Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
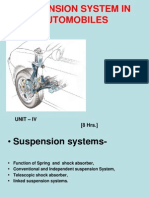
Body Construction
Hochgeladen von
Vaibhav Vithoba NaikOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Body Construction
Hochgeladen von
Vaibhav Vithoba NaikCopyright:
There are two distinct forms of frame construction in common use: 1.
The conventional pressed sheet frame to which all mechanical units are attached and on which the body is superimposed Body on Frame Construction 2. Frameless construction in which the body structure is so designed as to combine the functions of body and frame.
1. Body on Frame Construction
Body-on-frame is an old automobile construction technology. Mounting a separate body to a rigid frame which supports the drivetrain, engine, suspension etc. was the original method of building automobiles, and its use continues to this day. The original frames were made of wood (commonly ash), but steel ladder frames became common in the 1930s. The transmission system, powerplant, suspension, steering, wheels etc. are mounted on the frame on which body is finally mounted. The body is held to the chassis frame by a no. of body bolts passing through the base of the body and frame. This method is the traditional way of construction. Body-on-frame remains the preferred construction method for heavyduty commercial vehicles, especially those which are intended to carry and pull heavy loads, such as SUVs and trucks. They may be semi hand built as production on flow production lines is difficult.
Advantages of Body on Frame Construction
The body need not contribute to the overall strength of the vehicle. Body style variations are easier and cheaper with this form of construction. Body repair work is easier and cheaper. It can be easily altered Only possible construction for heavy vehicles
Disadvantages
As body is mounted on the chassis, body is along for the ride. Beams need depth and mass for rigidity therefore heavy in construction. Since it is a 2-D structure, torsional rigidity is very much low. Cannot be made completely on flow production lines.
2. Frameless/Unitary Construction
Evolution of design produced a body sufficiently robust to carry all the units which had earlier been held by frame. The unit consists of a no. of pressed sheet panels which are set up in a frame-work to hold them in the correct positions. The pressings are joined by either electric flash welding or spot welding. This all steel construction was introduced so that a separate frame can be eliminated. When suitably designed the body sheet is capable of withstanding various stresses without bracing. The thickness of the sheet metal depends on stress to be taken by the panels. Suitable stiffening and strengthening sections are placed at points of maximum load such as engine and suspension mountings. The entire unit can be made strong by using longitudinal and lateral members so that it would be able to carry the mechanical components and so do away with the separate frame. All the automobile components like powerplant, final drive, suspension, steering etc. are mounted on the body and bracing can be done by longitudinal or lateral members. In some cases a separate sub frame is used to mount engine and suspension.
Advantages of Unibody Construction
Reduced cost when manufactured in large nos. Light in weight due to absence of separate frame, therefore improved vehicle performance and fuel saving. Less weight therefore less inertia so accelerating and braking is quick. Lower body position may be obtained i.e. C.G remains close to ground thus resulting in increased stability. In this case the stresses are more evenly distributed over the whole assembly instead of being confined to the limited space of skeleton. Less body rattle and squeaks Greater rigidity.
Disadvantages
Reduction of strength due to lack of frame. Economical only for mass production
Repair in case of damage is complicated and expensive It restricts the types of bodies to certain extent.
