Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
L14CN: Domain Name System
Hochgeladen von
Ahmad ShdifatOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
L14CN: Domain Name System
Hochgeladen von
Ahmad ShdifatCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
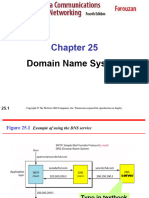
Figure 25.
1 E 25 1 Example of using the DNS service l f i th i
Chapter 25 Domain Name System
25.1
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
25.2
2525-1 NAME SPACE
To be unambiguous, the names assigned to machines g , g must be carefully selected from a name space with complete control over the binding between the names and IP addresses. addresses.
2525-2 DOMAIN NAME SPACE
To have a hierarchical name space, a domain name p , space was designed. In this design the names are designed. defined in an inverted-tree structure with the root at invertedthe top. The tree can have only 128 levels: level 0 top. levels: (root) to level 127. 127. Topics discussed in this section:
Label Domain Name Domain o
25.4
Topics discussed in this section:
Flat Name Space Hierarchical Name Space
25.3
Figure 25.3 Domain names and labels Figure 25.2 D i name space 25 2 Domain
25.5
25.6
Figure 25.4 FQDN and PQDN 25 4 d
Figure 25.5 D i 25 5 Domains
25.7
25.8
2525-3 DISTRIBUTION OF NAME SPACE
The information contained in the domain name space must be stored. However, it is very inefficient and also stored. unreliable to have just one computer store such a huge amount of i f t f information. I thi section, we di information. In this ti ti discuss th the distribution of the domain name space. space. Topics discussed in this section:
Hierarchy of Name Servers Zone Root Server Primary and Secondary Servers
25.9
Figure 25.6 Hi 25 6 Hierarchy of name servers h f
25.10
Figure 25.7 Z 25 7 Zones and domains dd i
Note
A primary server loads all information ; y from the disk file; the secondary server loads all information from p y the primary server. When the secondary downloads y information from the primary, it is called zone transfer.
25.11 25.12
2525-4 DNS IN THE INTERNET
DNS is a protocol that can be used in different platforms. platforms. In the Internet, the domain name space (tree) is divided into three different sections: generic sections: domains, domains country domains and the inverse domain. domains, domain.
Figure 25.8 DNS IN THE INTERNET 25 8
Topics discussed in this section:
Generic Domains Country Domains Inverse Domain
25.13 25.14
Figure 25.9 Generic domains
Table 25.1 Generic domain labels
25.15
25.16
Figure 25.10 Country domains
Figure 25.11 Inverse domain
25.17
25.18
2525-5 RESOLUTION
Mapping a name to an address or an address to a name is called name-address resolution. nameresolution. Topics discussed in this section:
Resolver Mapping Names to Addresses Mapping Addresses to Names Recursive Resolution Caching
Figure 25.12 R 25 12 Recursive resolution i l ti
25.19
25.20
Figure 25.13 It ti resolution 25 13 Iterative l ti
25.21
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MCSA Windows Server 2012 R2 Complete Study Guide: Exams 70-410, 70-411, 70-412, and 70-417Von EverandMCSA Windows Server 2012 R2 Complete Study Guide: Exams 70-410, 70-411, 70-412, and 70-417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks CH25Dokument20 SeitenComputer Networks CH25ECE-A010 Shivam MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCSA Windows Server 2012 R2 Installation and Configuration Study Guide: Exam 70-410Von EverandMCSA Windows Server 2012 R2 Installation and Configuration Study Guide: Exam 70-410Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication and Networking CHDokument29 SeitenData Communication and Networking CHUzair KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCSA Windows Server 2012 Complete Study Guide: Exams 70-410, 70-411, 70-412, and 70-417Von EverandMCSA Windows Server 2012 Complete Study Guide: Exams 70-410, 70-411, 70-412, and 70-417Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 25 - Domain Name SystemDokument26 SeitenChapter 25 - Domain Name SystemMuktadir MinexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domain Name SystemDokument29 SeitenDomain Name SystemDHANYASRI BOLLANoch keine Bewertungen
- ch25 CCNDokument29 Seitench25 CCNSudarshan NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- W 12 SKR 3200 LatesDokument22 SeitenW 12 SKR 3200 LatesLaili JamlusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session No.29Dokument35 SeitenSession No.29jayasai268853Noch keine Bewertungen
