Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
C&R
Hochgeladen von
Devina IreneOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
C&R
Hochgeladen von
Devina IreneCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
C&R 2 The selection of the equipment for an extraction process is influenced by the factors which are responsible for
limiting the extraction rate. Thus, if the diffusion of the solute through the porous structure of the residual solids is the controlling factor, the material should be of small size so that the distance the solute has to travel is small. On the other hand, if diffusion of the solute from the surface of the particles to the bulk of the solution is the controlling factor, a high degree of agitation of the fluid is required. There are four important factors to be considered: Particle size. Particle size influences the extraction rate in a number of ways. The smaller the size, the greater is the interfacial area between the solid and liquid, and therefore the higher is the rate of transfer of material and the smaller is the distance the solute must diffuse within the solid as already indicated. On the other hand, the surface may not be so effectively used with a very fine material if circulation of the liquid is impeded, and separation of the particles from the liquid and drainage of the solid residue are made more difficult. It is generally desirable that the range of particle size should be small so that each particle requires approximately the same time for extraction and, in particular, the production of a large amount of fine material should be avoided as this may wedge in the interstices of the larger particles and impede the flow of the solvent. Solvent. The liquid chosen should be a good selective solvent and its viscosity should be sufficiently low for it to circulate freely. Generally, a relatively pure solvent will be used initially, although as the extraction proceeds the concentration of solute will increase and the rate of extraction will progressively decrease, first because the concentration gradient will be reduced, and secondly because the solution will generally become more viscous. Temperature. In most cases, the solubility of the material which is being extracted will increase with temperature to give a higher rate of extraction. Further, the diffusion coefficient will be expected to increase with rise in temperature and this will also improve the rate of extraction. In some cases, the upper limit of temperature is determined by secondary considerations, such as, for example, the necessity to avoid enzyme action during the extraction of sugar. Agitation of the fluid. Agitation of the solvent is important because this increases the eddy diffusion and therefore the transfer of material from the surface of the particles to the bulk of the solution, as discussed in the following section. Further, agitation of suspensions of fine particles prevents sedimentation and more effective use is made of the interfacial surface.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
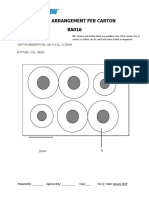
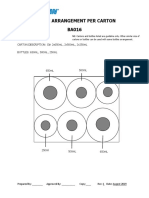
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA016: Carton Code: K1-20P2 CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 4X1.5L, 2X200ml BOTTLES: 1.5L, 200mlDokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA016: Carton Code: K1-20P2 CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 4X1.5L, 2X200ml BOTTLES: 1.5L, 200mlDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shah Alam: No. 5-2, Pusat Perdagangan One Puchong, Jalan OP 1/1 Off Jalan Puchong, 47160 Puchong, SelangorDokument1 SeiteShah Alam: No. 5-2, Pusat Perdagangan One Puchong, Jalan OP 1/1 Off Jalan Puchong, 47160 Puchong, SelangorDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottle Code Bottle Description FG Product Code FG Product Descriptions Formula Formula Desciptions Fill Vol (L) Bottles/PackDokument1 SeiteBottle Code Bottle Description FG Product Code FG Product Descriptions Formula Formula Desciptions Fill Vol (L) Bottles/PackDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA016: Carton Code: K1-20P2 CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 4X1.5L, 2X200ml BOTTLES: 1.5L, 200mlDokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA016: Carton Code: K1-20P2 CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 4X1.5L, 2X200ml BOTTLES: 1.5L, 200mlDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA016: Carton Code: K1-20P2 CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 4X1.5L, 2X200ml BOTTLES: 1.5L, 200mlDokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA016: Carton Code: K1-20P2 CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 4X1.5L, 2X200ml BOTTLES: 1.5L, 200mlDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA016: Carton Code: K1-20P2 CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 4X1.5L, 2X200ml BOTTLES: 1.5L, 200mlDokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA016: Carton Code: K1-20P2 CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 4X1.5L, 2X200ml BOTTLES: 1.5L, 200mlDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA010R01Dokument1 SeiteBA010R01Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
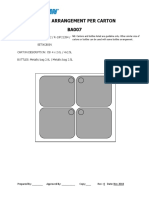
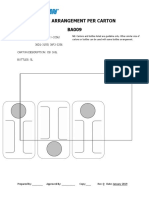
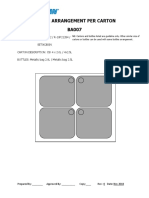
- BA007Dokument1 SeiteBA007Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment - :: EXPERIMENT 2.1. Colour and SmellDokument1 SeiteExperiment - :: EXPERIMENT 2.1. Colour and SmellDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
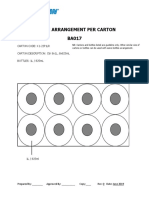
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA017: Carton Code: K1-22P1Lr CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 8x1L, 8x825mL BOTTLES: 1L / 825mLDokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA017: Carton Code: K1-22P1Lr CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 8x1L, 8x825mL BOTTLES: 1L / 825mLDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA010R01Dokument1 SeiteBA010R01Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA016R01Dokument1 SeiteBA016R01Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA010R01Dokument1 SeiteBA010R01Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA017: Carton Code: K1-22P1Lr CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 8x1L, 8x825mL BOTTLES: 1L / 825mLDokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA017: Carton Code: K1-22P1Lr CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 8x1L, 8x825mL BOTTLES: 1L / 825mLDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
