Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dictionary of Pharmacology-Khaled Bhuiyan
Hochgeladen von
bhuiyankhaledOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dictionary of Pharmacology-Khaled Bhuiyan
Hochgeladen von
bhuiyankhaledCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dictionary of Pharmacology
1st edition Md. Khaledur Rahman Bhuiyan,B.pharm(Running) Student Department of Pharmacy University of Asia Pacific Dhaka-1209,Bangladesh This is my first publication,so if there any problem then take it easily and contact with us. E-mail ID: bhuiyankhaled@gmail.com bhuiyankhaled@ymail.com Like us in facebook: http://www.facebook.com/pages/ThePharmacist/330151363706425
To My father for his uncompromising principles that guided my life. My mother for leading her children into intellectual. To My teachers: Abdul Mannan(Shere bangla nagar govt boys high school) Debabrata Kumar Sen(Mohhammadpur model college) Md. Tariqur Rahman(BCS 29th Batch,Police) Ms. Waheeda Nasreen(University of asia pacific) To Shere bangla nagar govt boys high school Mohhammadpur model college University of asia pacific
Md.Khaledur Rahman Bhuiyan
It is not a book which is written by me.It is a collection of word which will help the student to understand pharmacology. I would like to inform it is a short collection of pharmacological words which will help especially the pharmacy student. I wish to express my thanks to many other persons who have helped in preparing this book, including my teacher Ms. Waheeda Nasreen in the department of pharmacy at University of Asia Pacific.I am also grateful to Kaji Nusrat jahan and Md.Rejaul karim and Md.Aktarujjaman khan for their excellent secretarial services.
Dictionary of Pharmacology
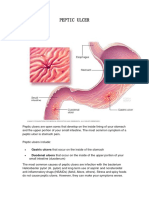
A Abdomen: The part of the trunk that lies between the thorax and the pelvis. Abortifacient: An agent that promotes abortion. Abortion: The giving birth to an embryo or fetus prior to the stage of viability (usually during first three months). Abscess: A circumscribed collection of pus. Acidity: The state of being acid referring to the gastric problems. Acne: A disease marked by pimples. A pimple. Adenitis: Inflammation of a gland. Agglutination: A process of union in wound healing. Ague: Malarial fever marked by chill, fever and sweating. Albuminuria: The presence of protein (Albumin) in urine. Alexeritic: a substance to counteract infection or poison. Alexipharmac: Preserving against poison, antidotal. Allergy: Hypersensitivity of the body cells. Alopecia: the state of being bald. Alterative: a substance used empirically to alter the course of a disease favourably. Amaurosis: Blindness Ambeicide: a substance which kills ameba. Amenorrhoea: Abnormal suppression or absence of menses. Amoebiasis: A diseased condition of intestine (Dysentery) or liver caused by the parasite amoeba (Entamoeba histolytica). Analgesic: a substance for killing pain. Anaphrodisiac: a substance to reduce sexual desire. Anemia: a deficiency in red corpuscles. Anodyne: a substance for killing pain. Anorexia: Loss of appetite. Ant fertility: An agent which checks or control fertility. Antacid: A drug which neutralizes the acidity of the gastric juice. Anthelminthic: killing certain types of worms. Anthrax: Carbuncle. Antiallergic: Any agent or measure that prevents, inhibits or alleviates an allergic reaction. Antibilious: a substance used to treat disorders of the gall bladder. Antidiarrhetic: a substance for counteracting diarrhea. Antidotal: a substance used to counteract a noxious substance. Antidote: An agent that neutralizes a poison or counteracts its effect. Antidysmenorrheic: a substance used to relieve painful menstruation.
Antiecbolic: a substance to counteract an abortifacient. Antiemetic: a substance to prevent vomiting. Antiemetic: Preventing or arresting vomiting. Antiepileptic: a substance to prevent or alleviate convulsive seizures. Antigalactagogue: An agent that diminishes or arrests the secretion of milk. Antihemorrhagic: a substance used to prevent excessive bleeding. Antihepatitic: a substance for the diseases of the liver. Antihistamic: An agent having an effect to relieve the symptoms of allergy. Anti-implantation: An agent which disturbs or prohibits the implantation (attachment) of the fertilized ovum. Antilithic: An agent which counteracts the development of stone or calculi. Antinephrititic: a substance used to ameliorate infection of the kidney. Antineuralgic: a substance used to alleviate the pain associated with irritated nerves. Antiperiodic: A drug which cures the periodic attack of a disease. Antiperodic: a substance used to counteract malaria or periodic fever Antiphlegmatic: Relieving inflammations. Antipruritic: Any agent which relieves or prevents itching. Antipyretic: Antiphlegmatic, A substance that reduces fever. Antirheumatic: a substance used to alleviate rheumatism (pain, swelling, and deformity of the joints). Antiscorbutic: a substance used to prevent scurvy. Antiseptic: a substance used to kill germs. Antispasmodic: a substance used to alleviate sustained, often painful, contractions of the muscles. Antispasmodic: Preventive or curative of convulsions or spasmodic affections. Antisplenitic: a substance used to alleviate inflammation of the spleen. Antitetanic: a substance used to counteract or alleviate the condition tetanus (tonic spasm of voluntary muscles). Antivenereal: a substance used to counteract venereal diseases. Anuria: Total suppression of urine. Anxiety: Restlessness. Aperient: a mild laxative. Aphrodisiac: a substance which stimulates sexual desire. Aphthae: Small white pustules on the mucous membrane of the mouth. Aphthosis: hoof and mouth disease. Apoplexy: a loss of consciousness, sensation, and voluntary motion as a result of obstruction of arterial flow to the brain. Appendicitis: inflammation of the appendix. Appetzer: A substance, which increases the desire to take food.