- E-Mail & DNSDokument42 SeitenE-Mail & DNSPrathyusha VallabhadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domain Name System: Mcgraw-HillDokument20 SeitenDomain Name System: Mcgraw-HillHamis RamadhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument101 SeitenUntitledsrinivasulu thiruveedulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domain Name SystemDokument18 SeitenDomain Name SystemDinesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 8 Application LayerDokument32 SeitenLec 8 Application LayersaziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Email and DNS.Dokument36 SeitenEmail and DNS.Ishant AryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domain RenameDokument12 SeitenDomain RenameKhodor AkoumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 08 - Configuring Domain Name ServiceDokument52 SeitenLect 08 - Configuring Domain Name Service815003Noch keine Bewertungen
- CS 1302 Computer Networks: - Unit - 5 - Application LayerDokument133 SeitenCS 1302 Computer Networks: - Unit - 5 - Application LayerBhavyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To DNS: in This ChapterDokument28 SeitenIntroduction To DNS: in This Chapterapi-3832698Noch keine Bewertungen
- Domain Name System (DNS)Dokument13 SeitenDomain Name System (DNS)oculusframesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 70-411 R2 Test Bank Lesson 08Dokument10 Seiten70-411 R2 Test Bank Lesson 08Mazaher MohamedaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suyash Sharma OS FileDokument28 SeitenSuyash Sharma OS FileEshanya SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Domain Name System (DNS) : TCP/IP Protocol SuiteDokument53 SeitenDomain Name System (DNS) : TCP/IP Protocol SuiteHarsh BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetDom ExamplesDokument4 SeitenNetDom ExamplesEyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocols-Domain Name System (DNS)Dokument22 SeitenProtocols-Domain Name System (DNS)Ali AbdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft TestKing 70-649 v2011-05-24Dokument241 SeitenMicrosoft TestKing 70-649 v2011-05-24felisiak123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Domain Name SystemDokument30 SeitenDomain Name SystemMoïse GuilavoguiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rohini 65577954848Dokument7 SeitenRohini 65577954848nareshkushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3.3.1Dokument22 SeitenChapter 3.3.1Harsh Vardhan kaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide 10 DNSDokument15 SeitenSlide 10 DNSbibek rauniyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active DirectoryDokument5 SeitenActive DirectoryHusain SeroorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - 692015 Unit 5 Application Layer 1 Cs 1302 Computer Networks UnitDokument73 SeitenDokumen - Tips - 692015 Unit 5 Application Layer 1 Cs 1302 Computer Networks UnitsaziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNS Configuration in LinuxDokument4 SeitenDNS Configuration in LinuxBuntha ChhayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercio Exame 70-410 Windows Server 2012Dokument227 SeitenExercio Exame 70-410 Windows Server 2012Domingos Loveres MassissaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DB2 UDB The Basics: Keith E. GardenhireDokument67 SeitenDB2 UDB The Basics: Keith E. GardenhireDharani Dinesh PathipatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Testking 70-410 v2016-03-03 by David 380qDokument352 SeitenMicrosoft Testking 70-410 v2016-03-03 by David 380qsethii_ankushNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Install An Linux or UnixDokument8 SeitenHow To Install An Linux or UnixSimranjeet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer: A: Exam Name: Exam Type: Exam Code: Total QuestionsDokument35 SeitenAnswer: A: Exam Name: Exam Type: Exam Code: Total QuestionsArpit MadhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNS LDokument2 SeitenDNS Lruh solNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Domain RenameDokument91 SeitenWhat Is Domain RenameZones UntrustedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced AD DS Infrastructure ManagementDokument27 SeitenAdvanced AD DS Infrastructure ManagementAbdul-alim BhnsawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN DNSDokument38 SeitenCN DNSdil_18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Domain Name System: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Dokument26 SeitenDomain Name System: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Ansh BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 070 216Dokument368 Seiten070 216ViorelBujorNoch keine Bewertungen
- UserGuide DNSbox300 PDFDokument142 SeitenUserGuide DNSbox300 PDFPulsmade MalawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Replication Promblem of DNSDokument4 SeitenReplication Promblem of DNSferro4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dos Commands Practical FileDokument14 SeitenDos Commands Practical FileSunil Kumar75% (4)
