Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Midterm Sample # 1 - GEO1111
Hochgeladen von
mhadd071Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Midterm Sample # 1 - GEO1111
Hochgeladen von
mhadd071Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Old Midterm #1 Questions
1.
Seismic velocity increases with:
1. 2. 3. 4.
depth and density liquid content compositional changes angle of reflection
2. 1. 2. 3. 4.
Cleavage of minerals is determined by its:
chemical composition internal arrangement of atoms/molecules hardness ability to form smooth crystal faces 3. Which of the following methods regarding the scientific method is true?
1. 2. 3. 4.
a hypothesis must be agreed upon by more than one scientist a theory is proved to be true, therefore may not be discarded a hypothesis cannot predict the outcome of scientific experiments a theory is a hypothesis that has withstood many scientific tests
4. 1. 2. 3. 4.
Sodium and calcium ions are similar in size and both have +1 charge. Therefore Na and Ca:
bond easily share electrons are polymorphs substitute for each other in minerals
5. 1. 2. 3. 4.
Oceanic crust is a modified strong and solid version of:
Mantle material Continental crust Oceanic sediments All of these
6. Cooling from a high-temperature molten state, Bowen theory predicts the last mineral group to crystallize in a magma: 1. 2. 3. 4. are framework silicates have coarse grain size are rich in calcium are the least resistant to weathering
7.
Which of the following is not a precursor to a volcanic eruption:
1. 2. 3. 4.
Increase in ground water temperature Increase in microseismicity Collapse of the caldera Bulging of topography
8. 1. 2. 3. 4.
In general, where would you expect the youngest tectonic plate material:
intraplate, hot spot spreading center mid-ocean ridge all of the above
9. 1. 2. 3. 4.
Most large-scale tectonic activity occurs:
at interior of beneath at boundaries of along the surface of
10. How can an intrusive sill be distinguished from an extrusive lava flow: 1. A sill is generally coarser-grained than a lava flow 2. Rocks above and below a sill will show evidence of heating, but only the rocks below a lava flow will show evidence of heating 3. Sills generally do not have vesicles, lava flows generally do have vesicles 4. All of these
11. In the rock record the preservation of crustal material is biased towards continental (not oceanic) material because:
1. 2. 3. 4.
oceanic crust is thicker continental crust is less dense continental crust is colder oceanic crust is weaker
12. How is heat primarily transmitted through the crust: 1. 2. 3. 4. radiation conduction convection advection
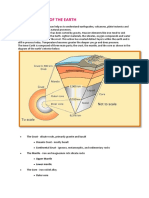
13. Which of the following statements regarding the layers of the Earth is true? 1. 2. 3. 4. lithosphere contains only the oceanic and continental crust asthenosphere overlies the lithosphere asthenosphere contains the oceanic crust and mantle lithosphere contains the crust and the upper part of the mantle
14. Vibrations of the Earth produced by rapid release of energy stored in rock subjected to stress is termed: 1. 2. 3. 4. eruption compression earthquakes extension
15. Viscous, air-borne material erupted from a volcano that contains little magma is called: 1. 2. 3. 4. ash flow eruption tephra lahar cinder cone
16. The asthenosphere is 1. 2. 3. 4. cool and strong cool and weak hot and strong hot and weak
17. The greatest volume of igneous rock is produced at: 1. 2. 3. 4. divergent plate margins convergent plate margins transform plate margins intraplate settings
18. Why do tectonic plates move: 1. 2. 3. 4. random drifting of continental crust on molten magma thermal convection within mantle electromagnetic pulses radiating from core all of the above
19. Chemical bonding that involves the loss or gain of valence electrons is termed: 1. 2. 3. 4. covalent bonding ionic bonding metallic bonding Van der Walls forces
20. The single most important characteristic controlling the explosiveness of an eruption is its viscosity, which is controlled by: 1. 2. 3. 4. composition of magma temperature of magma amount of dissolved gases within magma all of the above
21. Which description best corresponds to a granite: 1. 2. 3. 4. light-colored, fine-grained extrusive igneous rock rich in silica light-colored fine-grained intrusive igneous rock poor in silica light-colored, coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock rich in silica light-colored, coarse-grained extrusive igneous rock poor in silica
22. Which of the following help power the Earths heat engine: 1. radioactive decay 2. solar energy 3. igneous melting
4. geothermal energy
23. Which of the following statements about mineral chemistry is true? 1. 2. 3. 4. polymorphs have different structure and chemistry solid solution changes structure and chemistry solid solution changes structure and not chemistry polymorphs have different structure but same chemistry
24. According to Bowen, during crystallization of a magma, plagioclase feldspar:
1. 2. 3. 4.