Arrow poison: a substance used to poison arrows. Arthritis: inflammation of the articulating surfaces of the joints. Ascites: Abdominal dropsy; an accumulation of serous fluid in the peritoneal cavity. Asthenia: Debility; Weakness. Asthma: condition of the respiratory system associated with continuous difficulty in breathing. Astringent: a mildly binding substance. Athlet's foot: Referring to a fungus infection or eczematous eruption of foot Atony: Lack of tension or muscular power. Atrophy: Wasting or emaciation with loss of strength. Attenuant: An agent that dilutes fluid. B Bactericide: a substance used to kill bacteria. Balanitis: Inflammation of glans penis. Balds: Absence or decrease in the amount of hair; alopecia. Bark cloth: primitive clothing made from the inner bark of plants. Bechic: Controlling cough, cough remedy. Belly- ache: Colic; Pain in the abdomen; popularly stomach- ache. Beri- beri: Deficiency disease resulting mainly from deficiency of thiamine in the diet. Beriberi: a disease due to thiamin deficiency. Bile: The yellowish brown or green fluid secreted by the liver. Biliousness: Diseases resulted from mild disturbance of hepatic function marked by malaise, giddiness, vomiting, head- ache indigestion, constipation etc. Bleeding: Losing blood as a result of rupture or severance of blood vessels. Blenorrhagia: Discharge from mucous surfaces; gonorrhoea. Blisters: A collection of fluid beneath the epidermal layer of skin that forms the raised upper wall of the sac. Blood pressure: Marked by an increased or decreased blood pressure than the normal. Boils: swellings; a localized pyogenic infection. Bowel complaints: Problems in intestine. Bradycardiac: An agent which slow down rhythm of heart. Bronchitis: inflammation of the bronchial tubs. Bruises: Contusion usually producing a hematoma without rupture of the skin. Bubo: Inflammatory swelling of lymphatic gland, particularly in the groin or axilla.
C Calculus (Calculi): A hard and solid concretion formed in the body, especially in the urinary organs: stone. Cancer: a malignant tumor of any type. Candlenuts: seeds or fruits which are strung and burned like candles.. Carbuncle: A dangerous form of boil having a flat surface which discharges pus from multiple points. Cardiac: a substance supposed beneficial to the heart. Caries: Decay of teeth. Carminative: a substance which relieves flatulence (swelling of the stomach or intestines due to gases), and alleviates the pain. Catamenial: of menstruation. Cataplasm: a poultice or soft external application. Cataract: A loss of transparency of the crystalline lens of the eye. Catarrh: a cold or similar malady.. Cathartic: see purgative Caulk: gum of a plant used for caulking, mending, or pasting. Cephalalgia: Headache. Cerebral affections: Diseases of the cerebrum (brain). Chancer: A syphilitic ulcer. Chicha: a beverage which may be fermented. Chicle: a base for chewing gum. Chills: A sensation of cold with convulsive shaking of body. Chlorosis: A from of iron deficiency characterized by a great reduction of haemoglobin. Cholagogue: A drug which promotes flow of bile. Cholera: an infectious disease characterized by vomiting, cramps, fever, etc. Chologogue: a substance producing or increasing the flow of bile. Cicatrizant: Healing wound. Coffee substitute: a plant furnishing a beverage similar to coffee. Colitis: Inflammation of the colon. Collyrium: a local eye medication, i.e., eyewash. Congestion: To heap up, hyperaemia. Excess blood in an area. Conjunctivitis: inflammation of the trans parent membrane which covers the eyeball. Constipation: a condition in which bowel movements are infrequent or incomplete. Consumption: A wasting of the tissues of the body, usually tuberculous. Contraceptive: a substance to prevent conception.