- Domain Name System: DNSDokument64 SeitenDomain Name System: DNSDương NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Domain Name System: How DNS WorksDokument8 SeitenIntroduction To The Domain Name System: How DNS WorksDono1256Noch keine Bewertungen
- DNS Concepts: 2.1 A Brief History of Name ServersDokument22 SeitenDNS Concepts: 2.1 A Brief History of Name ServersrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- How DNS Support For Active Directory Works - Active DirectoryDokument13 SeitenHow DNS Support For Active Directory Works - Active DirectoryAnonymous NeRBrZyAUbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac DCDokument10 SeitenAc DCSdferwste SrqreNoch keine Bewertungen
- NT1330 Week 3 Assignment 3Dokument9 SeitenNT1330 Week 3 Assignment 3MahlikBrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing DNSDokument40 SeitenImplementing DNSSantoshSangroulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distributed File SystemDokument6 SeitenDistributed File SystemDimitrov GudipudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- W 2008Dokument21 SeitenW 2008ardeiandreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 290 ExamsDokument27 Seiten290 Examsaref1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 70-216: Network Directory ServicesDokument92 SeitenExam 70-216: Network Directory Servicesanon_667528756Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Official Course: Implementing Distributed Active Directory® Domain Services DeploymentsDokument28 SeitenMicrosoft Official Course: Implementing Distributed Active Directory® Domain Services DeploymentshieuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relational Database Design by ER - and EER-to-Relational MappingDokument39 SeitenRelational Database Design by ER - and EER-to-Relational MappingAhmad Shdifat100% (2)
- Advance SQLDokument103 SeitenAdvance SQLAhmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dragon FlyDokument10 SeitenDragon FlyAhmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRESENT CipherDokument3 SeitenPRESENT CipherAhmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Modeling Using The Entity-Relationship (ER) ModelDokument56 SeitenData Modeling Using The Entity-Relationship (ER) ModelAhmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Ethics: Chapter 8Dokument57 SeitenEngineering Ethics: Chapter 8Ahmad Shdifat50% (2)
- Engineering Ethics: Chapter 6Dokument27 SeitenEngineering Ethics: Chapter 6Ahmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Ethics: Chapter 3Dokument33 SeitenEngineering Ethics: Chapter 3Ahmad Shdifat100% (2)
- Engineering Ethics: Chapter 5Dokument43 SeitenEngineering Ethics: Chapter 5Ahmad Shdifat71% (17)
- Engineering Ethics: Chapter 7Dokument16 SeitenEngineering Ethics: Chapter 7Ahmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Ethics: Chapter 4Dokument60 SeitenEngineering Ethics: Chapter 4Ahmad Shdifat80% (5)
- Engineering Ethics: Chapter 1Dokument34 SeitenEngineering Ethics: Chapter 1Ahmad Shdifat100% (2)
- Engineering Ethics: Chapter 2Dokument39 SeitenEngineering Ethics: Chapter 2Ahmad Shdifat100% (1)
- 05 - Writing Common Engineering Documents-A (Ch5)Dokument30 Seiten05 - Writing Common Engineering Documents-A (Ch5)Ahmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 - Writing Letters, Memoranda, and E-Mail (Ch4)Dokument23 Seiten04 - Writing Letters, Memoranda, and E-Mail (Ch4)Ahmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light-Weight Encryption Processor Verilog CodeDokument22 SeitenLight-Weight Encryption Processor Verilog CodeAhmad Shdifat100% (1)
- 08 - Tables and Graphics (Ch7)Dokument17 Seiten08 - Tables and Graphics (Ch7)Ahmad Shdifat100% (1)
- AES AlgorithmDokument25 SeitenAES AlgorithmAhmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 - Writing To Get An Engineering Job (Ch10)Dokument31 Seiten11 - Writing To Get An Engineering Job (Ch10)Ahmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 - Writing Common Engineering Documents-B (Ch5)Dokument24 Seiten06 - Writing Common Engineering Documents-B (Ch5)Ahmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 - Some Guidelines For Good Engineering Writing (Ch2)Dokument16 Seiten02 - Some Guidelines For Good Engineering Writing (Ch2)Ahmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verilog Basics 9 FSMD Basics and ExampleDokument26 SeitenVerilog Basics 9 FSMD Basics and ExampleAhmad Shdifat100% (1)
