Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BASIC Report
Hochgeladen von
valfleiOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BASIC Report
Hochgeladen von
valfleiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
FEMFAT 4.
8 - BASIC
User Manual
2.10.2
How its done
Report
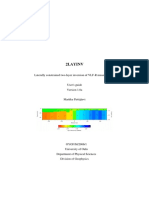
Here the information to be contained in the report file can be specified in more detail. The default setting is output of all information. If all possible entries are disabled the file will remain empty. The report file, which is saved with the *.pro (for protocol) extension, is an ASCII file and can be read and printed from any text editor program. Manual file name input must be confirmed using RETURN, otherwise FEMFAT will not save the information.
Report file *.pro
Figure 77 Analysis report data-entry screen
Two result records per surface node are sent to the report file, as soon as a boundary layer analysis is performed on the node. The first result record is with regard to the analysis using a porous base material, the second result record is with regard to the analysis using a pore-free boundary layer material. 2.10.2.1 Reportfile
All important data accumulated during calculation of the S/N curves, damage, stress redistribution, etc., are saved in the FEMFAT report file. The data
Page 125
FEMFAT 4.8 - BASIC
User Manual
saved in this file allow you to understand the analysis step for step at a later date. Header The report header contains information on the current FEMFAT version and short information on the analysis parameters. General input data Here it is possible to obtain information on the current analysis (e.g.: amplitude and mean stress records and load spectra etc.). Specimen material data Activation of material specimen data output leads to all data of all materials used being written clearly and concisely to the report file. Separate output of the material data to a different file can be achieved using "Material data". Status of influence factors on S/N curve The S/N curve status display offers an overview of the influence factors activated for the analysis. This simplifies control and documentation of the operational strength analysis.
New
Additionally, the file names of the FEM entities, stresses, load spectra and materials used in the analysis are exported to the report file.
2.10.2.2
Structural node data
Using this menu item information output for selected or for all of the analyzed nodes, with regard to the individual influence parameters, can be switched on or off dependent on the protocol output filter. Shell top and bottom damage values/safety factors Here, output of calculated total damage and endurance limit or static overload safety factors can be activated or deactivated. Damage analysis results at shell elements can be given for both sides of the shell. With 3D element nodes the data output command for the shell bottom data are ignored. Shell top and bottom maximum damage component Output of the amplitude and the mean stress class follows for the rainflow matrix spectrum step (= matrix element) which supplies the largest damage component, together with the corresponding number of load cycles and the stress levels at the analyzed nodes. Moreover, the following output follows for this load spectrum:
Page 126
FEMFAT 4.8 - BASIC
User Manual
o Amplitude stress: total stress tensor and equivalent stress after von Mises, and maximum and minimum principal normal stress at the investigated nodes. o Mean stress: total stress tensor and equivalent stress after von Mises, and maximum and minimum principal normal stress at the investigated nodes. o Fatigue strength, slope and endurance cycle limit of the calculated component S/N curve: local component S/N curve calculated for this load spectrum matrix element at the investigated node. Top and bottom stress gradient Output of the relative stress gradients determined in the analysis can be requested. Output of the relative stress gradient at the shell top and bottom if the node in question is a shell element corner node. With 3D element nodes, the relative stress gradient output command for the shell bottom data are ignored. Shell top and bottom mean stress redistribution tensor Output of the mean stress redistribution equivalent stress is only active concurrently with the FEMFAT PLAST program module. This tensor corresponds to the generated residual stress at the investigated nodes for the load spectrum matrix element with the largest damage value, if the linear range of the cyclic stabilized material law has been exceeded at these nodes when processing the load spectrum. Surface roughness The user-defined surface roughness at the node in question is exported to the report file. Technological parameter Activation of this parameter leads to output of the wall thickness taken into consideration for the analysis. At shell element nodes this wall thickness is determined from the neighboring elements, at 3D element nodes the userdefined wall thickness is used. Tempering condition Output of the user-defined tempering condition at the nodes in question, i.e. the given tensile strength, is performed. This tempering condition information is only relevant if a tempered steel (material class 16) was defined at the node in question and the influence parameter "Tempering condition" was enabled. Temperature influence The operating temperature defined at the nodes is exported to the FEMFAT report file if this check box is activated.