Contusion: An injury to soft parts without breaking the skin; bruise. Convulsion: A violent involuntary muscular contraction; spasm. Cordage: a substance used for rope. Corn: Wart. Cosmetic: a substance used to decorate the body. Costiveness: Constipation. Counter-irritant: An agent that cause irritation or a mild inflammation of the skin with the object of relieving a deep-seated inflammatory process. Cramp: Muscular contraction, muscle spasm. Croup: Any affection of the larynx of children, characterized by difficult and noisy respiration accompanied by a hoarse cough. Cutaneous: Relating to the skin. Cystitis: Inflammation of the bladder. D Dandruff: The presence of white scales in the hair of the scalp, due to the exfoliation of the epidermis. Deafness: Hearing loss. Debility: Weakness. Decoction: Liquid preparation obtained by boiling medicinal plant substances in water and extracting drugs by straining the preparation. Delirium: An extreme mental disturbance marked by excitement, restlessness and rapid succession of confused and unconnected ideas. Delivery: Childbirth. Demulcent: a soothing substance to reduce irritation. Deobstruent: a substance to clear stoppage to passages or pores in the body. An agent that removes an obstruction to secretion or excretion; resolvent Depilatory: a substance for the removal of hair. Depressant: a substance which retards any function. Depurative: a substance tending to purify or cleanse. Depurative: Tends to purify or removes waste products or foul excretion. Dermatosis: A nonspecific terms used to embrace any cutaneous eruptions. Detergent: An agent that purifies or cleanses. Diabetes: a disease in which the body is unable to metabolize sugar properly. Diaphoretic: A drug that increases the secretion of the sweat/ a substance that promotes perspiration Diarrhoea: an abnormally frequent discharge of more or less liquid stools. Diathesis: The constitutional or inborn state disposing to a disease. Digestive: a substance which aids digestion.
Diphtheria: An infectious disease of the throat and the air passage which become inflamed and swollen and are coated with a fibrinous exudates. Discutient: a substance for removing skin or growths on the skin. Disinfecant: An agent that destroys the germs or inhibiting their activity. Diuretic: A drug which increases the secretion and discharge of urine/ a substance which increases the flow of urine. Dizziness: A sensation of irregular and whirling motion. Dropsy: a general accumulation of fluid in the body. Dugouts: boats made of hollow logs. Dye and ink: substance used to stain or tint. Dysentery: A group of diseases characterized by painful diarrhoea often accompanied by blood and mucous caused by bacteria or protozoa/ diarrhea produced by irritation of the bowels. Dysmenorrhoea: Unusually painful and difficult menstruation. Dyspepsia: Indigestion. Dyspnoea: Difficult breathing, usually associated with serious heart or lung diseases. Dysuria: Difficult and painful urination. E Earache: a pain in the ear. Ecbolic: An agent that hastens delivery or produces abortion. Eczema: A skin diseases presenting multiform lesions, moist or dry often accompanied by burning and itching. Edema: Accumulation of excessive clear watery fluid in the tissues; dropsy. Elephantiasis: a disease in which the lymph vessels are blocked by a parasite. Emetic: An agent, which induces vomiting. Emmenagogue: a substance which stimulates the menstrual flow. Emollient: An agent, which allays irritation of the skin and alleviates swelling and pain. Empacho: an infant diseases resulting in diarrhoea, pale stools and sour vomit, attributed to diet of mother during pregnancy. Enema: a liquid preparation injected in to the rectum resulting in complete emptying of the bowel. Enteritis: inflammation of the intestinal tract by infectionor irritating foods. Epilepsy: A nervous disorder, characterized by attacks of unconsciousness or convulsion or both. Epistaxis: Nosebleed. Eruptions: The appearance of redness, spotting or lesions on the skin.
Erysipelas: St. Anthony's fire; a specific, acute inflammatory disease of the skin caused by Streptococcus. Escharotic: An agent capable of destroying tissues. Excitement: Stimulation. Expectorant: An agent that increases bronchial secretion and facilitates its expulsion. F Facial paralysis: Paralysis of the face. Fainting: Extremely weak, threatened with loss of consciousness. Fatigue: A state characterized by a lessened capacity for work and reduced efficiency, usually accompanied by a feeling of wariness, sleepiness or irritability. Febricula: Simple continued fever. Febrifuge: A remedy for fever. Felon: Whitlow. Fence posts: poles that take root as live trees when placed in the ground. Firewood: wood that burns when green. Fistula: A pathologic sinus or abnormal passage leading from an abscess cavity or a hollow organ to the surface, or from one abscess cavity or organ to another. Flatulence: The presence of an excessive amount of gas in the stomach and intestines. Flux: An excessive discharge of a fluid from the bowels or other organs, watery or bloody. Dysentery. Fomentation: The application of warmth and moisture in the treatment of diseases; poulticing. Fracture: A break; specially the bone or cartilage. Fungicide: a substance that kills fungi, e.g., ringworm. Furunculus: A boil.
G Galactagogue: a substance increasing flow of milk . Gargle: A throat wash. Gastralgia: Stomachache. Gastric: Relating to stomach. Giddiness: Dizziness. Gingiva: The gum. Gingivitis: Inflammation of the gingival tissue. Gleet: A chronic discharge from the urethra, following gonorrhoea. Glossitis: Inflammation of the tongue. Glycosuria: Excretion of sugar with urine. Gonorrhoea: An infectious venereal disease marked by inflammatory discharge from the genital organs. Gount: A metabolic disorder, characterized by a raised but variable blood uric acid level, recurrent acute arthritis, deposition of crystalline sodium urate in connective tissues and articular cartilage and progressive chronic arthritis. Gravel: A collection of tiny stone- like particles of uric acid, calcium oxalate or phosphates in the organs of the urinary system. Griping: Sharp pain due to the presence of some irritating substance in the bowels. Guinea worm: Avery slender worm infecting human beings through drinking contaminated water; it gradually works its way into subcutaneous tissues. Gum: The muscles (dense fibrous tissue) that surrounds the teeth. H Haematemesis: Vomiting of blood. Haematuria: Any condition in which the urine contains blood or red blood cells. Haemoptysis: spitting of blood. Hallucination: A subjective perception of what does not exist. Hallucinogen: a substance producing visions, illusions, etc. Headache: A diffuse pain in various parts of the head. Heart burn: A burning feeling in the regions of the chest and stomach, generally due to indigestion. Hemicrania: Migraine. Hemiplegia: Paralysis of one side of the body. Hemoptysis: The splitting of blood derived from the lungs or bronchial tubes. Hemorrhage: Bleeding, especially profuse, from any part of the body. Hemorrhoids: Piles. Hemorrhoids: varicose veins of the lower rectum and anus.