- Light-Weight Encryption Processor v2Dokument2 SeitenLight-Weight Encryption Processor v2Ahmad ShdifatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dobrolyubov On EducationDokument19 SeitenDobrolyubov On EducationVladi IlichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sourav Panda e Commerce PresenationDokument10 SeitenSourav Panda e Commerce Presenationsourav pandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alphabets of Life by Dr. Kim H. Veltman Scholars Edition Vol 2Dokument1.092 SeitenAlphabets of Life by Dr. Kim H. Veltman Scholars Edition Vol 2auraone777100% (3)
- Cave of Iapodes-An Early Slavic Shrine of Perun-KresnikDokument16 SeitenCave of Iapodes-An Early Slavic Shrine of Perun-KresnikprevisetraziteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection and Insight of Sigmund Freud & Erik Erikson TheoryDokument2 SeitenReflection and Insight of Sigmund Freud & Erik Erikson TheoryClipoy TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay OrganizationDokument8 SeitenEssay Organizationzagad04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Siqueiros Madre Proletaria Ok SubirDokument2 SeitenSiqueiros Madre Proletaria Ok Subirapi-265362622100% (1)
- Hilti Site Testing Brochure For Customers (Britain)Dokument4 SeitenHilti Site Testing Brochure For Customers (Britain)Suzaikumar R SanglikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of ABM2 NADokument45 SeitenFundamentals of ABM2 NASheena DumayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nietzsche's Übermensch and The Life Denying Filipino Catholics' BeliefDokument16 SeitenNietzsche's Übermensch and The Life Denying Filipino Catholics' BeliefRoyce Hernandez0% (1)
- Alhuda Cibe - Islamic Credit UnionDokument27 SeitenAlhuda Cibe - Islamic Credit UnionAlHuda Centre of Islamic Banking & Economics (CIBE)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mif M3Dokument32 SeitenMif M3MorvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPSA Reviewer PDFDokument15 SeitenPPSA Reviewer PDFKobe Lawrence VeneracionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colegio de Dagupan: College of NursingDokument38 SeitenColegio de Dagupan: College of NursingA'Lester Medina100% (4)
- PIL On TET Sent To Supreme Court by Vijay Kumar HeerDokument26 SeitenPIL On TET Sent To Supreme Court by Vijay Kumar HeerVIJAY KUMAR HEERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sorila, John Jhovir A.Dokument2 SeitenSorila, John Jhovir A.JJ SorilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSM English CatalogueDokument196 SeitenSSM English CatalogueSELCUK ONUKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bayan V Romulo Case Digest PDF FreeDokument2 SeitenBayan V Romulo Case Digest PDF FreeBae IreneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amonoy Vs GutierrezDokument8 SeitenAmonoy Vs GutierrezHarry PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07-Resolution-Philippine Long Distance Telephone Co. v. City of Davao GR No 143867Dokument24 Seiten07-Resolution-Philippine Long Distance Telephone Co. v. City of Davao GR No 143867Rio BarrotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amigo Manufacturing Inc., V. Cluett Peabody G.R. No. 139300 March 14, 2001Dokument2 SeitenAmigo Manufacturing Inc., V. Cluett Peabody G.R. No. 139300 March 14, 2001Konrad IbabaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Cycle Assessment of Electricity Generation in Mauritius - SIMAPRO PDFDokument11 SeitenLife Cycle Assessment of Electricity Generation in Mauritius - SIMAPRO PDFLeonardo Caldas100% (1)
- Ishomuddin Salviana DS Effendi Suzuki Kashimura - Islam Islamic Culture Japanese Culture Local Values Social ValuesDokument6 SeitenIshomuddin Salviana DS Effendi Suzuki Kashimura - Islam Islamic Culture Japanese Culture Local Values Social Valuesyaqut WHAFFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide To Prosperity and EnlightenmentDokument32 SeitenGuide To Prosperity and EnlightenmentAlmudena Paúl del ValleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 743025167499791617Dokument51 Seiten5 743025167499791617Raj BakhtaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book of Mormon: Scripture Stories Coloring BookDokument22 SeitenBook of Mormon: Scripture Stories Coloring BookJEJESILZANoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Database ConceptsDokument62 SeitenTopic 1 Database ConceptsNowlghtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Corporation CodeDokument17 SeitenRevised Corporation CodeMikey Fabella100% (9)
- Chapter 1: Introduction Aviation Industry: Mini Project On Vistara AirlinesDokument84 SeitenChapter 1: Introduction Aviation Industry: Mini Project On Vistara Airlinesselvaraj rapakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hist 708 Syllabus RevisedDokument11 SeitenHist 708 Syllabus Revisedapi-370320558Noch keine Bewertungen