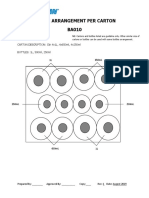
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA009Dokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA009Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA007Dokument1 SeiteBA007Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA017: Carton Code: K1-22P1Lr CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 8x1L, 8x825mL BOTTLES: 1L / 825mLDokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA017: Carton Code: K1-22P1Lr CARTON DESCRIPTION: CTN 8x1L, 8x825mL BOTTLES: 1L / 825mLDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google Keep Document PDFDokument1 SeiteGoogle Keep Document PDFDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bottle Arrangement Per Carton BA006Dokument1 SeiteBottle Arrangement Per Carton BA006Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Engineering AccountDokument2 SeitenSafety Engineering AccountDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEC 19 Full Report PDFDokument215 SeitenPEC 19 Full Report PDFDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poison Act 1952Dokument21 SeitenPoison Act 1952Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
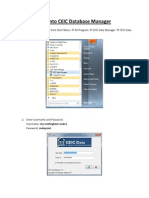
- How To Login Into CEIC Database ManagerDokument1 SeiteHow To Login Into CEIC Database ManagerDevina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0809Dokument4 Seiten0809Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- H83RED Exam Feedback Form 2011-2012Dokument2 SeitenH83RED Exam Feedback Form 2011-2012Devina IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Soil Texture and Soil StructureDokument24 SeitenSoil Texture and Soil StructureRaquel Bona Viñas100% (4)
- Dear White People Rhetorical AnalysisDokument9 SeitenDear White People Rhetorical AnalysisClaire LangenhorstNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFD - Driving Engineering ProductivityDokument5 SeitenCFD - Driving Engineering ProductivityBramJanssen76Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7qpg1a Ece Ec8701 Amwe Qb2Dokument2 Seiten7qpg1a Ece Ec8701 Amwe Qb2Gokul V100% (1)
- Petroleum Facilites of Germany 1945 112Dokument28 SeitenPetroleum Facilites of Germany 1945 112ENAK9000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Docit - Tips Contoh Manajemen Resikoxls Personal Protective EquipmentDokument12 SeitenDocit - Tips Contoh Manajemen Resikoxls Personal Protective EquipmentBambang SumantriNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLV JA3 Air Drain TrapDokument2 SeitenTLV JA3 Air Drain TrapMONANoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics of Power Generation Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Preparation For Competition Exams PDFDokument15 SeitenEconomics of Power Generation Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Preparation For Competition Exams PDFsalman bhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engg Colleges in TirunelveliDokument3 SeitenEngg Colleges in Tirunelveligpavi123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering CommunicationDokument1 SeiteEngineering CommunicationwowomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block Vibration TestDokument10 SeitenBlock Vibration TestMehedi Hasan50% (2)
- International MarketingDokument77 SeitenInternational MarketingSaki HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bobcat 853 Service Manual SN 512816001 Up Sn508418001 Up SN 509718001 UpDokument439 SeitenBobcat 853 Service Manual SN 512816001 Up Sn508418001 Up SN 509718001 UpEduardo Ariel Bernal80% (5)
- Transmission ALL U110824Dokument135 SeitenTransmission ALL U110824Екатерина КалашниковаNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIDIC Clause: Delegation of The Engineer'S Authority Revision: ? DateDokument6 SeitenFIDIC Clause: Delegation of The Engineer'S Authority Revision: ? DateTomoe GozenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bosch Lambda Sensor LSU 1 & 4.9Dokument10 SeitenBosch Lambda Sensor LSU 1 & 4.9Al CaracasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 425-3-Cooling Load-2007Dokument15 Seiten425-3-Cooling Load-2007zulkifroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agent-Based Modeling For Decision Making in Economics Under UncertaintyDokument20 SeitenAgent-Based Modeling For Decision Making in Economics Under UncertaintySammy SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyundai ManualDokument25 SeitenHyundai ManualDavor Profesor89% (18)
- Exposure Calculator Noise Level (L DB) Exposure Duration (Hours)Dokument2 SeitenExposure Calculator Noise Level (L DB) Exposure Duration (Hours)Gustavo AlcântaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- D601005184 Man 001Dokument17 SeitenD601005184 Man 001Riski Kurniawan100% (1)
- 004 - Hadoop Daemons (HDFS Only)Dokument3 Seiten004 - Hadoop Daemons (HDFS Only)Srinivas ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Organization Challenges of AgileDokument9 Seiten13 Organization Challenges of AgileroxrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abb Relays Catalouge PDFDokument180 SeitenAbb Relays Catalouge PDFABDUL GHAFOORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Earthing 8Dokument2 SeitenPipe Earthing 8raghavendran raghu75% (4)
- Quality Assurance in DialysisDokument11 SeitenQuality Assurance in DialysisHaribabu ArumugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pitting Trenching Activty eDokument2 SeitenPitting Trenching Activty eFARHA NAAZNoch keine Bewertungen
- PacketDokument10 SeitenPacketapi-248057958Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2016: Living From Your Center: Sanaya and Duane MessageDokument24 Seiten2016: Living From Your Center: Sanaya and Duane MessageELVIS100% (1)
- CV Equations Used in HysysDokument3 SeitenCV Equations Used in HysysBesan LaduNoch keine Bewertungen