Hemostatic: a substance for controlling bleeding. Hepatic: Pertaining to the liver. Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver. Hernia: Rupture; protrusion through its covering of any organ of the body. Herpes: A deep- seated vesicular eruptions of skin, characterized by acute inflammation. Hiccup: A diaphragmatic spasm causing a sudden inhalation, which is interrupted by a spasmodic closure of the glottis. Hoarseness: An unnaturally deep and harsh quality of the voice. Honey plant: a plant whose flowers are regularly visited by honey-producing bees., Hookworm: A worm of the genus Ancylostoma or Uncinaria. Hydragogue: a strong laxative, producing a water discharge from the bowels. Hydrocele: accumulation of serous fluid in a succulated cavity, specifically in the testis. Hydrophobia: Rabies. Hypertension: High blood pressure. Hypnotic: A drug which induces sleep. Hypocholesterolaemic: An agent which lowers cholesterol level. Hypochondriasis: A mental disorder in which the patient is tormented by melancholy views, particularly about his health. Hypoglycemic: A low concentration of sugar in the blood. Hysteria: A diseases in which a physically healthy patient has lost control over acts and feelings and suffers from imaginary aliments. I Impetigo: A contagious inflammatory skin diseases appears commonly on the scalp and tends to affect children and adolescents. Impotence: Lack of power in the male to copulate; sexual weakness. Indigestion: Failure of proper elaboration of the food in the alimentary tract. Indolent: Painless; inactive. Inflammation: Infection or irritation, characterized by pain, swelling, redness and heat. Influenza: Viral fever, characterized by fever, catarrhal inflammation, headache, insomnia, delirium or mental depression. Infusion: The steeping of a substance in water, in order to extract its soluble active principles. Insanity: Mental derangements. Insect repellent: a substance that repels insects.
Insecticidal: An agent that kills insects. Insecticide: a substance that kills insects. Insomnia: Wakefulness; inability to sleep. Intermittent fever: Fever, which is marked by intervals of normal temperature between periods of rise of temperature. Intoxication: Poisoning; Acute alcoholism. Ischuria: Suppression of urine. Itch: An irritating sensation in the skin that arouses the desire to scratch; common name for scabies. J Jaundice: a yellow tinge to the skin, eyes, etc., caused by an increase in bile pigment. K Kapok: a soft downy substance used for stuffing pillows, etc. Ketonuria: Presence of ketone in the urine. L Lachrymatory: An agent that induces the flow of tears. Lactagogue: Galactagogue. Lactifuge: an agent that checks the secretion of milk. Lactogogue: a substance which stimulates the flow of milk.. Laryngitis: Inflammation of the larynx. Laxative: a substance which helpe evacuate the bowels. Leishmaniasis: a tropical disease transmitted by flies. Leprosy: Chronic contagious diseases due to infection with Lepra bacillus. Leucoderma: A condition of the skin which there is loss of pigment wholly or partially. Leucorrhoea: A white or yellowish discharge from the vagina containing mucous and pus cells. Leukemia: Cancer of blood. Lithiasis: The formation of calculi, especially of biliary or urinary calculi. Lithontriptic: a substance for the remobal of stones, e.g., gallstones. Lithontriptic: an agent that effects/ removes calculi or stones formed in the urinary system. Lochia: The vaginal discharge flowing child birth. Loins: Lumbus; The part of the side and back between thorax and the pelvis.
