Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Limits Theory
Hochgeladen von
Dattatray NerkarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Limits Theory
Hochgeladen von
Dattatray NerkarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Prof.
Sunil Patils Tutorials
XII - Mathematics
1 LIMITS
LIMITS
AND
CONTINUITY
Definition : We say that lim f ( x) = l given any > 0, we can say find >0 such that , x a | f(x) l | < where 0 < | x a | < Standard Limits : xn an 1) lim = n a n 1 ( a > 0 n Q ) x a x a 2) lim 3) lim sin x =1 x 0 x
x
lim
sin kx =1 x 0 kx lim
x 0
x 0
lim
sin n kx (kx)
n
=1
; lim
tan x =1 x 0 x
a 1 = log a ; x 0 x
kx
1 = log a kx
ek x 1 ex 1 lim = log e = 1 4) lim = 1 ; x 0 x 0 kx x
1 x 0 1
5) lim(1 + x) x = e ; lim(1 + k x) k x = e x 0 6) lim log(1 + k x) log(1 + x) = log e = 1 ; lim = log e = 1 x 0 x 0 x kx 1 1 lim k = 0 ( k > 0) 7) lim = 0 ; x x x x
Algebra of limits : 1) lim [ f ( x) g ( x)] = lim f ( x) lim g ( x ) x a x a x a 2) lim [ kf ( x)] = k lim f ( x) x a x a 3) lim [ f ( x ) g ( x)] = lim f ( x ) lim g ( x) x a x a x a 4) lim [ f ( x) g ( x )] = lim f ( x) lim g ( x ) x a x a x a 5) If f(x) < g(x) then lim f ( x) lim g ( x) x a x a
lim g ( x )
x a 6) lim[ f ( x)] g ( x ) = l im f ( x) x a x a
Limits and Continuity -Theory -1
Prof. Sunil Patils Tutorials
XII - Mathematics
CONTINUITY
1) A function f is said to continuous at x = a if f(a) exists , xlim+ f ( x) exists , xlim f ( x) exists and a a
x a +
lim f ( x ) = lim f ( x) = f(a) x a
lim 2) A function f is said to continuous at x = a if f(a) exists , xa f ( x) exists lim then x a f ( x) = f(a) 3) Removable Discontinuity : lim If f(x) is such that : x a f ( x) exists and by redefining the function suitably at x = a 4) Continuity in an interval : A function f is said to continuous on [ a, b ] if i) f is continuous at every c ( a, b) i.e.
x c + x a
lim f ( x) f(a)
then f has a removable discontinuity at x = a and this discontinuity can be removed
lim f ( x) = lim f ( x) = x c lim f ( x) = f(a) and
f(c)
ii) f is continuous from the right at x = a and continuous from the left the left at x = b i.e.
x a + x b
lim f ( x ) = f(b)
5) Continuity of Standard function : i) A polynomial is continuous for all real values of x.
2 n If f ( x) = a0 + a1 x + a2 x + ......... + an x where n N and a0, a1, a2, an
are real constants then f is said to be a polynomial of degree n. ii) f(x) = sin x and f(x) = cos x are continuous for all real values of x 6) Algebra of Continuous Function: If f and g are both continuous at x = c then i) f g , ii) f g , iii) f g [ provided g(c) 0 ] are continuous at x = c
Limits and Continuity -Theory -2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Limit Contion DifferDokument25 SeitenLimit Contion DifferSayan Kumar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit Fact SheetDokument1 SeiteLimit Fact Sheetbala1307Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7 - Continuity and Differentiability PDFDokument16 Seiten7 - Continuity and Differentiability PDFthinkiitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuty and DifferentibilyDokument7 SeitenContinuty and DifferentibilythinkiitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check Continuity of Functions and Determine DiscontinuitiesDokument3 SeitenCheck Continuity of Functions and Determine Discontinuitiesksr131Noch keine Bewertungen
- Limit & Continuity (New Handout)Dokument9 SeitenLimit & Continuity (New Handout)Siti Khadijah Mohd ZainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus I: Advanced Level Pure MathematicsDokument27 SeitenCalculus I: Advanced Level Pure Mathematicsmasyuki1979Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus Exercise LimitDokument5 SeitenCalculus Exercise LimitfrancisecabanogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits: Calculus Cheat SheetDokument7 SeitenLimits: Calculus Cheat SheetPratiksh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.6 One SidedLimits&ContinuityDokument4 Seiten1.6 One SidedLimits&Continuitybd87glNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07-Limit ContDokument15 Seiten07-Limit ContAnonymous BnbPSoovbNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Notes For AB and BCDokument16 SeitenFinal Notes For AB and BCsapabapjava2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- MATH1010 University Mathematics Supplementary ExerciseDokument24 SeitenMATH1010 University Mathematics Supplementary ExercisepklfpklfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits: Formal Approach To LimitDokument2 SeitenLimits: Formal Approach To LimitShubham DewanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: MTHE01P03Dokument12 SeitenMathematics: MTHE01P03Tarek AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 16th OctDokument51 SeitenClass 16th OctmileknzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit and Continuity PDFDokument28 SeitenLimit and Continuity PDFrahul_agrawal165Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Engineering Maths 2Dokument59 SeitenFundamental Engineering Maths 2Luong MgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus I: Unit 2: Limits of FunctionsDokument44 SeitenCalculus I: Unit 2: Limits of FunctionsTÂN NGUYỄN DUYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Maths Important Questions Limits and DerivativesDokument9 SeitenClass 11 Maths Important Questions Limits and DerivativesRoy67% (6)
