateNextCombination(){ int previous = -1; int arrayindex = iterators.length - 1; for( ; arrayindex >=0 ; ){ if( iterators [ arrayindex ] == previous + 1 ){ previous = iterators[arrayindex]; arrayindex --; continue; } else if(items.get(iterators[arrayindex]).equals(items.ge t(iterators[arrayindex]-1))){ iterators[arrayindex]--; continue; } previous = iterators[arrayindex]; for(int j = 1 ; arrayindex <= iterators.length - 1 ; ){ iterators[ arrayindex ] = previous - j ; arrayindex ++; j++; } return; } hasNext = false; return; } public boolean hasNextCombo() { return hasNext; } public Collection<T> getCombo(){ Collection<T> founditems = Factory.someList(); for( int index = 0; index <k ; index++){ founditems.add(items.get(iterators[index] )); } generateNextCombination(); return founditems;
} public void reset() { for( int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--){ this.iterators[ i ] = n-i; } } }
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Dotnet Mod5Dokument23 SeitenDotnet Mod5Shabnam SaniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coming Up in VS 2005Dokument53 SeitenComing Up in VS 2005Elaiya KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Array of ObjectsDokument16 SeitenArray of ObjectsDao Manh Cong (K16HL)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Nguyen Huu Thang ID Student: GCD201443 Class: GCD1001 Lap 1Dokument7 SeitenName: Nguyen Huu Thang ID Student: GCD201443 Class: GCD1001 Lap 1Nguyen Huu Thang (FGW DN)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Package Import Public Class Public Static Void: "A" "D" "V" "C" "B" "J"Dokument5 SeitenPackage Import Public Class Public Static Void: "A" "D" "V" "C" "B" "J"Hari HaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foreach Int in Yield Return: (I Data) IDokument4 SeitenForeach Int in Yield Return: (I Data) Ianon_394655724Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aq PDFDokument2 SeitenAq PDFMouad YoussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Array Queue PDFDokument2 SeitenArray Queue PDFMouad YoussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Items Front Rear Count: ArrayqueueDokument2 SeitenItems Front Rear Count: ArrayqueueMouad YoussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- OperatorsDokument4 SeitenOperatorssaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code Java of SetDokument9 SeitenCode Java of SetNhung HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- My Collection1Dokument27 SeitenMy Collection1Sabyasachi BiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colectii Slide PDFDokument21 SeitenColectii Slide PDFMarin_1wqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06A ArrayOfObjectsDokument15 Seiten06A ArrayOfObjectsDo Cao Dat (K15 HL)Noch keine Bewertungen
- HACKATHONDokument10 SeitenHACKATHONDharam SekhonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Program T: Using Namespace Class Static Void Ref RefDokument4 SeitenProgram T: Using Namespace Class Static Void Ref RefAqua MarinchoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Generics: Compiled From Core JavaDokument11 SeitenJava Generics: Compiled From Core JavaUday KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2-List (Sequential List) Arraylist Class: Edited by Miss Nafisah AminDokument29 SeitenTopic 2-List (Sequential List) Arraylist Class: Edited by Miss Nafisah AminsofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GlobalContext Api - ReduxDokument2 SeitenGlobalContext Api - ReduxmohsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Structure AssignmentDokument7 SeitenData Structure AssignmentIrfan HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSE459 CSharp 07 EnumerationDokument39 SeitenCSE459 CSharp 07 EnumerationsamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Running Notes 9th and 11th JulyDokument15 SeitenClass Running Notes 9th and 11th Julynilesh kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DaafileDokument40 SeitenDaafileSanehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Queue NotesDokument12 SeitenQueue NotesTarun kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 5 - Bag Interface Implementation (ADT)Dokument8 SeitenHomework 5 - Bag Interface Implementation (ADT)Adnan SkulicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Tree AlgorithmDokument10 SeitenDecision Tree AlgorithmThe92% (13)
- Part of The Collections FrameworkDokument22 SeitenPart of The Collections FrameworkREEVAN SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB 1: OOP Review + Single Linked List + Doubly Linked List: N N n-1 n-1 1 0 N n-1 0Dokument32 SeitenLAB 1: OOP Review + Single Linked List + Doubly Linked List: N N n-1 n-1 1 0 N n-1 0Cao Minh QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- It Er AdoresDokument39 SeitenIt Er AdoresLuisitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB2Dokument5 SeitenLAB2Hưng LêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bootstrap BundleDokument122 SeitenBootstrap BundleBharat KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Better Programmer TaskDokument10 SeitenBetter Programmer Taskmahesh225Noch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Custom Enumerators: C# Cookbook, 2nd EditionDokument4 SeitenCreating Custom Enumerators: C# Cookbook, 2nd Editionxact33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q7) Write A C++ Program Using Types of Sorting.: 1. Bubble Sort 2. Insertion SortDokument19 SeitenQ7) Write A C++ Program Using Types of Sorting.: 1. Bubble Sort 2. Insertion SortAyush JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iksha ' Nusandhan: Laboratory Record Computer Science Workshop 2 (CSE 3141)Dokument28 SeitenIksha ' Nusandhan: Laboratory Record Computer Science Workshop 2 (CSE 3141)SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week1 MapDokument7 SeitenWeek1 Mapapi-3724182100% (1)