Lumbago: Pain in loins; Muscular rheumatism, a general term for backache in lumbar region. Lumbrichi: Intestinal worm. M Madness: Mentally ill condition. Malaise: A feeling of general discomfort or uneasiness. Malaria: Protozoan diseases, caused by the genus Plasmodium and transmitted by the Anopheles mosquito, causing fever, anemia and debility; Ague. Mange: a contagious skin disease of hairy animals. Mania: A mental disorder marked by dangerous excitement or insane or morbid craving. Marasmus: Emaciation or atrophy in the first year of life. Measles: An acute infectious disease, chiefly of children, marked by cold in head and appearance of white tiny spots on the inner side of the cheek and of rash all over the body. Menorrhagia: Abnormally excessive menstruation. Metritis: Inflammation of the uterus. Micturation: Urination. Migraine: Periodic attack of headache affecting one side of the head. Milktree: a tree with potable latex. Mosquito repellent: a substance that repels mosquitoes. Mumpes: An infections diseases marked by the inflammation of the glands near the ear. N Narcotic: A drug, which induces deep sleep; relieves pain. Nausea: A feeling that vomiting is about to take place, due to sickness in the stomach. Nauseant: An agent that causes nausea. Necklace material: a substance used in the making of rosaries. Nephritis: Inflammation of the kidneys. Nephrocirrhosis: Cirrhosis of kidneys. Nervine: An agent that increases nerve force and lessens irritability. Neuralgia: Nerve pain. Nightblindness: A diseases occurred due to lack or deficiency of vitamin A, in which the patient is incapable of seeing in the dark
Nunupa: unidentified seed or fruit (perhaps pimenta or ficus) used by the bayano cuna for making necklaces. O Obesity: Fatness; An increase in body-weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirement. Oedema: Swelling from the deposition of serous fluid into the cellular texture, which is synonymous to anasarca. Oil plants: plants used as a source of edible or useful oils. Oleagenous: Oily or having the qualities of oil. Oliguria: Scanty urination. Ophthalmia: Conjunctivitis. Orchitis: Inflammation of the testis. Otalgia: Pain in the ear or earache. Otitis: Inflammation of the ear. Otorrhoea: A purulent discharge from the ear. Oxytocic: Hastens child birth; promotes the rapidity of labour. Ozoena: Atrophic condition of the nasal mucous membrane with associated cristing and foetor. P Palsy: paralysis. Paralysis: Loss of power of movement or action. Parasiticidal: An agent that destroys parasites. Parturition: Child birth; labour. Pectoral: A drug to cure disorders of the chest. Pemphigus: Chronic bullous diseases; pyogenic infection. Pesticidal: Having the properties to destroy pests. Pesticide: a substance used for killing pests, e.g., mice. Pharyngitis: Inflammation of the pharynx. Phlegm: Inflammation. Phthisis: Consumption; Tuberculosis of the lungs. Piles: An inflamed condition of the veins in the rectal region; Hemorrhoids. Pimples: small pustules. Piscicide: a substance to kill or stupefy fish. Pityriasis: A scaly skin diseases. Pleurisy: Inflammation of the pleura associated with severe pain in the chest or sides.
Pneumonia: An acute infectious disease, characterized by inflammation of the lungs. Polyp: Any growth from a mucous membrane. Potherb: a plant part edible after cooking. Poultice: A paste of plant parts or drug applied to sore or inflamed part of the body to act as an emollient, relaxing, counter irritant; Cataplasm. Prolapse: The falling downward of an organ of the body from its normal position. Prostate gland: A chestnut shaped body that surrounds the beginning of the urethra in the male. Prurigo: A chronic skin diseases marked by the eruption of small, rounded, reddish pimples. Pruritis: Itching. Psoriasis: A common chronic inflammation of the skin, marked by rounded reddened patches, which are covered with dry silvery scales. Pterygium: A wing like excrescence of a triangular shape, extending from the conjunctiva to the cornea. Puerperium: The period between childbirth and the return of the womb to its normal condition. Pulmonary: Pertaining to the lungs. Purgative: a substance to relieve constipation. Pustule: A small circumscribed elevation on the skin, containing pus. Pyemia: A condition in which pyogenic bacteria circulate in the blood and from abscess where ever they lodge. Pyorrhoea: Purulent discharge from the gums. R Rabies: An infectious virus disease caused by the bite of an infected dog; Hydrophobia. Rafting: lightweight logs used in making rafts. Rash: A temporary eruption on the skin. Refrigerant: An agent that relieves feverishness and thrust or produces a feeling of coolness. Remittent fever: Fever in which the temperature fluctuates considerably, but does not drop to the normal. Renal: Relating to kidneys. Repellent: a substance supposed to keep bats away, a substance supposed to keep snakes away, a substance supposed to keep ticks away. Resolvent: Which reduces swelling or inflammation. Restorative: recovery or revitalization of health.
Retinitis: Inflammation of retina. Rheumatism: An indefinite terms used for pains and inflammation in the muscles, joints & tissues resulting in discomfort or disability. Rickets: A vitamin-D deficiency of the young, often marked by the faulty ossification of bone. Ringworm: A parasitic skin diseases usually marked by red, scaly, circular patches. Root edible-cooked: plants whose roots or underground parts are edible after cooking or processing. Root edible-raw: plants whose underground parts are edible unprocessed. Rubber sources: plants whose latices serve to make crude rubber. Rubefacient: A mild counter- irritant. Rubefacient: a substance producing redness of the skin. S Salt source: a plant that may be converted into a salt substitute. Scabies: A contagious itching skin diseases caused by a parasite. Scald: The lesion resulting from contact with hot liquid or steam; any crusted lesion or scaly lesion of the scalp. Schizophrenia: A mental disorder, characterized by a disorder in thinking processes, such as delusions and hallucinations and extensive withdrawal of the individuals interest from other people and the outside world, and the investment of it in his own. Sciatica: Neuralgic pain along the course of sciatica nerve caused by inflammation or injury to nerve. Screwworms: larvae or maggots of certain flies that burrow in the living body. Scrofula: Tuberculosis of the lymphatic glands, especially of the neck in which the glands become enlarged. Scurf: Dandruff. Scurvy: A deficiency diseases due to lack of vitamin C, characterized by extreme weakness, spongy gums, anemia, hemorrhages into the skin. Seborrhoea: Disease in which discharge forms white or yellow greasy scales on skin. Sedative: a substance used to quiet a person or put him to sleep. Seeds edible-cooked: plants whose seeds are edible after cooking or processing. Seeds edible-raw: plants whose seeds are edible without processing. Seeds poisonous: plant whose seeds are toxic. Seminal weakness: Relating to semen weakness; Impotency. Sexual debility: Sexual weakness: inability or less ability to intercourse.
