Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pa Tho Physiology - Type 1 Diabetes (Hanieyah Guro)
Hochgeladen von
Hanya Bint PotawanOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pa Tho Physiology - Type 1 Diabetes (Hanieyah Guro)
Hochgeladen von
Hanya Bint PotawanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
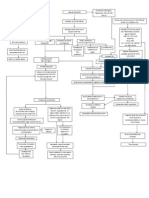
CNS Symptoms: (Moderate) Inability to concentrate Headache, Lightheadedness Confusion Memory lapses, Numbness of the lips and tongue,
Slurred speech, Impaired coordination, Emotional changes Irrational or combative behavior Double vision Drowsiness CNS Symptoms: (Severe) Disoriented behavior Seizures Difficulty arousing from Sleep Loss of consciousness
Idiopathic
Genetic: HLA DR3 and DR4
Age: <30 years old
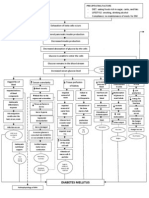
TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
Metabolic demand is increased Virus/Toxins Adrenergic Symptoms: (Mild) Sweating Tremor Tachycardia, Palpitation, Nervousness Hunger Autoimmune disorder Pathogenesis Serum Islet Cell Antibdies Immune system attacks self Manifestations Acute Complication Destruction of -cells of the Islet of Langerhans Serum C-peptide Levels Absolute Insulin Deficiency
`
LEGEND
Etiologic Factors Drug Therapy Surgical Management Diagnostic Test Nursing Diagnosis
Whole Pancreas Transplant Islet Cell Transplants Decreased Insulin Production
Chronic Complications
Pramlintide (Symlin)
Hypoglycemia (Glucose: < 60 mg/dl)
Insulin Therapy Decreased utilization of glucose by muscle, fat and liver Fatigue r/t decreased metabolic energy production
HbA1c Test (>8%) FBG Test (>126 mg/dl) OGT Test (>200 mg/dl)
Polyphagia
Cell Starvation
Hyperglycemia
Increased Lipolysis
Slow wound healing Weight loss
Proteolysis
Increased Gluconeogenesis
Increased Glycolysis
Glucose above threshold of renal tubules (>200mg/dl)
Formation of sugar-containing plasma proteins (fibrinogen, clotting factors, etc)
Glucose binds to HbA
Glucose reduced to Sorbitol (in cells with aldosereductase)
Increased Fatty Acids in circulation
Increased Amino Acids in circulation
Glucose production Glucosuria Urinalysis Ketone: (+) Glucose: (+5) Yeast Infections Increased susceptibility to infection Osmotic Diuresis Increased clotting tendency
HbA1c formation
Increased VLDL
Increased production of ketone bodies
Formation of Advanced Glycation End (AGE) products
O2 is less readily released to the periphery Thrombosis Polyuria Hyponatremia Hypokalemia Hypochloremia Dry mucous membrane Poor skin turgor Dry, scaly skin Thin, brittle hair & nails Polydipsia Fatigue Increase Temperature
Accumulates in the lens of the eye
Accumulates in schwann cells and neurons
Acidosis
AGEs binds to call membrane receptors
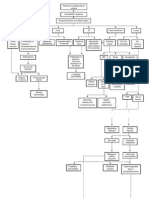
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS
Increased loss of water and electrolytes
Fluid and electrolyte imbalance r/t increased urine output
Impaired lenticular transparency
Reduced nerve conduction
Increased H+ and CO2
Deposition of collagen in blood vessels Serum Test Glucose: >300 mg/dl Ketones: (+) pH: >7.35 HCO3: <15mEq/L Na+: low K+ : low BUN: >20 mg/dl Creatinine: >1.5 mg/dl Urine Ketones: (+)
Water shifts from the ICF space to the ECF space
Impaired sin integrity r/t dehydration Hyperthermia r/t decreased body fluids Decreased cardiac output r/t decreased blood volume
Cataract
Polyneuropathy
Increased rate and depth of respiration
Reduced permeability and luminal narrowing
Sodium Bicarbonate Dehydration
Blurred Vision
Numbness tingling sensation
Kussmaul Respiration Metabolic Acidosis
MICROANGIOPATHY Ischemia of small blood vessels
Hyperosmolarity/Hyperviscosity
Hypovolemia
Weak, thready peripheral pulse
Risk for injury r/t altered sensory perceptions
Cell shrinkage Retinopathy Nephropathy Neuropathy
Slow blood flow
Ischemia
RAAS Mechanism
Hypertension
ABG pH: <7.35 PaCo2: >35 HCO3: <22
Impairement of cell lymphocytes Blindness Loss of glomerulos Increased susceptibility to infection Ris for infection r/t decreased leukocyte function
Cyanosis Nail Clubbing
Hypoxia
Ineffective tissue perfusion r/t decreased arterial flow/ less readily release of O2 to the periphery
Anaerobic metabolism
cell necrosis
Lactic Acid production Acute pain r/t increased lactic acid production
gangrene MACROANGIOPATHY
ESRD
Muscle Spasm Headache
Debridement Renal Artery Stenosis Cerebrovascular Disease Coronary Artery Disease Peripheral Vascular Disease
COMA Impaired tissue integrity r/t hypoxia
Cerebral Infarction Altered LOC Brain Damage
Myocardial Infarction
Congestive Heart Failure
DEATH
Presented by: HANIEYAH GRANDE GURO
Multiple Organ Failure