Page 127
FEMFAT 4.8 - BASIC
User Manual
2.10.2.3 Relative stress limit
Because of output of the node-referenced result data to the report file, bulky files may be produced during analysis of large models. The analysis duration is also noticeably extended by the large amount of write operations. Since one is generally only interested in detailed information on highly stressed regions of the entity, FEMFAT provides the option of restricting nodereferenced protocol output to these regions. You have two concrete options: The number of nodes in the active group in the analysis is kept small. In this case the analysis time is also automatically minimized. The practical difficulty here is that at the time of group creation (in the respective preprocessor or in the "Groups" menu item) the highly stressed areas are often not known or can only be collected in a group with difficulty. In addition to this, "white areas" occur during graphical visualization at those nodes that do not belong to the analysis group. However, care must also be exercised with this type of reduction: For flawless gradient creation a node layer and two element layers must be added around the region of interest. The node row is necessary for correct calculation of the gradient at the boundary of the region of interest and the second element layer for calculation of the correct stresses in this additional node row. The more elegant solution is use of a filter. A "relative stress limit" must be given, with which the node is analyzed but no node-referenced result data exported to the report file. The stress limit is always with reference to the local material fatigue strength. The filter default value is set to 90% when the program is started. That is, nodes with a maximum amplitude stress smaller than 90% of the local material fatigue strength are not exported to the report file. Output to the output file and graphical visualization of the results is not suppressed. In practice, this filter is recommended in combination with the analysis filter for reducing analysis times with large models (see the "Analysis parameters" menu item).
Page 128
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Guide to Using CAESAR II Software for Stress AnalysisDokument83 SeitenGuide to Using CAESAR II Software for Stress AnalysisSaúl Mendoza100% (5)
- Introduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15Von EverandIntroduction to the simulation of power plants for EBSILON®Professional Version 15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metamorphic Rocks ImagesDokument7 SeitenMetamorphic Rocks Imagesapi-289985616100% (1)
- AWC SDPWS2015 Commentary PrintableDokument52 SeitenAWC SDPWS2015 Commentary PrintableTerry TriestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inflatable Packers enDokument51 SeitenInflatable Packers enDavid LuhetoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatfree User ManualDokument33 SeitenFatfree User ManualLit Phen TuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blade-St: The Complete Steam Turbine Blade Analysis ToolDokument8 SeitenBlade-St: The Complete Steam Turbine Blade Analysis Toolramnadh803181Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Stress Analysis by Computer CAESAR II PDFDokument11 SeitenPipe Stress Analysis by Computer CAESAR II PDFAbhijeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrepreneurship WholeDokument20 SeitenEntrepreneurship WholeKrizztian SiuaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- SJ Mepla Manual Program EngDokument57 SeitenSJ Mepla Manual Program EngCuong HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsVon EverandArduino Measurements in Science: Advanced Techniques and Data ProjectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Usfos UM 08Dokument10 SeitenUsfos UM 08Preetham PjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhead Door Closers and Hardware GuideDokument2 SeitenOverhead Door Closers and Hardware GuideAndrea Joyce AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC - Patran Results PrimerDokument138 SeitenMSC - Patran Results PrimeralfredaoudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITSCM Mindmap v4Dokument1 SeiteITSCM Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backpropagation: Fundamentals and Applications for Preparing Data for Training in Deep LearningVon EverandBackpropagation: Fundamentals and Applications for Preparing Data for Training in Deep LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- C79 Service Kit and Parts List GuideDokument32 SeitenC79 Service Kit and Parts List Guiderobert100% (2)
- Zond-MT 1D: User GuideDokument25 SeitenZond-MT 1D: User GuideEmRan LeghariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens Power System Simulation For Engineers® (Pss/E)Dokument15 SeitenSiemens Power System Simulation For Engineers® (Pss/E)Dms8sa8INoch keine Bewertungen