is replaced by muscovite is replaced by quartz becomes richer in calcium becomes richer in sodium
25. How would you characterize ultramafic rocks and where do they come from?
1. 2. 3. 4.
rock that is rich in silica and comes from the mantle rock that is foliated and formed at convergent plate boundaries rock that is silica deficient and comes from the mantle rock that is intermediate in composition and comes from volcanic eruptions
26. Which description best corresponds to a basalt?
1. 2. 3. 4.
dark-colored, fine-grained intrusive igneous rock rich in silica dark-colored fine-grained extrusive igneous rock poor in silica dark-colored, coarse-grained intrusive igneous rock rich in silica dark-colored, coarse-grained extrusive igneous rock poor in silica
27. How would you characterize the eruption of a pyrhyolitic volcano: 1. 2. 3. 4. very explosive with much pyroclastic material quiet and effusive with pillow lavas explosive with viscous lavas rhyolite is an intrusive rock and does not form volcanoes
28. Give 4 definitive characteristics, which describe ice as a mineral. Ice is a naturally occurring mineral, has a crystalline structure, its solid when its cold outside, liquid when its hot, and has the same chemical composition.
29. Below is a diagram showing a crystalline structure of a specific group of minerals. What silicate system does it represent? What is the name of this mineral group? Give one evident physical property associated with this group of mineral that is a good reflection of its crystalline structure.
Double chained silicates, mineral group amphibole, evident physical property: cleavage
30. What is the fundamental difference between continental crust and continental lithosphere. Continental crust is a component of the lithosphere, main difference is strength. 31. P-waves and S-wave travel direction is controlled by:
1. 2. 3. 4.
density of the medium in which it is travelling reflection along boundaries of different mediums refraction at boundaries of different mediums all of the above
32. The P-wave shadow zone allowed for the discovery of what interior earth boundary?
1. 2. 3. 4.
core-mantle boundary crust-mantle boundary inner core-outer core boundary lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary 33. The Earths magnetic field is caused by: A. an offset of the cores rotational axis with respect to Earths rotation B. a large magma body near the North pole C. solar winds blowing charged particles towards the Earth D. liquid core flowing around solid inner core
34. In the Earth sciences, an assumption that the natural processes operating in the past are the same as those that can be observed operating in the present is the: A. Darwinian method B. plate tectonics C. principle of uniformitarianism D. none of the above 35. What scientific method involved the collection of data without regard for a model:
A. Inductive (Baconian) method B. Deductive (Darwinian) method C. Principle of uniformitarianism D. Pseudoscience 36. Which characteristics are used to classify igneous rocks: A. streak, hardness, luster B. mineralogy, streak, hardness C. texture, color, cleavage D. texture , mineralogy 37. Crystallizing at the Earths surface, you would expect mafic lava to be: A. coarse-grained with high SiO2 content B. coarse-grained with low SiO2 content C. fine-grained with high SiO2 content D. fine-grained with low SiO2 content 38. The basic structural building bloc of the majority of minerals is: A. silica tetrahedron B. carbon (diamond, graphite) C. Quartz D. primordial basalt 39. What is the logical geological/tectonic setting for a porphyritic rock of intermediate composition? What is the dominant source of the molten material? Based on its texture what is the extrusion or crystallization history of this rock? What would happen to the rock texture if it cooled more rapidly? 39. Porphyritic rock: crystals have different sizes. Larger crystals = phenocrysts are embedded in a matrix of fine crystals = groundmass. 2 cooling episodes caused the size discrepancy. Intermediate/andesitic composition is the consequence of partially molten mafic magma melting and intruding in felsic rock creates a type of magma of intermediate composition most often happens due to convergence of oceanic slabs wit continental plate lithospheric plate is lower in density and becomes subducted into the mantle partially molten magma of intermediate composition beings to rise due to thermal buoyancy in magma chamber very slow crystallization will cause large phenocrysts to form beneath Earths crust extruding to earths surface, magma undergoes fast crystallization which triggers the formation of finer crystals = groundmass even more rapid cooling microscopic crystals VERY rapid cooling formation of glass
