Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DS
Hochgeladen von
Trixie Al MarieOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DS
Hochgeladen von
Trixie Al MarieCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
-1Image
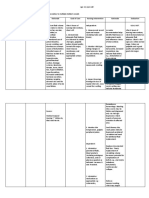
Generic Name Brand Name Classific ation Indicatio n Action
Ciprofloxacin Cipro Fluoroquinolone. Anti-infective A fluoroquinolone that inhibits the enzyme DNA gyrase in susceptible bacteria, interfering with bacterial cell replication. Therapeutic Effect: Bactericidal. 500mg tab BID PO Hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin or other quinolones; vaccinia, varicella, epithelial herpes simplex, keratitis, mycobacterial infection, fungal disease of ocular structure, use after uncomplicated removal of a foreign body. FREQUENT (5%U2%): Nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, vomiting, constipation, flatulence, confusion, crystalluria Superinfection (especially enterococcal or fungal), nephropathy, cardiopulmonary arrest, chest pain, and cerebral thrombosis may occur. Hypersensitivity reactions, including photosensitivity (as evidenced by rash, pruritus, blisters, edema, and burning skin), have occurred in patients receiving fluoroquinolones. Arthropathy may occur if the drug is given to children younger than 18 years. Sensitization to the ophthalmic form of the drug may contraindicate later systemic use of ciprofloxacin.
Dosage Contrain dication
Side effects Adverse effects
Nursing responsi bilities
BASELINE ASSESSMENT Question for history of hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin, quinolones. INTERVENTION/EVALUATION Evaluate food tolerance. Determine pattern of bowel activity. Monitor for dizziness, headache, visual changes, tremors. Assess for chest, joint pain. Ophthalmic: Observe therapeutic response. PATIENT/FAMILY TEACHING Do not skip doses; take full course of therapy. N Take with 8 oz water; drink several glasses of water between meals. N Eat and drink high sources of ascorbic acid (cranberry juice, citrus fruits) to prevent crystalluria. N Do not take antacids (reduces/destroys effectiveness). N Shake suspension well before using; do not chew microcapsules in suspension. N Sugarless gum or hard candy may relieve bad taste. N Ophthalmic: Explain possibility of crystal precipitate forming, usual resolution in 1U7 days.
Source
Saunders Nursing Drug Handbook 2007, and 2008
Image
Generic Name Brand Name Classificatio n Indication
Paracetamol Perfalgan Analgesic, muscle relaxant Relief to mild moderate pain, treatment of fever
Action
Decreases fever by inhibiting the effects of pyrogens on the hypothalamic heat regulating centers and by a hypothalamic action leading to sweating and vasodilation. Relieves pain by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis at the CNS but does not have anti-inflammatory action because of its minimal effect of peripheral prostaglandin synthesis. 600 mg IVTT then 300 mg IVTT q4 for T= 38 C Hypersensitivity; intolerance to tartazine (yellow dye #5), alcohol, table sugar, saccharine. Stimulation, drowsiness, nausea and vomiting, rash, cyanosis Hepatic seizure, renal failure, neutripenia, leucopenia, hemolytic anemia, Tell patient to read label on other OTC drugs advise patient to avoid taking more than one product containing paracetamol at one at a time. Advise patient to avoid alcohol, acute poisoning with liver damage may result, acute toxicity includes symptoms of nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. Teach patient to recognize signs of chronic overdose, malise, fever, sore throat. Inform patient that urine may become dark brown as result of phenecetin.
Dosage Contraindica tion Side effects Adverse effects Nursing responsibiliti es
Source
Drug Guide for Nurses Daviss
Image
Generic Name Brand Name Classificatio n Indication
Etericoxib ARCOXIA COX-2 inhibitor, non-steroidal antiinflammatory and antirheumatic products, coxibs. This medication is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), prescribed for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and gouty arthritis.
Action Dosage Contraindica tion Side effects 120 mg tab OD for pain Contraindicated in patients with peptic ulcer, severe heart disease, stroke, and hypersensitivity. Central Nervous System - Headache, dizziness, nervousness, depression, drowsiness, insomnia, vertigo and ringing in the ear. Heart - Chest pain, high blood pressure and fluid retention. Metabolic - Taste disturbances, mouth ulcer, loss of appetite and weight loss. Miscellaneous - Kidney damage, fever, GI disorders, muscle pain and influenza-like syndrome. GI disorders; ischemic cardiac events; hypersensitivity reactions, headache, dizziness, nervousness, depression, drowsiness, insomnia, vertigo, tinnitus, photosensitivity; blood disorders, fluid retention, hypertension; dry mouth, taste disturbance, mouth ulcers; appetite and wt changes; chest pain, fatigue, paraesthesia, influenza-like syndrome, myalgia. Renal toxicity.