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDokument3 SeitenIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- Chronic Renal FailureDokument3 SeitenChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDokument6 SeitenPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDokument1 SeiteDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Lab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Dokument9 SeitenLab Values Chart That Includes What Each Abnormal Might Indicate (Nursing)Linsey Bowen75% (8)
- Pathophysiology of DMDokument4 SeitenPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP: Chronic Renal FailureDokument14 SeitenNCP: Chronic Renal FailureJavie77% (13)
- Pathophysiology R2Dokument1 SeitePathophysiology R2Sydelle GravadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideVon EverandNursing: Lab Values: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schizophrenia UndifferentiatedDokument88 SeitenSchizophrenia UndifferentiatedHanya Bint Potawan75% (4)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDokument1 SeiteImpaired Skin IntegrityHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument2 SeitenImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASA 2018 Catalog WebDokument48 SeitenASA 2018 Catalog WebglmedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PatoDokument3 SeitenPatoJohn BisnarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jaundice: Common Bile Duct Hindrance To Bile Flow Manifests With Jaundice, Fever, PainDokument7 SeitenJaundice: Common Bile Duct Hindrance To Bile Flow Manifests With Jaundice, Fever, PainRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDokument11 SeitenNursing Care Plan Renal Failurenosevad88850% (2)
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDokument1 SeiteAcute GlomerulonephritisChinita SangbaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case of LeptospirosisDokument60 SeitenCase of LeptospirosisNoreen Cala-MayubayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusDokument3 SeitenPa Tho Physiology of Diabetes MellitusPong's Teodoro SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Renal Failure-7Dokument5 SeitenChronic Renal Failure-7GERA SUMANTHNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypothyroidismDokument43 SeitenHypothyroidismRama Krishnan100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of DMDokument5 SeitenPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Anemia Gravis: Kepaniteraan Ilmu Penyakit DalamDokument24 SeitenAnemia Gravis: Kepaniteraan Ilmu Penyakit DalamNerissaArvianaShintaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Left Sided Heart FailureDokument25 SeitenLeft Sided Heart FailurePaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemophilia Muscle Pain ManagementDokument26 SeitenHemophilia Muscle Pain Managementufjn4nfogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative NamesDokument67 SeitenAlternative NamespashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDokument1 SeitePathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Kesadaran MenurunDokument58 SeitenModul Kesadaran MenurunfwzmuhdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Factors and Pathophysiology of StrokeDokument4 SeitenRisk Factors and Pathophysiology of StrokeSherlyn KirisakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute ComplicationsDokument14 SeitenAcute ComplicationsGideon HaburaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationDokument39 SeitenPediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationRaghavendra DoddamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burn PathoDokument1 SeiteBurn PathoArlan AbraganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitochondrial DisordersDokument21 SeitenMitochondrial DisordersAtifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thyrotoxicosis PDFDokument17 SeitenThyrotoxicosis PDFBharat JamodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Manifestation and Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases & Overview of Parasitic Infections in AdultDokument20 SeitenClinical Manifestation and Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases & Overview of Parasitic Infections in AdultRiris SutrisnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shock PresentationDokument21 SeitenShock Presentationapi-283170120Noch keine Bewertungen