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Midterm Sample # 2 - GEO1111Dokument7 SeitenMidterm Sample # 2 - GEO1111mhadd071100% (2)
- ERSC 1P01 Midterm 2016Dokument8 SeitenERSC 1P01 Midterm 2016Gurleen DhaliwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 - Tectonics and LandformsDokument20 SeitenChapter 14 - Tectonics and LandformsAsmawi Bin Abdullah100% (1)
- Part - I (MCQ) (Compulsory)Dokument2 SeitenPart - I (MCQ) (Compulsory)Fatima BabarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Engineering GeologyDokument84 SeitenIntroduction To Engineering GeologyTan U-ShangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 2Dokument2 SeitenEx 2Anyak2014Noch keine Bewertungen
- Encyclopedia of Astrobiology - ADokument136 SeitenEncyclopedia of Astrobiology - ALogan NorrellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 3 Simulation ActivityDokument12 SeitenProblem Set 3 Simulation Activityapi-182809945Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Preparation and Coating Inspection Report for Tasiast Tailings ThickenerDokument2 SeitenSurface Preparation and Coating Inspection Report for Tasiast Tailings ThickenerRekhis OussamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IsostasyDokument2 SeitenIsostasyarqianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsDokument4 SeitenRock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsJACKSON SANDERS-PUGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Study Guide Sedimentary and Stratigraphy SequenceDokument25 SeitenFinal Exam Study Guide Sedimentary and Stratigraphy SequenceTHỊNH NGUYỄN HÁNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microfacies Analysis Depositional Settings and ResDokument19 SeitenMicrofacies Analysis Depositional Settings and ResWaleed HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Sample # 3 - GEO1111Dokument7 SeitenMidterm Sample # 3 - GEO1111mhadd071100% (1)
- Quiz #2: Seismic Waves and Layers of the EarthDokument1 SeiteQuiz #2: Seismic Waves and Layers of the EarthJamayka Jessa Jebulan Evaristo100% (1)
- GEOG 111 FInal NotesDokument17 SeitenGEOG 111 FInal NotesappleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Earth's Layers Cuarto BásicoDokument23 SeitenUnit 2 Earth's Layers Cuarto BásicoConstanza FillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 WeatheringDokument21 Seiten8 Weatheringnayvalente11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Mechanics Ass2 March 2017 1Dokument3 SeitenSoil Mechanics Ass2 March 2017 1ErDKushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock properties and mechanicsDokument5 SeitenRock properties and mechanicsElyssa Michelle Caringas MicuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Test Submission: Assignment #3 - Solar System ConceptsDokument7 SeitenReview Test Submission: Assignment #3 - Solar System ConceptsTeo Sok Hui100% (1)
- 5 - Folds, Faults & UnconformityDokument30 Seiten5 - Folds, Faults & Unconformitymoorpvr100% (1)
- Shearing Forces and Bending MomentsDokument12 SeitenShearing Forces and Bending Momentsjacob ellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsDokument4 SeitenRock Cycle Assessment Test ResultsJuno PajelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eesa06 MC Test Ch1-4Dokument9 SeitenEesa06 MC Test Ch1-4Minyan ZhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 WeatheringDokument25 Seiten3.1 WeatheringSipu GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adama Science and Technology UniversityDokument7 SeitenAdama Science and Technology UniversityLidet DinkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ©geobuddy - Net/Jrf, Gate/Gsi: InstructionsDokument9 Seiten©geobuddy - Net/Jrf, Gate/Gsi: InstructionsyunusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Mujtaba, Depositional & Diagenetic Environments of Carbonates of Chorgali Formation. PH.D ThesisDokument194 SeitenDr. Mujtaba, Depositional & Diagenetic Environments of Carbonates of Chorgali Formation. PH.D ThesisMuhammad Raiees Amjad100% (4)