Adverse effects
Nursing responsibiliti es
Assessment Before administering Celebrex, nurses must assess patients for any contraindications (factors or symptoms that indicate a treatment is not advised). Contraindications for the use of Celebrex include pregnancy, asthma and hypersensitivity to aspirin, iodides, other NSAIDs and sulfonamides. Celebrex is also contraindicated for the treatment of pain immediately before and after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Celebrex can cause several serious side effects including heart attack, stroke, high blood pressure, kidney failure, bleeding, anemia, liver failure and allergic reactions. Other side effects include stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, heartburn, nausea, vomiting and dizziness. Nurses should be aware of these side effects and should regularly assess for signs and symptoms of these conditions in patients undergoing Celebrex therapy. Administration Nurses must teach patients how to take Celebrex properly. In addition, they also must alert patients to the potential side effects of the drug. Celebrex should be taken with food or milk to lessen the chance of gastric upset. Patients should be taught never to crush, dissolve or chew this medication and to never exceed the prescribed dose as deaths have occurred. Patients also should be taught to discontinue Celebrex use and contact their physician if they have any gastrointestinal symptoms such as bloody stools or cramping. Bleeding, fatigue or bruising also should be reported. Patients experiencing difficulty breathing, chest pain, slurred speech or partial paralysis should seek immediate emergency assistance. Celebrex is often discontinued before surgery. Therefore patients should consult their physician before undergoing any surgical procedures. Evaluation Patients undergoing therapy with Celebrex should be evaluated on an ongoing basis to determine the efficacy of treatment. Signs that a patient is responding properly to treatment include decreased pain and inflammation. During the evaluation process, patients also should be assessed for side effects. If side effects are present, the patient's physician should be notified to determine if the benefits of treatment outweigh the symptoms or risks involved.
Read more: Nursing Responsibilities in Administering Celebrex | eHow.com http://www.ehow.com/list_6776858_nursing-responsibilities-administeringcelebrex.html#ixzz1ts3KL4YP
Source
http://www.medindia.net/doctors/drug_information/etoricoxib.htm#ixzz1t rzhaA2d
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- XVII. Health Teaching/RecommendationDokument2 SeitenXVII. Health Teaching/RecommendationTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- XVI. Nursing Care Plan 2Dokument2 SeitenXVI. Nursing Care Plan 2Trixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- XVI. Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenXVI. Nursing Care PlanTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Reaction Paper On Movie: A Beautiful MindDokument4 SeitenA Reaction Paper On Movie: A Beautiful MindTrixie Al Marie100% (2)
- XII. Doctors OrderDokument5 SeitenXII. Doctors OrderTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- X. SymptomatologyDokument1 SeiteX. SymptomatologyTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIII. Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenVIII. Anatomy and PhysiologyTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- IV. Family BackgroundDokument2 SeitenIV. Family BackgroundTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- IX. EtiologyDokument2 SeitenIX. EtiologyTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- V. Developmental DataDokument6 SeitenV. Developmental DataTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Male DisorderDokument2 SeitenMale DisorderTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vii RecDokument4 SeitenVii RecTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcknowledgementDokument1 SeiteAcknowledgementTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthermia NCPDokument3 SeitenHyperthermia NCPkaylejordan_29100% (2)
- Laennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDokument2 SeitenLaennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyTrixie Al Marie100% (3)
- Skull, Scalp & Hair: Physical Assessment Is AnDokument10 SeitenSkull, Scalp & Hair: Physical Assessment Is AnTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For HemothoraxDokument12 SeitenNCP For Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (1)