- Disease of Adrenal Gland: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, KemdDokument57 SeitenDisease of Adrenal Gland: Dr. Fatimah Eliana, SPPD, KemdDeby Tri Widia LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTD1Dokument1 SeiteCTD1David HosamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic BrainDokument48 SeitenOrganic BrainAalia RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic: StateDokument18 SeitenHyperosmolar Hyperglycaemic: StateRizki Rudwi PradestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etiology: I. Predisposing FactorDokument12 SeitenEtiology: I. Predisposing FactorIbcp SalvacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDokument3 SeitenCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyElmer Balgos Alinsog50% (4)
- Fluid/Electrolytes & Acid Base Balance: Michael Jenifer RN, MSN PathophysiologyDokument74 SeitenFluid/Electrolytes & Acid Base Balance: Michael Jenifer RN, MSN PathophysiologyonukwughaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypoglycemia: DR Putra Hendra SPPD UnibaDokument17 SeitenHypoglycemia: DR Putra Hendra SPPD UnibaThariq MuslimNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLE-combined 2 ArshadDokument71 SeitenSLE-combined 2 ArshadarshadsyahaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scleroderma, Sjogren's SyndromeDokument31 SeitenScleroderma, Sjogren's SyndromeSalomeSibashviliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leukemias: Care SettingDokument11 SeitenLeukemias: Care SettingTinNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAL CARDIOMYOPATHIESDokument53 SeitenFINAL CARDIOMYOPATHIESAmosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Emergencies in Dogs and CatsDokument29 SeitenEndocrine Emergencies in Dogs and CatsSteffi AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine Yr3 NotesDokument3 SeitenMedicine Yr3 Notesismah_haron_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with DiabetesDokument47 SeitenManaging Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with DiabetesTamzid Rabby TanmoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For "LEUKEMIAS"Dokument11 SeitenNursing Care Plan For "LEUKEMIAS"jhonroks75% (12)
- Arterial DisordersDokument40 SeitenArterial DisordersSalman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids & Electrolytes Imbalance GuideDokument37 SeitenFluids & Electrolytes Imbalance GuideSHAFIQNoch keine Bewertungen
- HE Pit Ipd2014Dokument49 SeitenHE Pit Ipd2014HendraDarmawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For LEUKEMIASDokument12 SeitenNursing Care Plan For LEUKEMIASMaverick LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept MapDokument4 SeitenConcept Mapdejosep_informaticsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Values WorksheetDokument57 SeitenLab Values WorksheetpcbthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arterial Blood GasesDokument16 SeitenArterial Blood GasesPraneetha NouduriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complication Diabetes Mellitus: Klinik Diabetes Terpadu Rs Islam KlatenDokument53 SeitenComplication Diabetes Mellitus: Klinik Diabetes Terpadu Rs Islam KlatenAdam HartonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Sclerosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandMultiple Sclerosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Hypovolemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herbal MedicinesDokument6 SeitenHerbal MedicinesHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationDokument2 SeitenImpaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDokument2 SeitenImpaired Physical MobilityHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSN - 4C: PresentorsDokument52 SeitenBSN - 4C: PresentorsHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDokument4 SeitenRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herbal MedicinesDokument6 SeitenHerbal MedicinesHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDokument4 SeitenRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Breathing PatternDokument1 SeiteImpaired Breathing PatternHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDokument4 SeitenRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychotropic DrugsDokument49 SeitenPsychotropic DrugsHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSHC Ordr PRC FormatDokument4 SeitenMSHC Ordr PRC FormatHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hanieyah Guro OR DR PRC FormatDokument4 SeitenHanieyah Guro OR DR PRC FormatHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway ClearanceHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jose Rizal: 'Those Who Cannot See Where They Came From Will Never Get To Where They Are Going.'Dokument55 SeitenJose Rizal: 'Those Who Cannot See Where They Came From Will Never Get To Where They Are Going.'Anne Ginez BilledoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akiya - DiphtheriaDokument52 SeitenAkiya - DiphtheriaHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOH Officials