- Geosphere and GeochemistryDokument20 SeitenGeosphere and GeochemistrygengkapakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Final Exam NotesDokument14 SeitenGeology Final Exam NotesKuhoo UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial PDFDokument37 SeitenTutorial PDFEber GamboaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Geology Questions and AnswersDokument33 SeitenEngineering Geology Questions and AnswersGovind Shriram Chhawsaria100% (1)
- Introduction To Petroleum GeologyDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To Petroleum Geologyابوالحروف العربي ابوالحروفNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Geology About Malekhu AreaDokument65 SeitenReport On Geology About Malekhu Areabimal0% (1)
- Brief Idea of Silicate Structure of Rock Forming MineralsDokument28 SeitenBrief Idea of Silicate Structure of Rock Forming MineralsMounika NallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Groundwater Hydrogeology ExplainedDokument97 SeitenGroundwater Hydrogeology ExplainedKazi Shihab ShahriarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eesa06 Lecture Notes Lec1 Lec7 EESA06 2018Dokument15 SeitenEesa06 Lecture Notes Lec1 Lec7 EESA06 2018RAYYAN ADEELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geomorphology Notes by Swagat PradhanDokument51 SeitenGeomorphology Notes by Swagat PradhanDanis KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is soil made of and how does it formDokument3 SeitenWhat is soil made of and how does it formHanzel Asuncion LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Geol 2nd Edition Reed Wicander DownloadDokument14 SeitenTest Bank For Geol 2nd Edition Reed Wicander DownloadChristine TiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mineralogy and Crystallography MCQDokument40 SeitenMineralogy and Crystallography MCQAmit RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Sciences MCQsDokument2 SeitenEarth Sciences MCQsRaheem Ullah KakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structures Favouring Groundwater Movement and OccurrenceDokument22 SeitenStructures Favouring Groundwater Movement and OccurrencecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Stones, Their Properties and TestsDokument9 SeitenTypes of Stones, Their Properties and TestsJitender Kumar100% (1)
- Asx Announcement: Drilling Results From Eloise DeepsDokument13 SeitenAsx Announcement: Drilling Results From Eloise Deepsenaobona shopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vikram University MSC Geology CBCS SyllabusDokument20 SeitenVikram University MSC Geology CBCS SyllabusSelim RezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Public Service CommissionDokument4 SeitenFederal Public Service CommissionMustafa KhattakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geochemistry Interview Questions and Answers 1931 PDFDokument12 SeitenGeochemistry Interview Questions and Answers 1931 PDFpeterjo raveloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ternary Phase DiagramsDokument40 SeitenTernary Phase Diagramsviky kava100% (1)
- 3.1 Weathering and SoilsDokument21 Seiten3.1 Weathering and SoilsjjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEOPHYSICS TWO MARKSDokument9 SeitenGEOPHYSICS TWO MARKSArunodhaya NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and The Other Terrestrial WorldsDokument27 SeitenChapter 10 Planetary Atmospheres: Earth and The Other Terrestrial WorldsEdwin ChuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz #2Dokument2 SeitenQuiz #2Raphonzel AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iit-Jam Geology Free Solved PaperDokument23 SeitenIit-Jam Geology Free Solved Paperpankaj_mbmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Geology Questions and AnswersDokument5 SeitenEngineering Geology Questions and Answerssingh khan100% (1)
- Petrology Document SummaryDokument15 SeitenPetrology Document SummaryTricia Ann DesturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9Dokument20 SeitenLecture 9briceboris100% (1)
- Geology IN - Mid-Ocean Ridge Basalts (MORB), Oceanic Crust and Ophiolites PDFDokument3 SeitenGeology IN - Mid-Ocean Ridge Basalts (MORB), Oceanic Crust and Ophiolites PDFpranowo_ibnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcaniclastic Sediments - Composition, Classification and DiagenesisDokument45 SeitenVolcaniclastic Sediments - Composition, Classification and DiagenesisDavid A. Cuéllar100% (3)