The frame has therefore disappeared from the make-up of the quantity produced car finding a place only in larger vehicles and those vehicles which are more individually produced.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Audi Q7 4MB 4M 2015-2017 Service ManualDokument8.540 SeitenAudi Q7 4MB 4M 2015-2017 Service Manualpeter11100% (1)
- Garelli Clymer ManualDokument121 SeitenGarelli Clymer ManualLucas LorandiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Transmission - Lecture Notes CompleteDokument156 SeitenAutomotive Transmission - Lecture Notes CompleteAkshay PundeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVT BikeDokument4 SeitenCVT BikeSurajJereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Suspension System Power Point PresentationDokument30 SeitenActive Suspension System Power Point PresentationJAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrail Safety Question and AnswerDokument20 SeitenIndustrail Safety Question and AnswerVaibhav Vithoba Naik89% (19)
- Bleo HolmDokument4 SeitenBleo HolmperrychemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercedes-Benz Engine OM 471 PDF ManualDokument225 SeitenMercedes-Benz Engine OM 471 PDF Manualabdulrahman elsaied100% (5)
- Cummins China 6BT5.9 G2Dokument5 SeitenCummins China 6BT5.9 G2Sbastian100% (4)
- Vehicle FrameDokument17 SeitenVehicle FrameashokkdesignNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chasis DesignDokument19 SeitenChasis DesignTANMAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Transmission - NotesDokument34 SeitenAuto Transmission - Notesvandanaharikumar100% (2)
- Steering System AEDokument46 SeitenSteering System AEShubham GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Whom It May ConcernDokument96 SeitenTo Whom It May ConcernKamal SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gearboxes ClassDokument35 SeitenGearboxes ClassNaveen Vachipalli100% (1)
- Front Axle & Steering SystemsDokument35 SeitenFront Axle & Steering SystemsVishnu Rajeswaran100% (1)
- Final Drive and DifferentialDokument9 SeitenFinal Drive and DifferentialVasantha SeelanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheel-Balancing SSOUDokument14 SeitenWheel-Balancing SSOUSumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Front Wheel DriveDokument24 SeitenFront Wheel DriveHamnuren ManabilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Double Wishbone Suspension System of BAJA VehicleDokument8 SeitenDesign of Double Wishbone Suspension System of BAJA VehicleSai Krishna SKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suspension DynamicsDokument30 SeitenSuspension DynamicsZoscalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication of Four Wheel Steering SystemDokument14 SeitenFabrication of Four Wheel Steering SystemRenju PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open DifferentialDokument7 SeitenOpen DifferentialMikael Bezerra Cotias Dos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering SystemDokument37 SeitenSteering SystemSandeep Magapu100% (1)
- Be Sem 8 Automobile Engineering NotesDokument75 SeitenBe Sem 8 Automobile Engineering NotesVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (7)
- Automobile Differential Unit FinalDokument25 SeitenAutomobile Differential Unit FinalSyed Zain100% (1)
- Design of Clutch Plate For Light Motor Vehicle NewDokument14 SeitenDesign of Clutch Plate For Light Motor Vehicle NewKedar BardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SychromeshDokument19 SeitenSychromeshManny AnacletoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suspension System in AutomobilesDokument27 SeitenSuspension System in AutomobilesJainul PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaf SpringDokument34 SeitenLeaf SpringjonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted byDokument34 SeitenSeminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted bySouraj PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Drum Brake SystemDokument1 SeiteChapter 4 Drum Brake Systemvijendra1125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Transmission: Clutch and Gear BoxDokument28 SeitenAutomotive Transmission: Clutch and Gear BoxMohan100% (1)
- Classification of Chassis Mte1Dokument12 SeitenClassification of Chassis Mte1Ryan CalicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 TTWDokument67 SeitenUnit 4 TTWMohsin EngrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automobile Engineering in Brakes Lecture NotesDokument3 SeitenAutomobile Engineering in Brakes Lecture NotesraamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Steering Vs Manual SteeringDokument2 SeitenPower Steering Vs Manual SteeringShashank ChheniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Steering SystemsDokument36 SeitenAutomotive Steering SystemsDineshBirdi67% (3)
- Mech Disc BrakesDokument19 SeitenMech Disc BrakesAKHIL KUSHWAHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Study and Analysis of Disk Brake SystemDokument30 SeitenStudy and Analysis of Disk Brake SystemzahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- AT6602 - Chassis Component DesignDokument14 SeitenAT6602 - Chassis Component Designpavanrane100% (3)