- 2layinv ManuDokument12 Seiten2layinv ManuAdides Gidson SimanjuntakNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACTEDRMedeso Weld Fatigue V1802Dokument42 SeitenACTEDRMedeso Weld Fatigue V1802alpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulase DesignerDokument9 SeitenSimulase Designerdeepalakshmi chandrasekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequency of Simulation Results File WritingDokument4 SeitenFrequency of Simulation Results File WritingpotriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision HistoryDokument9 SeitenRevision HistoryalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Nec 2Dokument81 Seiten4 Nec 2ag1tatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF Explorer For Windows DRAFT Documentation - Calibration Data FilesDokument3 SeitenRF Explorer For Windows DRAFT Documentation - Calibration Data Filesagga2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Nec 2Dokument81 Seiten4 Nec 2Joze VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4nec2 ManualDokument79 Seiten4nec2 ManualAmador Garcia IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinbeam Design Software: General UseDokument5 SeitenSinbeam Design Software: General Usexerxes92005Noch keine Bewertungen
- MAUD Tutorial - Hippo Texture Analysis Wizard: 1 Introduction and PurposeDokument11 SeitenMAUD Tutorial - Hippo Texture Analysis Wizard: 1 Introduction and PurposeRicardinho T Aureliano Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Utomatic Ynamic Ncremental Onlinear Nalysis: ADINA System 8.7 Release NotesDokument25 SeitenUtomatic Ynamic Ncremental Onlinear Nalysis: ADINA System 8.7 Release NotesCarlos Gustavo MéndezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SiLENSe 5.1 ReleaseNotesDokument10 SeitenSiLENSe 5.1 ReleaseNotesPawan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSYS numerical and finite element analysis labDokument56 SeitenANSYS numerical and finite element analysis labMuthulakshmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 D Frame Truss Analysis HelpDokument33 Seiten2 D Frame Truss Analysis HelpJose Antonio Alegria RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 87 TwofltDokument5 Seiten87 TwofltMourad BenderradjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Download H64RFP project file and start ADS designDokument15 SeitenDownload H64RFP project file and start ADS designakeedtheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Res 1 DDokument7 SeitenRes 1 DDeokumar Lachhman100% (1)
- Prota - Post Analysis ProcessesDokument4 SeitenProta - Post Analysis ProcessesA KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fea Lab Manual PDFDokument57 SeitenFea Lab Manual PDFKrishna Kalyan100% (1)
- Abaqus Analysis User's ManualDokument82 SeitenAbaqus Analysis User's ManualAbhishek ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multipactor Manual 160Dokument35 SeitenMultipactor Manual 160Sergei_V_7521Noch keine Bewertungen
- TELEMAC Code InstructionsDokument24 SeitenTELEMAC Code Instructionsjdj2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arc FlashDokument26 SeitenArc Flashmohamed_elhadadNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATPDraw 5 User Manual UpdatesDokument51 SeitenATPDraw 5 User Manual UpdatesdoniluzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial GIS WATERDokument18 SeitenTutorial GIS WATERMohammad Risky NaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kiefner & Associates, Inc. Pipe Assessment Spreadsheet DocumentationDokument8 SeitenKiefner & Associates, Inc. Pipe Assessment Spreadsheet DocumentationkmprabhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trans Basic ConceptsDokument13 SeitenTrans Basic ConceptsSakshi AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ls Dyna PaperDokument10 SeitenLs Dyna PaperSaw RexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated Instructions For CNSA SolverDokument9 SeitenUpdated Instructions For CNSA Solvermattcs90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Framecad-Bs En1991-13-2006Dokument11 SeitenFramecad-Bs En1991-13-2006Aie BantuganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 NFT Application GuideDokument57 Seiten8 NFT Application GuideSuleman JahangirNoch keine Bewertungen
- MESYS Shaft Calculation GuideDokument28 SeitenMESYS Shaft Calculation GuideZoebairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap10pdprop Pt4Dokument25 SeitenChap10pdprop Pt4leobalmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW11.0.120-HWDesktop ReleasenotesDokument62 SeitenHW11.0.120-HWDesktop ReleasenotesAltairKoreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 NGubeljakDokument6 Seiten06 NGubeljakvahid_shoeibiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 19 FEM Global LocalDokument22 SeitenExercise 19 FEM Global LocalMining HarsantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Readme ATPDrawDokument6 SeitenReadme ATPDrawPalmer DionicioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1SP02 EMC32 DataReduction V1Dokument46 Seiten1SP02 EMC32 DataReduction V1AndreeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 156 - Understanding Dynamic Random AnalysesDokument20 Seiten156 - Understanding Dynamic Random AnalysesSameOldHatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric Reentry Trajectory OptimizationDokument30 SeitenAtmospheric Reentry Trajectory OptimizationAnonymous REw1YIq4q7Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2DRing FragmentO Instructions PDFDokument5 Seiten2DRing FragmentO Instructions PDFCarlos Manuel Urpi MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patch Antenna Design Using MICROWAVE STUDIO: 2. Simulation WorkflowDokument4 SeitenPatch Antenna Design Using MICROWAVE STUDIO: 2. Simulation Workflowhoiyen92Noch keine Bewertungen