Sialagogue: A drug, which promotes salivation. Sinus: Suppurating tract or fistula. Slough : Necrotic tissue in the process of separating from the viable portion of the body. To shed or cast of. Snakebite cures: plants used in treatment of snakebite. Soap plants: cleansing plants used to produce a lather of saponin. Soporific: a substance producing sleep. Sore throat: a pain or itch in the throat. Sores: A wound, ulcer or skin lesion; painful. Sorethroat: Inflammation or pain in the throat. Sour Eructation: Raising of gas or of a small quantity of acid fluid from the stomach. Spasmogenic: An agent that cause spasm. Spasmolytic: An agent that arrest spasm. Spermatorrrhoea: The involuntary discharge of semen with orgasm. Spice: a substance used to add flavor to food, beverage, or tobacco. Spleen: The organ that filters blood and prevents infection. Splenitis: see spleen disease. Sprains: An injury to a joint, with possible rupture of some of the ligaments but without dislocation or fracture. Stimulant: An agent that cause increased functional activity. Stomachache: Pain in the stomach. Stomachic: Which promotes the functional activity of the stomach. Stomatitis: Inflammation of the mouth. Stones: Calculus. Strangury: Painful and drop by drop urination with tenesmus. Stricture: A circumscribed narrowing or stenosis of a tubular structure. Struma : A scrofulous tumour. Stuttering: Hesitation in speech; defective utterance; Stammer. Styptic: Arrest or stops bleeding. Sudorific: a substance that induces sweating. Sunstroke: a stroke due to excessive exposure to the sun. Suppository: a solid medication to insert in any cavity other than the mouth. Suppurative: a substance supposed to bring infections to a head. Suppurative: Forming pus. Syphilis: A chronic venereal diseases. T
Taeniacide: An agent which kills Taenia (Tapeworm). Tanbark: a plant whose bark produces much tannin or is used in tanning. Tauta: unidentified choco medicine for eye irritation. The plant is grated and squeezed and the exudate used as a collyrium. Tea plant: a plant that is boiled to make a beverage. Tenesmus: A painful spasm of the anus with an urgent desire to evacuate the bowel or bladder. Tetanus: An infections disease, marked by painful contraction in the muscles. Thatch plant: a plant used for making shelter. Thirst: A desire to drink. Tinder: a plant with parts that are incendiary. Tobacco substitutes: plants which are smoked like tobacco. Tonsillitis: Inflammation of a tonsil. Tooth extraction plants: plants used to facilitate the removal of teeth. Toothache plants: plants used to cure aching teeth. Torchwood: plants whose wood catches and retains fire easily. Tranquillizing: Calming of a person suffering from nervous tension, anxiety etc. Tuberculosis: Infectious diseases caused by tubercle bacillus, attacking all tissues, specially the lungs. Tumor: any swelling having Inflammation; Neoplasm. Tympanites: Swelling of the abdomen from gas in the intestinal or peritoneal cavity. Typhoid: Infectious diseases caused by bacteria, causes fever and intestinal disorders. U Ulcer: An open sore on the skin. Unconsciousness: Loss of consciousness (Awareness). Unguent: an ointment for burns. Urethritis: Inflammation of the urethra, the canal which extends from the bladder and discharges the urine. Urticant: Producing urticaria. Urticaria: A skin eruption characterized by the appearance of intensely itching wheals; an allergic disease Uterine: Relating to the uterus (womb), in which the fertilized egg developed into the child. V
Vaginits: Inflammation of the vagina, the genital canal in the female. Vasodilator: An agent which causes dilation of blood vessels. Venereal: Relating to or resulting from sexual intercourse. Vermicides/Vermifuge: A drug which kills or expels intestinal worms. Vermifuge: a substance for expelling worms. Vermin: Parasitic insects, such as lice, bedbugs. Vertigo: Dizziness. Vesical calculi: Stones in bladder. Vesicant: An agent that produces blisters. Visceral: Relating to the viscera, an organ, mainly of the abdominal. Vomiting: The ejection of matter from the stomach through oesophagus and mouth. Vulnerary: a substance for healilng wounds and sores. W Wart: A hypertrophy of or growth on the skin. Water sources: plants used to quench the thirst. Whitlow: A suppurative inflammation of a finger or toe. Whooping cough: An acute infectious disease characterized by peculiar spasmodic attacks of coughing. Wine sources: plants used in wine production. Y Yellow fever: an infectious tropical disease.