- Assignment ClutchDokument624 SeitenAssignment ClutchSubhash KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drive ShaftDokument8 SeitenDrive ShaftAkshat SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPLETE Report (Braking Department)Dokument30 SeitenCOMPLETE Report (Braking Department)Dinie Abdullah ZamawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suspention SystemDokument25 SeitenSuspention SystemraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Pneumatic BrakesDokument14 SeitenHydraulic Pneumatic Brakesabyzen100% (1)
- TyreDokument24 SeitenTyrepRAMOD g pATOLENoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering SystemDokument15 SeitenSteering SystemSatya NarayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DifferentialDokument12 SeitenDifferentialRaghul PrasaathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vehicle Dynamics Course Plan 2019Dokument11 SeitenVehicle Dynamics Course Plan 2019Girish ChandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Wheels & Tyres Final ADokument17 Seiten06 Wheels & Tyres Final Aanishsukumar000gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Roll Bar or Stabilizer and AnglesDokument13 SeitenAnti Roll Bar or Stabilizer and AnglesPavan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brake Dynamics Lesson PDFDokument29 SeitenBrake Dynamics Lesson PDFapi-293844827Noch keine Bewertungen
- ClutchDokument22 SeitenClutchIsaiah LuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRAKESDokument46 SeitenBRAKESDianna MadejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering System and TyresDokument32 SeitenSteering System and TyresFraolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layout of Chassis & Types of Drives of AutomobilesDokument12 SeitenLayout of Chassis & Types of Drives of Automobilesrajmeha67% (3)
- Cone Clutch: Definition, Diagram, Working, Uses (With PDF)Dokument3 SeitenCone Clutch: Definition, Diagram, Working, Uses (With PDF)sameerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 7 Suspension SystemsDokument25 SeitenChap 7 Suspension Systemszetseat100% (2)
- A Technical Seminar On: Suspension SystemDokument24 SeitenA Technical Seminar On: Suspension SystemRanjan suvarnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Optimization of Two Wheeler (Bike) ChassisDokument5 SeitenDesign Optimization of Two Wheeler (Bike) ChassisPrakash KatdareNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Clutches WorkDokument8 SeitenHow Clutches WorkSachenderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automobile Chasis: Project OnDokument41 SeitenAutomobile Chasis: Project OnSai CoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No 1 AutomobileDokument4 SeitenExperiment No 1 Automobiledimpesh silarpruiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex1 LabDokument6 SeitenEx1 LabRamesh Kavitha Sanjit 18BME0677Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Modern Chassis: A Practical Manual of Automotive Chassis and Suspension DesignVon EverandThe Modern Chassis: A Practical Manual of Automotive Chassis and Suspension DesignBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- 16.04.2019 Fire Traingle and Its Importance.Dokument1 Seite16.04.2019 Fire Traingle and Its Importance.Vaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (1)
- 22.04.2019 - Confined Space A Dangerous SpaceDokument1 Seite22.04.2019 - Confined Space A Dangerous SpaceVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- DO's and DON'Ts Working in Confined SpaceDokument1 SeiteDO's and DON'Ts Working in Confined SpaceVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (3)
- 19 UlabourlawshbDokument197 Seiten19 UlabourlawshbSaipramod JayanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18.04.2019 Type of Fire ExtinguisherDokument1 Seite18.04.2019 Type of Fire ExtinguisherVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (2)
- Interview: Safety Officers & SupervisorsDokument25 SeitenInterview: Safety Officers & SupervisorsVaibhav Vithoba Naik0% (1)
- 3.05B - Mock Drill Report - DISH 10.03.14Dokument4 Seiten3.05B - Mock Drill Report - DISH 10.03.14Vaibhav Vithoba Naik88% (8)
- 1Dokument54 Seiten1Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safeguard of W Omen and C Hildren Provisions in Standard Bidding DocumentDokument23 SeitenSafeguard of W Omen and C Hildren Provisions in Standard Bidding DocumentVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.05A - Onsite Emergency Plan - Rev 10 - 2013Dokument47 Seiten3.05A - Onsite Emergency Plan - Rev 10 - 2013Vaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety While Working On PipelinesDokument6 SeitenSafety While Working On PipelinesVaibhav Vithoba Naik0% (1)