- Unit 5 LimitsDokument10 SeitenUnit 5 LimitsbabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityDokument41 SeitenLimits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityAan SajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits Formulae Standard Formulae of LimitsDokument5 SeitenLimits Formulae Standard Formulae of Limitstesttry13Noch keine Bewertungen
- IB 11derivatives (52 59)Dokument3 SeitenIB 11derivatives (52 59)sam_punxtar16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Continuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberDokument8 SeitenContinuity and Differentiation: Points To RememberAakash ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTPDF3 The Derivatives Basic Differentiation Rules and The Chain Rule PDFDokument38 SeitenMTPDF3 The Derivatives Basic Differentiation Rules and The Chain Rule PDFLuis FonbuenaNoch keine Bewertungen
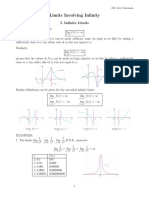
- Limits Involving InfinityDokument12 SeitenLimits Involving InfinityAde RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part I: Calculus: Chapter 2: LIMITSDokument38 SeitenPart I: Calculus: Chapter 2: LIMITSNguyễn ViệtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derivatives FormulasDokument5 SeitenDerivatives Formulas007phantomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knf1013 Week9 Differentiation Compatibility ModeDokument37 SeitenKnf1013 Week9 Differentiation Compatibility ModeSyura PisyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limit Esy Continui DadDokument18 SeitenLimit Esy Continui Dadlector_961Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Group C) : Matcts@nus - Edu.sgDokument23 Seiten(Group C) : Matcts@nus - Edu.sglzyabc597Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.3 Limit Rules and ExamplesDokument2 Seiten2.3 Limit Rules and ExamplesbillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 Continuity and DifferentiabilityDokument39 SeitenNCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 Continuity and DifferentiabilityVidyakulNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Continuity & DifferentiationDokument31 SeitenNCERT Continuity & Differentiationmastermohit1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 - Limits and ContinuityDokument20 SeitenChapter 10 - Limits and ContinuityAnkit PokhrelNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Mathematics and Physics, The University of QueenslandDokument1 SeiteSchool of Mathematics and Physics, The University of QueenslandVincent LiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics CalculusDokument11 SeitenMathematics CalculusAnish NaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 28 Continuity & Diffrentiability Part 1 of 1Dokument23 Seiten28 Continuity & Diffrentiability Part 1 of 1Mehul JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASCALC Lesson 1.1 - Limit of A FuncitonDokument82 SeitenBASCALC Lesson 1.1 - Limit of A FuncitonRaymond James OconerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calc Study PDFDokument7 SeitenCalc Study PDFRussell FromUpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foss Lecture3 AppendixDokument4 SeitenFoss Lecture3 AppendixJarsen21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Correct Answer Is B) Lim F (X)Dokument8 SeitenCorrect Answer Is B) Lim F (X)AneelaMalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limits Exercises With AnswersDokument17 SeitenLimits Exercises With Answersabd_93100% (3)
- Math 55 LE1 Reviewer NotesDokument6 SeitenMath 55 LE1 Reviewer NotesJc QuintosNoch keine Bewertungen
- M53 Lec1.4 ContinuityDokument49 SeitenM53 Lec1.4 Continuitykennethleo69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gabarito Aula3 AtualizadoDokument7 SeitenGabarito Aula3 AtualizadojoseleydysonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 01 Differentiation PDFDokument24 Seiten09 01 Differentiation PDFSri DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentiation Mod Theory eDokument14 SeitenDifferentiation Mod Theory eHussain AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 21-Analytic Geometry and Calculus: Iff X Is A Rational, For All X The Domain of F, Lim F (X) F (A)Dokument2 SeitenMath 21-Analytic Geometry and Calculus: Iff X Is A Rational, For All X The Domain of F, Lim F (X) F (A)Hanny Pearl S. CamerinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 8: Limits and Continuity-Intuitive ApproachDokument28 SeitenChapter - 8: Limits and Continuity-Intuitive ApproachaviralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 13 Newton Raphson MethodDokument30 SeitenLec 13 Newton Raphson MethodMuhammad Bilal Junaid100% (1)