- Caesar IIDokument26 SeitenCaesar IIasokkNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversVon EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Test Strategies for 2D/3D Integration for NoC-based Multicore ArchitecturesVon EverandDesign and Test Strategies for 2D/3D Integration for NoC-based Multicore ArchitecturesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spouses Mariano Z. Velarde and Avelina D. VELARDE, Petitioners, vs. COURT OF Appeals, David A. RAYMUNDO and GEORGE RAYMUNDO, RespondentsDokument11 SeitenSpouses Mariano Z. Velarde and Avelina D. VELARDE, Petitioners, vs. COURT OF Appeals, David A. RAYMUNDO and GEORGE RAYMUNDO, RespondentsRobyn JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH2070 Computer Project: Organise Porject FoldDokument4 SeitenMATH2070 Computer Project: Organise Porject FoldAbdul Muqsait KenyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Aeronautics BoardDokument2 SeitenCivil Aeronautics BoardJayson AlvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electrical Design of A PLC Panel (Wiring Diagrams) - EEPDokument6 SeitenBasic Electrical Design of A PLC Panel (Wiring Diagrams) - EEPRobert GalarzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec - Ray Theory TransmissionDokument27 SeitenLec - Ray Theory TransmissionmathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- John GokongweiDokument14 SeitenJohn GokongweiBela CraigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between OS1 and OS2 Single Mode Fiber Cable - Fiber Optic Cabling SolutionsDokument2 SeitenDifference Between OS1 and OS2 Single Mode Fiber Cable - Fiber Optic Cabling SolutionsDharma Teja TanetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bob Duffy's 27 Years in Database Sector and Expertise in SQL Server, SSAS, and Data Platform ConsultingDokument26 SeitenBob Duffy's 27 Years in Database Sector and Expertise in SQL Server, SSAS, and Data Platform ConsultingbrusselarNoch keine Bewertungen
- B3 Zoning Diagram, Atlantic Yards/Pacific ParkDokument4 SeitenB3 Zoning Diagram, Atlantic Yards/Pacific ParkNorman OderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salary Slip Oct PacificDokument1 SeiteSalary Slip Oct PacificBHARAT SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- MSBI Installation GuideDokument25 SeitenMSBI Installation GuideAmit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Altitude Compensator Manual 10-2011Dokument4 SeitenHigh Altitude Compensator Manual 10-2011Adem NuriyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broker Name Address SegmentDokument8 SeitenBroker Name Address Segmentsoniya_dps2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Discretionary Lending Power Updated Sep 2012Dokument28 SeitenDiscretionary Lending Power Updated Sep 2012akranjan888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentos de Medición y Herramientas de Precisión Starrett DIAl TEST INDICATOR 196 A1ZDokument24 SeitenInstrumentos de Medición y Herramientas de Precisión Starrett DIAl TEST INDICATOR 196 A1Zmicmarley2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- People vs. Ulip, G.R. No. L-3455Dokument1 SeitePeople vs. Ulip, G.R. No. L-3455Grace GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bancassurance Black Book Rahul 777-2Dokument62 SeitenBancassurance Black Book Rahul 777-2Shubham ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Thi Chuyen Hai Duong 2014 2015 Tieng AnhDokument4 SeitenDe Thi Chuyen Hai Duong 2014 2015 Tieng AnhHuong NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- E2 PTAct 9 7 1 DirectionsDokument4 SeitenE2 PTAct 9 7 1 DirectionsEmzy SorianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric Bursting StrengthDokument14 SeitenFabric Bursting StrengthQaiseriqball100% (5)
- TX Set 1 Income TaxDokument6 SeitenTX Set 1 Income TaxMarielle CastañedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Management: Nestlé's Approach To Green Management 1. Research and DevelopmentDokument6 SeitenGreen Management: Nestlé's Approach To Green Management 1. Research and DevelopmentAbaidullah TanveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yamaha Nmax 155 - To Turn The Vehicle Power OffDokument1 SeiteYamaha Nmax 155 - To Turn The Vehicle Power Offmotley crewzNoch keine Bewertungen