Directory Execom MembersDokument2 SeitenDOH Officials Directory Execom MembersHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angina PectorisDokument2 SeitenAngina PectorisHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDokument1 SeiteDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mr. Bean's diagnostic blood test resultsDokument2 SeitenMr. Bean's diagnostic blood test resultsHanya Bint PotawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Art of Now: Six Steps To Living in The MomentDokument5 SeitenThe Art of Now: Six Steps To Living in The MomentGiovanni AlloccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundermax Exterior Technic 2011gb WebDokument88 SeitenFundermax Exterior Technic 2011gb WebarchpavlovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of ClimateDokument18 SeitenElements of Climateእኔ እስጥፍNoch keine Bewertungen
- ML AiDokument2 SeitenML AiSUYASH SHARTHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Gautam Samhita CHP 1 CHP 2 CHP 3 ColorDokument22 SeitenGautam Samhita CHP 1 CHP 2 CHP 3 ColorSaptarishisAstrology100% (1)
- Letter of MotivationDokument4 SeitenLetter of Motivationjawad khalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- QP (2016) 2Dokument1 SeiteQP (2016) 2pedro carrapicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Specifications For Fiberbond ProductDokument8 SeitenMechanical Specifications For Fiberbond ProducthasnizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADIET Digital Image Processing Question BankDokument7 SeitenADIET Digital Image Processing Question BankAdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lyceum of The Philippines University Cavite Potential of Peanut Hulls As An Alternative Material On Making Biodegradable PlasticDokument13 SeitenLyceum of The Philippines University Cavite Potential of Peanut Hulls As An Alternative Material On Making Biodegradable PlasticJayr Mercado0% (1)
- Pharmacokinetics and Drug EffectsDokument11 SeitenPharmacokinetics and Drug Effectsmanilyn dacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet PDFDokument6 SeitenDatasheet PDFAhmed ElShoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Communication QuestionsDokument14 SeitenDigital Communication QuestionsNilanjan BhattacharjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Implementation: Name: Rasheed Campbell School: Kingston College Candidate #.: Centre #: 100057Dokument12 SeitenChemistry Implementation: Name: Rasheed Campbell School: Kingston College Candidate #.: Centre #: 100057john brownNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOR 8th Ed 2013Dokument467 SeitenSOR 8th Ed 2013Durgesh Govil100% (3)
- Guidance Notes Blow Out PreventerDokument6 SeitenGuidance Notes Blow Out PreventerasadqhseNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDE Procedure - Radiographic TestingDokument43 SeitenNDE Procedure - Radiographic TestingJeganeswaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Projectiles Without Air ResistanceDokument4 SeitenLesson Plan: Lesson: Projectiles Without Air ResistanceeltytanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap ThufingteDokument10 SeitenSap ThufingtehangsinfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic First AidDokument31 SeitenBasic First AidMark Anthony MaquilingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Finite Element Methods (2001) (En) (489s)Dokument489 SeitenIntroduction To Finite Element Methods (2001) (En) (489s)green77parkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garlic Benefits - Can Garlic Lower Your Cholesterol?Dokument4 SeitenGarlic Benefits - Can Garlic Lower Your Cholesterol?Jipson VargheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRS Design Guidelines PDFDokument46 SeitenSRS Design Guidelines PDFLia FernandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotary Twin Scew Brochure UK HRDokument20 SeitenRotary Twin Scew Brochure UK HRNguyễn Hữu DũngNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Temple of ChaosDokument43 SeitenThe Temple of ChaosGauthier GohorryNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVCCI UPI Form No. 3 Summary ReportDokument2 SeitenHVCCI UPI Form No. 3 Summary ReportAzumi AyuzawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenROV Digital I/O and Analog Channels GuideDokument8 SeitenOpenROV Digital I/O and Analog Channels GuidehbaocrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24.postpartum Period-Physiological Changes in The MotherDokument16 Seiten24.postpartum Period-Physiological Changes in The MotherHem KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil LiquefactionDokument12 SeitenSoil LiquefactionKikin Kikin PelukaNoch keine Bewertungen