- C++ Chapter 6Dokument5 SeitenC++ Chapter 6Ajwa AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSE/IT 213 - : New Mexico TechDokument75 SeitenCSE/IT 213 - : New Mexico TechketerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Koustubh Java Practicle Assignment 2Dokument11 SeitenKoustubh Java Practicle Assignment 2rdlolgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TreeSet ExamplesDokument8 SeitenTreeSet ExamplesMatthew ClementeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Object Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 40Dokument31 SeitenObject Oriented Programming (OOP) - CS304 Power Point Slides Lecture 40Sameer HaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- @override: Public Class Extends Int Public Void While Try CatchDokument2 Seiten@override: Public Class Extends Int Public Void While Try CatchMihail BoranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lists - How To Build Your Own: Atul Prakash Reference: Look at Arraylist - Java Implementation in JavaDokument19 SeitenLists - How To Build Your Own: Atul Prakash Reference: Look at Arraylist - Java Implementation in Javaavinashf02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jalab RecordDokument50 SeitenJalab Recordsssttt1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- If2225d - Tugas 6 & 7 - 3411181167Dokument19 SeitenIf2225d - Tugas 6 & 7 - 3411181167anissa azhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Data Structures: Topic 1Dokument11 SeitenBasic Data Structures: Topic 1Anahit SerobyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create Class IntegerSet For Which Each Object Can Hold Integers in TDokument6 SeitenCreate Class IntegerSet For Which Each Object Can Hold Integers in TBILAL FAZULNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section01 SolutionsDokument15 SeitenSection01 SolutionsTawsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Lab Exercise - 6Dokument5 SeitenJava Lab Exercise - 6Dhanush DhoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 13 22z433Dokument5 SeitenExperiment 13 22z433T.K. SanthoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Cheat Sheet Made by Abdul MalikDokument6 SeitenPython Cheat Sheet Made by Abdul MalikRaji RayapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bilješke Oop: Swingworker ExampleDokument6 SeitenBilješke Oop: Swingworker ExampleGeneral IrohNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrowserDokument3 SeitenBrowserananthvijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stack NotesDokument9 SeitenStack NotesTarun kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full HackerrankDokument108 SeitenFull HackerrankPradyumna HathwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 Java Collections - PolitoDokument12 Seiten08 Java Collections - PolitoAnnaBalzarettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Last SizeDokument4 SeitenFirst Last SizeMouad YoussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionVon EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and ScienceDokument16 SeitenInternational Journal of Research in Pharmacy and ScienceCdma Nastiti FatimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Nirav Vyas Numerical Method 4 PDFDokument156 SeitenDr. Nirav Vyas Numerical Method 4 PDFAshoka Vanjare100% (1)
- Diana's DisappointmentDokument3 SeitenDiana's DisappointmentDubleau W100% (4)
- Flash Memory - Cache MemoryDokument3 SeitenFlash Memory - Cache MemoryIsham IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training: A Project Report ON & Development Process at Dabur India LimitedDokument83 SeitenTraining: A Project Report ON & Development Process at Dabur India LimitedVARUN COMPUTERSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nichols, Ashton. The Loves of Plants and Animals: Romantic Science and The Pleasures of NatureDokument15 SeitenNichols, Ashton. The Loves of Plants and Animals: Romantic Science and The Pleasures of NatureBarbara RossinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy To Teach The Internal Standard MethodDokument3 SeitenUsing FTIR-ATR Spectroscopy To Teach The Internal Standard MethodEdgar VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Models of OrganizationDokument5 SeitenSix Models of Organizationmh_sadri100% (1)
- RESUMEEE JurnalDokument6 SeitenRESUMEEE JurnalnaufalarifnurrohmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expert Guide To Cognos Audit DataDokument30 SeitenExpert Guide To Cognos Audit Dataleonardo russoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wiegers Getting The Most Out of Requirements Management ToolDokument9 SeitenWiegers Getting The Most Out of Requirements Management ToolAmreshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Many Worlds InterpretationDokument26 SeitenMany Worlds InterpretationahsbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE2113-Chapter 9 - Center of Gravity and Centroid - DraftDokument18 SeitenPE2113-Chapter 9 - Center of Gravity and Centroid - DraftMohammed AlkhalifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP S3100V2 MIB CompanionDokument401 SeitenHP S3100V2 MIB CompanionWagner VictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Prevention of HypertensionDokument7 SeitenPrimary Prevention of HypertensioncinthyaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) 64 Bit Ripple Carry Adder Code With OutputDokument4 Seiten1) 64 Bit Ripple Carry Adder Code With OutputKALAIPRIYAN MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test AgileDokument16 SeitenTest Agilejuan carlos tipismanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marana Karaka SthanaDokument20 SeitenMarana Karaka SthanaKamal RanathungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sport, Race and Ethnicity: Coakley CHP 9Dokument16 SeitenSport, Race and Ethnicity: Coakley CHP 9Arief MoertopoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idsl 830 Transformative Change Capstone ProjectDokument33 SeitenIdsl 830 Transformative Change Capstone Projectapi-282118034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nota Avant GardeDokument5 SeitenNota Avant GardePeisan GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environment Setup - User Manual PDFDokument38 SeitenEnvironment Setup - User Manual PDFambrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- LinuxDokument76 SeitenLinuxRanganathan NagendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- KABIR HASION CV Executive-1 PDFDokument2 SeitenKABIR HASION CV Executive-1 PDFraiyanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal PhilosophyDokument22 SeitenLegal Philosophygentlejosh_316100% (2)
- An Introduction To Genre Theory: January 1997Dokument16 SeitenAn Introduction To Genre Theory: January 1997pratolectusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joseph Cote WeeblyDokument2 SeitenJoseph Cote Weeblyapi-232220181Noch keine Bewertungen
- Recovering The Essence in Language - EssayDokument3 SeitenRecovering The Essence in Language - EssayOnel1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mva - 2008 India School Rick LoydDokument86 SeitenMva - 2008 India School Rick Loydamar_saxena60857Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elaine Risley's Character DevelopmentDokument12 SeitenElaine Risley's Character Developmenterlooay100% (1)