THANK YOU ALL
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Medical TermsDokument3 SeitenMedical TermsMelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower GI Chapter Summary: Constipation, Diarrhea, Appendicitis & MoreDokument8 SeitenLower GI Chapter Summary: Constipation, Diarrhea, Appendicitis & MoreRebeccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 DiseasesDokument90 Seiten12 DiseasesMaryam TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyspepsia BrochureDokument5 SeitenDyspepsia BrochureJns RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Manisha 2 Year, M.SC NursingDokument47 SeitenPeptic Ulcer Disease: Manisha 2 Year, M.SC NursingManisha ShakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute GastroenteritisDokument6 SeitenAcute GastroenteritisJarelle Guinto RomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nikhilesh Choudhury 2023Dokument18 SeitenNikhilesh Choudhury 2023palashshome091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nephrotic Syndrome and Homeopathy - May 10Dokument5 SeitenNephrotic Syndrome and Homeopathy - May 10Sajeer C Salim100% (1)
- 2300 - Module 8 - Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary EmergenciesDokument14 Seiten2300 - Module 8 - Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary Emergenciesmegan.abbinkNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Body: Abdomen. AppendixDokument8 SeitenThe Human Body: Abdomen. AppendixMubin Ebine BaridNoch keine Bewertungen
- تعاريف الباطنية العملي.Dokument5 Seitenتعاريف الباطنية العملي.wowila6489Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Cystitis Case StudyDokument8 SeitenAcute Cystitis Case StudyNoreen TicongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grand Case PresentationDokument44 SeitenGrand Case PresentationAilyn LoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urine TermsDokument3 SeitenUrine TermsSarah ZungailoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gallbladder Inflammation Causes Severe PainDokument6 SeitenGallbladder Inflammation Causes Severe PainSabiha WaseemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Picture of The Colon: Prev NextDokument4 SeitenPicture of The Colon: Prev NextGlare RhayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study of Acute GastritisDokument12 SeitenCase Study of Acute Gastritisstudent_01960% (5)
- Gastric UlcerDokument5 SeitenGastric UlcerSalma NazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CholecystitisDokument60 SeitenCholecystitistammycristobalmd100% (15)
- GERD (Heart Burn) : Gastrointestinal DisordersDokument7 SeitenGERD (Heart Burn) : Gastrointestinal DisordersKateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental of Nursing: Unit Eleven and TwelveDokument45 SeitenFundamental of Nursing: Unit Eleven and Twelveጀኔራል አሳምነው ፅጌNoch keine Bewertungen
- $egrpl QDO VRXQGV: &RQVL Ghudw L RQVDokument3 Seiten$egrpl QDO VRXQGV: &RQVL Ghudw L RQVjegan555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gastritis:: By: Prof. Dr. Nadia AtherDokument9 SeitenGastritis:: By: Prof. Dr. Nadia AtherlailaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive DisordersDokument11 SeitenDigestive DisordersNoah PontinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Term PQRSTDokument37 SeitenMedical Term PQRSTTika Arizon R NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendicitis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDokument4 SeitenAppendicitis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDella FerginaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Emergencies Guide: Visceral Pain, Bleeding & TreatmentDokument104 SeitenGI Emergencies Guide: Visceral Pain, Bleeding & TreatmentSuhaeb AlmarafyNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Does Seeing Blood in Your Stools MeanDokument4 SeitenWhat Does Seeing Blood in Your Stools MeanpetroquipNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nursing Assessment of Peptic UlcerDokument14 SeitenThe Nursing Assessment of Peptic UlcerVelia suwandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic List Q&ADokument63 SeitenTopic List Q&APop D. MadalinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disusun Oleh Kelompok 8Dokument6 SeitenDisusun Oleh Kelompok 8Sania oktaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastroenteritis in ChildrenDokument48 SeitenGastroenteritis in ChildrenKelsingra FitzChivalry FarseerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Disease, Definition, Description, Causes and PreventionDokument5 SeitenDifferent Disease, Definition, Description, Causes and PreventionTheoSebastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study of Acute GastritisDokument12 SeitenCase Study of Acute GastritisANCHAL SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Latin/Greek Roots and Affixation: - Asthen - Emia - Itis - Oma - OsisDokument8 SeitenLatin/Greek Roots and Affixation: - Asthen - Emia - Itis - Oma - OsisGherca OvidiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Storing A Urine SampleDokument8 SeitenStoring A Urine SampleMarz DempseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic UlcerDokument6 SeitenPeptic UlcerXAcheronXNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResearchDokument38 SeitenResearchHelen McClintockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Appendicitis Learning LogDokument10 SeitenAcute Appendicitis Learning Logsuman subediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical GlossaryDokument5 SeitenMedical GlossaryMihaela AmariuteiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis and Treatment of AmebiasisDokument2 SeitenDiagnosis and Treatment of AmebiasisEmmeline Dycangchon-GarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequent Urination Causes and SymptomsDokument11 SeitenFrequent Urination Causes and SymptomsJimmy GillNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUTORIAL SCENARIO B GROUP 2Dokument55 SeitenTUTORIAL SCENARIO B GROUP 2Septi Fadhilah SPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kingston School of Management & Science: Student's SignatureDokument16 SeitenKingston School of Management & Science: Student's SignatureRK ORIGINALS MUSICNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectal Bleeding FactsheetDokument2 SeitenRectal Bleeding FactsheetRilnia Metha SofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is gastritis? Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of stomach inflammationDokument5 SeitenWhat is gastritis? Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of stomach inflammationjaiologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Lower GI DisordersDokument43 SeitenManagement of Lower GI DisordersAilyn LoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CholecystitisDokument4 SeitenCholecystitisAmik, Aila H.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic UlcerDokument6 SeitenPeptic UlcerAyesha FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Lymphocytic LeukemiaDokument8 SeitenAcute Lymphocytic LeukemiaLezah OrarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crohn's DiseaseDokument38 SeitenCrohn's Diseasetintukmathew100% (1)
- 8 Causes of Periumbilical Pain and When To Seek Emergency HelpDokument8 Seiten8 Causes of Periumbilical Pain and When To Seek Emergency HelpJohn Rodney PicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDokument5 SeitenPeptic Ulcer DiseasecookieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 9ABC - English For Pharmacy and Engineering Students - Vocabulary & ThesaurusDokument33 SeitenSession 9ABC - English For Pharmacy and Engineering Students - Vocabulary & Thesauruslyra ayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amebic LADokument3 SeitenAmebic LAVanessa Joy Lamayo TombocNoch keine Bewertungen
- GastritisDokument6 SeitenGastritisNader Smadi100% (5)
- 4 Examining Gastrointestinal SystemDokument75 Seiten4 Examining Gastrointestinal SystemSafi MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pancreatitis: Pancreatitis Is Inflammation in The Pancreas. TheDokument27 SeitenPancreatitis: Pancreatitis Is Inflammation in The Pancreas. ThenikkimaxinevaldezNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to Gastritis and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to Gastritis and Related ConditionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- PHARYNGITISDokument25 SeitenPHARYNGITISWesam TayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emerging and Re-Emerging Disease in NepalDokument25 SeitenEmerging and Re-Emerging Disease in NepalBinayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunity Question Paper For A Level BiologyDokument2 SeitenImmunity Question Paper For A Level BiologyJansi Angel100% (1)
- Koller 1980Dokument11 SeitenKoller 1980..Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument4 SeitenDrug StudyJan DeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy PostoperativeDokument6 SeitenLaparoscopic Appendectomy PostoperativeDamal An NasherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corneal Ulcer Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument15 SeitenCorneal Ulcer Diagnosis and TreatmentKumar jit MaityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Clinical ParasitologyDokument64 SeitenIntroduction to Clinical Parasitologyhakdog hakdogNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Inayati Habib PPRA Peran Manajemen RSDokument43 SeitenDR - Inayati Habib PPRA Peran Manajemen RSBudi IstriawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Laboratory GuideDokument28 SeitenDiagnostic Laboratory Guideendalehadgu2866Noch keine Bewertungen
- MMRDokument2 SeitenMMRShrinivas YuvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asepsis and Infection Control Nursing SchoolDokument20 SeitenAsepsis and Infection Control Nursing Schoolleonardo orozco100% (1)
- Antibiotic treatment guidelines for common infectionsDokument21 SeitenAntibiotic treatment guidelines for common infectionsnovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normanhurst Boys 2021 Biology TrialsDokument33 SeitenNormanhurst Boys 2021 Biology TrialsHewadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation Liver Function TestsDokument74 SeitenEvaluation Liver Function TestsMeylinda LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesDokument148 SeitenOral Manifestations of Systemic DiseasesGaurav Gupta100% (1)
- Claforan PDFDokument41 SeitenClaforan PDFAtta Muhammad MemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Language PaperDokument7 SeitenTest Language PaperAmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infection MCQDokument49 SeitenInfection MCQalh basharNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDC 118387 DS1Dokument132 SeitenCDC 118387 DS1Sina AyodejiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProjectDokument36 SeitenProjectAbhinav JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NP 1 To 5 Focus210-D WITHOUT AnswersDokument5 SeitenNP 1 To 5 Focus210-D WITHOUT AnswersMarkie CubosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proteose Peptone for Cultivating MicroorganismsDokument1 SeiteProteose Peptone for Cultivating MicroorganismscinthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Tweets - ZikaDokument151 SeitenSample Tweets - ZikaAlisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethical Issues in HIV ConfidentialityDokument12 SeitenEthical Issues in HIV ConfidentialityVinia A. VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 2 - UASDokument32 SeitenQuiz 2 - UASIsma RatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Parasitology LabDokument19 SeitenMedical Parasitology Labnaiemo100% (1)
- School Environmental Health & Safety Inspection FormDokument3 SeitenSchool Environmental Health & Safety Inspection FormAnonymous hYjCsYJCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fever with Rash: Measles or RoseolaDokument78 SeitenFever with Rash: Measles or RoseolaRiyan AgusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communicable Disease Nursing2Dokument43 SeitenCommunicable Disease Nursing2CAÑADA, JOHANNELYN M.Noch keine Bewertungen