- Basic Differentiation FormulasDokument6 SeitenBasic Differentiation FormulasRevathi AnbunesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 C O N I C S: ParabolaDokument6 Seiten5 C O N I C S: ParabolaDattatray NerkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Complex NumbersDokument10 Seiten3 - Complex NumbersDattatray NerkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- B y A X B y A X: Circle Parabola Ellipse HyperbolaDokument1 SeiteB y A X B y A X: Circle Parabola Ellipse HyperbolaDattatray NerkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Mathematical Logic: Statement: A Declarative Sentence Which Is Either True or False But Not Both Is Called ADokument4 Seiten1 Mathematical Logic: Statement: A Declarative Sentence Which Is Either True or False But Not Both Is Called ADattatray NerkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Equations and ExpDokument20 SeitenQuadratic Equations and ExpSundar LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EkwasionDokument17 SeitenEkwasionMarichu Pajaron100% (1)
- Maths Cheat Sheet PDFDokument1 SeiteMaths Cheat Sheet PDFDaniel SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allen: Number, Ranking & Ordering TestDokument10 SeitenAllen: Number, Ranking & Ordering TestAnant DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- MathSlov 50-2000-2 5Dokument10 SeitenMathSlov 50-2000-2 5mirceamercaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 1Dokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 1Ajay GMNoch keine Bewertungen
- JIMS TemplateDokument2 SeitenJIMS TemplateKresnha PangadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Krull-Akizuki Theorem in The AbstractDokument8 SeitenThe Krull-Akizuki Theorem in The AbstractMohamed KhalifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herstein Topics in Algebra Solution 5 5Dokument6 SeitenHerstein Topics in Algebra Solution 5 5NandhiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 TestDokument9 Seiten7 TestЕралы БегалыNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytic Equations: 4.1 Power SeriesDokument21 SeitenAnalytic Equations: 4.1 Power SeriesPop RobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- HXC2021 Trial S2Dokument7 SeitenHXC2021 Trial S2Gurukul AcademyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zero and Negative ExponentsDokument9 SeitenZero and Negative ExponentsGhlends Alarcio GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Oxford 1st Year Past PaperDokument4 SeitenMaths Oxford 1st Year Past PaperJammy44110% (1)
- Fuchs and The Theory of Differentian EquationsDokument26 SeitenFuchs and The Theory of Differentian EquationsSebastián Felipe Mantilla SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 6-Differentiation of Logarithmic and Exponential Functions FunctionsDokument30 SeitenLesson 6-Differentiation of Logarithmic and Exponential Functions FunctionsRegie SalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex ManifoldsDokument204 SeitenComplex Manifoldsrianlopes100% (2)
- Obstructions To Algebraizing Topological Vector BundlesDokument17 SeitenObstructions To Algebraizing Topological Vector BundlesThileni WickramaratneNoch keine Bewertungen
- InequalitiesDokument40 SeitenInequalitiesYhong BarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood, Sweat & TearsDokument6 SeitenBlood, Sweat & TearsSapphire SteeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Periodical - Math 10Dokument3 Seiten1st Periodical - Math 10Mitzi Marie AlojadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- OperationswithintegersDokument4 SeitenOperationswithintegersLedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Aptitude English Rs AggarwalDokument25 SeitenQuantitative Aptitude English Rs AggarwalkningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Questions and Answers MA (101) Mathematics TMJA CoorayDokument9 SeitenModel Questions and Answers MA (101) Mathematics TMJA CoorayRashan PeirisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To RadicalsDokument42 SeitenIntroduction To RadicalsJerwin Fusingan EdadezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech 1st Sem: Maths: Vector AlgebraDokument9 SeitenBtech 1st Sem: Maths: Vector AlgebraTechno India GroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powerpoint MathDokument10 SeitenPowerpoint MathKristell Alipio67% (6)
- Grade 6 Mathematics FinalDokument177 SeitenGrade 6 Mathematics FinalMary Jane Rayos CarpioNoch keine Bewertungen
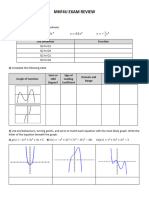
- Mhf4u Exam ReviewDokument29 SeitenMhf4u Exam ReviewJulia ZhouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 2.7 Nonlinear Inequalities: NameDokument4 SeitenSection 2.7 Nonlinear Inequalities: Namesarasmile2009Noch keine Bewertungen