- Environmental LithosphereDokument44 SeitenEnvironmental LithosphereRichard II RemisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geology Review - FinalDokument10 SeitenGeology Review - FinalstephenpilsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report: ME2151-2 MetallographyDokument4 SeitenLab Report: ME2151-2 Metallographyandy100% (1)
- A10VO Regulator Teory PDFDokument45 SeitenA10VO Regulator Teory PDFmohammad100% (2)
- Army Public School Bhopal: TOPIC:-" "Dokument20 SeitenArmy Public School Bhopal: TOPIC:-" "Gourav Pathariya100% (1)
- Phono Par PDFDokument8 SeitenPhono Par PDFvranceanu.ovidiu-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- GHS COMPLIANT LABELDokument2 SeitenGHS COMPLIANT LABELsemeneh haile100% (1)
- SR 6898 1 Tevi de Otel PDFDokument1 SeiteSR 6898 1 Tevi de Otel PDFCRISTIAN SILVIU IANUCNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Institute of Public Health and The Environment, PO Box 1, 3720 BA Bilthoven, The Netherlands. Tel. 31-30-2749111, Fax. 31-30-2742971Dokument23 SeitenNational Institute of Public Health and The Environment, PO Box 1, 3720 BA Bilthoven, The Netherlands. Tel. 31-30-2749111, Fax. 31-30-2742971Saras Unggul UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linx Duct Friction CalculatorDokument12 SeitenLinx Duct Friction CalculatorLeonardo Martinho DobrianskyjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Light Weight ConcreteDokument14 SeitenDevelopment of Light Weight ConcreteAmit ChouguleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Wet Lab PDFDokument4 SeitenScience Wet Lab PDFMalachi MillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylinder Design Standards WSNZDokument5 SeitenCylinder Design Standards WSNZjamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd International Conference On The Advancement of Materials and Nanotechnology 2013 - ICAMN III 2013Dokument5 Seiten3rd International Conference On The Advancement of Materials and Nanotechnology 2013 - ICAMN III 2013Khairol Anuar MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Cell Division and Cell Communication UnitDokument6 SeitenUnit 4 Cell Division and Cell Communication Unitapi-237676607Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hempel NORSOK Coating Systems: NORSOK M-501: Frequently Asked QuestionsDokument1 SeiteHempel NORSOK Coating Systems: NORSOK M-501: Frequently Asked Questionspiscesguy78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tool Wear MechanismDokument9 SeitenTool Wear MechanismDevansh AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filled Bulb Temperature Sensors Learning Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDokument4 SeitenFilled Bulb Temperature Sensors Learning Instrumentation and Control Engineeringmohamed abourayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ginger CandyDokument8 SeitenGinger CandyRizka Arifani Kromodimedjo100% (2)
- Engineering Design Guideline Separator Vessel Rev01Dokument28 SeitenEngineering Design Guideline Separator Vessel Rev01Yan Laksana50% (4)
- How To Conduct Bunker Survey - Marine Surveyor InformationDokument1 SeiteHow To Conduct Bunker Survey - Marine Surveyor InformationgustavoseseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitoring of BioprocessDokument41 SeitenMonitoring of BioprocessSandiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F2 = 30 kNm)2/4) 70 × 109 N/m2Dokument11 SeitenF2 = 30 kNm)2/4) 70 × 109 N/m2Don ValentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class X Science Question PaperDokument24 SeitenClass X Science Question PaperKalpna RaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CaseStudy2 WindmillDokument8 SeitenCaseStudy2 WindmillAnthony BergemannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gasoline Composition Determined by 1H NMR SpectrosDokument7 SeitenGasoline Composition Determined by 1H NMR SpectrosabdulganijNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cassini Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer (Inms) InvestigationDokument119 SeitenThe Cassini Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer (Inms) InvestigationDima FontaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- JR Elite& AIIMS S60 NEET WET - 14 (14-11-23) SyllabusDokument1 SeiteJR Elite& AIIMS S60 NEET WET - 14 (14-11-23) SyllabussindhukarnikapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sika RepDokument2 SeitenSika Repthe pilotNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Finite Element AnalysisDokument32 SeitenFor Finite Element AnalysisZhenhe SongNoch keine Bewertungen