- NCP HemothoraxDokument3 SeitenNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Community Health Nursing Principles - CHN PrinciplesDokument2 SeitenCommunity Health Nursing Principles - CHN PrinciplesTrixie Al MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Common Medical Surgical MedicationsDokument36 SeitenCommon Medical Surgical MedicationsAshley Etheredge100% (1)
- Antibiotics and Their Types, Uses, Side EffectsDokument4 SeitenAntibiotics and Their Types, Uses, Side EffectsSpislgal PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Study 2Dokument3 SeitenDrug Study 2Adrienne GarlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FluroquinolonesDokument29 SeitenFluroquinolonestummalapalli venkateswara rao0% (1)
- Prescribing Antibiotics and Analgesics in ChildrenDokument4 SeitenPrescribing Antibiotics and Analgesics in ChildrenPreetam PatnalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 - Urological Infections - LR PDFDokument106 Seiten18 - Urological Infections - LR PDFSandraYulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ciprofloxacin Induced Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDokument8 SeitenCiprofloxacin Induced Systemic Lupus ErythematosusAvelox FloxNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemotherapyDokument253 SeitenChemotherapyalmskein100% (1)
- Pharmacology Test 3 Drug ListDokument32 SeitenPharmacology Test 3 Drug ListSHRIKANTNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTS COPD Updated Action Plan Editable PDFDokument12 SeitenCTS COPD Updated Action Plan Editable PDFLorensia Fitra DwitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2006 4266b1!01!03 Ketek Briefing DocumentDokument186 Seiten2006 4266b1!01!03 Ketek Briefing Documentbmartindoyle6396Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Chapter 9: Antibiotics: AminoglycosidesDokument7 Seiten1 Chapter 9: Antibiotics: AminoglycosidesWendy EscalanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rovamycin 3868 DR 1256036243912Dokument6 SeitenRovamycin 3868 DR 1256036243912Ahmed El AlfyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lower Limb Tendinopathies Etiology, Biology and Treatment-Springer International (2016)Dokument202 SeitenThe Lower Limb Tendinopathies Etiology, Biology and Treatment-Springer International (2016)Tony Miguel Saba Saba100% (1)
- Evaluation of The Clinical Efficacy of Marbofloxacin (Zeniquin) Tablets For The Treatment of Canine Pyoderma - An Open Clinical TrialDokument7 SeitenEvaluation of The Clinical Efficacy of Marbofloxacin (Zeniquin) Tablets For The Treatment of Canine Pyoderma - An Open Clinical TrialjenNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Are Odontogenic Infections Best ManagedDokument5 SeitenHow Are Odontogenic Infections Best ManagedNurfidini AzmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treating Osteomyelitis: Antibiotics and Surgery: BackgroundDokument11 SeitenTreating Osteomyelitis: Antibiotics and Surgery: BackgroundCarolina MachadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Notes On Antibiotics - Emtyazology Book 2nd EditionDokument18 SeitenPractical Notes On Antibiotics - Emtyazology Book 2nd EditionmajdNoch keine Bewertungen
- 019537s082 020780s040lbl PDFDokument43 Seiten019537s082 020780s040lbl PDFShahab Ud DinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Fixed Dose Combination of Cefixime and Ofloxacin PDFDokument8 SeitenEvaluation of Efficacy and Safety of Fixed Dose Combination of Cefixime and Ofloxacin PDFAlyn Paul EmnacenNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTI Guidelines IDSA 2010Dokument18 SeitenUTI Guidelines IDSA 2010Ati'ul Ma'rifah HambalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.20140209 Question PaperDokument16 Seiten2.20140209 Question PaperdrpnnreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fapas Food Chemistry Programme 2016Dokument48 SeitenFapas Food Chemistry Programme 2016Vishal SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia 1Dokument15 SeitenCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia 1Jaime BarraganNoch keine Bewertungen
- PANRE and PANCE Review Antimicrobial PharmacologyDokument27 SeitenPANRE and PANCE Review Antimicrobial PharmacologyThe Physician Assistant Life100% (2)
- Final 1 - 4Dokument53 SeitenFinal 1 - 4Wgr SampathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry ProjectDokument11 SeitenChemistry ProjectRhythm's PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ofloxacin and Ornidazole TabletsDokument4 SeitenOfloxacin and Ornidazole TabletsSonal Kasbe100% (1)
- Drug Study 1Dokument4 SeitenDrug Study 1bibet_martijaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patzakis Open Fracture Management PDFDokument15 SeitenPatzakis Open Fracture Management PDFNurul AtiahNoch keine Bewertungen