- THERMODYNAMICSDokument12 SeitenTHERMODYNAMICSVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 .Basic KinematicsDokument24 SeitenModule 1 .Basic KinematicsVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- P 4 (1 05) PSI Plant Safety Inspection (35) Jul.2012Dokument35 SeitenP 4 (1 05) PSI Plant Safety Inspection (35) Jul.2012Vaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (9)
- Safety in Working at HeightDokument106 SeitenSafety in Working at HeightVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (12)
- Fundamentals and Types of MechanismDokument60 SeitenFundamentals and Types of MechanismVaibhav Vithoba Naik88% (8)
- Module 1 .Basic KinematicsDokument24 SeitenModule 1 .Basic KinematicsVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straight Line Motion Mechanisms OldDokument28 SeitenStraight Line Motion Mechanisms OldVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (4)
- Theory of MachineDokument21 SeitenTheory of MachineVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering System (Notes On Tom)Dokument8 SeitenSteering System (Notes On Tom)Vaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (1)
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDokument21 SeitenSecond Law of ThermodynamicsVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lathe MachineDokument34 SeitenLathe MachineVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (1)
- Engine SensorsDokument6 SeitenEngine SensorsVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faults in Grinding WheelDokument2 SeitenFaults in Grinding WheelVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials and FinancialDokument267 SeitenMaterials and Financials9894035903100% (1)
- GateDokument6 SeitenGateParveen SwamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansys ManualDokument59 SeitenAnsys ManualVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (3)
- NVHDokument1 SeiteNVHVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (1)
- An Efficient Generic Method For Calculating The Properties of Combustion ProductsDokument13 SeitenAn Efficient Generic Method For Calculating The Properties of Combustion ProductsCarlos Gilberto Villamar LinaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- BR Aeam50 004 - 201210 PDFDokument16 SeitenBR Aeam50 004 - 201210 PDFSabahNoch keine Bewertungen
- T&T Petroleum SystemsDokument111 SeitenT&T Petroleum SystemsDanny Dukeran100% (1)
- UNIT-I (Engine Construction) .Ppt2Dokument47 SeitenUNIT-I (Engine Construction) .Ppt2dhavalNoch keine Bewertungen
- J66Dokument4 SeitenJ66chhoan_nhunlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GG 8335 BelarraDokument12 SeitenGG 8335 BelarraJavi LucciNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethanol Production PidDokument18 SeitenEthanol Production PidCyduck GuevarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minipak 6 AtexdatasheetDokument6 SeitenMinipak 6 AtexdatasheetSaravanan MathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irrigation PumpsDokument36 SeitenIrrigation PumpsLopez Larry John P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vortec 4 3L v-6 Industrial - SFLBDokument3 SeitenVortec 4 3L v-6 Industrial - SFLBAlan FernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cummins NTA855-G1Dokument5 SeitenCummins NTA855-G1Franyusmid Gómez BolivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chevrolet Caprice - 062942Dokument9 SeitenChevrolet Caprice - 062942Abdul RhaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AvK DIG 156Dokument1 SeiteAvK DIG 156Galih Trisna NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 250kva Cummins Diesel Generator Silent TypeDokument7 Seiten250kva Cummins Diesel Generator Silent TypeThumula FernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liebherr LR 1200Dokument24 SeitenLiebherr LR 1200Shailesh KhodkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEW Equivalent Products TableDokument1 SeiteDEW Equivalent Products TableednsmnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic NotesDokument31 SeitenThermodynamic NotesraminabkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Balance Estimation For OilDokument4 SeitenMaterial Balance Estimation For OilPraveen Ran SubheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Drum Vibratory Rollers: BW124-40 SeriesDokument4 SeitenSingle Drum Vibratory Rollers: BW124-40 SeriesVlad SuteuNoch keine Bewertungen
- S70me-C8 5Dokument406 SeitenS70me-C8 5Xahid HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dacia Logan 1 5 Dci 85 DEFGBDokument5 SeitenDacia Logan 1 5 Dci 85 DEFGBBorborean Andrei TiberiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Feasibilty Study of Development of A Gas Fired Termal Power Facility in Sheberghan Volume 1Dokument54 Seiten1 Feasibilty Study of Development of A Gas Fired Termal Power Facility in Sheberghan Volume 1Nana Silvana AgustiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marine Engines ABATO WeichaiDokument14 SeitenMarine Engines ABATO Weichaiarf89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vessel & Facility Management: RefuellingDokument4 SeitenVessel & Facility Management: RefuellingMohamedNoch keine Bewertungen